Earthsc 2G03 Midterm #2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/190
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:09 AM on 3/31/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
191 Terms
1
New cards
Main 3 Types of Glacial Landforms
* Erosional
* Depositional
* Glaciofluvial / Glaciolacustrine
\
* Depositional
* Glaciofluvial / Glaciolacustrine
\
2
New cards
Formative Processes resulting in Glacial **Erosional Landforms**
* Glacial Abrasion
* Glacial Abrasion + rock fracture
* Erosion by ice + frost shattering
* Rock crushing
\
* Glacial Abrasion + rock fracture
* Erosion by ice + frost shattering
* Rock crushing
\
3
New cards
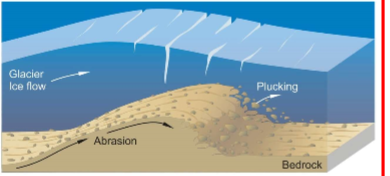
Glacial Abraison
\
* Forms glacial erosional landforms
* Forms streamlined features
* Glacier pushes rocks against the surface, resulting in abrasion
* Very wide range of scale
* Includes;
* Glacial troughs / U-shaped valleys
* Hanging valleys
* Fjord
* Grooves
* Plastically molded forms
* Striations
* Glacial polish
* Forms glacial erosional landforms
* Forms streamlined features
* Glacier pushes rocks against the surface, resulting in abrasion
* Very wide range of scale
* Includes;
* Glacial troughs / U-shaped valleys
* Hanging valleys
* Fjord
* Grooves
* Plastically molded forms
* Striations
* Glacial polish
4
New cards
Glacial Troughs / U-shaped Valleys
* Glacial abrasion landform
* Biggest clue that a landscape underwent glaciation
* Valleys were smoothed and carved out by the heavy glaciers
* Biggest clue that a landscape underwent glaciation
* Valleys were smoothed and carved out by the heavy glaciers

5
New cards
Hanging Valley
* Glacial abrasion landform
* Smaller valleys full of ice flow into each other, they combine and push down on surface forming a valley underneath, as the ice retreats a well defined high-elevation valley is left behind
* Smaller valleys full of ice flow into each other, they combine and push down on surface forming a valley underneath, as the ice retreats a well defined high-elevation valley is left behind

6
New cards
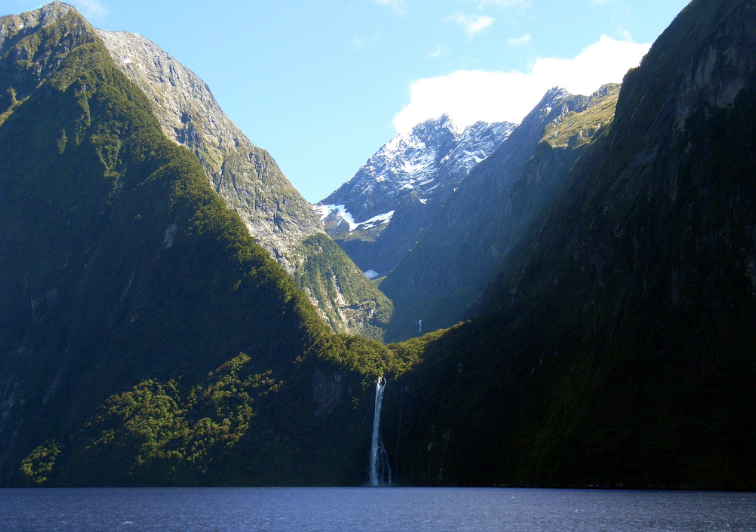
Fjord
* Glacial abrasion landform
* U-shaped valleys where sea level is high enough it fills with water
* ‘In-filled flooded valleys’
* Carved out by same glacial processes as other valleys
* Not rivers!
* U-shaped valleys where sea level is high enough it fills with water
* ‘In-filled flooded valleys’
* Carved out by same glacial processes as other valleys
* Not rivers!

7
New cards
Grooves
* Glacial abrasion landform
* Smaller scale U-shaped carved out formation
* Smaller scale U-shaped carved out formation

8
New cards
Plastically Molded Forms (p-forms)
* Glacial abrasion landform
* Forms as a result of abrasion in areas with different lithologies (softer and rougher materials)
* Results in smooth forms which look like rock forming lava deposits
* Forms as a result of abrasion in areas with different lithologies (softer and rougher materials)
* Results in smooth forms which look like rock forming lava deposits

9
New cards
Striations
* Glacial abrasion landform
* Smallest scale abrasion evidence
* Scratched exposed bedrock
* Direction of striations tell direction of glacial movement
* Smallest scale abrasion evidence
* Scratched exposed bedrock
* Direction of striations tell direction of glacial movement

10
New cards
Glacial Polish
* Glacial abrasion erosional landform
* Completed smoothing of rock surface
* Almost looks like ice
* Completed smoothing of rock surface
* Almost looks like ice

11
New cards
Glacial Abrasion + Rock Fracturing
* Forms glacial erosional landforms
* Combination of these two processes produces partly streamlined landforms from meters to kilometers in size
* Includes;
* Roche Moutonnee
* Crag and Tail
* Tarn
\
* Combination of these two processes produces partly streamlined landforms from meters to kilometers in size
* Includes;
* Roche Moutonnee
* Crag and Tail
* Tarn
\
12
New cards
Roche Moutonnee
* Glacial Abrasion + Rock Fracturing erosional landform
* Upside experiences polishing and is smooth
* Downside experiences plucking and is rough
* Upside experiences polishing and is smooth
* Downside experiences plucking and is rough

13
New cards
Crag and tail
* Glacial Abrasion + Rock Fracturing erosional landform
* More vertically developed and larger than Roche Mountonnee
* Reverse of Roche Mountonnee
* Smooth side is down ice
* Sharp side is up ice
* Ice flows over resistant rock which isnt able to pluck / abraid
* Soft material is eroded and deposited on the down ice side
* More vertically developed and larger than Roche Mountonnee
* Reverse of Roche Mountonnee
* Smooth side is down ice
* Sharp side is up ice
* Ice flows over resistant rock which isnt able to pluck / abraid
* Soft material is eroded and deposited on the down ice side

14
New cards
Tarn
* Glacial Abrasion + Rock Fracturing erosional landform
* Bowl-shaped isolated lake in mountain
* Formed as glacier retreats in a cirque
* Bowl-shaped isolated lake in mountain
* Formed as glacier retreats in a cirque

15
New cards
Glacier Ice and Frost Shattering
* Forms glacial erosional landforms
* Large residual (100m-100km) landforms left behind as ice retreats
* Mostly found in Alpine regions
* Includes;
* Horn
* Col
* Arete
* Large residual (100m-100km) landforms left behind as ice retreats
* Mostly found in Alpine regions
* Includes;
* Horn
* Col
* Arete
16
New cards
Horn
* Glacier Ice and Frost Shattering erosional landform
* Sharp pyramidal peak
* Sharp pyramidal peak

17
New cards
Col
* Glacier Ice and Frost Shattering erosional landform
* Lowest part of mountain range between peaks
* Almost like a plateau
* Lowest part of mountain range between peaks
* Almost like a plateau

18
New cards
Arete
* Glacier Ice and Frost Shattering erosional landform
* Saw-toothed sharp ridges along edges of valley
* Saw-toothed sharp ridges along edges of valley

19
New cards
Nunatak
\
* ‘Glacial island’
* High elevation flat bedrock that has not been glaciated and has not undergone glacial erosion
* ‘Glacial island’
* High elevation flat bedrock that has not been glaciated and has not undergone glacial erosion

20
New cards
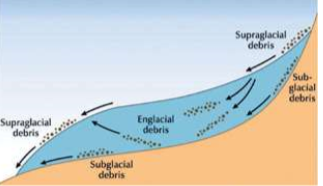
Glacial depositional landforms
\*Primarily made of till
* Supraglacial
* Ice contact (edge of glacier)
* Subglacial
* Supraglacial
* Ice contact (edge of glacier)
* Subglacial
21
New cards
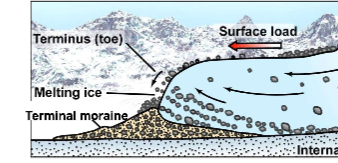
Ice Contact
* Glacial depositional landform
* Till
* Material transported by glaciers
* Moraine
* Material (till) dumped at end of glacier
* Till
* Material transported by glaciers
* Moraine
* Material (till) dumped at end of glacier
22
New cards
Erratics
* Supraglacial depositional landform
* Large-stone (material) that doesn’t fit the local geology
* Was carried by glacier
* Can range greatly in size
* Large-stone (material) that doesn’t fit the local geology
* Was carried by glacier
* Can range greatly in size

23
New cards
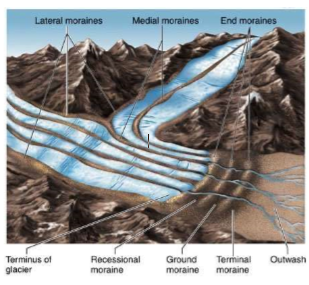
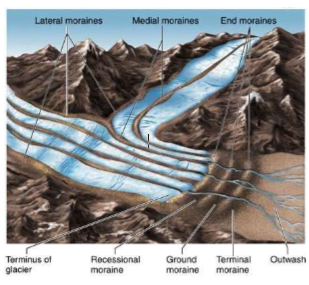
Types of moraines
* Lateral
* Medial
* End
* Terminal
* Recessional
* Ground
* Medial
* End
* Terminal
* Recessional
* Ground
24
New cards
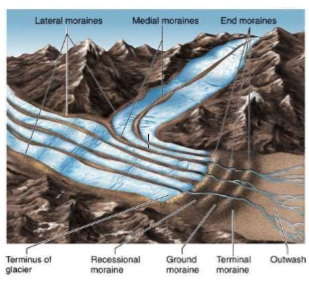
Lateral Moraine
* Supraglacial and ice contact depositional landform
* Formed along the side of a valley glacier
* Formed along the side of a valley glacier
25
New cards
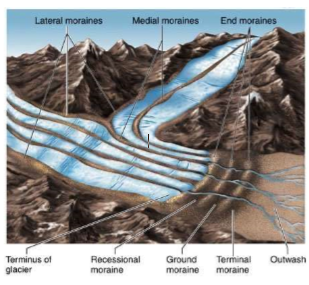
Medial Moraine
* Supraglacial and ice contact depositional landform
* Formed by the joining of two lateral moraines at a glacier confluence
* Formed by the joining of two lateral moraines at a glacier confluence
26
New cards
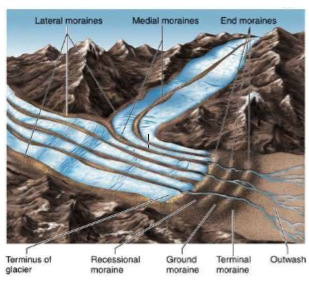
End Moraine
* Supraglacial and ice contact depositional landform
* Formed at a glacier down-ice margin
* Formed at a glacier down-ice margin
27
New cards
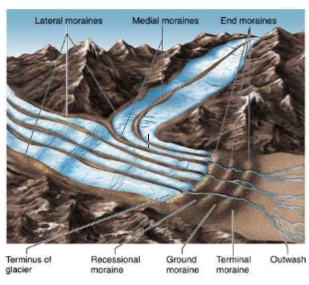
Terminal Moraine
* Supraglacial and ice contact depositional landform
* End moraine at peak extent of glacier
* Furthest down-ice moraine which formed
* End moraine at peak extent of glacier
* Furthest down-ice moraine which formed
28
New cards
Recessional Moraine
* Supraglacial and ice contact depositional landform
* End moraine marking a time of temporary stall in glacier retreat
* Gives us clues of locations where glaciers briefly paused
* And also rate of glacier movement!
* End moraine marking a time of temporary stall in glacier retreat
* Gives us clues of locations where glaciers briefly paused
* And also rate of glacier movement!
29
New cards
Ground Moraine
* Supraglacial and ice contact depositional landform
* Sheet of till
* Not enough to form proper mound
* Sheet of till
* Not enough to form proper mound
30
New cards
Drumlins
* Subglacial depositional landform
* Similar to Craig and Tail and Roche Mountannee, but not formed by abraison/erosion
* Has pockets underneath where material may be deposited as glacier moves
* Steep side = up ice
* Down side = down ice
* If you find one drumline you typically find more together
* Similar to Craig and Tail and Roche Mountannee, but not formed by abraison/erosion
* Has pockets underneath where material may be deposited as glacier moves
* Steep side = up ice
* Down side = down ice
* If you find one drumline you typically find more together

31
New cards
Types of Glacial Sediment based on how they are transported
* Glacial (till)
* Ice directly
* Glaciofluvial
* Melted glacial water rivers
* Glaciolacustrine
* Melted glacial water lakes
* Ice directly
* Glaciofluvial
* Melted glacial water rivers
* Glaciolacustrine
* Melted glacial water lakes
32
New cards
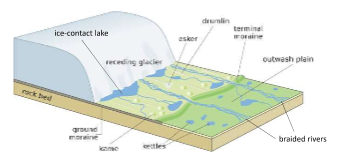
Glaciofluvial Landforms
* Typically found in the same region as glacial landforms
33
New cards
Eskers
* Glaciofluvial landform
* Channelized water either flowing beneath ice or edge of ice
* When ice melts it leaves these deposits behind
* Channelized water either flowing beneath ice or edge of ice
* When ice melts it leaves these deposits behind

34
New cards
Kames
* Glaciofluvial landforms
* Dome of glacial material that got dumped as ice retreated fast
\
* Dome of glacial material that got dumped as ice retreated fast
\

35
New cards
Kettle Lakes
* Glaciofluvial landforms
* Formed as a result of melted blocks of ice creating lakes, in which glacial material deposited around it
* Formed as a result of melted blocks of ice creating lakes, in which glacial material deposited around it

36
New cards
Why are glacial landforms important?
* They are crucial for groundwater and freshwater resource or storage
37
New cards
Permafrost
* Zones of permanently frozen ground (more than 2 years)
* Covers 25% of Earth’s land surface
* Covers 25% of Earth’s land surface
38
New cards
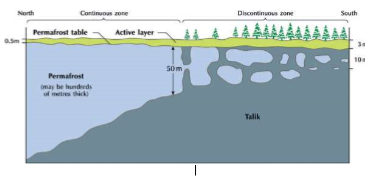
Ground Ice
* May be continuous or discontinuous
* Contains an active layer, permafrost table, and possibly talik
\
* Contains an active layer, permafrost table, and possibly talik
\
39
New cards
Continuous Ground Ice
* Entire column below ground is frozen
40
New cards
Discontinuous Ground Ice
* Pockets of frozen ground with unfrozen sections
\
\
41
New cards
Active layer of Ground Ice
* Thin layer of on top of ground that seasonally thaws and refreezes
\
\
42
New cards
Permafrost Table
* The line which separates seasonal thawing / melting of ice and permafrost
43
New cards
Talik
* Unfrozen soil around permafrost
44
New cards
Periglacial Processes
* Frost weathering
* Ice expansion in solid bedrock
* Mass displacement
* Occurs in unconsolidated material (soil), as water gets into soil pores and freezes it pushes the soil particles apart
* Frost cracking (thermal contraction)
* When material undergoes change of temp quickly it can crack
* Solifluction
* Ice expansion in solid bedrock
* Mass displacement
* Occurs in unconsolidated material (soil), as water gets into soil pores and freezes it pushes the soil particles apart
* Frost cracking (thermal contraction)
* When material undergoes change of temp quickly it can crack
* Solifluction
45
New cards
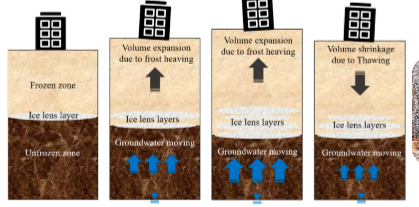
Frost Heave (Frost Action)
* Periglacial process
* Common in discontinuous layers
* Air pockets in soil fill with water then eventually freeze and cause an ice lens which is enough force to displace the surface above
* Can go up and down throughout the season
* Very dynamic!
* Big problem with construction in Northern/Colder climates
* Common in discontinuous layers
* Air pockets in soil fill with water then eventually freeze and cause an ice lens which is enough force to displace the surface above
* Can go up and down throughout the season
* Very dynamic!
* Big problem with construction in Northern/Colder climates
46
New cards
What does periglacial mean?
* Landscape which undergoes seasonal thawing and melting
47
New cards
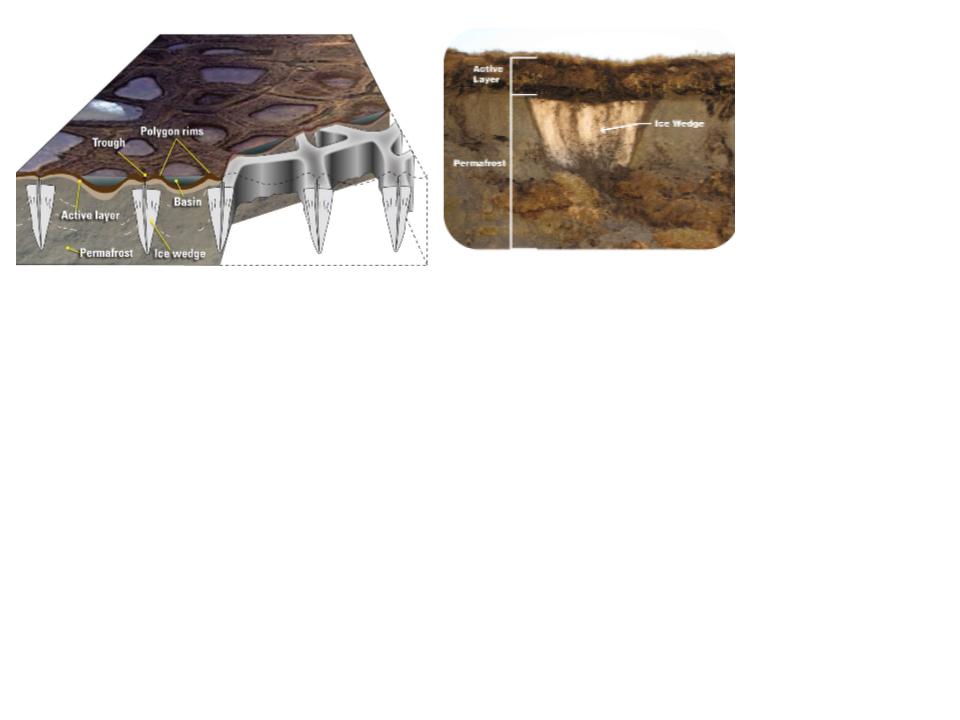
Ice Wedges
* Periglacial landform
* Vertical areas of solid frozen ice
* Can form polygon-shaped landforms
* Vertical areas of solid frozen ice
* Can form polygon-shaped landforms

48
New cards
Frost Mounds
* Periglacial landforms
* Formed by pockets of soil which were filled with water than froze
* Small-scale mounds of frozen ground
* Formed by pockets of soil which were filled with water than froze
* Small-scale mounds of frozen ground

49
New cards
Pingos
* Periglacial landform
* Look like little volcanoes
* Formed as a giant version of ice mound
* Large-scale
* Look like little volcanoes
* Formed as a giant version of ice mound
* Large-scale

50
New cards
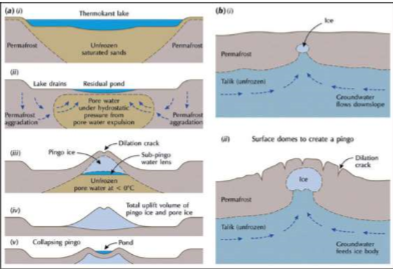
Pingo Formation Process
* Can be formed if there is a lake, underneath the lake there is unfrozen ground, as the lake drains (such as in the dry season) the unfrozen ground underneath begins freezing forming a bubble of ice that pushes upwards as the ice expands + grows, also forming cracks ontop
* Can be formed if there is cavity in soil that got filled with groundwater, and resulting in the formation of an ice bubble underneath pushing against the surface. Only occur in places with access to a lot of groundwater, so that the ice bubble can be large
* Can be formed if there is cavity in soil that got filled with groundwater, and resulting in the formation of an ice bubble underneath pushing against the surface. Only occur in places with access to a lot of groundwater, so that the ice bubble can be large
51
New cards
Thermokarst
* Periglacial landform
* Irregular terrain characterized by topographic depressions and hummocks between them
* Results mainly from thawing of ground ice such as the melting of ice wedges and material collapsing
* Sign of warming
* Irregular terrain characterized by topographic depressions and hummocks between them
* Results mainly from thawing of ground ice such as the melting of ice wedges and material collapsing
* Sign of warming

52
New cards
Processes leading to **patterned ground** periglacial landform
* Patterning
* Cracking (frost/thermal), wedges, frost heave
* Sorting
* Frost heave
* As it freezes larger material goes off to the side and small grained material is left in the middle
* Slope
* Different patterns on steep vs. flat slopes
* Convection cells
* Water circulation cells with warm + cold water
* Cracking (frost/thermal), wedges, frost heave
* Sorting
* Frost heave
* As it freezes larger material goes off to the side and small grained material is left in the middle
* Slope
* Different patterns on steep vs. flat slopes
* Convection cells
* Water circulation cells with warm + cold water

53
New cards
Stone Circles
* Type of patterned ground periglacial landform
* Larger material forms ring, while depression in middle is filled with finer sand (frost heave)
* Larger material forms ring, while depression in middle is filled with finer sand (frost heave)

54
New cards
Polygons
* Type of patterned ground periglacial landform
* Similar to ice wedge polygons but smaller scale
* Similar to ice wedge polygons but smaller scale

55
New cards
Stone Stripes
* Type of patterned ground periglacial landform
* Tend to happen in very steep areas
* Common in hilly areas
* Sorting of the finer and coarser material in a linear form
* Tend to happen in very steep areas
* Common in hilly areas
* Sorting of the finer and coarser material in a linear form

56
New cards
Hummocks
* Type of patterned ground periglacial landform
* Opposite of stone circles
* Little ‘bulbs'/nets’
* Opposite of stone circles
* Little ‘bulbs'/nets’

57
New cards
Types of Sea Level
* Eustatic
* Local
\
* Local
\
58
New cards
Eustatic Sea Level
* Global sea level
* Volume of water
* Volume of ocean basins
* Can grow or sink (plate tectonics)
* What most people think about when you say sea level
* Volume of water
* Volume of ocean basins
* Can grow or sink (plate tectonics)
* What most people think about when you say sea level
59
New cards
Local Sea Level
* Relative elevation between average sea surface and coastline of land mass
* Depends on
* Eustatic sea level
* Plate tectonics
* Isostatic adjustments
* Depends on
* Eustatic sea level
* Plate tectonics
* Isostatic adjustments
60
New cards
Is global sea level on the rise?
* Yes!
61
New cards
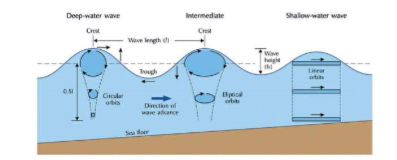
Waves
* Undulations formed by wind blowing over a water surface
* Energy transfer from wind to water
* Self-sustaining and propagates beyond the area they first formed
* Orbits larger at surface
* Currents become more elliptical and there is more forward motion closer to shore
* Energy transfer from wind to water
* Self-sustaining and propagates beyond the area they first formed
* Orbits larger at surface
* Currents become more elliptical and there is more forward motion closer to shore
62
New cards
What do waves depend on?
* Wind duration
* Wind velocity
* Fetch (distance over which wind travels)
* Wind velocity
* Fetch (distance over which wind travels)
63
New cards
What causes bending waves?
* Wave refraction
* Wave diffraction
* Wave diffraction
64
New cards
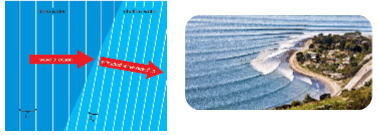
Wave Refraction
* Change in wave speed due to change in water depth
* As waves moves from deeper to shallower water, the waves slow down and crush together, while their front steepens
* Waves bend towards the direction they became shallower first
* As waves moves from deeper to shallower water, the waves slow down and crush together, while their front steepens
* Waves bend towards the direction they became shallower first
65
New cards
Wave Diffraction
* Waves bend around obstacles as they approach them and through narrow openings
\
\

66
New cards
Surf
* The max height a wave reaches as it begins to break
\
\
67
New cards
Swash
* Waves crashing on beach
\
\
68
New cards
Backwash / Undertow
* Water being pulled back / retreated into the ocean
\
\
69
New cards
What determines how waves will break?
* How much energy and steepness of coastline
\
\
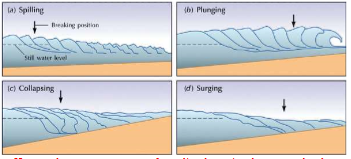
70
New cards
Constructive Waves
* Net shoreward movement of beach material
* More material from ocean transfer to beach
* Includes;
* Surging
* Spilling
* Collapsing
\
* More material from ocean transfer to beach
* Includes;
* Surging
* Spilling
* Collapsing
\
71
New cards
Destructive Waves
* Net seaward movement of beach material
* Acts as erosion agent, scatter out the beach
* Includes:
* Plunging
\
* Acts as erosion agent, scatter out the beach
* Includes:
* Plunging
\
72
New cards
Types of nearshore currents
* Longshore current
* Rip currents
\
* Rip currents
\
73
New cards
Longshore Currents
* Wind acts parallel to coastline
* Moves material in direction of current
* Parallel to beach
* Zig-zaggy motion
\
* Moves material in direction of current
* Parallel to beach
* Zig-zaggy motion
\

74
New cards
Rip Currents
* Where undertow converges and makes very strong currents that funnels outwards
* Causes a lot of erosion
* Self-sustaining
* Happens at regular intervals
* Safety hazard when swimming
* Swim parallel to beach to exit current!
* Causes a lot of erosion
* Self-sustaining
* Happens at regular intervals
* Safety hazard when swimming
* Swim parallel to beach to exit current!
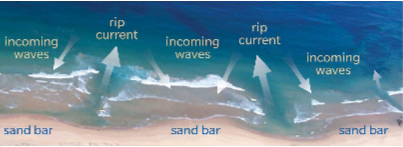
75
New cards
Types of Non-wind waves
* Tides
* Tsunamis
* Storm-induced
* Surges
* Seiches
* Tsunamis
* Storm-induced
* Surges
* Seiches
76
New cards
Tides
* Semi-diurnal
* Two high tides and two low tides per day
* Extra large and low tides depending on the season
* Moon is gravitationally pulling water on surface of Earth
* When moon and sun is on same side of Earth that’s when the highest tides are
* Much more predictable then wind-waves
* Two high tides and two low tides per day
* Extra large and low tides depending on the season
* Moon is gravitationally pulling water on surface of Earth
* When moon and sun is on same side of Earth that’s when the highest tides are
* Much more predictable then wind-waves
77
New cards
Tsunamis
* Usually caused by earthquakes which causes a vertical disturbance in the ocean
* Bunch up taller as it gets closer to shore
* Don’t have a characteristic break… simply a wall of water
* Can completely change what a coastline can look like
* Not a primary geomorphic agent since they happen so rarely
* Retreats ocean water as it gets close to shoreline, this is the biggest warning sign
\
* Bunch up taller as it gets closer to shore
* Don’t have a characteristic break… simply a wall of water
* Can completely change what a coastline can look like
* Not a primary geomorphic agent since they happen so rarely
* Retreats ocean water as it gets close to shoreline, this is the biggest warning sign
\
78
New cards
Surges
* Caused by storms which apply a lot of atmospheric pressure
* When there’s a storm the pressure is so low that the ocean water elevates
* When there’s a storm the pressure is so low that the ocean water elevates
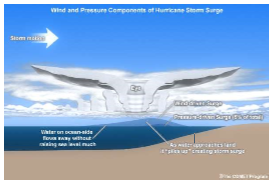
79
New cards
Seiches
* Very rare
* Occur in lakes or small bodies of water
* Entire water level of lake ‘tilts’ due to the wind
* Occur in lakes or small bodies of water
* Entire water level of lake ‘tilts’ due to the wind
80
New cards
How are coasts classified by?
* Coast material
* Material/lithology
* Bedrock or unconsolidated
* Solubility
* Coastal agencies
* Geographical setting
* Vegetation
* Currents
* Historical Factors
* Tectonics
* Glacial
* Sea level
* Human
* Material/lithology
* Bedrock or unconsolidated
* Solubility
* Coastal agencies
* Geographical setting
* Vegetation
* Currents
* Historical Factors
* Tectonics
* Glacial
* Sea level
* Human
81
New cards
Dominant coastal geomorphic agents
* Waves
* Tides
* Fluvial
* Ice
* Tides
* Fluvial
* Ice
82
New cards
Coastal Geomorphic Processes
* Erosional
* Headlands/capes
* Depositional
* Beaches/bars
\
* Headlands/capes
* Depositional
* Beaches/bars
\
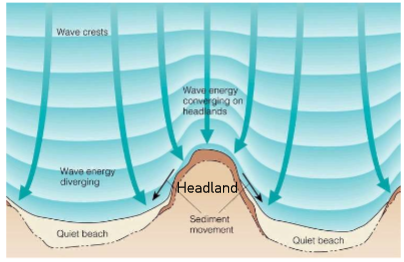
83
New cards
Erosional Coastal Geomorphic Processes
\
* Shoreline weathering
* Salt crystal
* Abrasion
* Biological
* Wave erosion
* Shoreline weathering
* Salt crystal
* Abrasion
* Biological
* Wave erosion

84
New cards
Depositional Coastal Geomorphic Processes
\
* Sediment transport and deposition
* Varying sediment sources
* Biological activity
* Coral reefs
* Sediment transport and deposition
* Varying sediment sources
* Biological activity
* Coral reefs

85
New cards
What does cliff retreat (near the ocean) depend on?
* Driving forces = wave force
* Resisting forces = material resistance
* Resisting forces = material resistance
86
New cards
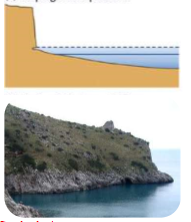
Sloping shore platform
* Type of coastal erosional landform
* Gently sloping
* No beach, exposed bedrock
\
* Gently sloping
* No beach, exposed bedrock
\
87
New cards
Horizontal shore platform
* Type of coastal erosional landform
* Flat-surface and a suddenly deeper surface
* Usually occurs in areas with different geological layers
* Consisting of resistant rock and more easily erodible rock
* No beach, exposed bedrock
* Flat-surface and a suddenly deeper surface
* Usually occurs in areas with different geological layers
* Consisting of resistant rock and more easily erodible rock
* No beach, exposed bedrock

88
New cards
Plunging Cliff
* Type of coastal erosional landform
* Vertical all the way down to sea floor
* No beach, exposed bedrock
* Vertical all the way down to sea floor
* No beach, exposed bedrock

89
New cards
Cliff-Based Notches
* Coastal erosional landform
* Wave action erodes bottom of formation
* Not stable
* Wave action erodes bottom of formation
* Not stable

90
New cards
Marine Potholes
* Coastal erosional landform
* Looks similar to salt crystal weathering
* Wave action erodes weaker spots of rock forming these potholes
* Looks similar to salt crystal weathering
* Wave action erodes weaker spots of rock forming these potholes

91
New cards
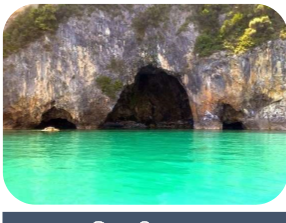
Sea Caves
* Coastal erosional landform
* Eroded at weaker spots
* Possibly as a fault line or joint
* Cave-like features
* Eroded at weaker spots
* Possibly as a fault line or joint
* Cave-like features
92
New cards
Arches
* Coastal erosional landform
* Significantly eroded cave
* Defined offshore headland still connected onshore by a top platform
\
* Significantly eroded cave
* Defined offshore headland still connected onshore by a top platform
\

93
New cards
Stacks
* Coastal erosional landform
* Entire section of coast eroded away
* The only thing that remains are isolated columns made up of resistant material
* Entire section of coast eroded away
* The only thing that remains are isolated columns made up of resistant material

94
New cards
Stumps
* Eroded away stacks

95
New cards
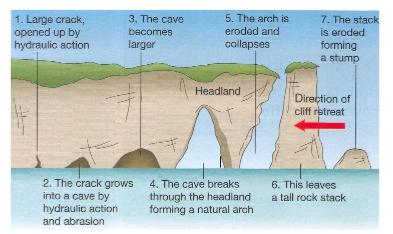
Timeline of coastal erosional landforms
1. Crack opens up
2. Cave forms
3. Cave breaks through headland forming arch
4. Arch disconnects and erodes more forming stack
5. Stack erodes away forming stump
96
New cards
Beaches
* Coastal depositional landform
* Lower energy environments
* Material eroded at headlands are deposited here
* Aggregate beaches cover 20% of Earth’s coasts
* Large diversity in beach morphology
\
* Lower energy environments
* Material eroded at headlands are deposited here
* Aggregate beaches cover 20% of Earth’s coasts
* Large diversity in beach morphology
\

97
New cards
Tombolo
* Coastal depositional landform
* Two islands connected by a bar
* Can be indicative of a spit forming or a spit splitting
* Two islands connected by a bar
* Can be indicative of a spit forming or a spit splitting

98
New cards
Spit
* Coastal depositional landform
* Longshore current pushes sand across shore, creating a curved arm of sand
* Longshore current pushes sand across shore, creating a curved arm of sand

99
New cards
Sandbars
* Coastal depositional landform
* Temporary accumulation of sand offshore
* Can occur at a naturally shallow area or an area where that are a lot of obstacles slowing down waves causing deposition
* Temporary accumulation of sand offshore
* Can occur at a naturally shallow area or an area where that are a lot of obstacles slowing down waves causing deposition

100
New cards
Barrier Islands
* Coastal depositional landform
* Off-shore island which is typically tide-dominated
* Off-shore island which is typically tide-dominated
