Fatty acid synthesis & Amino acid metabolism
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Why is excess glucose converted into fat & not glycogen?
easier to store fat as less water is needed to store it
fat is more energy dense
Why would the [NADPH]/[NADP] ratio be kept high?
Favours reductions & fatty acid synthesis
Why would the [NAD]/[NADH] ratio be kept high?
Favours glycolysis
How is carbon exported from the mitochondria into the cytosol?
citrate is synthesised in mitochondria:
oxaloacetate + acetyl-CoA —→ citrate + CoASH
ATP-citrate-lyase in cytoplasm:
ATP + citrate + CoA —→ oxaloacetate + acetyl-CoA + ADP + Pi
What is the first stage of fatty acid synthesis?
Biotinyl-enzyme + HCO3- + ATP + ADP + Pi —→ carboxybiotinyl-enzyme
carboxybiotinyl-enzyme + acetyl-CoA —→ malonyl-CoA
Reaction occurs in 2 steps: a CO2 activation & a carboxylation
*NB - this is the committed & the rate limiting step of fatty acid synthesis
What is the second stage of fatty acid synthesis?
Acetyl CoA binds to phosphopantotheine on acyl-carrier protein on fatty acid synthase. Acetyl group then shifted to the cysteine residue also on fatty acid synthase. Then malonyl CoA binds to phosphopantotheine.
So at the end of this stage: Acyl group bound to the cysteine residue & malonyl group bound to phosphopantotheine.
What is the third stage of fatty acid synthesis?
Acetyl group from acetyl-CoA reacts with bound malonyl-CoA to form butyryl-CoA and CO2.
What is the fourth stage of fatty acid synthesis?
2 carbons from malonyl-CoA are added in a condensation reaction to butyryl-CoA to form a 6 carbon fatty acid over the course of…
Initial condensation
reduction with NADPH
dehydration
Reduction with NADPH
6 carbon molecule is formed.
What is the 5th stage of fatty acid synthesis?
6 carbon molecule keeps reacting with malonyl-CoA & goes through the cycle 7 times total, extending the chain by 2 carbons each rotation until it reaches C16 and forms palmitate.
Effectively, what does the malonyl-CoA act as during fatty acid synthesis?
a 2 carbon donor to acetyl-CoA
*NB - 3rd carbon released as CO2 in the formation of butyryl-CoA
What molecules inhibit acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC)?
glucagon
adrenaline
palmitoyl-CoA
AMPK through phosphorylation
What molecules activate ACC?
insulin
citrate
ChREBP - transcription factor that upregulates enzyme that is itself regulated by nutrients
How can malonyl-CoA be recycled?
malonyl-CoA decarboxylase can convert malonyl-CoA to acetyl-CoA & CO2
Describe the structure of fatty acid synthase.
Very large molecule that has an acyl-carrier protein (ACP) bound to a phosphopantotheine residue.
Also bound to a cysteine residue too.
What are the 4 ways fatty acid synthesis & oxidation can be controlled?
control of malonyl-CoA synthesis
control of phosphorylation of ACC
control of glucose uptake by insulin
control of TAG synthesis
How can malonyl-CoA synthesis be controlled?
Insulin activates acetyl-CoA carboxylase by stimulating its dephosphorylation —→ increases malonyl-CoA
Glucagon increases ACC phosphorylation —→ decreases malonyl-CoA
How is the control of ACC phosphorylation achieved?
Direct phosphorylation - 5’-AMP increases phosphorylation via AMPK
Allosteric effectors - citrate, palmitoyl-CoA
How does insulin control TAG synthesis?
Stimulates the enzymes that add acyl groups to glycerol
Stimulates glucose metabolism to provide glycerol backbone for TAG synthesis.
How is nitrogen excreted in mammals?
as urea
ideal because water soluble, neutral pH & non-toxic
What prosthetic group is used by aminotransferases?
pyridoxal phosphate
transfers from a large number of amino acids to glutamate, alanine & aspartate.
What is the role of alanine?
carrier of ammonia & pyruvate from skeletal muscle to the liver.
*NB - links amino acid metabolism with the Cori cycle.
Describe stage 1 of the glucose-alanine cycle.
excess ammonia + glutamate —→ glutamine.
catalyst: glutamine synthetase
requires energy from ATP hydrolysis
Describe stage 2 of the glucose-alanine cycle.
Glutamine enters the liver and is acted on by glutaminase. NH4+ is liberated in the mitochondria. Glutamate is reformed.
*NB - liver also releases N2 from glutamate as NH3 using glutamate dehydrogenase in oxidative deamination.
Why is glutamate dehydrogenase unusual?
Can use either NAD or NADP as a cofactor
allosterically regulated by GTP & ADP
What are the stages of the urea cycle?
Ammonia + bicarbonate —→ carbamoylphosphate. (also requires 2 ATP)
carbamoylphosphate + ornithine —→ citrulline
aspartate + citrulline + ATP —→ argininosuccinate
argininosuccinate —→ fumarate + arginine
arginine —→ urea + ornithine (hydrolysis reaction)
What is the ‘Krebs bicycle’/aspartate-arginosuccinate shunt?
connection between the CAC and urea cycle
What can ammonia toxicity cause?
Death
hepatic encephalopathy - ammonia accumulates in brain & draws in water. Brain swells in the skull
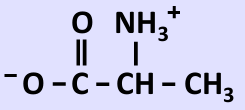
What amino acid is this?
Alanine
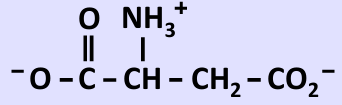
What amino acid is this?
aspartate
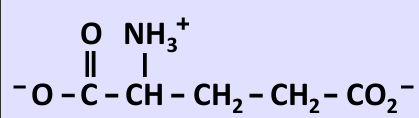
What amino acid is this?
glutamate