BIOL 145 - Week 5 - Simpson college
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
114 Terms
Annual plants
Cycle completed in single season
Biennial plants
Cycle completed in two growing seasons
Perennial plants
Cycle takes several to many growing seasons or plant produces flowers on new growth, while other plant parts persist indefinitely
There are two major classes of flowering plants
Magnoliopsida (dicots) & Liliopsida (monocots)
Flowers occur as specialized branches at
Tips of peduncles or pedicels (stalk of single flower)
Receptacle
Swollen end of peduncle or pedicel
What is collectively called corolla
Petals
What is called a calyx
Sepals
What are calyx and corolla called together
Perianth
Superior Ovary
Calyx and corolla attached to receptacle at base of ovary
Inferior Ovary
Receptacle grows up and around the ovary
Carpel
Leaf with ovules on margins
Inflorescence
Group of flowers on a body
Exocarp
Skin
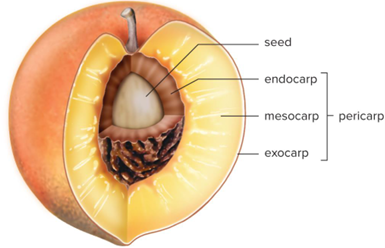
Endocarp
Inner boundary around seed(s)
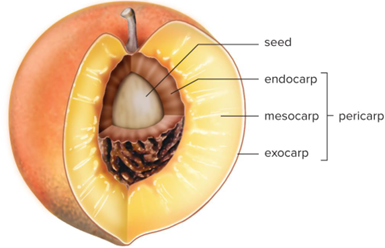
Mesocarp
Tissue between exocarp and endocarp
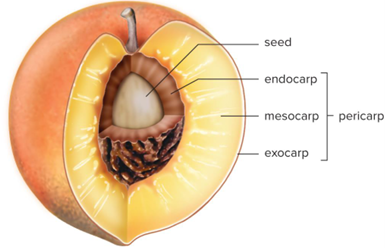
Mesocarp, endocarp, and exocarp can be called together what?
Pericarp
Fleshy Fruits
Mesocarp at least partly fleshy at maturity
Simple fleshy fruits develop from
Flower with single pistil
Drupe
Simple fleshy fruit with single seed enclosed by hard, stony endocarp (pit)
Hesperidium
Berry with a leathery skin that contains oils
True berry
With thin skin and relatively soft pericarp
Berries
From compound ovary, with more than one seed, and with fleshy pericarp
Pepo
Relatively thick rind
Dry Fruits
Mesocarp dry at maturity
Dehiscent fruits
Split at Maturity
Capsules
Consist of at least two carpels, and split in a variety of ways
Aggregate Fruits
Derived from single flower with several to many pistils (raspberries)
Cotyledons
Food storage organs that function as “seed leaves”
Embryo
cotyledons and plantlet
Plumule
Embryo shoot
Epicotyl
Stem above cotyledon attachment
Hypocotyl
Stem below cotyledon attachment
Radicle
Tip of embryo that develops into root
Germination is
beginning or resumption of seed growth
After ripening (seed germination)
Embryo composed of only of few cells when fruit ripens; seeds will not germinate until embryo develops
Scarification
Artificially breaking dormancy
Epigeous germination
Hypocotyl lengthens, bends and becomes hook-shaped. Top of hook emerges from ground, pulling cotyledons above ground.
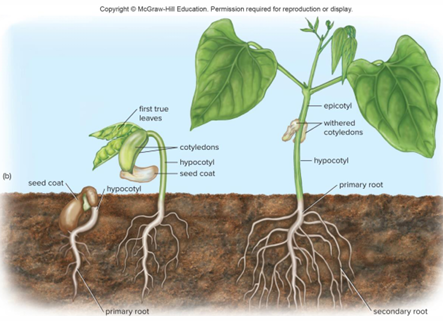
Hypogeous germination
Hypocotyl remains short and cotyledons do not emerge above surface
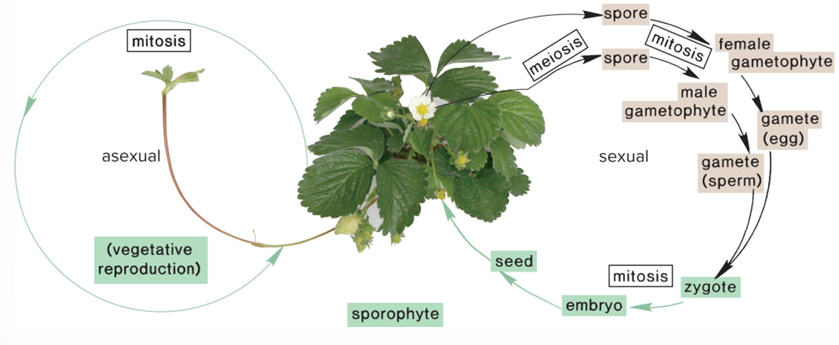
Asexual reproduction
Production of cells identical in chromosomes with cells from which they arose
Homologous chromosomes =
chromosome pairs
Meiosis: Division I (Meiosis I or Reduction Division)
Number of chromosomes reduced to half
Meiosis: Division II (Meiosis II or Equational Division)
No further reduction in chromosome number
Sporophytes develop from
zygotes and produce sporocytes
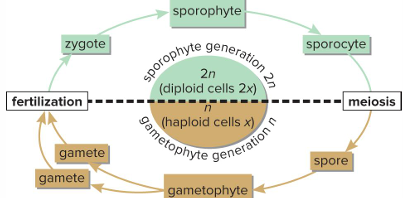
Sporocyte undergoes meiosis
Produces 4 haploid spores
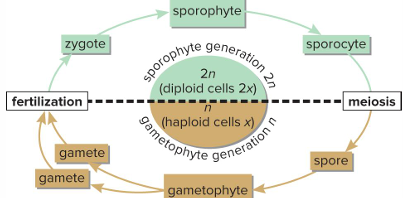
Gametophytes develop from
Spores
Rule 1 for Alteration of Generations
First cell of gametophyte generation is a spore, and last is a gamete
Rule 2 for Alteration of Generations
Any gametophyte cell contains half the chromosomes as the sporophyte generation
Rule 3 for Alteration of Generations
First cell of sporophyte generation is a zygote, and last cell is a sporocyte
Rule 4 for Alteration of Generations
Any sporocyte cell contains twice as many chromosomes as the gametophyte generation
Rule 5 for Alteration of Generations
Change from sporophyte to gametophyte generation occurs as a result of meiosis
Rule 6 for Alteration of Generations
Change from gametophyte to sporophyte occurs as a result of fertilization.
Chromosomes composed two types of large molecules
DNA and protein
RNA
Contains ribose, instead of deoxyribose sugars; single stranded; thymine replaced by uracil
Translation
RNA translated to produce proteins
Messenger RNA (mRNA)
Translated to produce proteins
Transfer RNA (tRNA)
Machinery for translation
Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
Machinery for translation
Promoter
Region at beginning of every gene signals transcription enzymes to begin copying gene
Terminator
DNA sequence at end signals transcription enzymes to fall off
Mutations are
changes in a DNA sequence
Mutagens
Agents that alter DNA sequences
Mutagens examples
Ultraviolet light, Ionizing radiation, Certain chemicals
Aneuploid
Carries one or more extra chromosome(s), or is missing one or more chromosome(s)
Polyploid
Has at least one complete extra set of chromosomes
Gregor Mendel help create what?
PUNNETT SQUARE
Homozygous
Both alleles identical
Heterozygous
Alleles are contrasting
Phenotype
Organism’s physical appearance
Genotype
Genetic information responsible for contributing to phenotype
Law of dominance
For any given pair of alleles, one (dominant) may mask the expression of the other (recessive)
Law of unit characters
Factors (alleles), which always occur in pairs, control the inheritance of various characteristics. Genes are always at the same position (locus) on homologous chromosomes
Monohybrid cross
F1 plants intercrossed to produce F2 generation
Dihybrid cross
Start with parents differing in two traits
Law of independent assortment
Factors (genes) controlling two or more traits segregate independently of each other
Testcross
Cross between a plant having a dominant phenotype with a homozygous recessive plant
Why a testcross
Determine whether plant with dominant phenotype is homozygous or heterozygous
Backcross
A cross between a hybrid and one of its parents
Quantitative traits exhibit
Range of phenotypes rather than discrete phenotypes as studied by Mendel
Extranuclear DNA
In mitochondria and chloroplasts
Linked genes
Genes together on a chromosome
Hardy-Weinberg law
Proportions of dominant alleles to recessive alleles in a large, random mating population will remain same from generation to generation in the absence of forces that change those proportions
Forces that can change proportions of dominant to recessive alleles
Small populations & Selection
Selection
Most significant cause of exception to H-W (Hardy-Weinberg Law)
Small populations
Random loss of alleles can occur if individuals do not mate as often