8.2.2 Regulation of transcription and translation
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
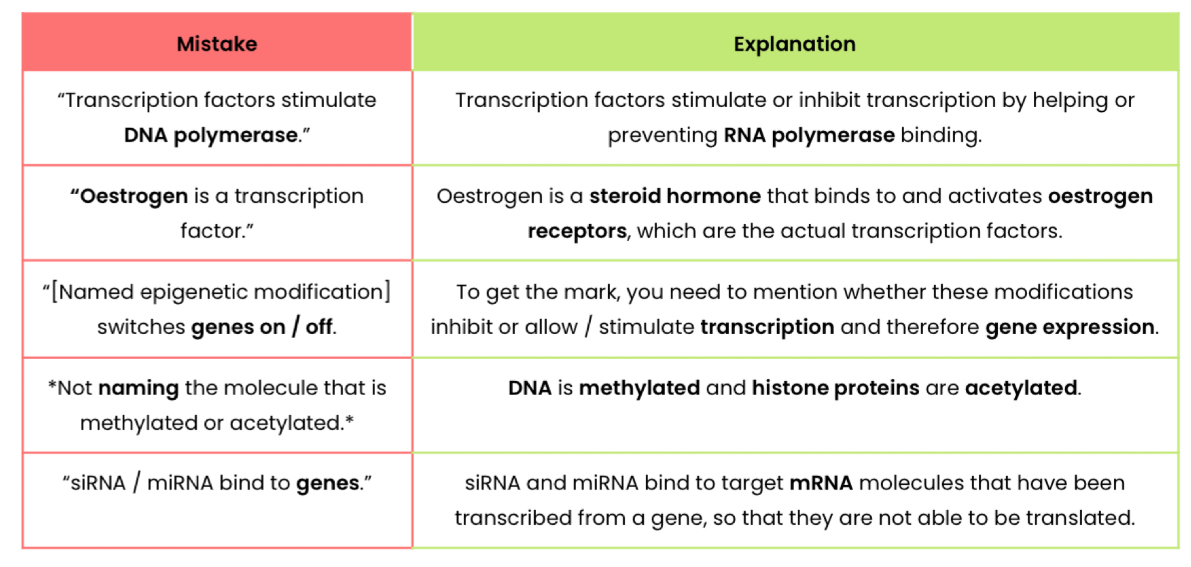
What are transcription factors?
proteins which regulate (stimulate or inhibit) transcription of specific target genes in eukaryotes
By binding to a specific DNA base sequence on a promoter region
Describe how transcription can be regulated using transcription factors
Transcription factors move from cytoplasm to nucleus
Bind to DNA at a specific DNA base sequence on a promoter region (before / upstream of a target genes)
This stimulates or inhibits transcription (production of mRNA) or target gene(s) by helping or preventing RNA polymerase binding
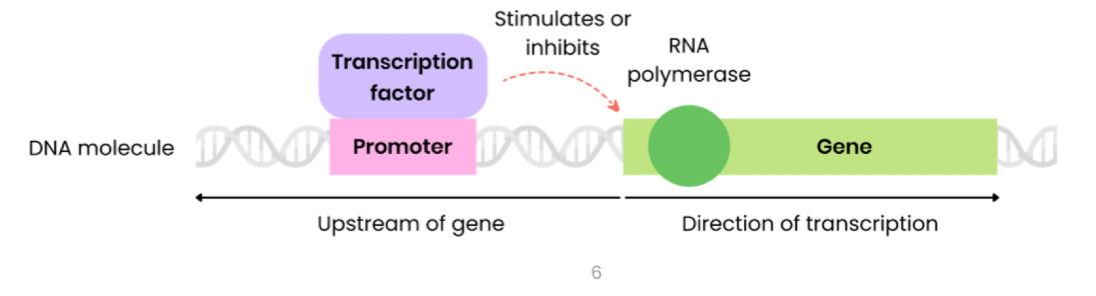
Explain how oestrogen affects transcription
Oestrogen is a lipid-soluble steroid hormone so diffuses into cell across the phospholipid bilayer
In cytoplasm, oestrogen binds to its receptor, an inactive transcription factor, forming an oestrogen-receptor complex
This changes the shape (tertiary structure) of the inactive transcription factor, forming an active transcription factor
The complex diffuses from cytoplasm into the nucleus
Then binds to a specific DNA base sequence on the promoter region of a target gene
Stimulating transcription of target genes forming mRNA by helping RNA polymerase to bind
Explain why oestrogen only affects target cells
Other cells do not have oestrogen receptors
Describe what is meant by epigenetics
heritable changes in gene function / expression without changes to the base sequence of DNA
Caused by changes in the environment (e.g. diet, stress, toxins)
Describe what is meant by the epigenome
all chemical modifications of DNA and histone proteins - ( e.g. methyl groups on DNA and acetyl groups on histones)
Summarise the epigenetic control of gene expression in eukaryotes
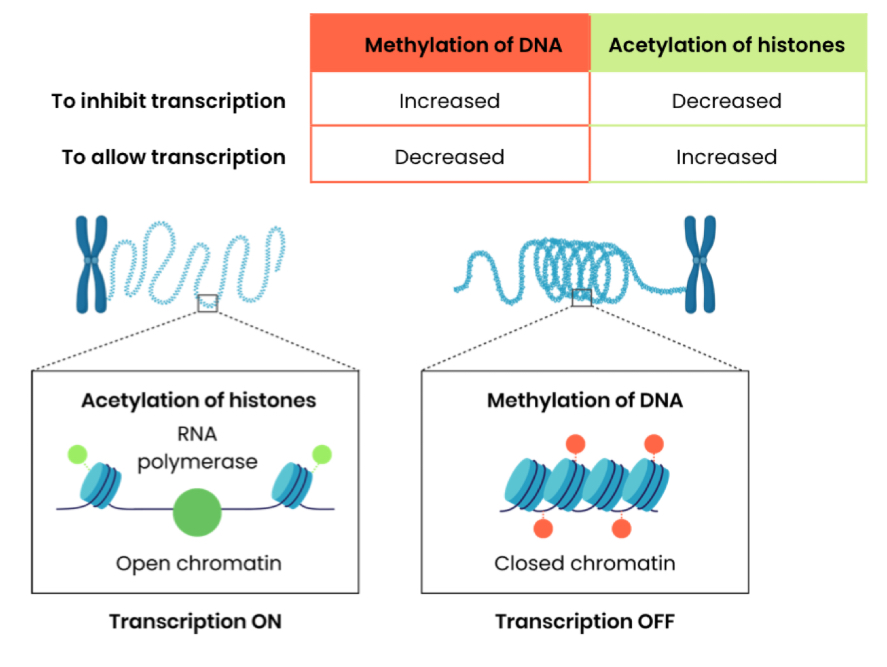
Explain how methylation and acetylation can inhibit transcription
Methylation:
Increased methylation of DNA - methyl groups added to cytosine bases in DNA
So nucleosomes (DNA wrapped around histone) pack more tightly together
Preventing transcription factors and RNA polymerase binding to promoter
Acetylation:
Decreased acetylation of histones increases positive charge of histones
So histones bind DNA (negatively charged) more tightly
Preventing transcription factors and RNA polymerase binding to promoter
Explain the relevance of epigenetics on disease development and treatment
environmental factors (e.g. diet, stress, toxins) can lead to epigenetic changes
These can stimulate / inhibit expression of certain genes that can lead to disease development
→ increased methylation of DNA OR decreased acetylation of histones inhibits transcription
→ decreased methylation of DNA OR increased acetylation of histones stimulates transcription
Diagnostic tests can be developed that detect these epigenetic changes before symptoms present
Drugs can be developed to reverse these epigenetic changes
What is RNA interference (RNAi)?
inhibition of translation of mRNA produced from target genes, by RNA molecules e.g. siRNA, miRNA
This inhibits expression of (silencing) a target gene
This happens in eukaryotes and some prokaryotes
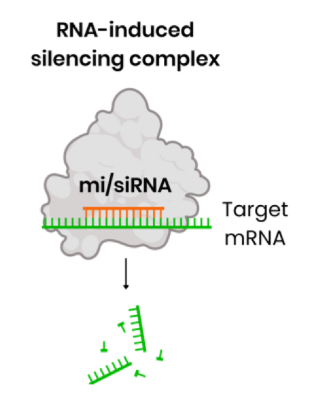
Describe the regulation of translation by RNA interference
Small interfering RNA (siRNA) or micro-RNA (miRNA) is incorporated into / binds to a protein, forming an RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC)
siRNA synthesised as double-stranded RNA → 1 strand incorporated
miRNA synthesised as a double stranded hairpin bend of RNA → both strands incorporated
Single-stranded miRNA / siRNA within RISC binds to target mRNA with a complementary base sequence
This leads to hydrolysis of mRNA into fragments which are then degraded OR prevents ribosomes binding
Reducing / preventing translation of target mRNA into protein
Exam insights: common mistakes