Long-Term Memory: Interference, Distortion, and Enrichment
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Trace Decay Theory
The theory suggesting memory traces fade over time.
Proactive Interference
Old memories hinder retrieval of new memories.
Retroactive Interference
New memories hinder retrieval of old memories.
Lateral Inhibition
Suppression of one memory trace by another.
Tip-of-the-Tongue Phenomenon
Inability to retrieve a known memory.
Consolidation
Stabilizing memories to become semi-permanent.
Reconsolidation
Restoring memory trace after retrieval.
Amnesia
Severe impairment in memory function.
Retrograde Amnesia
Loss of memories before amnesia onset.
Anterograde Amnesia
Inability to form new long-term memories.
Korsakoff's Syndrome
Memory disorder from thiamine deficiency.
Confabulation
Filling memory gaps with false information.
Skill Learning
Learning tasks through repetition and practice.
Priming
Enhanced processing due to prior exposure.
Associative Learning
Linking stimuli or responses through conditioning.
Classical Conditioning
Learning through pairing stimuli to elicit responses.
Instrumental Conditioning
Associating behavior with consequences (rewards/punishments).
Neuroplasticity
Brain's ability to change shape through learning.
Synaptogenesis
Formation of new synapses in the brain.
Neurogenesis
Creation of new neurons in the brain.
Environmental Enrichment
Enhanced brain development from complex environments.
Standard Condition (SC)
Basic housing condition for lab animals.
Impoverished Condition (IC)
Limited stimulation environment for lab animals.
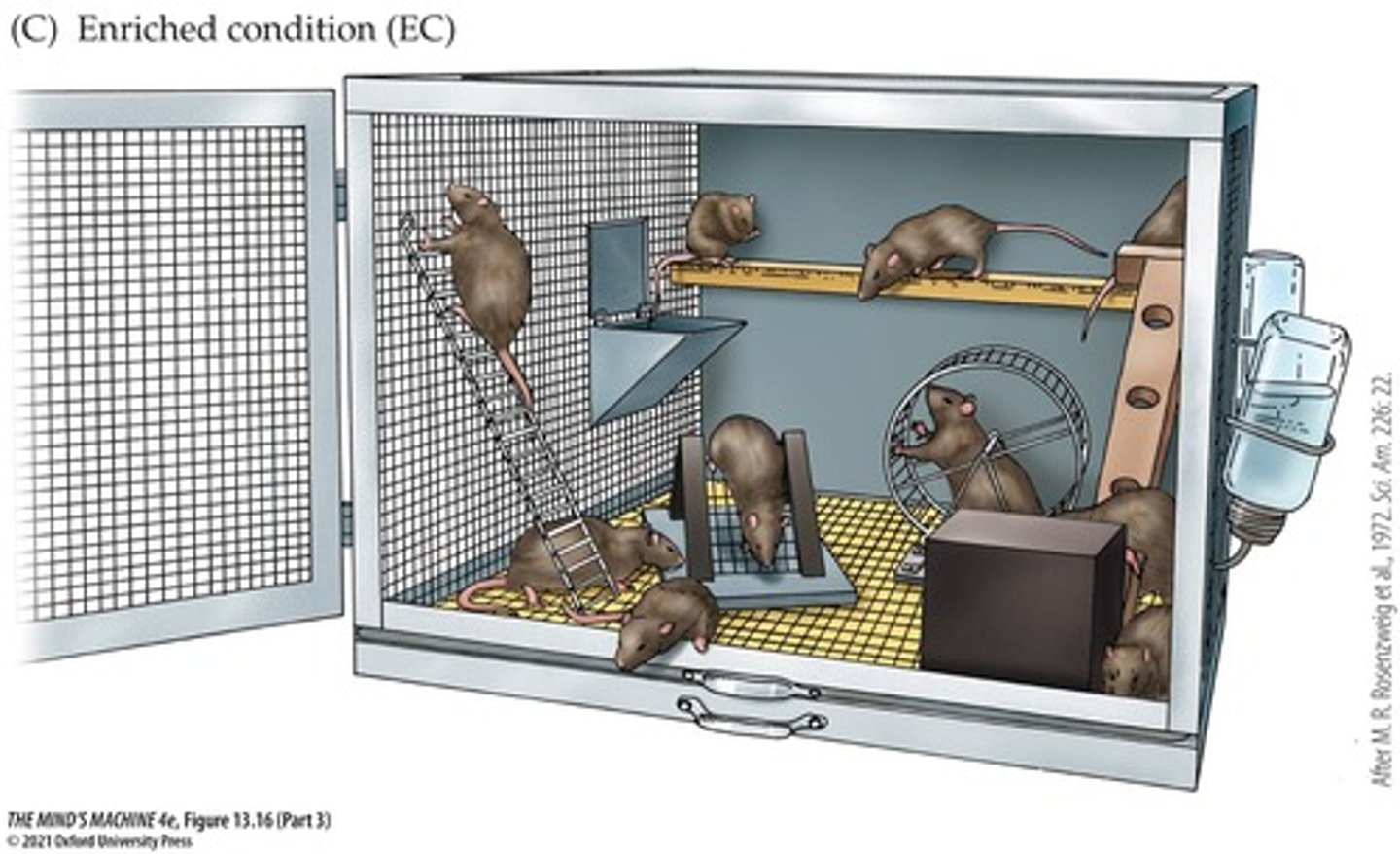
Enriched Condition (EC)
Stimulating environment promoting brain growth.
Cholinergic Activity
Acetylcholine action enhancing cognitive functions.
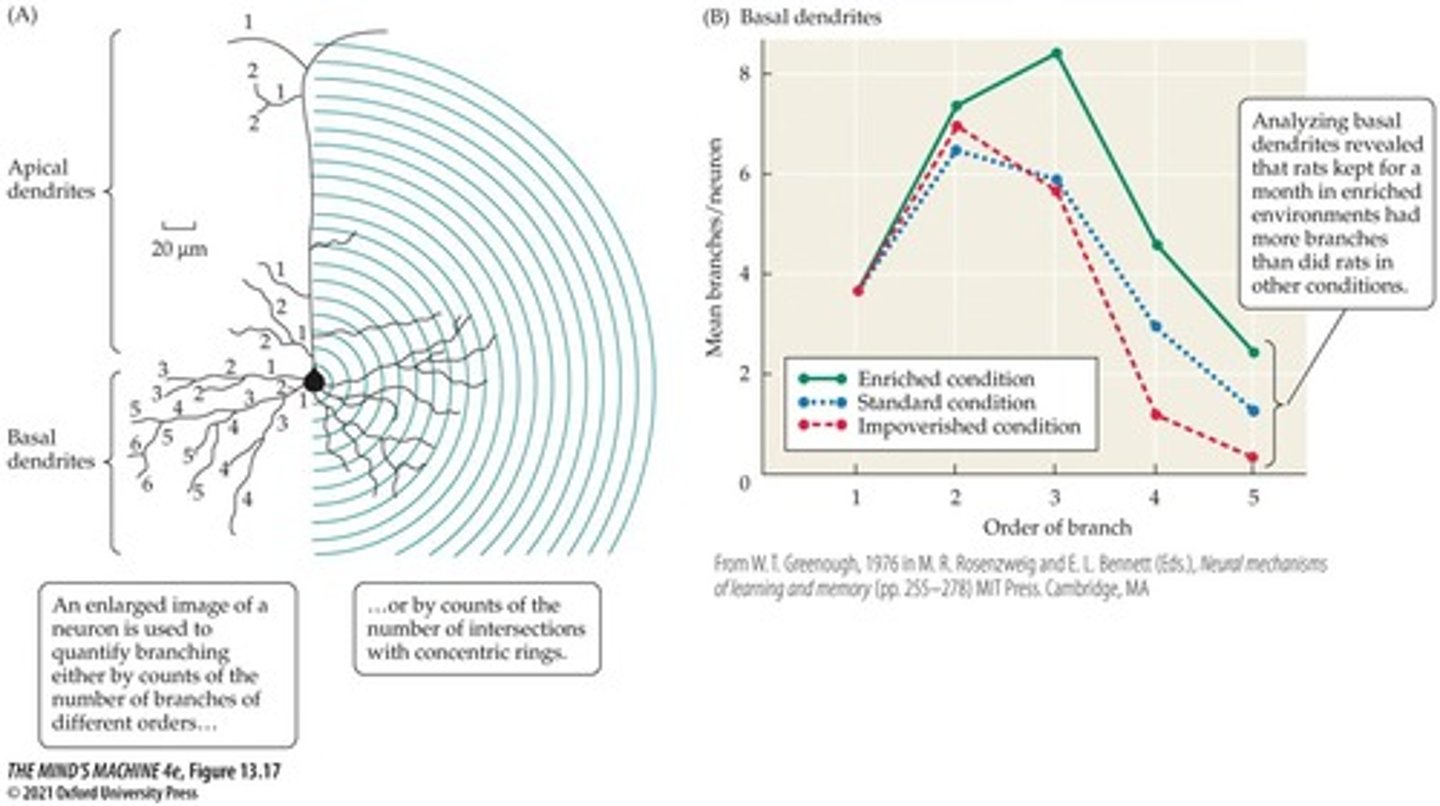
Dendritic Branching
Growth of dendrites improving neuron connectivity.
Cortical Synapses
Connections between neurons in the cortex.