7 - Fragile Environments
1/40
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Deforestation: Tropical regions such as Amazon rainforest and Southeast Asia
* Dried up watercourses + ponds
* Lowering of water table
* Vegetation becomes degraded/completely lost
* Increased soil erosion as bare soil is exposed to wind
* Increase in salt content of soil
* Soil becomes less usable
* Increasing presence of dry, loose sand
Characteristics of deforestation 🌲
Sawn tree trunks
Burned saplings
Land loses tree cover
Soil exposed to erosive effects of wind + rain
How drought causes desertification 🐫
Lack of rainwater leads to vegetation dying + water table getting lower → soil gets exposed → soil erosion → desertification
High rainfall in 1950’s & 60s encouraged people to settle and farm in marginal areas
Mean annual rainfall in Sahel = low - 40% lower than avg. in last 30yrs
Severe drought in 70s + 80s → crops failed and accelerated desertification
How population pressure causes desertification 🐫
More pressure on land, vegetation + soil
More deforestation
Increased use of marginal land for grazing
Pop. doubles every 20yrs, now at 260m
Many nomadic tribes in Tuareg settling in one place - urbanisation is rapidly occurring in Mali (less land for food prod.)
Mali’s pop. grows by 3.1%/year but food prod. only growing by 2%/year
How fuel supply causes desertification 🐫
Trees chopped for fuel wood - soil exposed to erosion
Dung burned for fuel rather than being applied to soil as fertiliser
90% of families in Sahel cook with fuel wood
90% of highland forest cover destroyed since 1900
14% of total Forest lost from 1990-2005
How overgrazing causes desertification 🐫
Not allowing soil nutrients to be replenished → crops fail → soil left bare → soil erosion
Too many animals strip vegetation back to soil → Trampling compacts soil making it hard for vegetation to grow
Eastern Sahel: Number of sheep and goats - 30m in 1961 to over 100m in 2009
Ethiopia: 50m sheep + goats, 50m cattle
How migration causes desertification 🐫
As desertification takes hold, people forced to migrate - puts pressure on other areas, often leading to desertification there
People attracted to favourable farming conditions
Over 1m Somalians living in East African refugee camps
Camps cause deforestation as people don’t treat land well
Deforestation, soil compaction and pollution from poor sanitation can lead to desertification
How timber (logging) causes deforestation 🌲
Globally 32% of causes for deforestation
‘Clear felling’ particularly destructive - whole areas of forest destroyed
Valuable trees such as mahogany especially sought after
How agriculture causes deforestation 🌲
Globally 32% of causes of deforestation
Areas are cleared for plantation (palm oil, rubber, coffee etc.), crops (soya) or cattle - areas are seeded with grass for cows to eat. Meat from these animals is often exported for large sums of money.
How mining causes deforestation 🌲
Large areas of forest are cleared for open-cast mining of gold, iron and copper - large or small scale. e.g. Carajas mine
How transport causes deforestation 🌲
Roads built to allow access for mining, timber extraction and cattle ranching. New roads allow settlers to access new areas and fell more trees. e.g. Trans Amazonian Highway
How settlement causes deforestation 🌲
Brasilia was built to encourage people to move away from coastal areas
‘Welcome to the Amazon’ - encouraged people to settle along high way and cut the surrounding rainforest to grow crops.
Indigenous people
Kayapo tribe, Amazonia, Brazil
Shifting cultivation - cleared small areas for food production and when soil is exhausted move on to another area. This allows the forest to regenerate
How HEP (hydro-electric power) causes deforestation 🌲
Requires construction of hydro-electric dam
Rivers are dammed and huge areas of forest are flooded as a result
Water is allowed to pass through channels in the dam which turns turbines, creating electricity.
HEP = renewable, clean, green energy (some GHGs released during construction + methane from rotting veg in reservoir)
How Milankovitch cycles cause climate change naturally
Over long timescales, there have been big changes in climate due to 3 changes:
Earth’s orbit changes shape. Sometimes circular, sometimes elliptical
Earth’s axis tilts. Sometimes more upright, sometimes on its side - 22.2ᵒ-24.5ᵒ
Earth’s axis wobbles, like a spinning top about to fall over
These changes alter amount of sunlight Earth receives & affect where sunlight falls on Earth’s surface
How solar variation causes climate change naturally
Sunspots + solar flares = dark areas on Sun’s surface, number of them constantly changes
Lots of spots = MORE solar energy fired from Sun to Earth = warmer Earth
How volcanic activity causes climate change naturally
Large + explosive eruptions can change Earth’s climate
Eruptions produce ash + sulfur dioxide
If ash + gas rise high enough, they spread around Earth in stratosphere by high-level winds
Blanket of ash + gas stops some sunlight reaching Earth’s surface. Sunlight is reflected off ash + gas back into space, cooling the planet and lowering avg. temp.
E.g. 1991 - Mt. Pinatubo, Philippines, 17m tonnes of sulfur dioxide, reduced global sunlight by 10%, cooled planet by 0.5ᵒC for a year
How industry + transport cause enhanced greenhouse effect
Fossil fuels burned
GHGs build up in atmosphere
Trap + absorb long wave radiation (infrared) = energy that Earth should reradiate back into space
Causing gradual increase in world temp.
How agriculture causes enhanced greenhouse effect
From fertiliser manufacture, food storage + packing, up to 1/3 of human GHGs from agriculture
Nitrous oxides released during tilling
Methane emissions from animals
Causing gradual increase in world temp.
How deforestation causes enhanced greenhouse effect
Reduced carbon sink (trees locking less CO₂ in their wood)
Chopping down/burning trees releases CO₂ into atmosphere
Causing gradual increase in world temp.
Impact of desertification 🐫 on agricultural output
Decline in condition of soil + increasing shortage of water = lower agricultural productivity
Crops fail + livestock die
Impact of desertification 🐫 on nutrition + famine
Decline in agricultural output → food shortages (famine) and poor diet
People can survive famine for some time but after a while, human body can’t cope → starvation + possibly death
Young + elderly badly affected
Malnutrition, famine, starvation are all impacts of overpopulation
Impact of desertification 🐫 on migration
Eventually situation is so bad that people face difficult choice: die where you are or migrate in hope of finding somewhere you can raise enough food to survive
Impact of deforestation 🌲 on biodiversity
Rainforests have highest biodiversity. More than 2/3 of world’s plant species and 1/2 animals species are found there
Rainforest provides resources: food, timber, medicines, fibres for clothing, resins for glues
Global biodiversity reduced + some species may become extinct. Estimated 137 plant, animal and insect species are being lost every day/50,000 a year
Impact of deforestation 🌲 on local climate
Deforestation disrupts water cycle - felling of trees → transpiration + evapotranspiration are reduced → less moisture is return to atmosphere → local climate = drier
Combination of increasing dryness and rising temperatures is not good for people or commercial farming
Increased drought events, such as 2005, 2010 and 2015. These have contributed to tree mortality and reduction in rainfall over the rainforest.
Impact of deforestation 🌲 on global climate
Reduces carbon sink → more GHGs in atmosphere, contributing to climate change
Impact of deforestation 🌲 on economic development
Developing countries - deforestation can stimulate much-needed economic development
Brazilian economy has benefitted from selling resources of its vast area of rainforest
Benefits are only short-term unless something is done to replace forest that is cleared
Impact of deforestation 🌲 on soil erosion
Less rainwater will be intercepted by vegetation + more will reach the surface. As water flows across surface, it may erode soil and carry it away towards rivers
Rainforest soil is poor quality with few nutrients. Nutrients in rainforest are found in vegetation itself and in leaf litter/humus layer on top of soil
Loss of vegetation leaves less nutrient-rich leaf litter on forest floor + encourages soil erosion and leaching, further reducing soil quality and making it less useful for agriculture
How climate change causes rising sea levels
Caused by thermal expansion caused by warming of ocean (water expands as it warms)
Caused by increased melting of land-based ice, such as glaciers and ice sheets, e.g. Antarctica, Greenland
e.g. Miami and London would be affected by 1m rise
How climate change causes more hazards
Global warming will increase extreme weather
More extreme weather = more frequent + more intense natural hazards, such as tropical storms, tornadoes, heatwaves, droughts + cold snaps
Warmer seas = more intense storms
Tropical storms have increased in frequency, intensity and power + more continuous rainfall events (causing flooding) since 1980
Frequent + longer droughts = desertification + heatwaves increasing
How climate change causes ecosystem changes
Changes in climate from global warming change the distribution of ecosystems
The general warming will push world’s biomes towards poles. e.g. in N hemisphere, coniferous forests will intrude tundra, and tundra on the ice desert
Change in climate could cause farming to be pushed towards more arid conditions, resulting in other areas of farmland becoming less productive
How climate change causes reduced employment opportunities
Significant amount of world’s economic wealth is generated in coastal areas.
Sea rises = no coast
The need to retreat from coast will have negative impact on employment as coastal farmland, cities, tourist resorts + ports are abandoned to rising sea
How climate change causes changing settlement patterns
Development of low-lying areas will have to stop
Massive volumes of migration away from coasts - pattern of settlement will change almost beyond recognition
How climate change causes health + wellbeing challenges
Warming climate will change distribution of diseases, e.g. malaria will occur at higher latitudes and altitudes
In parts of the world that get drier, water will be scarcer, so people will be forced to use unclean water, leading to outbreaks of water-borne diseases, such as cholera and typhoid becoming more frequent and widespread. Mortality rates would then rise
Human well-being will be badly affected by upheaval and movement of people + economic activities from coastal areas, which causes human distress + personal insecurity
How climate change causes food supply shortages
Climate change could disrupt food availability, reduce access for food + affect food quality
Projected changes in temp., precipitation + reduction in water availability can all result in reduced agricultural production
Can lead to conflict as people forced to migrate for food + water
Decline in water sources may make it difficult for some farmers to continue their type of farming. May need to change crop type or be forced out of farming
Rise of 2ᵒC = 200m more people experiencing hunger
Rise of 3ᵒC = 500m more people experiencing hunger
Water-spreading weirs 🏜️
To reclaim degraded, rock-hard farmland that water couldn’t penetrate, farmers dig a grid of planting pits, then added organic matter, such as manure, to bottom of basins
Planting pits improve soil fertility + agricultural productivity in several ways: *
Concentrate nutrients + water precisely where they’re needed for plant growth
Soil + organic matter such as leaves blown by wind gather in pits
Insects are attracted to organic matter, digging channels that enhance soil structure + improve water filtration & retention
Insects help break down organic matter, making nutrients more easily available to roots
Pits retain water for long periods, allowing crops to survive during dry spells
Farmers can dig pits during dry season, don’t have to wait until rain comes to prepare land for planting

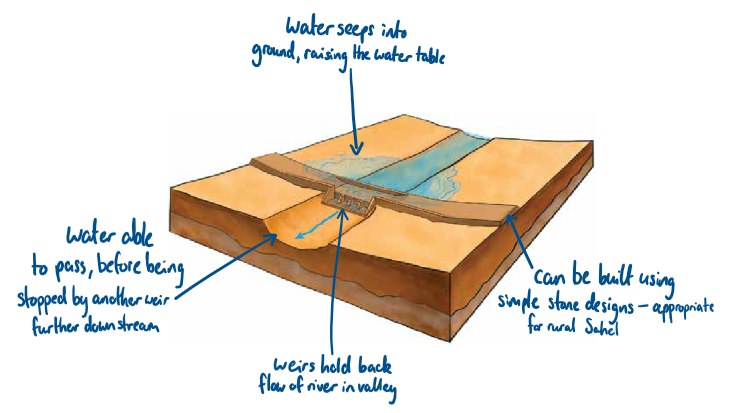
Simple stone lines (bunds) are placed along contours of slopes. Stones are collected from local area.
Prevent movement of water down slope, encouraging infiltration + improving soil moisture so crops can be grown again
Simple, cheap technique has improved crop yields by 50%
To ensure optimum results, only requires a simple tool, costing $6, helping farmers to align stones properly along contours of the land. Correct use of this tool can be mastered in a day despite low levels of education and literacy in the area.
Use of magic stones (+ other strategies) has helped rehabilitate over 200k hectares of unproductive land, with around 500k people benefitting from subsequent increase in food production.
Brazil rainforest conservation strategies 🌲
The Forest Code
Created in 1965
Law that requires all landowners in Amazon to maintain 35-80% of their property under rainforest
Problem: difficult to enforce + monitor what’s happening
Protected areas
Amazon Region Protected Areas (ARPA) scheme
Created in 2022 by Brazilian govt.
Over 10 year period, 45m hectares made into parks + reserves
Replanting projects
Project in Atlantic rainforest near Rio de Janeiro (REGUA) has shown it’s possible to recreate rainforest cover similar to original
Collect seeds from remaining primary forest, grow them in nurseries and replant them in deforested areas
US-Brazil Partnership hope what has been learnt from REGUA will help Brazil’s promise in 2015 to restore 12m hectares of land now abandoned by commercial farmers due to fertility + productivity issues
Brazilian Govt. - Cultivation of commercial timber e.g. eucalyptus (fast growing) on plantations outside rainforest. There are now 5m hectares of plantations.
UK (developed) response to global warming + climate change
Climate Change Act (2008) commits to cutting emissions by at least 80% from 1980 levels
Tried to reduce reliance on fossil fuels as primary energy source; now = 85% of energy production but today burning more gas (cleaner-burning fuel) and less coal
Reduce overall energy consumption by using energy more efficiently; consumption has fallen by 18% since 2005
Bangladesh suffers extreme flooding, which will worsen with climate change
Poor water quality
Adjust crop-type to a more salt-tolerant crop
Swap to more lucrative fish/shrimp farming
Floating schools: schools built on floating plants = no interruption to education
Floating farmland: people collect water hyacinth, build a rectangular raft out of it, and plant vegetable seedlings
Buoyancy of floating garden allows it to rise with water levels