1.1 The market system
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
the three different economic group/agents
consumers, firms, governments
What is the economic objective of each group?
consumers- to maximise their benefit/satisfaction
firms- to maximise profit
governments- to maximise the welfare of its citizens
Goods
Physical items that are tangible and can be physically taken away by the consumer
Services
Intangible items that firms provide that can't be physically touched
Needs
Things consumers require for basic human survival. Water, food, shelter, clothes, warmth
Wants
Things which consumers desire to have. They are not a necessity.
The basic economic problem
Consumers, firms, and governments have unlimited needs and wants. However resources are limited/finite (scarcity)
Factors of production
Land- Natural resources used to make the final product
Labour- Human resources used to make the final product
Capital- Man made resources used to make the final product
Enterprise- The supervision of the other three FOP to produce the final product
Why do economic agents have to make decisions
Firms, consumers. and governments have to make choices because of the economic problem.
Define opportunity cost
The benefits given up/foregone of the next best alternative
What are the three economic questions?
1. What to produce- the needs and wants of consumers
2. How to produce- FOPs
3. For whom?
What is revenue
What firms receive in exchange for selling a product
What is a product
A good or service
Calculate profit
Revenue-cost
Calculate total revenue
quantityxprice
What does it mean if the economy produces at any point on the PPC
It means that all the economies available resources (land labour capital enterprise) are being fully utilised
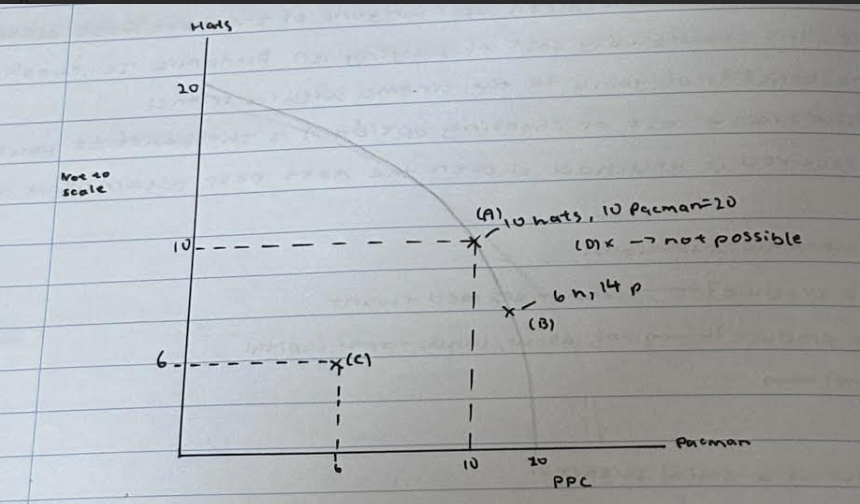
What does it mean if the economy produces below the PPC
It means that the economy is not fully utilising all of it's available resources, therefore there is a spare capacity of resources within the economy
What does it mean if the economy produces above the PPC
It is unobtainable in the short run because the FOP are fixed in the short-run but variable in the long run. However it is obtainable in the short run because the FOP are variable in the long run which could illustarte economic growth.
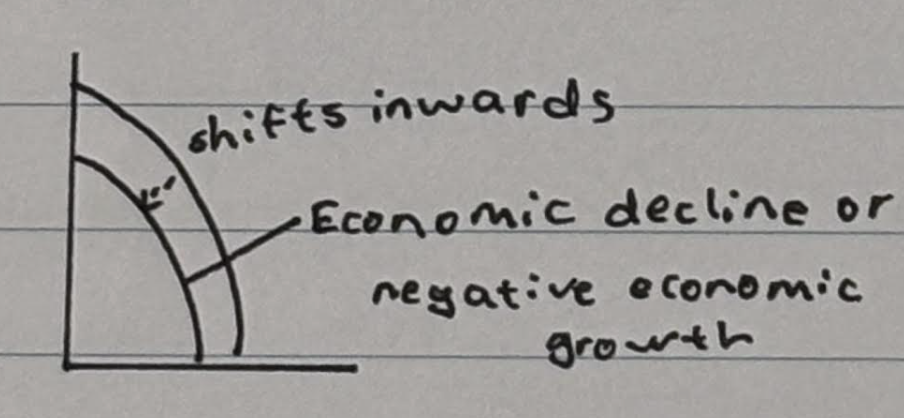
What happens when the PPC shifts inwards
Show economic decline or negative economic growth
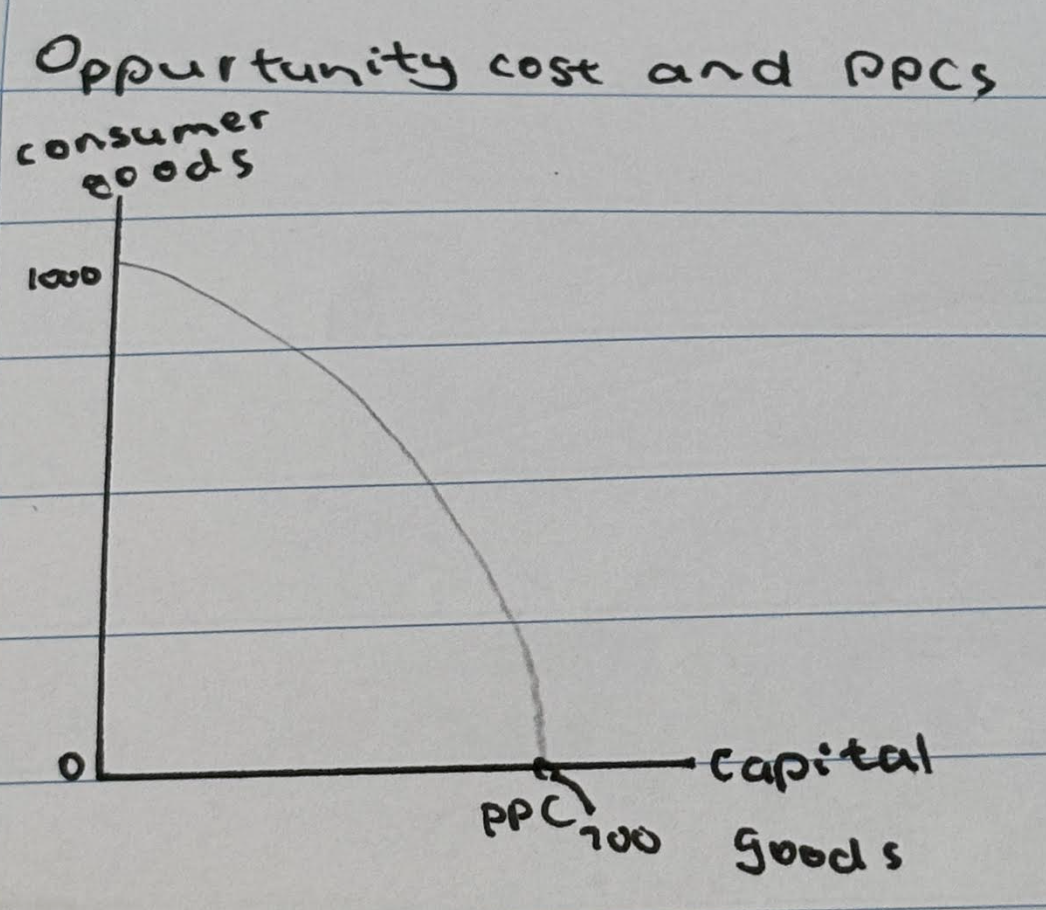
Opportunity cost and PPCs
The opportunity cost of allocating all the available resources towards producing 1,000 consumer goods is 700 capital goods. The opportunity cost of allocating all resources towards 700 capital goods is 1,000 consumer goods.
Causes of economic growth
1. increase in birth rate
2. increase in money spent in education (labour, enterprise)
Causes of economic decline
1. Increasing the school leaving age
2. harvest failure (land)
3. natural disaster (land, labour, capital)
4. pandemic
When will PPC increase
PPC will increase if quantity and/or quality of FOP increases
What do classical+modern economists argue?
classical- consumers will always make economic choices based on rationality (maximising their benefit)
modern- do not always make economic choices based on rationality
Reasons why consumers may not maximise their benefit
- consumers are not always good at calculating their benefits
- struggle to break bad habits and make good ones
- sometimes copy others' behaviour, influencers and peer pressure
- consumers seek short term gratification and do not consider the long term
- low income, healthier things usually cost more
- the power of advertising, social media
- addiction
- lack of time
- emotional e.g stressed, tired
- lack of information/ education/ misinformation
Reasons why producers may not maximise their profit
- producers may have managers that revenue maximise or sales maximise
- producers may prioritise caring for customers
- producers may complete charitable work.
What is demand
The quantity of a product which consumers are willing and able to buy at a given price
What does the Law of demand state?
When the price of a product increases, the quantity demanded decreases (inversely proportional) because less people are willing and able to buy the product at a higher price, and vice versa.
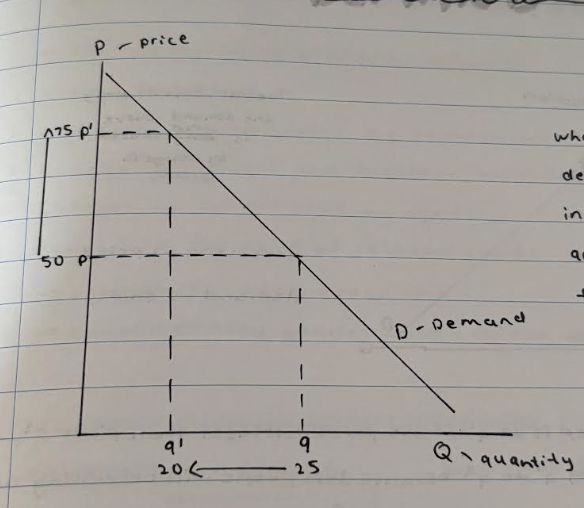
What are the movements along the demand curve caused by?
Movements —> change in price
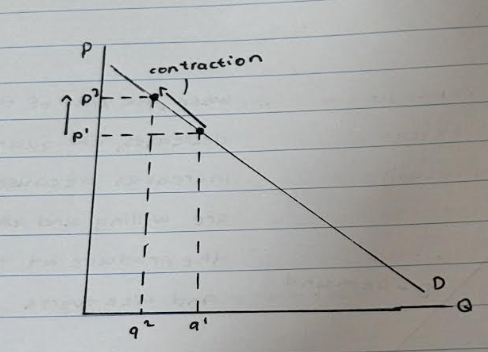
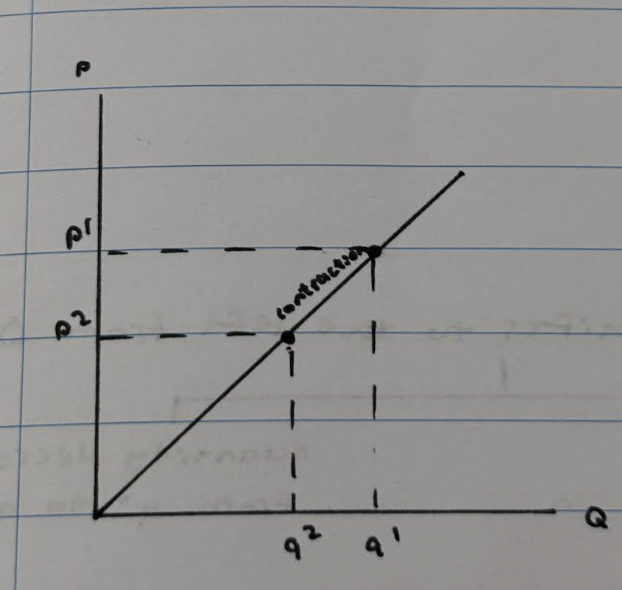
What happens when there is a contraction in demand?
At p1, the quantity demanded is at q1. If the price increases from p1 to p2, the quantity demanded will decrease from q1 to q2 because less people are willing and able to buy the product at a higher price, causing a movement along the demand curve known as the contraction in demand.
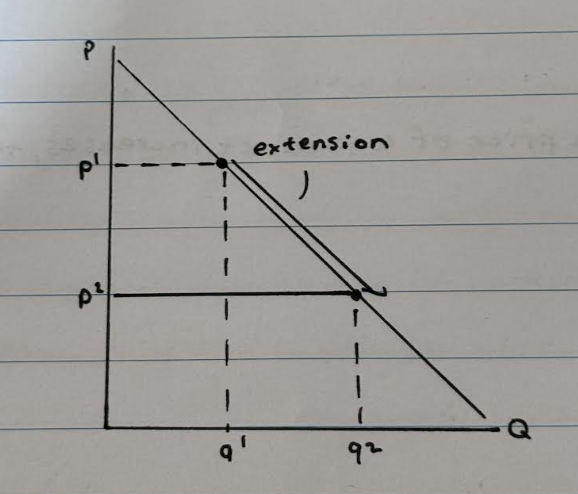
What happens when there is an extension in demand?
At p1, the quantity demanded is at q1. If the price decreases from p1 to p2, the quantity demanded will increase because more people are willing and able to buy the product at a lower price, causing a movement along the demand curve known as an extension in demand.
What are shifts on the demand curve caused by?
They are caused by change in demand (increase/decrease)
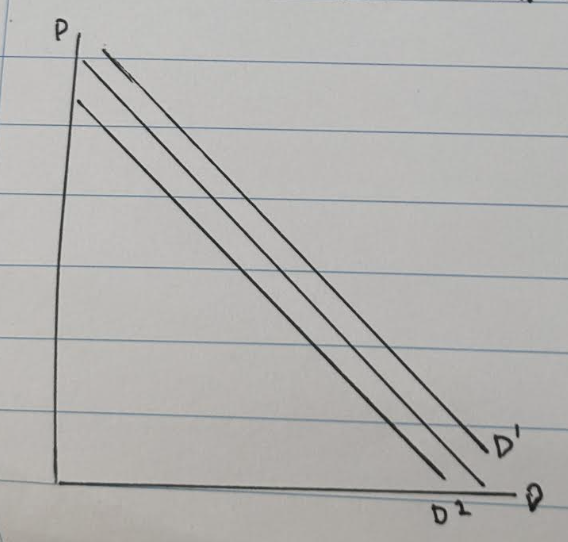
What happens to the demand curve when the demand increases?
Shift of the demand curve to the right (outward shift) from D to D1
What happens to the demand curve when the demand decreases?
Shift of the demand curve to the left (inward shift) from D to D2
What are the factors that cause a shift in demand?
- change in income
- change in demographics e/g population changes
- changes in tastes and fashions, seasonal products
- changes in advertising budgets
- changes in the price of related goods
-> substitutes (pepsi, cola)
-> complimentary goods (cake+coffee)
Price of substitute goods increases. (Pringles, Lays)
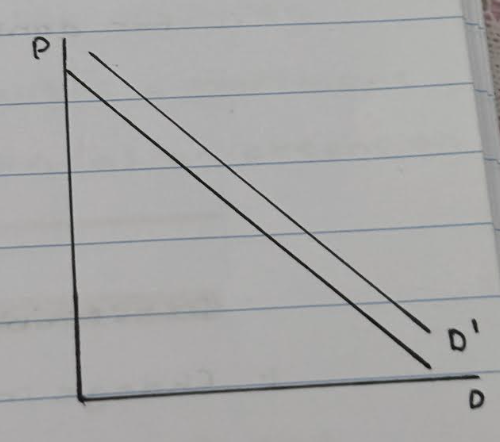
Analyse each stepping stone
1. The price of pringles has increased
2. Therefore the demand for pringles decrease
3. Subsequently the demand for lays increases
4. Therefore the demand curve for lays shifts from the right D to D1.
Price of substitute goods decreases. (Pringles, Lays)
1. The price of pringles has decreased
2. Therefore the demand for pringles increase
3. Subsequently the demand for lays decrease
4. Therefore the demand curve for lays shifts from the left D to D2.
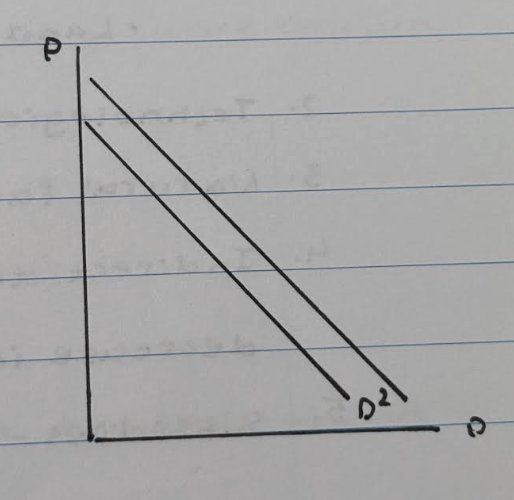
Price of complimentary goods increases. (donuts, coffee)
1. The price of donuts has increased
2. Therefore the demand for donuts decrease
3. Subsequently the demand for coffee decreases
4. Therefore the demand curve for coffee shifts to the left D to D2.
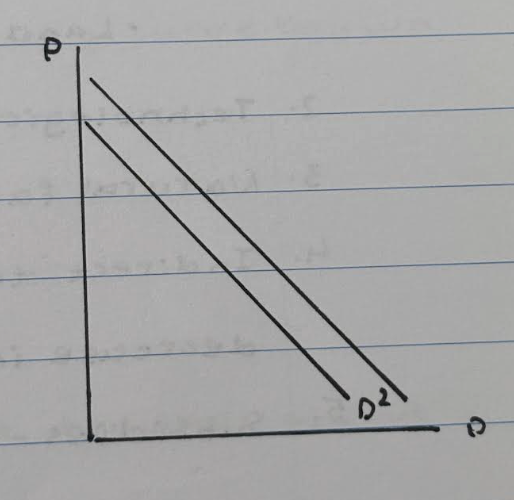
Price of complimentary goods decreases. (donuts, coffee)
1. The price of donuts has decreased
2. Therefore the demand for donuts increase
3. Subsequently the demand for coffee increases
4. Therefore the demand curve for coffee shifts to the right D to D1.
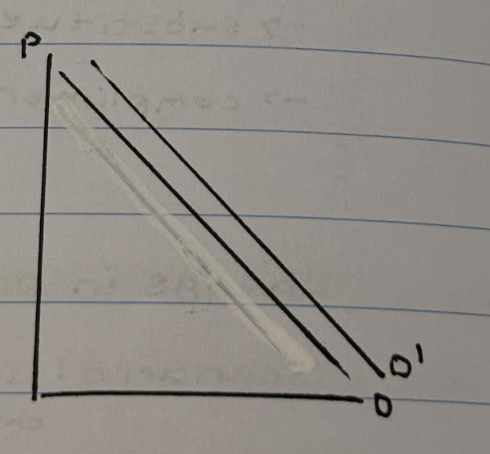
What are the determinants of supply (factors which cause a shift in supply)
- change in cost of production
e.g cost of production (FOP) increases, firms will be less willing and able to supply the product, therefore supply decreases
- technological advancements e.g faster machinery --> increase in supply
- Natural factors e.g pandemic, weather --> harvest)
- Indirect taxes--> increase VAT --> increase in cost of production--> decrease in supply
- subsidies- money given by the government to firms -> firm's cost of production decreases --> supply increases
What is cost?
Cost to the firm making the product
What is price?
What consumers pay for the product
What is supply?
The quantity of a product firms are willing and able to sell at a given price
What is the law of supply?
When the price of a product increases, the quantity firms and willing and able to supply to the market increases because the high amount of profit they will achieve.
How are movements along the supply curve caused by?
change in price
What happens when there is a extension in demand?
At p1, the quantity demanded is at q1. If the price increases from p1 to p2, the quantity supplied will increase causing a movement along the supply curve known as an extension in supply.
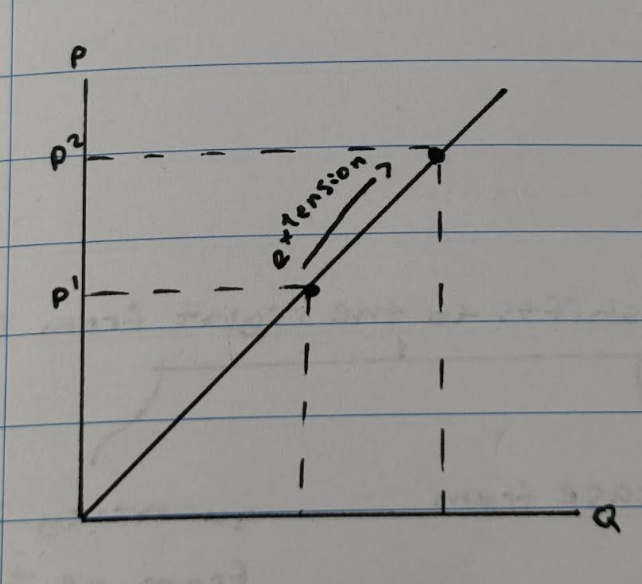
What happens when there is a contraction in demand?
If the price increases from p1 to p2, the quantity supplied will decrease causing a movement along the supply curve known as a contraction in supply.
What causes a shift in the supply curve?
It is causes by changes in supply (increase/decrease)
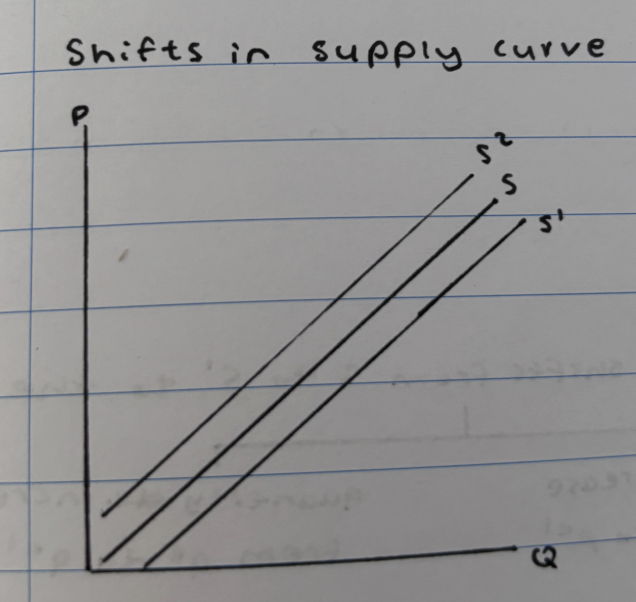
What happens when supply (cost of production) increases?
Supply curve shifts towards the right from s to s1.
What happens when supply (cost of production) decreases?
Supply curve shifts towards the left from s to s2.
What is the equilibrium point?
It is where demand and supply intersect.
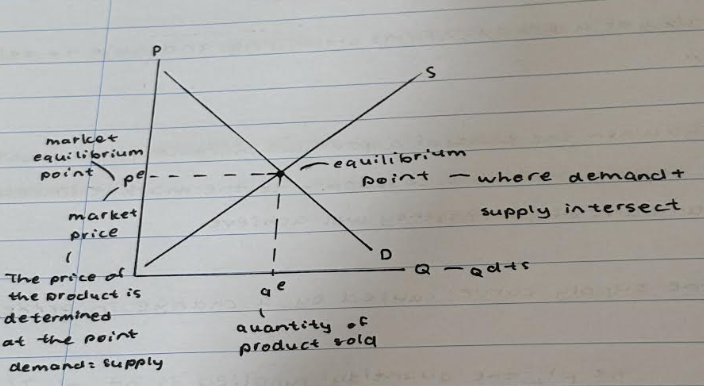
What is market equilibrium point?
It is the market price and the price of a product is determined at the point demand=supply
What is qe?
Quantity of product sold.
What does Q equal to?
Qd+s
What happens to the market equilibrium point when demand increases?
Demand curve shifts to the right form D t D1
- price increase from pe to pe1
- quantity increases from qe to qe1
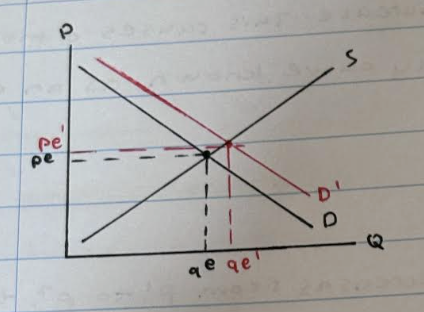
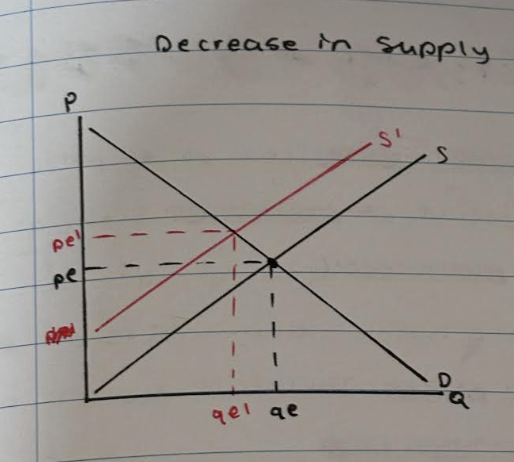
What happens to the market equilibrium point when demand decreases?
Demand curve shifts to the left form D to D1
- price decrease from pe to pe1
- quantity decreases from qe to qe1
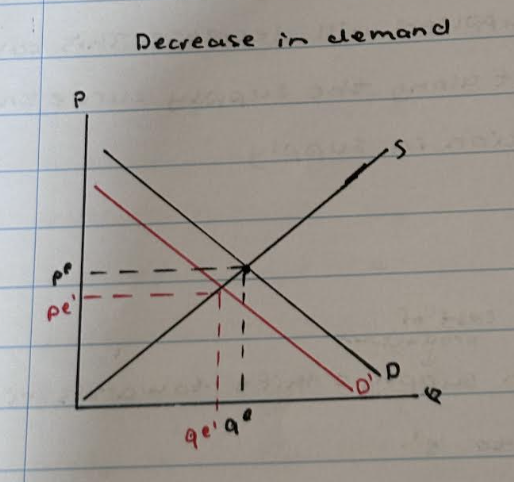
What happens to the market equilibrium point when supply increases?
Supply curve shifts to the left form s to s1
- price decrease from pe to pe1
- quantity increases from qe to qe1
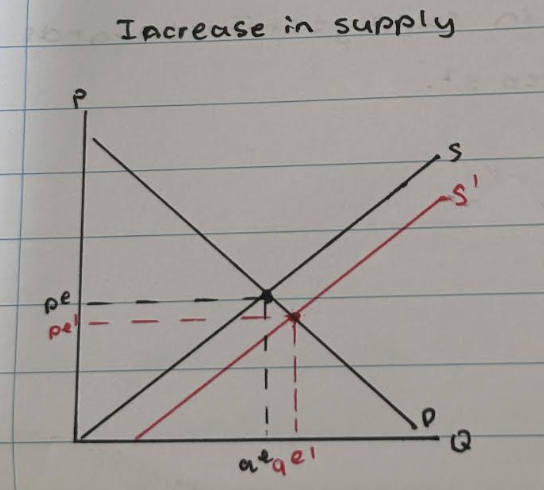
What happens to the market equilibrium point when supply decreases?
Supply curve shifts to the right form s to s1
- price increase from pe to pe1
- quantity decreases from qe to qe1
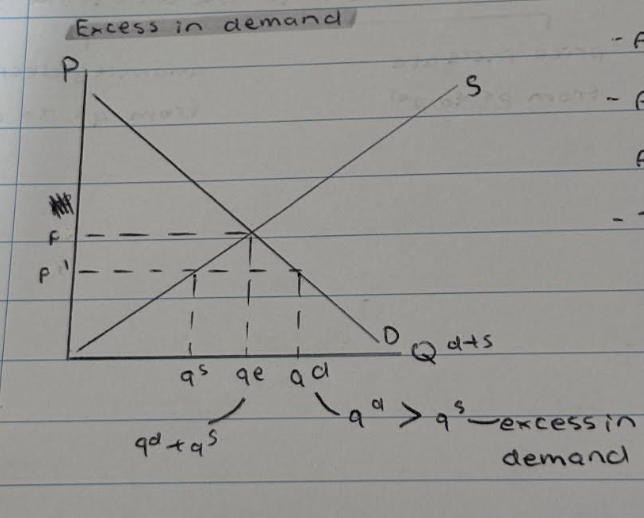
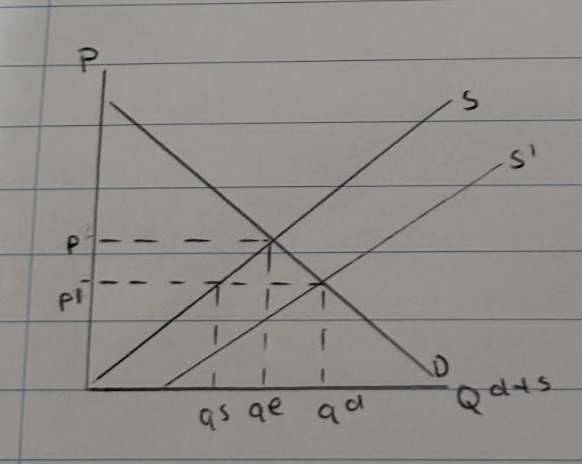
What happens when there is an excess in demand?
- A decrease in price from p to p1
- As a result, qd increases from qe to qd. Also qs decreases from qe-qs
- Therefore supply and demand is in disequilibrium because qd>qs, so there is an excess in demand
What happens to supply when there is an excess in demand?
- The excess in demand sends a signal to firms to supply more
- As a result, supply shifts from s to s1
- Therefore, qd and qs are at the same point, so equilibrium occurs
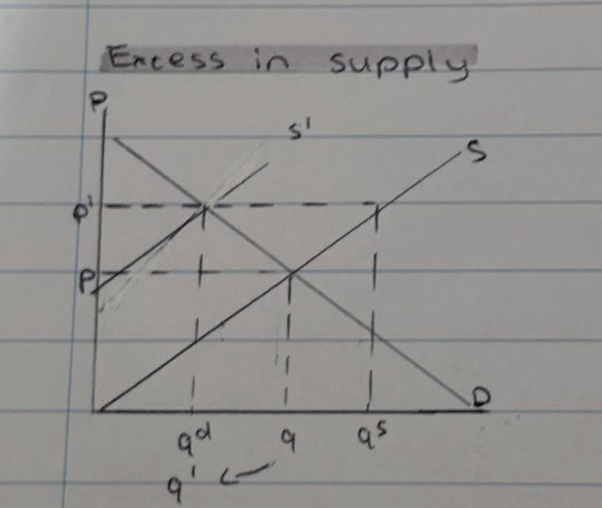
What happens when there is an excess in supply?
- An increase in price from p to p1 resulting in disequilibrium because qs is greater than qd
- This sends a signal to firms to decrease supply from s-s1
- As a result equilibrium occurs because demand+supply are at the same point (q1)
Define price elasticity of demand
PED measures the responsiveness of the quantity demanded to a change in price.
Formula for PED
% change in quantity demanded / % change in price
Formula for %change
difference/original x 100
Why is the answer to PED always negative
It's either +/- or -/+
If the answer is ∞
product is perfectly elastic
>1
elastic --> very responsive
<1
inelastic --> not very responsive
0
perfectly inelastic
do you ignore the - in the answer
yes
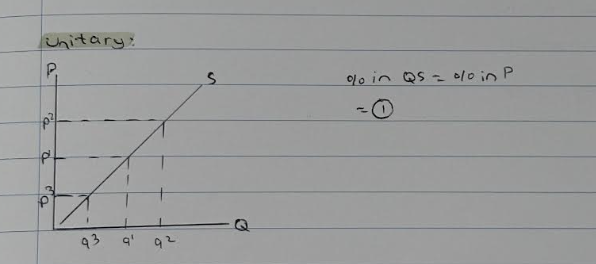
unitary
%change in QD= %change in P

elastic
%change in QD > %change in P . demand is very responsive to a change in price

inelastic
%change in QD < %change in P . Demand isn't very responsive to a change in price.

perfectly inelastic

perfectly elastic

Questions about the characteristics of a product
1. necessity or luxury
2. number of substitutes
3. what % income is the price of the product
ped short term
- inelastic
- lack of time
- difficult to break bad habits
ped long term
- elastic
- time to consider
- time to break bad habits
Describe one reason why deamand for a product usually becomes more elastic over time
In the short term, consumers may not be able to find an alternative product to switch to (1) and so its only in the longer term that they might have more opportunity to look at substitutes (1).
Concert tickets to see the most popular music artists can sell out for very high prices. Explain one reason why the demand for these tickets might be price inelastic (3)
One reason is that there are no substitutes (1) if they want to see the artist performing live (1) the consumer will have no choice but to pay a high amount (1)
Six months after the price for a soft drink increased, its price elasticity of demand (PED) changed from -1.5 to -2.0. Explain one reason why the demand for the product such as a soft drink, usually becomes more elastic over time. (3)
In the short term, consumers may not be able to break their habit (1). But in the time they are able to reduce consumption (1), meaning that they buy less of the sugary products (1).
What is price elasticity of supply?
PED measures the responsiveness of supply to a change in price
formula for price elasticity of supply?
% change in quantity supplied / % change in price
Why is ans always positive
if p increases, qs also increases, so +/+
if p decreases, qs also decreases, so -/-
numerical values of PES
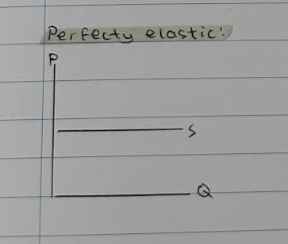
Perfectly elastic ∞
elastic >1
unitary 1
inelastic <1
perfectly inelastic 0
unitary
perfectly elastic
perfectly inelastic

elastic
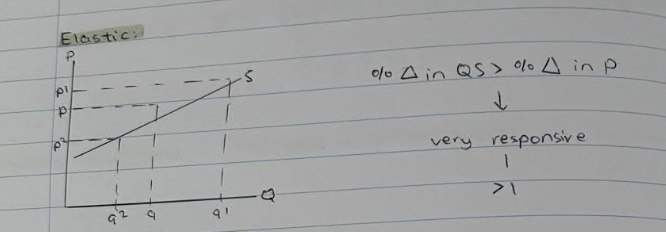
inelastic
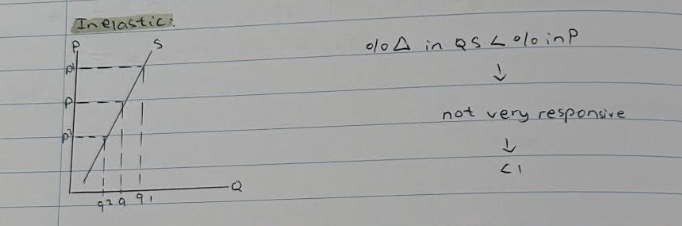
factors which determine whether Pes is elastic or inelastic
Availability of factors of production (resources). Lots—> elastic. low—> inelastic
stock availability. high—> elastic. low—> inelastic (stock levels)
spare capacity high —> elastic. low —> inelastic
time short. short run —> inelastic long run—> elastic (it takes time to grow and make products)
what does income elasticity if demand measure?
yed measures the responsiveness of the quantity demanded to a change in income
formula of yed
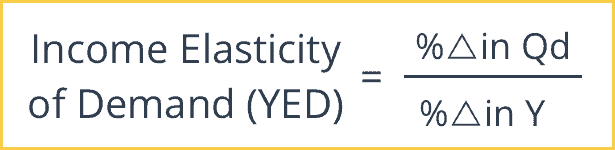
numerical values
-1, 0, 1 —> income elastic
less than -1 and greater than 1 —> income elastic
positive values of YED
Y (inc) ; D (inc) +/+=+
Y (d) ; D (d) -/+= +
normal goods
negative values of YED
Y (inc) ; D (d) -/+=-
Y (d) ; D (in) -/+= -
inferior goods (usually a need)
define normal goods
demand increases for a normal good when income increases
define inferior goods
as households income increases, the demand for an inferior good will decrease
flowchart for inferior goods (basic white bread)
household income increases
households are more willing and able to buy more luxury products e.g sourdough bread
as a result, the demand for inferior goods decreases
market failure?
occurs when there has been a small misallocation of resources. When left to the free market/market forces (demand+supply)