12-01: Functional Groups and Linkages
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/56
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
1
New cards
Water
________ is required and it is used up → it is a reactant.
2
New cards
double bond
The ________ indicates that it is an ester linkage.
3
New cards
C
________ and H form a non polar bond so hydrocarbons are non polar.
4
New cards
What is in an organism
1. Carbohydrates
2. Lipids
3. Proteins
4. Nucleic Acids
5. Water
2. Lipids
3. Proteins
4. Nucleic Acids
5. Water
5
New cards
Molecules
________ interact with each other at specific regions of their ________ (changes the dynamic of the ________ that allow it it interact differently)
6
New cards
Monomers
Single units that make up molecules
7
New cards
Anabolic reactions
build up substances
8
New cards
Catabolic reactions
break down substance
9
New cards
Both catabolic and anabolic reactions occurring in an organism
metabolism
10
New cards
1 atom loses an e
and 1 gains an e-
11
New cards
Sharing the e
less fairly
12
New cards
Covalent
∆EN < 0.4 → share equally
13
New cards
Polar covalent
∆EN = 0.5-1.7
14
New cards
One atom has a stronger hold on e
they share
15
New cards
Because of Oxygen (O)s EN, e
tend to spend more time near the O atom than near the Hydrogen (H) atoms
16
New cards
The unequal sharing e
creates a slight difference in the charge between the ends/poles of the molecule
17
New cards
the O end is δ
and the H ends are δ+
18
New cards
Cohesion
water molecules are attracted to other water molecules
19
New cards
Adhesion
water is a polar molecule and thus attracts other polar molecules
20
New cards
London dispersion forces
very weak attraction between molecules, even non polar ones
21
New cards
Dipole dipole attraction
attractive force between 2 polar molecules
22
New cards
H bonding
special kind of dipole dipole attraction; between 2 polar molecules with Hydrogen bonded to N, O, or F
23
New cards
Organic compound
compound that contains carbon-hydrogen bonds (may also contain other elements like O, N, etc) and is often found in organisms
24
New cards
Classifying FGs
if it has the FG, then it is classified that certain way
25
New cards
Polymer
A naturally occurring or synthetic compound consisting of large molecules made up of a linked series of repeated simple monomers
26
New cards
Catabolic reactions
Reactions that break down a substance
27
New cards
Anabolic reactions
Reactions that build up a substance
28
New cards
Metabolism
Both catabolic and anabolic reactions occurring in an organism (combination of all reactions happening)
29
New cards
Covalent bonds
2 non metals share e-
30
New cards
Ionic bonds
1 atom loses e-, 1 atom gains e- (between a metal and a nonmetal)
31
New cards
Electronegativity
The strength in which an atom attracts electrons
32
New cards
Covalent ∆EN
∆EN < 0.4
33
New cards
Polar covalent ∆EN
∆EN = 0.5-1.7
34
New cards
Ionic ∆EN
∆EN > 1.7 (atom with greater EN takes e- from atom with lesser EN, both become charged)
35
New cards
Polar covalent bonds
One atom has a stronger hold on e- they share
One end of the molecule gets slightly positively charged and one end gets slightly negatively charged
δ+ → one end gets + charge (weaker EN)
δ- → one end gets - charge (stronger EN)
One end of the molecule gets slightly positively charged and one end gets slightly negatively charged
δ+ → one end gets + charge (weaker EN)
δ- → one end gets - charge (stronger EN)
36
New cards
Water is polar --> it has polar covalent intramolecular bonds
Because of Oxygen (O)’s EN, e- tend to spend more time near the O atom than near the Hydrogen (H) atoms
The unequal sharing e- creates a slight difference in the charge between the ends/poles of the molecule
the O end is δ- and the H ends are δ+
Due to its polarity, water forms H bonds with itself
Very weak bonds, but many of which come together and become very strong together
The unequal sharing e- creates a slight difference in the charge between the ends/poles of the molecule
the O end is δ- and the H ends are δ+
Due to its polarity, water forms H bonds with itself
Very weak bonds, but many of which come together and become very strong together
37
New cards
Cohesion (water forms bonds through)
Water molecules are attracted to other water molecules
38
New cards
Adhesion (water forms bonds through)
Water is a polar molecule and therefore attracts other polar molecules
39
New cards
Intermolecular forces
Bonds between molecules
40
New cards
Intramolecular forces
Bonds within a molecule
41
New cards
London dispersion forces (intermolecular force)
Very weak attraction between all molecules (even non polar ones). Increases with molecule size
42
New cards
Dipole dipole attraction (intermolecular force)
Attractive force between 2 polar molecules
43
New cards
H bonding (intermolecular force)
Special kind of dipole dipole attraction, between 2 polar molecules with Hydrogen bonded to Nitrogen, Oxygen, or Fluorine
44
New cards
Carbon
Backbone of nearly every biological molecule (exception: water)
45
New cards
Organic compound
Compound that contains Carbon-Hydrogen bonds (may also contain other elements like Oxygen, Nitrogen, etc) and is often found in organisms
46
New cards
Why are functional groups added?
Carbon and Hydrogen form a non polar bond --> hydrocarbons are non polar
polarity can be achieved by adding other atoms, which is why they are added
polarity can be achieved by adding other atoms, which is why they are added
47
New cards
Functional groups change the dynamic of the molecule which allow it to
Interact differently, meaning that it can react differently
48
New cards
After a reaction between 2 molecules' functional groups, a _______ will be formed
Linkage
49
New cards
Why can monomers link to form polymers?
Functional groups react
50
New cards
Classifications
If a molecule has the functional group, it can then be classified in a given way
51
New cards
Hydrolysis reactions
Water is used to break down/rupture, catabolic, water required and used up as a reactant
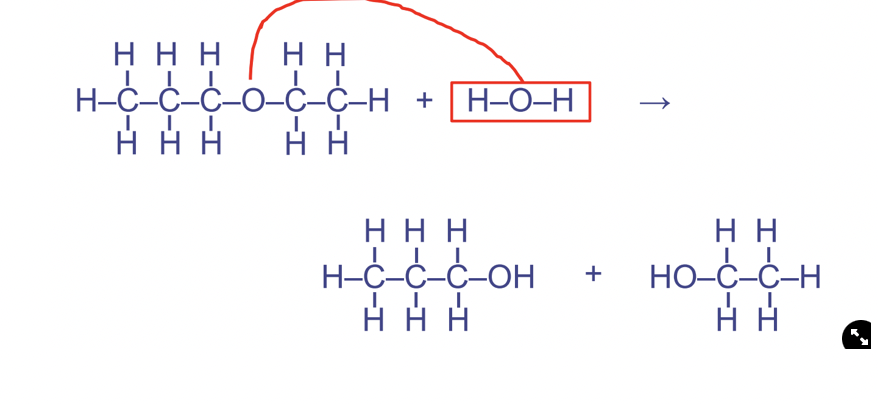
52
New cards
Dehydration synthesis reaction
Condenses smaller particles into larger ones, anabolic, used to build up molecules, water is released as a product
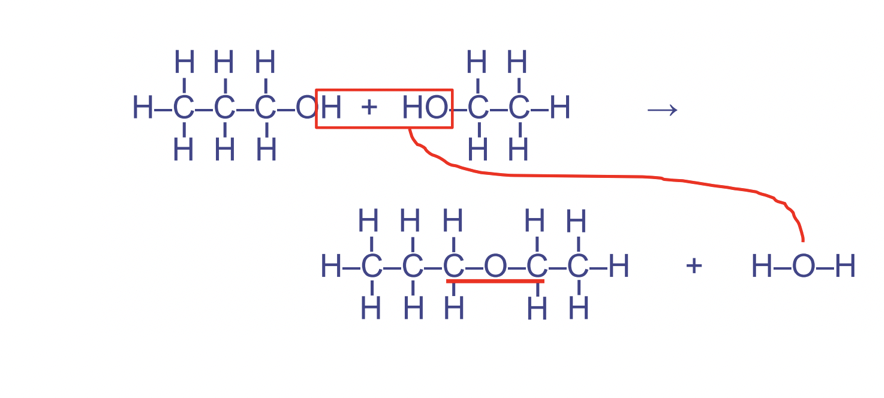
53
New cards
Linkages that form in ___________ reactions
Dehydration synthesis
54
New cards
Ether linkages
Between 2 hydroxyl functional groups
Forms the pattern COC
Forms the pattern COC
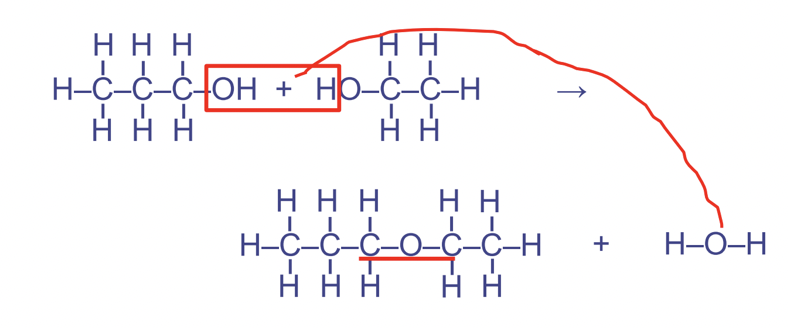
55
New cards
Ester linkages
Between a hydroxyl and carbonyl functional groups
Forms the pattern OCO
* the double bond indicates that it is a _________ linkage
Forms the pattern OCO
* the double bond indicates that it is a _________ linkage
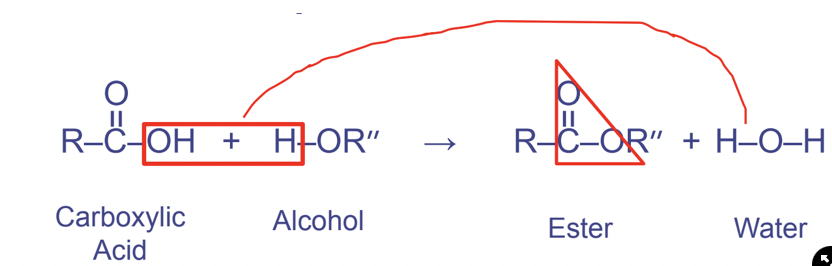
56
New cards
Phopshate ester linkages
Between hydroxyl and phosphate functional groups
- Used in phospholipids and nucleic acid (instructs cells, DNA & RNA)
Forms the pattern OPO
- Used in phospholipids and nucleic acid (instructs cells, DNA & RNA)
Forms the pattern OPO
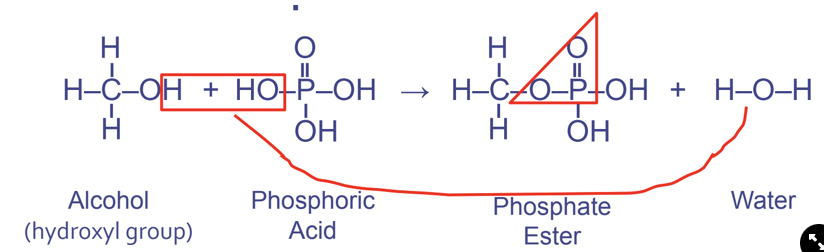
57
New cards
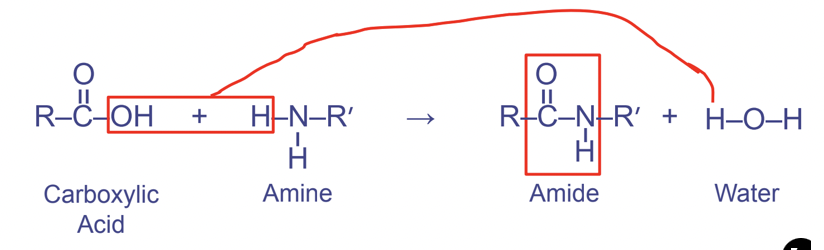
Peptide linkages
Between carboxyl and amino functional groups
- Links amino acids together
Forms the pattern OCNH
- Links amino acids together
Forms the pattern OCNH