Plant Science Exam 3
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
One Chromosome =
1 DNA Molecule
Chromosomes of Complex Organisms
Paired
How many chromosome pairs might a plant have?
4-630
Cells with 1 of each chromosome
Haploid (1n or n)
Cells with 2 of each chromosome
Diploid (2n)
Which type of cells undergo meiosis?
Diploid
Mitosis
Exact copy of original cell
Common way of cell division
Meosis
Produces 4 haploid cells from 1 diploid cell
Usually for reproduction
Creating genetic variation in offspring
3 Types of Life Cycles
Simple Organisms
Complex Animals
Land Plants
Life Cycle of Simple Organisms
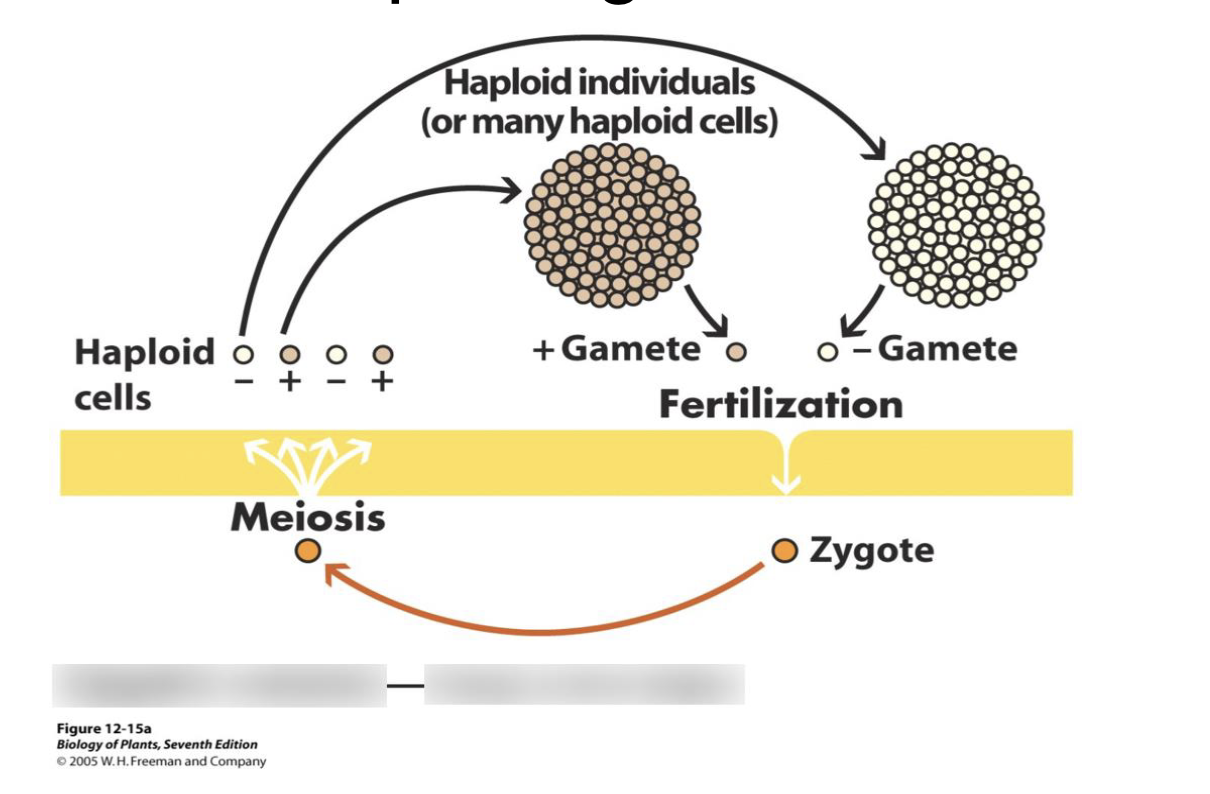
Life Cycle of Most Animals
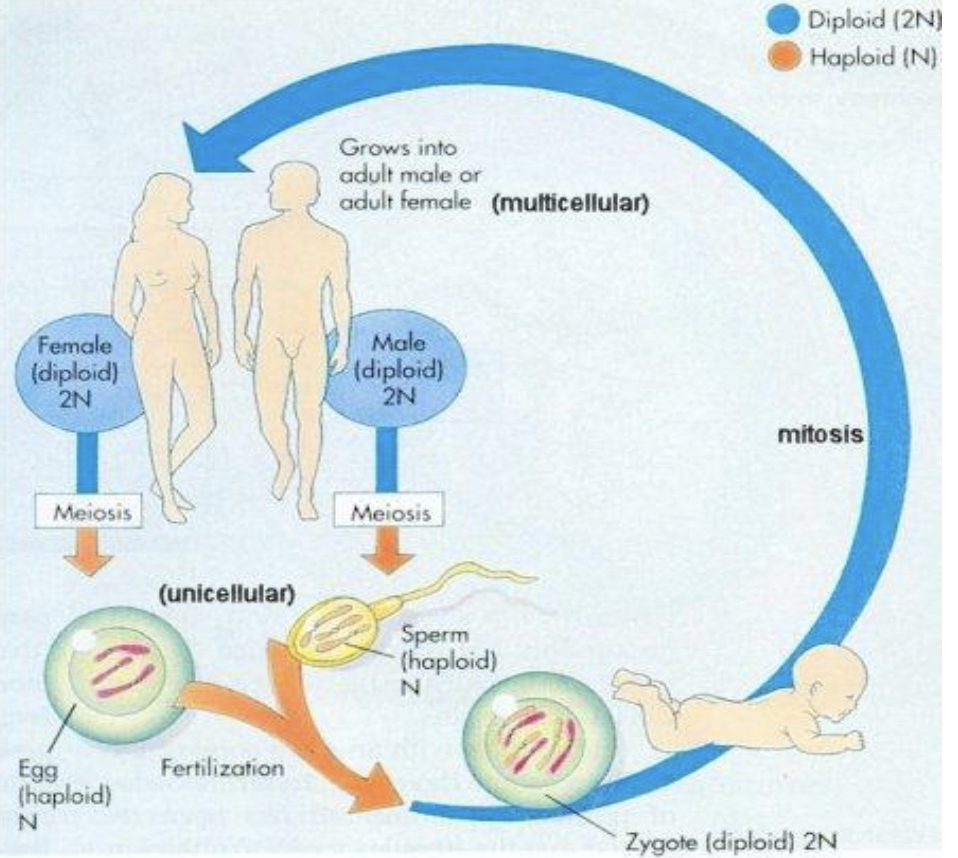
Life Cycle of Land Plants
Which is the most complicated life cycle?
Life Cycle of Flowering Plants
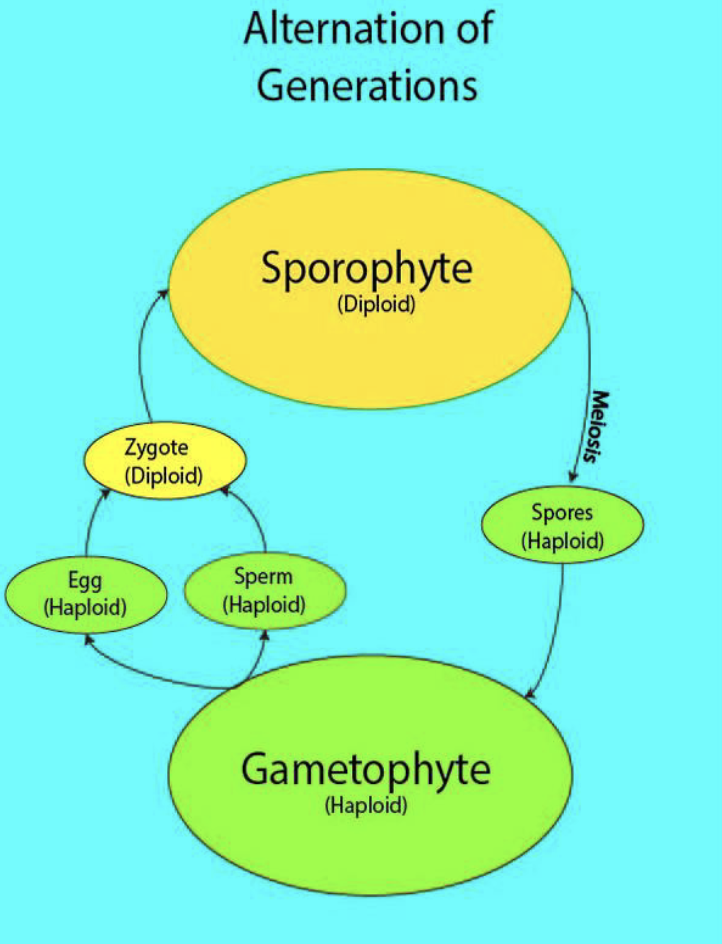
Which life cycle is called ‘alternation of generations?’
Life Cycle of Flowering Plants
Flowering Plants
Most structures reduced in size
1 generation kept on previous generation in seed plants
Hold the haploid generation
Flower
Modified leaves
2 vegetable parts
Don’t contribute cells to future generations
2 reproductive parts
Contribute cells to future generations
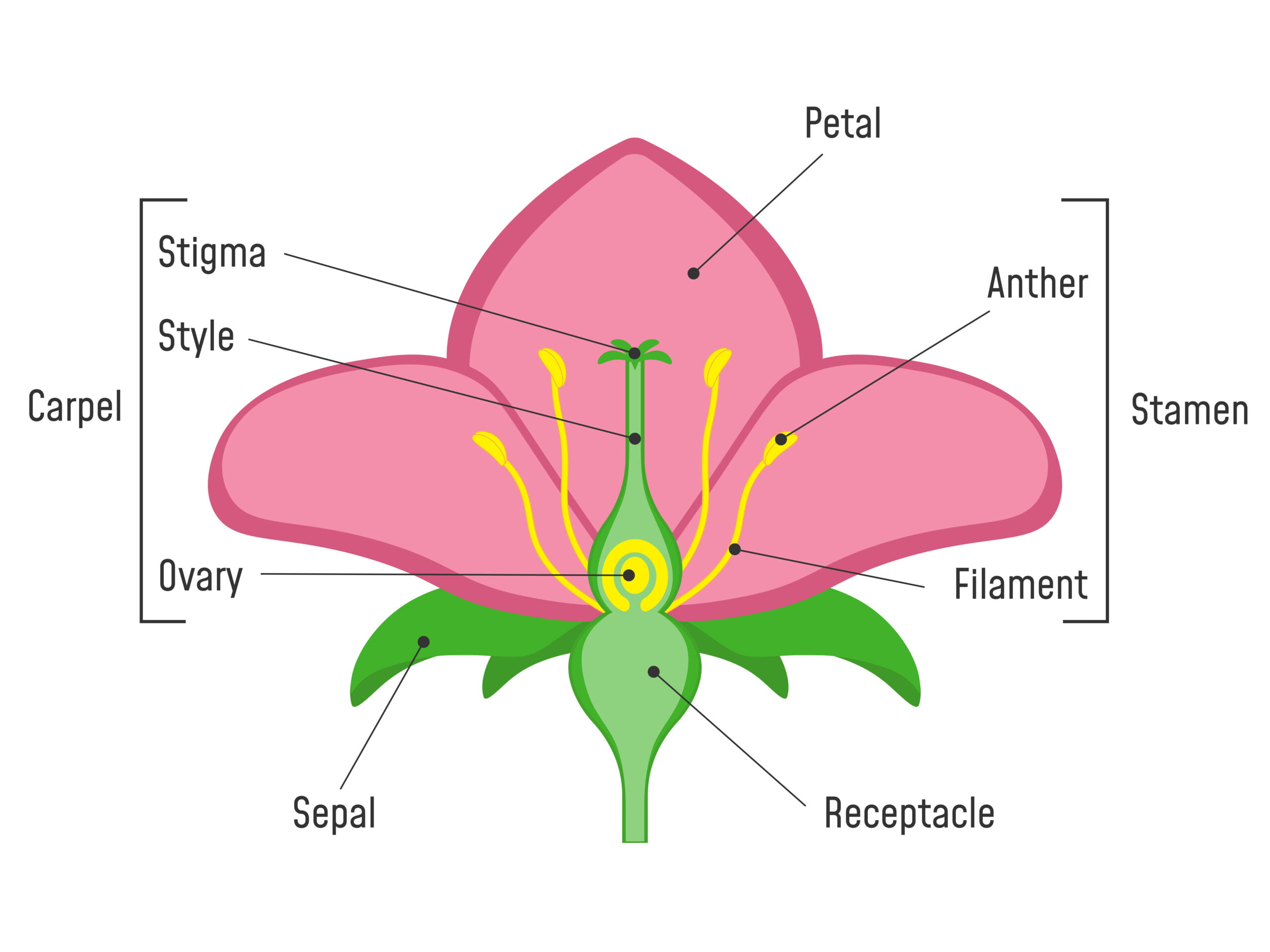
4 Main Parts of Flowers
Sepals
Petals
Stamens
Carpels
Sepals
Vegetative
Most leaf-like part
Usually green
Usually with functional stomata
Petals
Vegetative
Pigmented
Attract pollinators
Usually no functional stomata
Can be associated with nectar glands
Can be fused into a tube, partially fused, or separate
Stamens
Reproductive
Produce pollen grains
Consists of filament & anther
Anther - 4 pollen chambers
Pollination Methods
Insects
Birds
Wind
Water
Mammals
Carpels
Reproductive
3 Parts
Stigma
Style
Ovary
Seed Production
Zygote divides many times
Basal cell & embryonic ball produced
Then suspensor
Embryo establishes polarity
Integuments harden into seed coat
Endosperm nucleus divides thousands of times
Top Agricultural Crop Families
Grass (most common)
70% of farmland
Tomato
Bean
Cabbage
Melon
Carrot
Plants in the Solanaceae (Nightshades)
Food plants
Psychoactive plants
Ornamentals
Spice Families
Mint
Myrtle
Saffron
Most expensive
Ginger
Cinnamon
Licorice
Perfumes
Basic ingredients are odorants that are extracted
Volatile oils
Medicinal Plants
Used to treat/cure illness
Usually accidental discovery
¼ to ½ modern medicines derived from plants
Herbalists = strong plant solutions
Homeopaths = dilute solutions
Types of Medicinal Plants
Yams
Birth control
Foxglobes
Stabilizes arrythmia
Poppies
Opioids
Cinchona Tree
Malaria
Willows
Salicylic acid
Periwinkles
Tumors
Psychoactive Plants
Affect mainly the central nervous system
Cause hallucinations, delusions, etc.
Can be fatal
Types of Psychoactive Plants
Coca
Cocaine
Peyote
Marijuana
THC
Opium/Heroin
Nicotine
LSD
Nicotine is a part of what family?
Tomato
Stimulating Beverages
Have caffeine or other stimulant
E.g. tea, chocolate, coffee
What country is the #1 grower of coffee?
Brazil
Alcoholic Beverages
Contain ethanol
Fermented
Uses fungus to convert glucose into ethanol
Beer, wine
Distilled
Concentrates ethanol
Textiles
Derived from…
Seed Hairs
Cotton
Stems
Linens
Lignified Leaf Fibers
Agave
Flax
Linen
Stem tissues provide strong fabric
Superior to cotton
More expensive
Hemp
Marijuana family
Stem tissues provide tough, durable fabric
Genetically Modified Crops (GMO)
Non-plant genes incorporated
Can be unknown / unpredictable
E.g. golden rice, Morningstar corn
Vegetative Parts of Flower
Sepals
Petals
Reproductive Parts of Flower
Stamen
Carpels
Cell Division vs Sex Cell Division
Mitosis - Cell division
Meiosis - Sex cell division
Parts of a Flower
Alternation of Generations
Life cycle that involves a switch between two multicellular stages: haploid gametophyte (sexual) and diploid sporophyte (asexual)
Pollen Tube & Pollen Grain
After landing on the stigma, the pollen grain germinates and forms a pollen tube, which is a narrow tube that grows down through the style and the ovule, carrying the sperm cells for fertilization
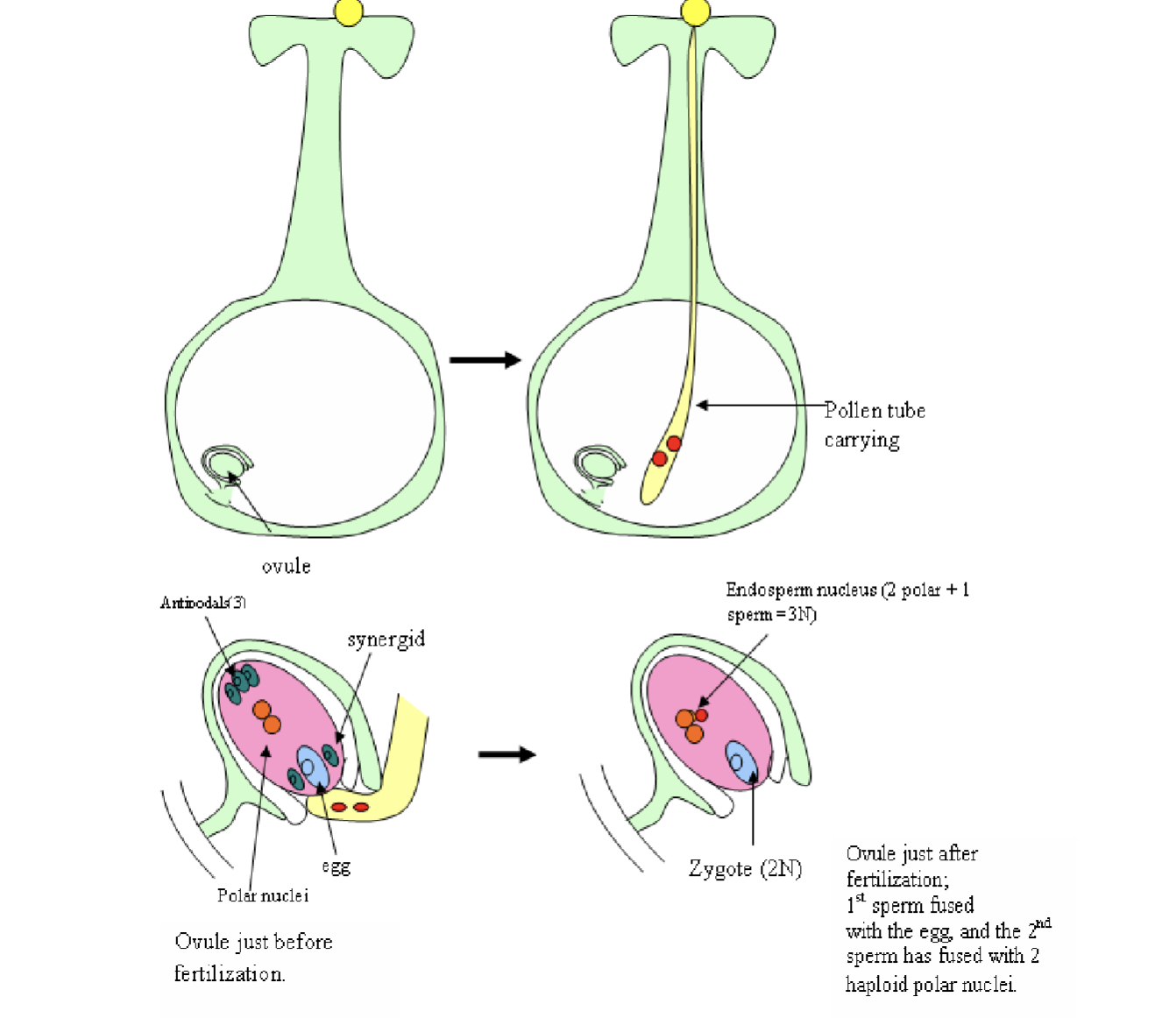
How is reproduction in flowering plants better than conifers
Flowering plants have double fertilization, where one sperm fertilizes the egg and the second fertilizes the central cell to form the endosperm. The second sperm in conifers does not fuse with anything.
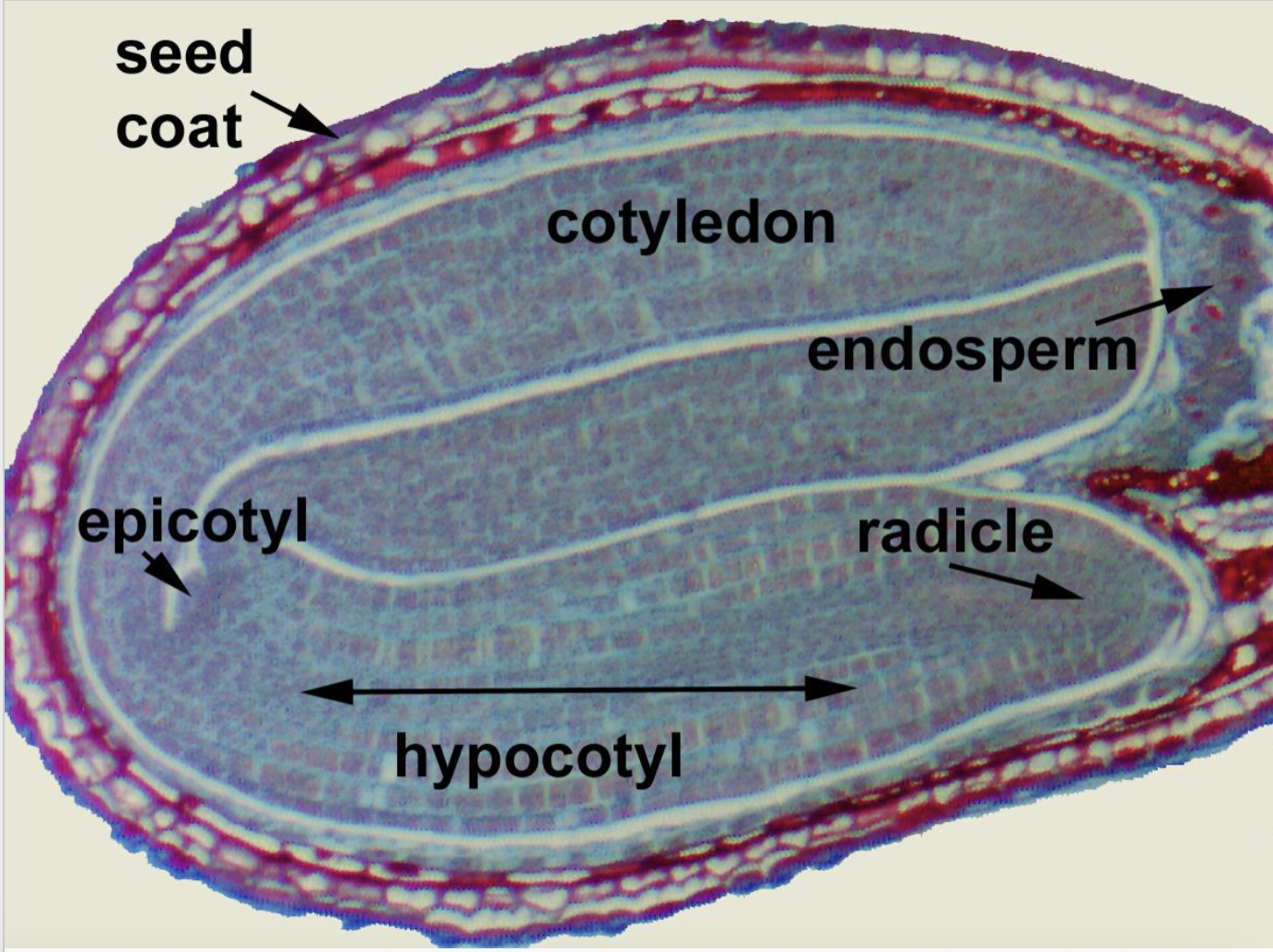
Parts of a Seed
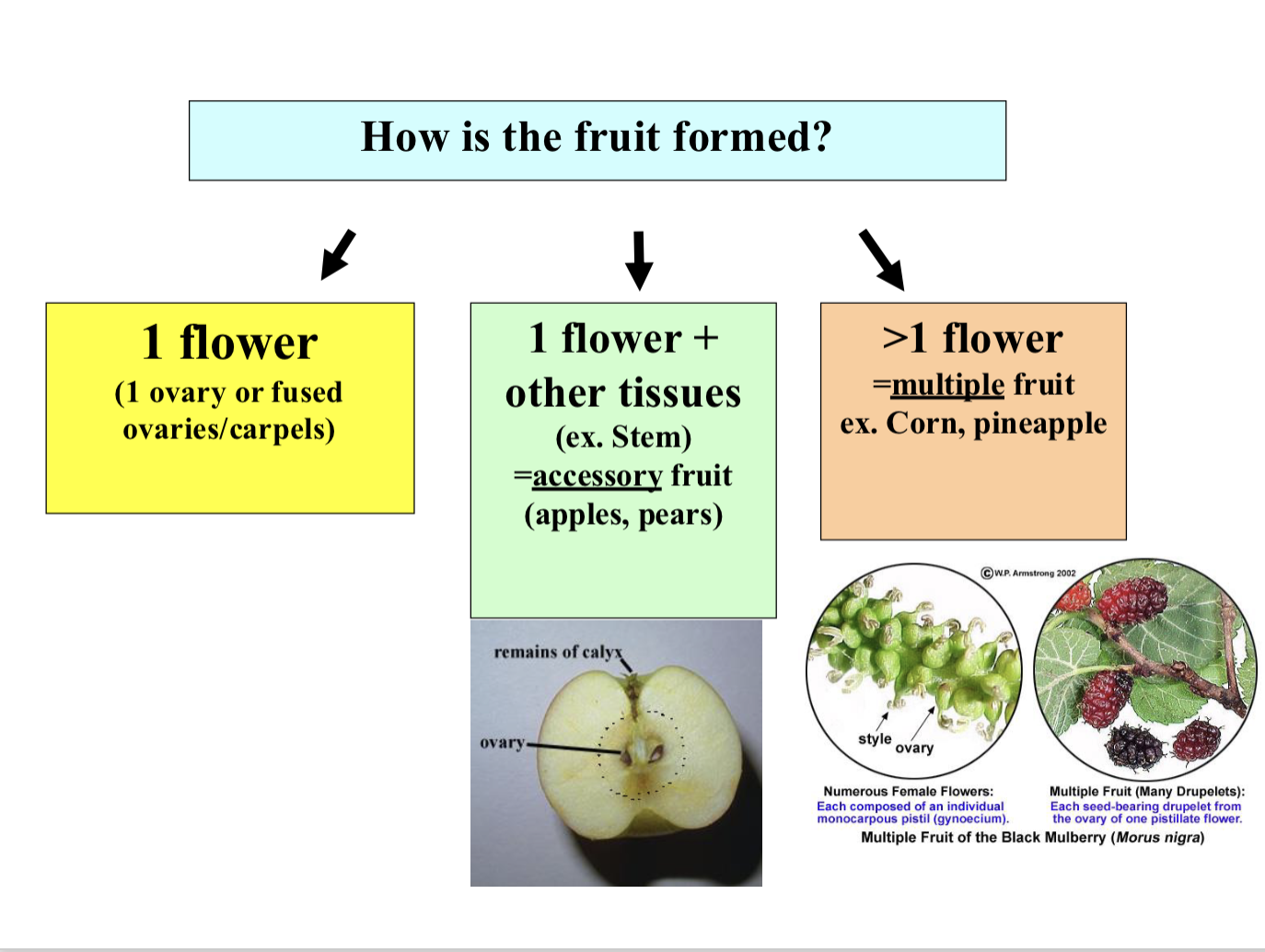
Fruit Types
1 flower
Aggregate (multiple ovaries)
e.g. strawberry
Simple (1 ovary)
Fleshy
e.g. berry
Dry
e.g. nut, legume
1 flower + other tissues (accessory)
e.g. apple, pear
> 1 flower (multiple)
e.g. corn, pineapple
Tillers
Clones that grow from grass plants
Tomato Family Paradox
Highly toxic