Chapter 6 - Theorems/ideas - Matrix Algebra
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Properties of the Inner Product:
For vectors u, v, w, in Rn and scalar c:
Guarantees:
Inner products behave nicely with addition/scalars and detect zero vectors.
This is used to prove orthogonality, lengths, projections, Gram-Schmidt
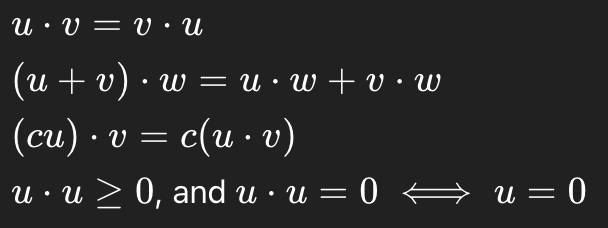
Pythagorean Theorem
Orthogonality → squared lengths add
Shows right angle algebraically, used in best approximation proofs
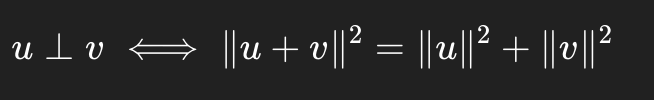
Othogonal sets are independent
If {u1,…,up} is an orthogonal set of nonzero vectors, then it is linearly independent
Guarantees:
Orthogonal + nonzero → basis automatically
First way to prove basis without row reduction
Coordinates in an Orthogonal Basis
If {u1,…,up} is an orthogonal basis for W and y in W
Guarantees:
Unique coordinates without solving systems
Used in projections, least squares, Gram-Schimdt
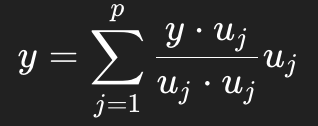
Orthonormal Columns Test
An m x n matrix U has orthonormal columns if:
UTU = I
Guarantees:
Quick test for orthonormality
Appears constantly in QR, projections, least squares
Orthogonal Decompostion Theorem
Every y in Rn can be written uniquely as:
Guarantees:
Unique split into “in-subspace” + “perpendicular error”.
Foundation of least squares

Best Approximation Theorem
Guarantees:
Projection is the closest point in W
Explains why least squares works
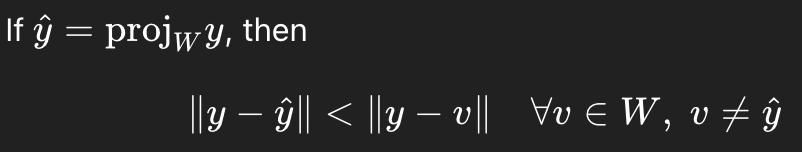
Projection Matrix Formula
If U = [u1…up] has orthonormal columns,
Guarantees:
Projections can be done with a matrix multiplication
fast projections; shoes projection matrices satist P² = P
![<p>If U = [u<sub>1</sub>…u<sub>p</sub>] has orthonormal columns, </p><p></p><p>Guarantees: </p><p>Projections can be done with a matrix multiplication</p><p></p><p>fast projections; shoes projection matrices satist P² = P</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3438d1bb-7e95-430d-91db-71f680f361b4.png)
Gram-Schmidt Process
Given a basis {x1,…,xp} Gram-Schmidt produces an orthogonal basis {v1,…,vp} spanning the same space
Guarantees:
Any basis → orthogonal basis
Required before QR and orthonormalization
QR Factorization
If A has linearly independent columns, then A = QR where:
Q has orthonormal columns
R is upper triangular with positive diagonal entries
Guarantees:
Every full rank matrix admits QR