Nonlinear Pharmacokinetics, PHT, and CBZ- Krysiak
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
When the rate of drug admin= rate of drug metabolism and excretion that is known as…
steady state
Nonlinear pharmacokinetics can apply to which of the following processes? SATA
a. absorption
b. distribution
c. renal elimination
d. hepatic elimination
a,b,c,d
What is nonlinear pharmacokinetics?
concentration and dose are NOT PROPORTIONAL
conc either increases/decreases more/less than expected
What are some examples of drugs that exhibit saturable metabolism also known as michaelis-menten kinetics?
PHENYTOIN
theophylline
What is Michaelis-Menten kinetics?
also known as Saturable Pharmacokinetics
occurs when the number of drug molecules overwhelms the enzymes' ability to metabolize the drug
PRACTICE:
How does doubling the dose affect serum drug concentrations in Michaelis-Menten kinetics?
It will yield much higher than expected serum drug concentrations
In Michaelis-Menten kinetics, what parameters are not constant?
Clearance of the drug
t ½
In Michaelis-Menten kinetics, what parameters are constant?
Vd
What is Vmax in Michaelis-Menten kinetics?
Maximum metabolic capacity when the enzyme is saturated
What is Km in Michaelis-Menten kinetics?
Substrate concentration at which V = ½ Vm
In Michaelis-Menten kinetics, clearance, elim rate, and time to steady state changes so what cannot be calculated in a traditional manner?
t ½
What is the indication for fosphenytoin?
short-term parenteral admin
100mg of phenytoin would be ______mg fosphenytoin PE.
100
Why does fosphenytoin have less risk of CV collapse or CNS depression than IV phenytoin?
does not contain propylene glycol
What is the salt factor of phenytoin sodium?
What is the salt factor of phenytoin acid?
Na= 0.92
acid= 1
Phenytoin acid is not to be used for what?
once daily dosing
What amount of phenytoin is toxic? lethal?
>30 mcg/ml = toxic
>100mcg/ml= lethal
What are the max IV rates for phenytoin and fosphenytoin?
phenytoin—> do not exceed rate of 50mg/min
fosphenytoin—> do not exceed rate of 150mg PE/min
Does hypoalbuminemia lead to a higher or lesser chance of phenytoin toxicity?
What value is considered hypoalbuminemia?
more (phenytoin 92% protein bound—> hypoalbuminemia would lead to more free drug= toxicity)
alb < 3 gm/dL

recognize this is the equation used if you have to calculate a corrected phenytoin level!!!
(equation given on exam)

How do you calculate phenytoin Vd?
Vd= phenytoin Vd x weight
phenytoin Vd= 0.7L/kg
To calculate Vd, what weight do we use?
a. ideal body weight
b. adjusted body weight
c. actual body weight
d. corrected body weight
c.
When do you administer a phenytoin loading dose?
newly diagnosed and phenytoin naive
pt. on phenytoin but has low level
How frequently should you administer oral phenytoin?
in 3 divided doses of IR
1-2 divided doses of ER
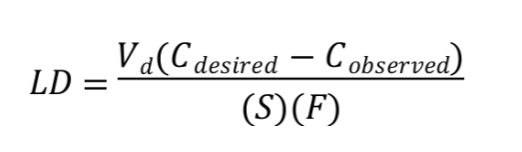
Recognize this is the equation for calculating a loading dose of phenytoin.
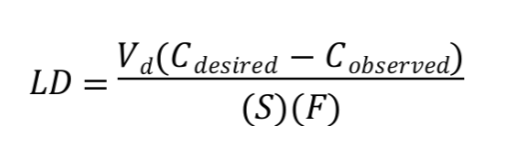
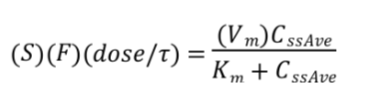
In the michaelis-menten equation, what do we assume for Km and Vm?
Km= 4mg/L
Vm= 7mg/kg/day
What is t90%?
minimum time a pt. must have received a maintenance dose before assuming the pt. is at steady state
What is the therapeutic range for total phenytoin in general?
10-20 mcg/ml
5-10 mcg/ml may be good for some pts.
BBW of carbamazepine?
thrombocytopenia, aplastic anemia or agranulocytosis
What is the Vd for Carbamazepine?
adults: 1.2 L/kg
children: 1.9L/kg
What’s unique about carbamazepine metabolism? How does that relate to dosing?
AUTOINDUCTION!!!
pts. can’t be initially placed on dose of CBZ that will result in safe/effective outcomes
star with 1/4- 1/3 of usual dose
About how many days does it take to titrate up the dose of carbamazepine to the desired dose?
21-28 days
Is dose reduction of CBZ required in renal failure?
no
CBZ is an inducer and substrate of what enzymes?
CYP3A4, 1A2, 2C9 inducer
CYP3A4 substrate
What disease state effects the dosing of CBZ?
hepatotoxicity
When is the pseudolinear pharmacokinetic method indicated?
only indicated to determine estimate of CBZ concentration after dose change