(T)Chapter 8: Net Present Value and Other Investment Criteria Terms
1/24
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Capital Budgeting Decision
The process of planning and evaluating long-term investments to determine their potential profitability and financial viability. It involves assessing various investment projects to allocate capital effectively.
Net present value (NPV)
the difference between an investment’s market value and its cost
Estimating NPV
involves calculating the present value of expected future cash flows and subtracting the initial investment cost.
Discounted cash flow (DCF) valuation
(a) calculating the present value of a future cash flow to determine its value today (b) the process of valuing an investment by discounting its future cash flows
Net present value rule
an investment should be accepted if the net present value is positive and rejected if it is negative
Payback period
the time it takes for an investment to generate an amount of cash equal to the initial investment.

Payback rule
an investment is acceptable if its calculated payback period is less than some prespecified number of years
Cash flow
the net amount of cash being transferred into and out of a business.
Average accounting return (AAR)
an investment’s average net income divided by its average book value

Average net income
the total net income generated by an investment averaged over its useful life.
Average book value
the average value of an asset over its useful life, calculated as the initial cost minus accumulated depreciation divided by the number of years.
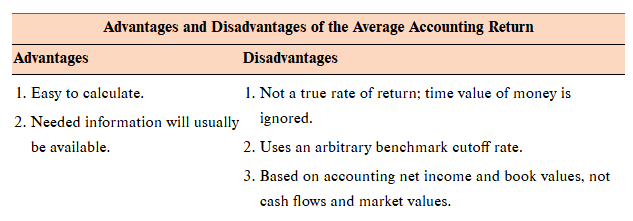
Average accounting return rule
a project is acceptable if its average accounting return exceeds a target average accounting return
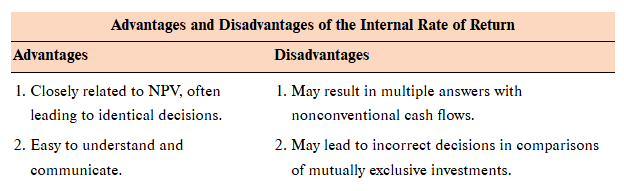
Internal rate of return (IRR)
the discount rate that makes the net present value of an investment zero
IRR rule
an investment is acceptable if the IRR exceeds the required return. It should be rejected otherwise
Discounted cash flow
method for valuing an investment by estimating future cash flows and discounting them to present value.
Net present value profile
a graphical representation of the relationship between an investment’s net present value and various discount rates
Conventional cash flow
initial investment is negative and all the rest are positive
Independent cash flow
the decision to accept or reject this project does not affect the decision to accept or reject any other; each project stands alone in terms of cash inflows and outflows.
Multiple rates of return
the possibility that more than one discount rate will make the net present value of an investment zero
Modified internal rate of return (MIRR)
a financial metric that calculates the profitability of potential investments while accounting for the time value of money and cost of capital.
This Discounting Approach
is used to determine the net present value of cash flows by applying different rates to reflect the risk and timing of cash inflows.
The Reinvestment Approach
is a method that assumes interim cash flows from an investment are reinvested at the internal rate of return instead of the cost of capital.
The Combination Approach
is a method that evaluates investment projects by combining both the financing and reinvestment effects of cash flows, thus providing a comprehensive analysis of their profitability.
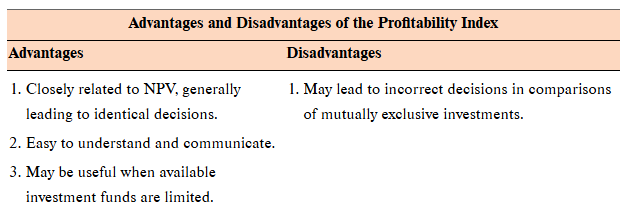
Profitability index (PI)
the present value of an investment’s future cash flows divided by its initial cost (aka benefit-cost ratio)
Capital Budgeting
the process of planning and managing a firm's long-term investments, assessing potential expenditures or investments and deciding which projects to pursue based on expected returns.