Chemistry - Module 1: Carbon Compounds
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:55 AM on 5/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
1
New cards
type of reaction: alkane + oxygen
combustion
2
New cards
product of reaction: alkane + oxygen
carbon dioxide + water
3
New cards
explain cracking
Process of breaking down large hydrocarbons into smaller and more useful molecules. This is done through heat, pressure, and catalysts.
4
New cards
conditions of thermal cracking
high temperatures (450-750°C) and pressures (up to 70 atm)
5
New cards
conditions of catalytic cracking
zeolites (complex aluminosilicates of the form Al2O5Si \n associated with positive ions) along with lower temperatures (\~500°C) and moderately \n low pressures
6
New cards
product of: alkene + halogen
dihaloalkane
7
New cards
reaction mechanism of: alkene + halogen
electrophilic addition
8
New cards
conditions of: alkene + halogen
organic solvent(CCl4)
9
New cards
type of reaction of: alkene + halogen
addition reaction
10
New cards
product of: alkene + aqueous halogen
haloalkane +acid halide
11
New cards
type of reaction: alkene + aqueous halogen
addition
12
New cards
reaction mechanism of: alkene + aqueous halogen
electrophilic addition
13
New cards
product of: alkene + Cold H+/KMnO4
diol, alcohol
14
New cards
reaction mechanism of: alkene + Cold H+/KMnO4
electrophilic addition
15
New cards
type of reaction: alkene + Cold H+/KMnO4
redox, partial oxidation
16
New cards
product of: alkene + Hot H+/KMnO4
carbonyl → ketone, carbonyl → aldehyde → carboxylic acid, carbonyl → methanal → carbon dioxide + water
17
New cards
product of: alkene + conc H2SO4
alkyl hydrogensulfate → alcohol
18
New cards
type of reaction: alkene + conc H2SO4
hydration
19
New cards
conditions of reaction: alkene + conc H2SO4
heat + water
20
New cards
product of alkene + hydrogen
alkane
21
New cards
conditions of: alkene + hydrogen
150C and catalyst like palladium (Pd-C), platinum (PtO2) or nickel (Ra-Ni
22
New cards
type of: alkene + hydrogen
hydrogenation
23
New cards
products of oxidation of primary alcohols w/ oxidizing agents
Hot H+/KMnO4: carboxylic acid
Cold H+/KMnO4: aldehydes
Hot H+/K2Cr2O7 in reflux: carboxylic acid
Cold H+/KMnO4: aldehydes
Hot H+/K2Cr2O7 in reflux: carboxylic acid
24
New cards
products of oxidation of secondary alcohols w/ oxidizing agents
Hot H+/KMnO4: ketone
Cold H+/KMnO4: ketone
Hot H+/K2Cr2O7 in reflux: ketone
Cold H+/KMnO4: ketone
Hot H+/K2Cr2O7 in reflux: ketone
25
New cards
product of: alcohol + carboxylic acid
ester
26
New cards
conditions of: alcohol + carboxylic acid
heated under reflux, conc H2SO4,
27
New cards
type of reaction: alcohol + carboxylic acid
esterification
28
New cards
product of: alcohol + conc H2SO4
alkene + water
29
New cards
type of reaction: alcohol + conc H2SO4
dehydration
30
New cards
conditions of: alcohol + conc H2SO4
180C
31
New cards
components of iodoform test
iodine (I2) and NaOH
32
New cards
positive test observation of iodoform
pale yellow precipitate
33
New cards
state steps of iodoform reaction
Step 1: Formation of NaIO by reaction between I2 and NaOH.
Step 2: (If the sample is an alcohol) Oxidation of the alcohol by NaIO to form a carbonyl compound.
Step 3: Substitution of the hydrogen atoms of the methyl group with iodine atoms.
Step 4: Cleavage of the carbon-carbon bond to release triiodomethane (iodoform) from the rest of the molecule by hydroxide ions.
Step 2: (If the sample is an alcohol) Oxidation of the alcohol by NaIO to form a carbonyl compound.
Step 3: Substitution of the hydrogen atoms of the methyl group with iodine atoms.
Step 4: Cleavage of the carbon-carbon bond to release triiodomethane (iodoform) from the rest of the molecule by hydroxide ions.
34
New cards
what does iodoform test for?
methyl ketones and methylene groups, (-CH3)
35
New cards
product of hydrolysis of: haloalkanes
alcohol and the hydrogen halide
36
New cards
condition of alkaline hydrolysis of: haloalkanes
NaOH
37
New cards
product of: carbonyl + With NaCN(aq)/H+(aq)
hydroxynitrile, otherwise known as cyanohydrins.
38
New cards
mechanism of: carbonyl + With NaCN(aq)/H+(aq)
nucleophilic addition
39
New cards
product of carbonyl + LiAlH4
Aldehydes are reduced to primary alcohols while ketones are reduced to secondary alcohols
40
New cards
conditions of carbonyl + LiAlH4
carefully dried ethoxyethane (diethyl ether), acid
41
New cards
product of carbonyl + NaBrH4
Aldehydes → primary alcohols
ketones → secondary alcohols
ketones → secondary alcohols
42
New cards
state observation of Brady’s Reagent (2,4-DNP)
aldehyde, ketone: red/orange ppt
43
New cards
state observation of Tollen’s Reagent
aldehyde: silver mirror formed
44
New cards
state observation of Fehling’s Solution
aldehyde: red ppt
ketone: remains blue
ketone: remains blue
45
New cards
state observation of carbonyl + dilute H+/MnO4
aldehyde: purple to colourless
ketone: remains purple
ketone: remains purple
46
New cards
product of carboxylic acid + NaOH
alkanoate/carboxylate salt and water
47
New cards
type of reaction of carboxylic acid + NaOH
neutralization
48
New cards
product of carboxylic acid + NaHCO3
alkanoate/carboxylate salt, water, carbon dioxide
49
New cards
products of hydrolysis of esters
alkaline: carboxylate salt + alcohol
acid: carboxylic acid + alcohol
acid: carboxylic acid + alcohol
50
New cards
product of amine + dilute acid
amine salt
51
New cards
mechanism of benzene reactions
electrophilic subsititution
52
New cards
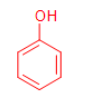
\
phenol
53
New cards
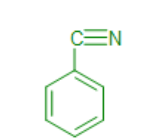
benzonitrile
54
New cards
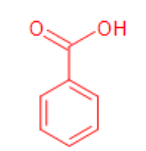
benzoic acid
55
New cards
product of benzene + halogen
aryl halide or haloarene
56
New cards
type of reaction of benzene + halogen
halogenation
57
New cards
conditions of benzene + halogen
Fe3+ or Al3+ catalyst
58
New cards
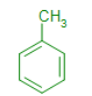
methylbenzene or toluene
59
New cards
conditions of nitration of benzene
Conc. H2SO4, Conc. HNO3, 50C
60
New cards
explain the mechanism of nitration of benzene
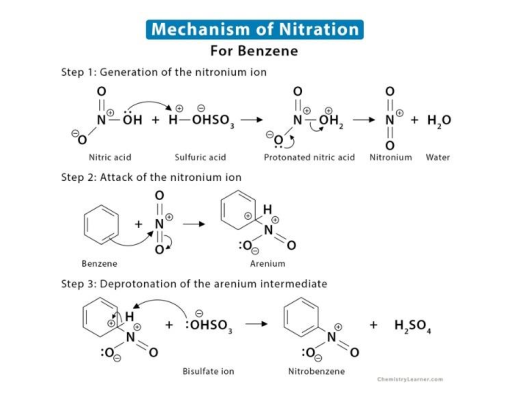
61
New cards
conditions for reduction of nitrobezene
Sn, conc HCl, reflux
62
New cards
product of phenol + acyl halide
organic ester, inorganic acid
63
New cards
product of bromination of phenol
aryl halide
64
New cards
product of phenol + NaOH
sodium phenoxide ion + water
65
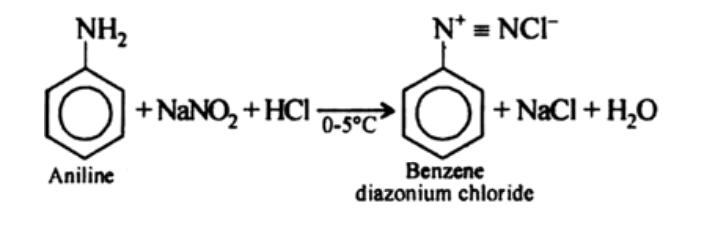
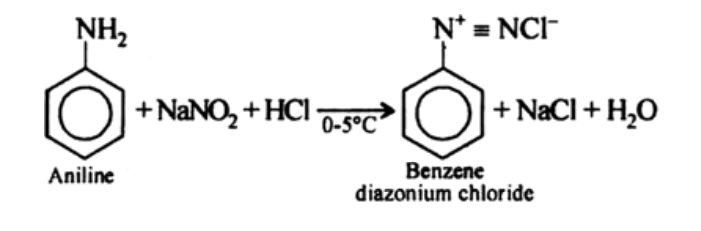
New cards
products of Diazotization
benzene diazonium chloride, sodium chloride and water
66
New cards
reagents/conditions of Diazotization
0-5C,NaNO2/HCl
67
New cards
product of Coupling w/ Diazonium Salt
azo compound +HCl
68
New cards
conditions of Coupling w/ Diazonium Salt
alkaline medium
69
New cards
uses of azo compounds
dyes or as intermediates in organic synthesis
70
New cards
which is stronger reducing agent: LiAlH3, NaBrH4
LIAlH3 stronger than NaBrH4
71
New cards
Differentiate between electrophilic substitution and nucleophilic substitution.
nucleophilic substitution: nucleophiles like OH-, CN- attracted to positively charged Carbon atom; occurs in haloalkanes
\
electrophilic substitution: electrophiles like NO2+ substitute Hydrogen in a benzene ring
\
electrophilic substitution: electrophiles like NO2+ substitute Hydrogen in a benzene ring
72
New cards
Differentiate between electrophilic addition and nucleophilic addition.
nucleophilic addition: nucleophiles added to the positively charged Carbon in a carbonyl compound
\
electrophilic addition: electrophiles added across the electron rich pi bond of alkenes
\
electrophilic addition: electrophiles added across the electron rich pi bond of alkenes