Alkanes
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
what is an organic compound?
compound that contains carbon which is covalently bonded to one other element, e.g. hydrocarbons
what is a hydrocarbon?
a compound made of only carbon and hydrogen atoms
what is an unsaturated compound?
compound with at least one carbon-carbon double or triple bond
what is a saturated compound?
compound containing only single carbon to carbon bonds
are cycloalkanes and alkanes saturated or unsaturated compounds?
saturated: have the full amount of hydrogens possible
what are cycloalkanes?
saturated hydrocarbons made up of carbon atoms bonded together in a ring formation
what are alkanes?
Saturated hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n+2, either branched or linear, are not ringed structures
cycloalkanes general formula?
CnH2n
are cyycloalkanes alkanes?
no, theyre similar to alkanes but are not a type of alkane
2 potential structures for alkanes?
branched or linear
what are branches alkanes?
alkane where carbons arent all in a straight line
what are linear alkanes?
alkanes where carbons are all in a straight line
what do fluency quizzes in chemistry help you understand and remember?
the fundamentals of chemistry
5 ways we represent molecules?
skeletal formula
displayed formula
molecular
empirical
structural
what is a molecular formula?
the actual number of atoms of each element in a molecule
rule for writing a molecular or empirical formula?
you write the actual number of carbon atoms, the hydrogen, then the others in alphabetical order (same for any written formula)
what is the empirical formula?
The simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element in a compound
when would a molecule have the same molecular and empirical formula?
when we cannot simplify the numbers equally into whole numbers
what is the displayed formula?
A displayed formula shows how all the atoms are arranged and all the bonds between them
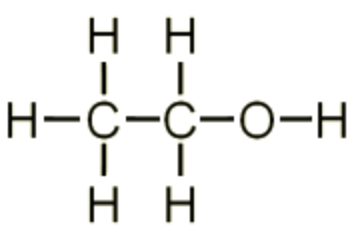
how are atoms and bonds represented in displayed formulas?
atoms with symbols, bonds with a line (1 line is a single bond, 2 is a double etc)
is combustion of alkanes exothermic or endothermic?
exothermic, a lot of energy is released when alkanes are combusted
why are alkanes good fuels?
they release a large amount of energy when they burn, the more carbon in the alkane the greater the amount of energy released
what is complete combustion?
when a substance burns completely in oxygen producing carbon dioxide gas and water vapour
general combustion reaction?
Hydrocarbon + O2 (g) --> CO2 (g) + H2O (g)
hydrocarbon + oxygen (g) --> carbon dioxide (g) + water vapour (g)
what is incomplete combustion?
when a fuel burns in insufficient oxygen, so the fuel doesnt combust completely
when does incomplete combustion occur?
when there arent enough moles of oyxgen gas available to produce carbon dioxide gas
2 possible reaction pathways of incomplete combustion?
either 2 gases produced or 1 solid and 1 gas:
Hydrocarbon + O2 (g) --> Carbon monoxide (CO) (g) + H2O (g)
Hydrocarbon + O2 (g) --> C (s) + H2O (g)
why is burning fuels a problem?
releases pollutants causing pollution and more problems: health and environmental
what type of pollutants are C02 (g) and H20 (g)?
greenhouse gases
how does an excess amount of greenhouse gases encourage global warming?
they absorb heat in the atmosphere
more combustion = more gases = more heat absorption = long term global warming
what is the greenhouse effect?
the process by which gases hold heat in the atmosphere, this keeps our planet warm and allows us to live, but if theres too many gases then it becomes a problem
what is a pollutant?
substances that are harmful to the environment and have a negative effect e.g. greenhouse gases
what is pollution?
process of releasing pollutants into
pollutants from incomplete combustion?
carbon monoxide gas (CO),
water vapour,
solid carbon = soot
why is complete combustion preferred over incomplete?
complete causes long-term issues which are preferred over the immediate issues from incomplete
complete releases more energy per mol. (more efficient)
complete is cheaper as we burn less fuel for the same amount of energy
complete is not immediately harmful but has long-term issues
why do we use combustion despite the long-term or immediate consequences?
it releases a lot of energy which we can use to power technology, transport etc
issues caused by carbon monoxide?
toxic: CO interferes with the bodies ability to carry oxygen, meaning organs receive insufficient oxygen and the body cant function properly
flammable: CO reacts easily with oxygen = flame
what pollutant is produced in old cars? how?
carbon atoms = soot = smog
very limited oxygen in engines = incomplete combustion = solid carbon produces
high engine temperatures cause atoms to clump together = soot which is released into the atmosphere and rises
what type of pollution does soot cause? how?
smog: soot particles are small and light, so they rise and easily build up in the atmosphere
issues with smog?
reduces amount of sunlight to the plants, reducing crop growth (global dimming = reflection of the suns light)
respiratory issues such as athsma
what is produced in the combustion of a compound with sulfur present?
SO2, sulfur dioxide
what is produced in the combustion of a compound with nitrogen present?
NO, nitric oxide
is burning alkanes or organic compounds more exothermic?
burning organic compounds doesn't produce as much energy as burning alkanes
why does having organic compounds make a fuel less efficient? what do we do about it?
burning organic compounds doesn't produce as much energy as burning alkanes, so chemists remove them from fuel, but some are left over (impurities)
what are impurities?
any unwanted organic compounds found in fuel/small amounts of other unwanted substances
why do we aim for only alkanes in fuel?
they are the most efficient and also cheaper, burning organic compounds doesn't produce as much energy as burning alkanes
where is sulfur dioxide (SO2) roduced?
mainly powerplants
health issues caused from sulfur dioxide?
high concentration of SO2 in the air causes difficulty breathing which can cause respiratory issues such as athsma
environmental issues caused from sulfur dioxide and the process?
acid rain: SO2 reacts with water vapour in the clouds = an acid (liquid) = acid rain
SO2 (g) + H20 (g) -> H2SO3 (l)
does not harm our skin but causes soil to become more acidic so crops have difficulty growing
it causes lakes and rivers to become more acidic, killing wildlife
reaction between SO2 (g) and H20 (g) in the clouds?
SO2 (g) + H20 (g) -> H2SO3 (l)
what is placed inside powerplant chimneys to reduce SO2 pollution?
a mesh coated with solid calcium oxide, CaO (s)
process of reducing S02 pollution in a powerplant?
combustion in a powerplant = SO2
SO2 rises and comes in contact with CaO (s)
neutralisation reaction occurs and a harmless solid is produced
most SO2 reacts so less is released into the atmosphere, reducing the effects
neutralisation reaction between sulfur dioxide and calcium oxide in a powerplant chimney?
SO2 (g) + CaO (s) -> CaSO3 (s)
reaction between calcium carbonate and sulfur dioxide in flue gas desulphariastion
CaCO3 + SO2 → CaSO3 + CO2
how is the reduction of SO2 pollution efficient?
CaO (s) is broken up into very small pieces and scattered onto a mesh
large surface area = more frequent successful collisions = faster reaction so SO2 is removed from the chimney efficiently and less is released into the atmosphere
what is flue gas desulfurisation and the purpose?
CaO and CaCO3 are basic and can be used to remove acid oxides such as SO2 from power station chimneys,
purpose is to reduce sulfur dioxide pollution by replacing it with less harmful solids
what can calcium sulfate in flue gas desulphirisation be used for
The reaction forms calcium sulfate(IV) which is used to make plasterboard
how can sulfur dioxide can be removed from flue gases using calcium oxide or calcium carbonate?
flue gas desulfurisation
what type of reaction occurs during flue gas desulfurisation?
acid-base reaction as CaCO3 and CaO are bases and SO2 is an acidic oxide (non-metal oxide).
process of flue gas desulfurisation?
Waste gases from coal-fired power stations are directed into a scrubbing chamber.
In the scrubbing chamber, a wet slurry containing calcium oxide (CaO) and calcium carbonate (CaCO₃) is sprayed into the gases.
The reaction between sulfur dioxide and calcium compounds leads to the removal of sulfur:
Initial reaction: CaO (s) + 2H₂O (l) + SO₂ (g) + ½O₂ (g) → CaSO₄·2H₂O (s)
Further oxidation: CaSO₄·2H₂O (s) → CaSO₄ (solid form of gypsum)
to produce a constant supply of energy, what conditions are required in engines?
constant supply of oxygen (from air flowing through the engine),
combustion needs to meet the activation energy, so high temperatures are required
true or false: complete and incomplete combustion occur in engines
true:
sometimes theres an oxygen surplus = complete combustion = CO2 and H20 (g),
other times: 02 deficit = incomplete combustion = pollutants
what are unburnt hydrocarbons?
when alkanes in petrol dont undergo combustion and are released as gases,
occurs when some alkanes dont combust and turn into a gas, then released into the atmosphere
what pollutants occur from unburnt hydrocarbons?
smog: reflection of the sun's light reduces sunlight reaching plants (global dimming)
all pollutants petrol engines give out?
carbon dioxide gas, carbon monoxide gas, solid carbon particulate, water vapour, unburnt hydrocarbons, nitric oxide
how does nitric oxide pollution occur from engines?
due to high temperatures in the engine, N2 gas in the air combusts (high temperatures required)
N2 (g) + O2 (g) -> 2NO (g)
combustion of nitrogen in the engine?
N2 (g) + O2 (g) -> 2NO (g)
nitrogen + oxygen -> nitric oxide
types of pollution caused from nitric oxide?
acid rain
respiratory issues
how does nitric oxide create acid rain?
NO (g) itself isnt acidic, so when released into the atmosphere it reacts with oxygen = nitrogen dioxide (g) which then reacts with oxygen and water vapour in clouds = nitric acid = acid rain
reaction between nitric oxide and oxygen in the air?
2NO (g) + O2 (g) -> 2NO2 (g)
reaction between nitric oxide, oxygen and water vapour?
4NO2 (g) + O2 (g) + 2H2O (g) -> 4HNO3 (l) in clouds = acid rain
to reduce pollution in engines, why do we only reduce C (s), unburnt hydrocarbons, NO and CO?
it is difficult to reduce carbon dioxide and water vapour,
C, NO and CO have immediate health issues compared to the long-term effects
how are solid carbon particles (soot) reduced in cars?
a filter is added to the exhaust, which catches the C particles before they enter the atmosphere
what is used to reduce the amount of unburnt hydrocarbons, NO and CO entering the atmosphere in cars?
catalytic converter: catalyst in a device (converter) which converts 1 gas to another,
gas enters catalytic converter and is converted into another gas
types of metal catalysts in thee catalytic converter?
either platinum, palladium, rhodium or iridium, or a mix
how is the catalytic converter efficient?
metal catalyst spread out thinly over a mesh, increasing surface area, increasing rate, reducing amount of pollutants in atmosphere;
less metal is needed = cheaper
reaction in catalytic converter to remove unburnt hydrocarbons?
O2 (g) + unburnt hydrocarbon -> CO2 (g) + H2O (g)
why is it better to release greenhouse gases (CO2 + H20) instead of unburnt hydrocarbons?
unburnt hydrocarbons -> smog which has immediate effects to health and environment, it is safer for your health to release greenhouse gases as they cause long-term effects,
in short term it is better
reaction in catalytic converter to remove CO and NO?
when NO and CO hit the converter, they react together
2NO (g) + 2CO (g) -> N2 (g) + 2CO2 (g)
why is it better to release nitrogen gas compared to CO and NO?
its inert (does not react) so is harmless and will just build up in the atmosphere (no effect),
it'll only combust into nitric oxide at very high temperatures which cant be achieved in the atmosphere
why is it better to release carbon dioxide compared to CO and NO?
its better in the short term,
NO and CO have immediate effects to the environment and your health, whereas CO2 is long-term
what is crude oil?
fossil fuel formed from organic remains and is mixture of different hydrocarbons, mainly alkanes, in a liquid state
why is crude oil a 'fossil fuel'?
it contains fossils
how is crude oil formed?
It is a fossil fuel formed over millions of years when plankton and other sea creatures die, fall to the sea bed and become covered/compressed by layers of sand and silt. Sand and silt means that no oxygen gets to the dead bodies. The heat from internal earth processes and pressure from compression builds up and slowly converts organic matter into crude oil
why do we separate crude oil into fractions?
crude oil itself isnt actually useful due to the presence of impurities, so we separate it so we can extract the useful fuels and use that oil instead (alkanes, alkenes etc)
separated to make sure the fuels made from crude oil is efficient and useful
how do we separate crude oil?
fractional distillation
why are less useful compounds called impurities?
theyre less efficient
what is oil called where impurities aren't removed?
crude oil
why do many alkanes have different physical properties?
there are large variations in weight and structure in crude oil
in homologous series there is a gradual chance in physical properties across the series, large difference in weight and structure = larger difference in physical properties
what do the alkanes present in a fuel determine?
its physical properties and therefore its usage
what is a crude oil fraction?
hydrocarbons with similar boiling points
why does each fraction of crude oil have a different use?
each batch contains alkanes with similar molecular weights and therefore similar properties so each batch has a different use
process of fractional distillation?
crude oil enters a furnace and is converted into a vapour
vapour is passed into the column through the bottom
as vapour rises up the column it cools
alkanes condense at their boiling point
liquids are led out of the column at different heights = different fractions
what does the boiling point of alkanes in crude oil depend on?
size of molecules:
in a homologous series molecule size increases, so van der waals forces increases so b.p. increases
conditions at the top of the fractionating column?
small molecules:
lowest temperature, least viscous molecules and short chains condense here, low boiling points, very volatile, flammable, light in colour
conditions at the bottom of the column?
large molecules:
highest temperature, most viscous, long chains, high boiling points, not flammable (poor fuels), molecules dark in colour
where do larger alkanes condense?
lower down the column due to the higher boiling point as theres more van der waals forces to break
list of fractions from top to bottom?
LPG (bottled gas) (20 degrees)
petrol/gasoline (for vehicles) (70 degrees)
naphtha (lighter fuel) (chemicals) (110 degrees)
kerosene (jet fuels) (180 degrees)
diesel oil (trucks) (250 degrees)
fuel oil (ships, factories and central heating) (300 degrees)
lubricating oils, waxes and polishes (340 degrees)
bitumen (roads and roofing) (400 degrees)
why are products with short carbon chains collected at the top of the column?
products with short carbon chains have lower boiling points due to less van der waals forces present, meaning they rise higher up the column before reaching their boiling point and are therefore collected at the top of the column
why are products with long carbon chains collected at the bottom of the fractionating column?
they have higher boiling points due to the presence of more van der waals forces, meaning they dont rise very far up the column before they reach their boiling point, they condense and are collected at the bottom