Chp. 6 Thermodynamics/Thermochemistry Remember
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Thermodynamics/Thermochemistry
is the study of energy
Energy
is the capacity to do work or produce heat
Law of Conservation of Energy
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, just transferred
1st Law of Thermodynamics
The energy in the universe is constant
State Functions
depend only on the current state of the system. P, V, T, energy
Heat
heat flows from hot to cold: high KE [kinetic energy], high velocity particles collide with cold/slower particles, making them speed up, increasing their KE
When T is up, KE is up
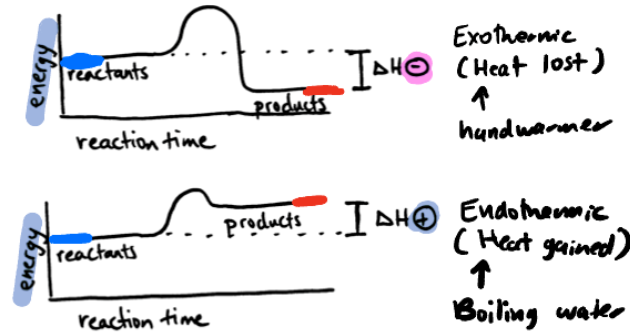
Exothermic
Exo - exist, thermic - heat
Heat energy flows out of a system into its surroundings. (hot pack)
EX. burning paper & burning a candle
Endothermic
Endo - in, thermic - heat
Heat energy flows into a system from its surroundings. (cold pack)
EX. ice cube melting & Cooking an egg
the First Law of Thermodynamics
energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred between a system and its surroundings through heat and work
ΔE = q + w
Δ = delta = ‘change of’
ΔE = change in internal energy of a system (joules)
q = heat
w = work
+q = heat flows into the system (endothermic)
-q = heat flows out of the system (exothermic)
-w = the system does work (loses energy)
+w = the surroundings do work on the system
Pressure-Volume Work
the work done by a gas when it expands or contracts against an external pressure
w = -PΔV
P = pressure
ΔV = Vf - Vi (change in volume)
Vf = final volume, Vi = inital volume
1 L x atm = 101.3 J !!
Calorimetry
is the science of measuring heat
ΔE = q + w
w = -PΔV
q = smΔT
where s = specific heat capacity,
m = mass, and ΔT = Tf - Ti (Tf: final & Ti: inital)
Specific Heat Capacity (s)
is the energy required to raise the temperature one degree Celsius for one gram of substance
s for H2O = 4.184 J/(g x oC)
= 1 calorie,
s for Fe = 0.45 J/(g x oC)
Molar Heat Capacity
is the same except for 1 mol of substance
J/(mol x oC)
so the “q” equation would have mols for “m,” instead of mass
Enthalpy (H)
is the heat energy
q = H at constant P
Hess’s Law
The enthalpy change (ΔHro) for a reaction is the sum of the enthalpy changes for a series of reactions, that add up to the overall reaction
Steps
For each reaction:
1) Check to see, if the compounds are on the correct sides of the reaction. **If not, reverse the entire reaction, & change the sign of ΔH
2) Check to see, if all the unwanted compounds will cancel completely. **If not, multiply an entire reaction by a # so that they do cancel completely & multiply ΔH by that same #