dysphagia final
1/173
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
174 Terms
clinical
Which comes first in assessment, clinical or instrumental eval?
false
done AFTER screening
T/F: Clinical examination is done before a problem has been identified (usually not by SLP).
all
Screening should be provided to --- patients in a category.
true positive: identified with true disease
true negative: identified with true absence of disease
false positive: identified with false disease
false negative: identified with false absence of disease
matching ~
A: identified with true disease
B: identified with true absence of disease
C: identified with false disease
D: identified with false absence of disease
terms ~ true positive / false positive / true negative / false negative
Sensitivity
:a test's ability to designate an individual with a disease as positive (few false negatives)
Specificity
a test's ability to designate an individual without a disease as negative (few false positives)
greater PPV
The more specificity in a test, the less likely the person with a positive test will be free of the disease = ---.
greater NPV
The more sensitivity in a test, the less likely the person with a negative test will have the disease = ---.
Positive predictive value
: probability that a patient with positive test result actually has the disease
Negative predictive value
: probability that a patient with negative test result actually does not have the disease
aspiration of saliva
a patient complaining of coughing when not eating may be a symptom of what?
consequences
With clinical evaluations, we watch a matching set of symptoms, signs, and ---.
difficulty chewing
match the sign and symptom:
Poor dentition; Tongue, jaw, lip weakness
difficulty initiating swallow
match the sign and symptom:
Xerostomia; Tongue weakness
Drooling
match the sign and symptom:
Infrequent swallows
nasal regurgitation
match the sign and symptom:
Bolus enters nasopharynx on VFS
swallow delay
match the sign and symptom:
Slow oropharyngeal transport on VFS
Food sticking
match the sign and symptom:
Residue in the esophagus on VFS
coughing and choking
match the sign and symptom:
Cough on test swallows
coughing when not eating
match the sign and symptom:
Aspiration of saliva on VFS
Reguritation
match the sign and symptom:
Positive pH probe study for acid reflux
weight loss
match the sign and symptom:
Measured weight below ideal standard
medical history
physical examinations
test swallow observations
what are the three main components of evaluation?
hospital records
What is the number one resource for medical history?
clinical observations
oral cavity inspections
cranial nerve assessment
aspects of physical inspection of swallowing:
50
If chest rise and fall rates are more than --- cycles per minute can indicate difficulty and/or abnormality.
~2-4 cm
What is the length for larynx elevation in a typical adult?
Alertness
Neuromuscular adequacy
Airway protection
swallow tests are reserved for patients who have demonstrated adequate:
false
T/F: Having failure in one swallow trial guarantees consistent failure.
3
Each bolus volume should be trialed --- times.
swallow safety
swallow efficiency
physiology
What do we look for in test swallows? (3)
cervical auscultation
-What is a method of making a judgment of delayed swallow response?
-technique for listening to a swallow response, involving a stethoscope placed at the level of the larynx
tongue
What causes the initial sound during cervical auscultation?
pharynx / esophagus / open
during cervical auscultation:
1st low-frequency burst: bolus enters ---
2nd low-frequency burst: bolus enters ---
3rd high-frequency burst: airway is ---
-Failure on thin or thick liquids
-wet voice or cough after swallow
-inability to self-feed
red flags for impaired airway protection: (3)
The 3-oz (85 ml) Water Test
Name the assessment:
Patients drink 3 oz. of water from a cup at self-determined pace, examiner notes cough or wet-hoarse voice for one minute
Impaired pharyngeal response
Male
Disabling stroke (Barthel <60)
Incomplete oral clearance
Palatal weakness or asymmetry
>70yrs of age
6 variables with significant predictive value for aspiration:
100 / 70
---% sensitivity and ---% specificity reported when a 50 ml water test is combined with a 2% drop in SpO2 in acute stroke patients, indicating aspiration.
McGill Ingestive Skills Assessment (MISA)
Name the assessment:
-Assesses functional eating skills in natural environment
-Designed initially for nursing home residents
Self-feeding*
Solid ingestion*
Texture management (variety of foods)*
In the MISA, what are the test areas that can show predicted value of time to death?
true
T/F: If a patient receives a score of <178 on the MASA, they are classified as having dysphagia.
Functional Oral Intake Scale (FOIS)
name the assessment:
documents patient's functional eating status
Functional Oral Intake Scale (FOIS)
Functional Oral Intake Scale (FOIS)

90% of patients who truly have the disease show positive results
A test shows 90% sensitivity, what does this mean?
90
---% of positive outcomes are truly positive
look at psychometrics (sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV)
efficiency
feasibility
easy to implement
good reliability (intra and interrater)
What factors impact the choices of a "good" assessment?
false
have LOWER odds
T/F: Patients who are tube dependent have the same odds of full recovery as someone without a feeding tube.
gag reflex shows pharyngeal constriction
"ah ah ah"
if they are able to do falsetto phonation
How do we directly evaluate the pharynx? (3)
thin liquids / solids / solids
pharyngeal dysphagia ~ difficulty with ----
oral dysphagia ~ difficulty with ---
esophageal dysphagia ~ difficulty with ---
mild dysphasia
aspiration
A patient scores 169 on the MASA, what does this indicate?
(2 items)
D
All the following rationales regarding clinical examination of swallowing are correct EXCEPT
A. Defining potential cause
B. Establishing a working hypothesis for the swallowing disorder
C. Establishing a tentative tx plan
D. Diagnosing an underlying disease
A
A dysphagia screening test with high sensitivity means
A. Most patients with dysphagia can be identified correctly
B. Most people with no dysphagia can be identified correctly
C. There is a high probability that a patient with a positive (abnormal) test result actually has dysphagia.
D. There is a high probability that a person with a negative (normal) test result actually has dysphagia.
A
Individuals with solid food dysphagia are more likely to have disorders of esophageal origin.
A. True
B. False
D
What is the associated sign with "food sticking"
A. Infrequent swallows
B. Bolus enters nasopharynx on VFS
C. Slow oropharyngeal transport on VFS
D. Residue in the esophagus on VFS
C
Clinical evaluation includes all the following, except
A. Obtaining a medical history
B. Inspecting the physical swallowing musculature
C. Conducting radiographic studies
D. Observing swallowing competence with test swallows
A
Oxygen saturation rates lower than 90% may indicate patients at risk for swallowing impairment.
A. True
B. False
A
Which test is specifically built to detect aspiration in patients with tracheostomy?
A. Modified Evans blue dye tests
B. Oxygen saturation tests
C. Videofluoroscopy
D. Water tests
B
Which of the following is a standardized test that evaluates a patient's functional eating skills in a natural environment?
A. Mann Assessment of Swallowing Ability
B. McGill Ingestive Skills Assessment
C. Mini Nutritional Assessment
D. Modified Barium Swallow Study
F - 6
What is the FOIS level in the following scenario? "Patient is eating a 'regular' diet except for salad, rice, meat, and bread"
A. Nothing by mouth (NPO) (1)
B. Tube dependent with minimal attempts at food or liquid (2)
C. Tube dependent with consistent intake of liquid or food (3)
D. Total oral diet of a single consistency (4)
E. Total oral diet with multiple consistencies but requiring special preparation or compensations (5)
F. Total oral diet with multiple consistencies without special preparation but with specific food limitations (6)
G. Total oral diet with no restriction (7)
C - 3
What is the FOIS level in the following scenario? "Patient on PEG but drinks different liquids daily and has tried some pudding level foods"
A. Nothing by mouth (NPO) (1)
B. Tube dependent with minimal attempts at food or liquid (2)
C. Tube dependent with consistent intake of liquid or food (3)
D. Total oral diet of a single consistency (4)
E. Total oral diet with multiple consistencies but requiring special preparation or compensations (5)
F. Total oral diet with multiple consistencies without special preparation but with specific food limitations (6)
G. Total oral diet with no restriction (7)
To determine the need for and the direction of swallowing rehabilitation
What is the purpose of MBS for speech pathologists?
lateral view for aspiration
AP view for symmetrical contraction
Name the best views of videofluoroscopy for aspiration and symmetrical oropharyngeal contraction.
VFE landmarks
landmarks
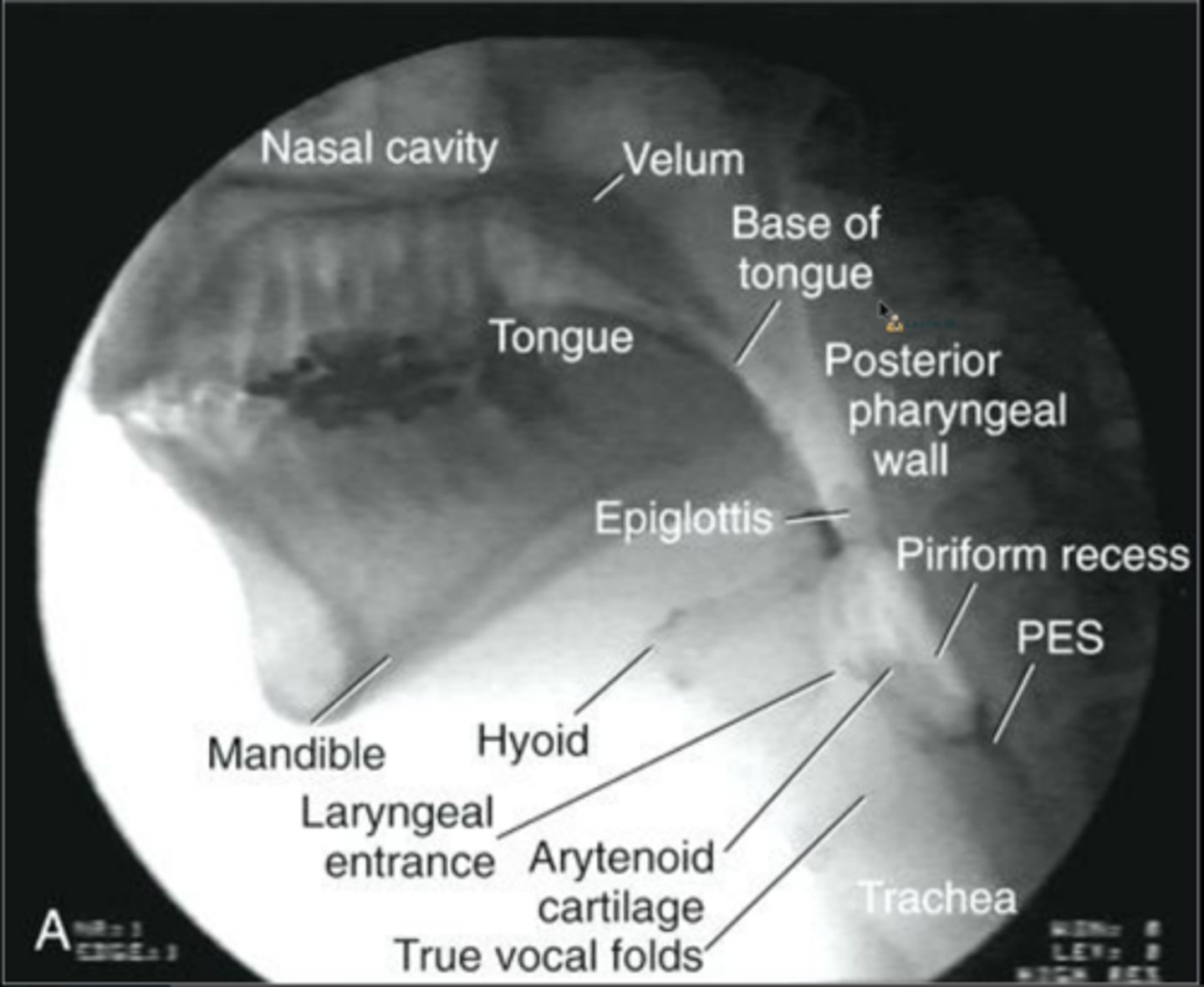
When the patient is at clear risk
When the clinical question has been answered
The issue of "when to stop" videofluoroscopy exam is not always clear, but two general guidelines are...
true
T/F: Recent work has suggested the order of bolus presentation does not impact the interpretation or outcome of fluoroscopic swallowing studies.
residue
There is a linear relationship between consistency and ---.
lower
Generally, the thicker the bolus, the --- the risk of airway compromise.
poor interrater reliability between clinicians
What is a downside of videofluoroscopy?
Modified Barium Swallow Impairment tool (MBSImp)
What is a highly validated and used tool for videofluoroscopy?
linear
There is a --- relationship between bolus volume and airway compromise and residue.
individualized
--- protocols are more common and advised for VFS.
a problem / penetration / aspiration / silent aspiration
The Penetration/Aspiration Scale interpretations:
more than 3 is considered ---
4-5 is considered ---
6-8 is considered ---
8 is considered ---
Pen/Asp Scale
name the exam:
This is NOT a dysphagia severity scale, it only ranks the depth of material entrance into the airway and patient's response.
Dysphagia Outcome and Severity Scale (DOSS)
name the exam:
-levels severity of dysphagia based on VFS data
-good interrater agreement
-downside: has not been validated
B
All the following indications suggest that an imaging swallowing examination is needed EXCEPT...
A. Respiratory issues create suspicion of dysphagia
B. Patient is too medically compromised
C. Swallowing safety is a concern
D. Dysphagia characteristics are unclear
D
All the following are among the objectives of Videofluoroscopy EXCEPT
A. Evaluating anatomy of swallowing mechanism
B. Evaluating swallow physiology
C. Identifying patterns of impaired swallow physiology
D. Evaluating the sensory aspect of swallowing
C
A patient reports a feeling of food being stuck after swallowing. VFS of oral-pharyngeal stages shows no sign of dysfunction. What is the next step?
A. Recommend thickened liquids for 3-5 days
B. Refer to ENT
C. Request an esophageal evaluation
D. Refer to psychologist
A
A patient shows no aspiration but increased residue on 5mL thick liquid. What would be appropriate to trial next?
A. 5 mL thin liquid
B. 5 mL pudding
C. 10 mL thin liquid
D. 10 mL thick liquid
B
A patient aspirates on 5mL thin liquid. What would be appropriate to trial next?
A. 5 mL thin liquid
B. 5 mL thick liquid
C. 5 mL pudding
D. 10 mL thin liquid
Purpose
Materials
Process of evaluation
list some similarities between endoscopy and videofluoroscopy: (PMP)
Technique
Image perspective
Portability
Repeatablity
Duration of examination
Sensory component
list some differences between endoscopy and videofluoroscopy: (TIPRDS)
Vocal cord closure
Laryngeal elevation
Epiglottic inversion
Pharyngeal closure
"White out"
Pharyngeal release
Laryngeal descent
Epiglottic return
Vocal fold re-opening
what do we see during a FEES exam?
58 / 7 / 35
Patterns of Maximal Vocal Fold Closure:
% = closed along entire glottis
% = posterior opening
% = no contact with small triangular opening
uvula and larynx
For endoscopy, between the --- and --- is the best place to start.
false
T/F: Decisions are often made on imaging alone.
fluoroscopy
Fluoroscopic vs. Endoscopic Swallowing Examinations:
-initial evaluation
-esophageal dysphagia
endoscopy
Fluoroscopic vs. Endoscopic Swallowing Examinations:
-paresis/paralysis
-anatomic deviations
-evaluate secretions
-patient cannot be transported
-repeated use
-biofeedback
true
T/F: Overuse of instrumental can weaken basic clinical precursor skills.
accuracy interpreting VFSS
Clinical knowledge of swallowing physiology is a significant predictor of ----.
clinical expertise / best research findings + patient values
Traditional clinical management focuses on --- and evidence based research focuses on ---.
best research evidence
patient values
clinical expertise
List the three parts of EBP:
Effectiveness
--- study: Treatment applied to a group to achieve a desired outcome with no control group for comparison.
Efficacy
--- study: Treatment applied to a group with a disorder and to another (control) group without the disorder to achieve a desired outcome.
systematic reviews of RCTs / expert opinion
What is the highest level of research? Lowest?
safely / adequate
General treatment consideration:
Can the patient --- resume or increase --- oral intake?
Passive Interventions
name the treatment choice:
-Limited patient engagement
-e.g. Oral hygiene, diet changes
active interventions
name the treatment choice:
-Patient engaged
-e.g. Techniques & maneuvers (Valsalva)
environmental interventions
name the treatment choice:
-Changes to the environment to facilitate feeding and swallowing
-e.g. Dining rooms, special mealtimes
behavioral
medical
surgical
What are the three categories of treatment options?
medical options
name the treatment option category:
-dietary modifications
-Pharmacological Management