Lec 31 Colorectal Cancer
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
What screening modalities are available for colorectal cancer? How often do these modalities need to happen?
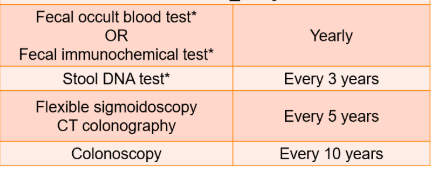
When should screening begin for average risk patients?
Age 45 for men and women
Which molecular tests need to be obtained for colorectal cancer to guide treatment decisions?
KRAS/NRAS mutation: Damage to growth-control genes that makes cancer cells grow out of control.
BRAF mutation: A broken signal gene that tells cells to divide too much.
dMMR/MSI-H: dMMR means the cell’s DNA repair system is broken, leading to high microsatellite instability (MSI-H) and lots of DNA errors. A broken DNA repair system that lets lots of mistakes build up.
HER2 amplification: Too many HER2 signals making cells grow way too fast
What treatment modalities can be used for rectal cancer stages I, II, III?
Surgery
Resection of primary tumor
Radiation
Neoadjuvant: Improves resectability of primary tumor
Adjuvant: decreases risk of local recurrence
Chemotherapy
Combined with radiation or alone
Neoadjuvant: improves resectability of primary tumor (TNT)
Adjuvant: eradicate micrometastatic disease, improve disease free survival (DFS)
In rectal cancer, doctors use a mix of surgery, chemo, and radiation (before or after surgery) to shrink the tumor, remove it, and prevent it from coming back.
What are the common chemotherapy regimens used for adjuvant treatment of colon cancer? (Based on risk and stage)
Stage I & Low risk II MSI-H | Surveillance, no adjuvant tx |
Low risk II | Surveillance OR Consider adjuvant chemo:
|
High risk II | Adjuvant chemo
|
Low Risk III | Adjuvant chemo
|
High risk III | Adjuvant chemo
|
What unusual side effects can occur with oxaliplatin?
Peripheral neuropathy
Chemo induced nausea/vomiting
Hepatotoxicity
Pulmonary fibrosis
What therapies can be used with the KRAS/NRAS G12C mutation and KRAS/NRAS wild type in stage IV colon cancer
KRAS/NRAS G12C mutation:
Adagrasib (with cetuximab)
Sotorasib (with panitumumab)
KRAS/NRAS wild type
Panitumumab/Cetuximab
What therapies can be used with the HER2 amplification mutations in Stage IV colon cancer?
HER2 amplification
Trastuzumab + [pertuzumab, lapatinib, or tucatinib]
Fam-Trastuzumab deruxtecan-nxki
What therapies can be used with the BRAF mutations in Stage IV colon cancer?
BRAF mutation
Encorafenib (always in combo with pani)
What therapies can be used with the dMMR/MSI-H mutations in Stage IV colon cancer?
dMMR/MSI-H:
Pembrolizumab
Nivolumab (with or without ipilimumab)
Treatment algorithm for Stage IV cancer based on mutations (8. What regimens could be considered for first-line treatment in a patient with stage IV RAS WT, BRAF WT colon cancer?)
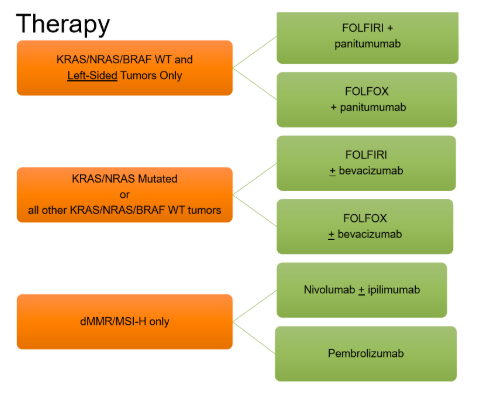
What regimens could be considered for first-line treatment in a patient with stage IV RAS mutated rectal cancer?
Same as colon
What regimens could be considered for first-line treatment in a patient with MSI-H Stage IV rectal cancer?
Same as colon
How do you manage acute diarrhea from irinotecan? How do you manage delayed diarrhea from irinotecan?
Acute Phase: Within 24 hours of infusion | Delayed Phase: 24 hours after infusion |
During tx: Atropine IV or SubQ After tx: diphenoxylate/atropine (Lomotil) tablets 1-2 PO QID PRN | Loperamide + Fluids & Electrolytes |
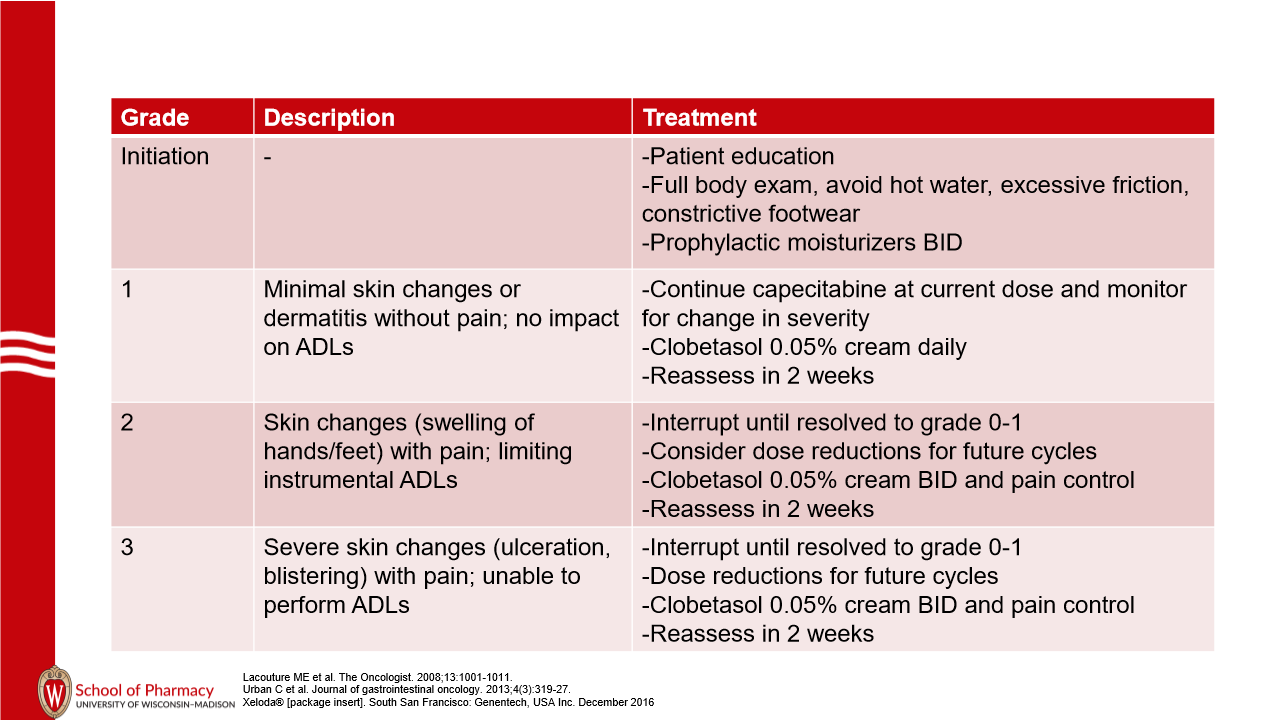
How is the hand-foot syndrome arising from capecitabine and 5FU best prevented, and how is it treated if it occurs?
Prevention: Prophylactic moisturizer BID, avoid hot water, excessive friction, and constrictive footwear
Why is leucovorin added to colorectal chemotherapy regimens that include 5FU or capecitabine?
Tightens the binding of 5FU metabolite (fdump) to thymidylate synthase → promotes anticancer effect of FOLFOX
Not necessary with capecitabine because it’s a prodrug of 5FU so slower metabolism → longer exposure to anticancer effect
What drugs are most commonly tried for the treatment of oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy?
Duloxetine
Gabapentin
What is the preemptive management of EGFR-inhibitor rash? How does it differ from the treatment of rash from Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors?
Both use a steroid cream as an option but there are no antibtioics for immune checkpoint rash and its not preemptive tx
