HAP study guide part 4: Histology
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Mitochondria
power house, produces ATP
Nucleus
contains and protects genetic materials (DNA)
Cytoskeleton
Provides cell structures
Cell Membrane
Contains what enters and exits the cell
Endoplasmic Reticulum
packages protein
Active transport
needs energy to move from low to high concentration
Passive transport
doesnt need energy to move through the channel moves from high to low concentration
diffusion
movement from phospholipid bilayer from high to low concentration
facilitated diffused
moving down concentration ( high- low ) using a channel protien to move large or charged particle
osmosis
movement of water to balance concentratio
histology
the study of tissue structure
simple cell arrangement
one layer of cells
stratified cell arrangement
multiple cell layers
what is the epithelial function
protection, absorbs substances, filtration , and secretion ( release substances)
what is the epithelial characteristic
highly cellular little matrix
what is the connective tissue function
bind, protect
cytoskeleton
specialized to help build and maintain the vast
what is the connective tissue characteristic
mostly matrix very few cells
what is muscle function
pump blood and movement
what does muscular cells have
have abundant mitochondria to meet the demands of energy for muscle contraction
what is the muscular system characteristic
highly cellular little matrix
which 2 cells are highly cellular little matrix
muscular and epithelial
nervous cells are specialized for
sending electro chemical signals
what is nervous system function
generate and conduct nerve impulses
which 2 have more matrix very few cells
nervous, connective
what does heavy smoking do
accumulate foreign particles
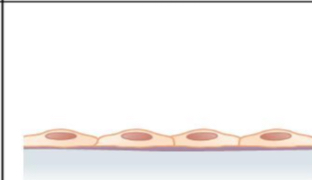
what tissue is this
simple squamous epithelial
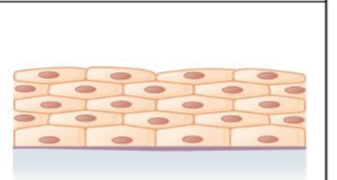
what tissue is this
stratified squamous epithelial
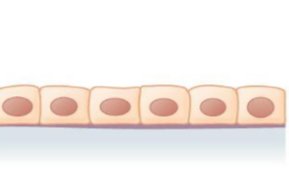
what tissue is this
simple cuboidal epithelial
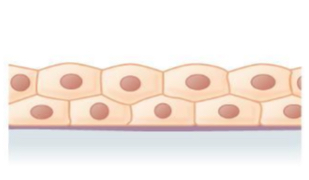
what tissue is this
stratified cuboidal epithelial
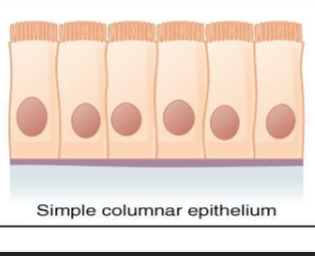
what tissue is this
simple columnar epithelial

what tissue is this
stratified columnar epithelial
what tissue is this
psuedostratified columnar epithelial
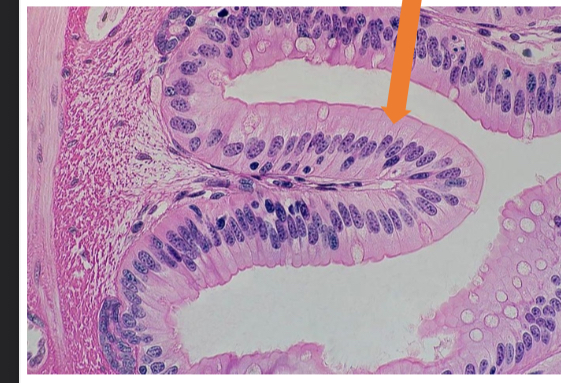
what tissue is this
simple columnar epithelial
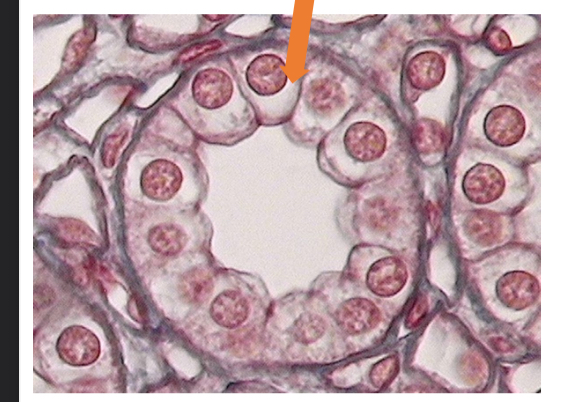
what tissue is this
simple cuboidal epithelial
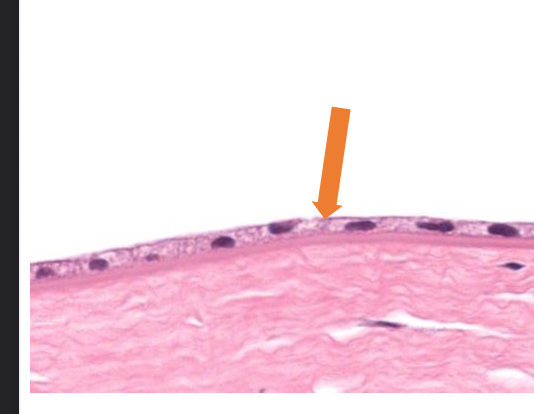
what tissue is this
simple squamous epithelial
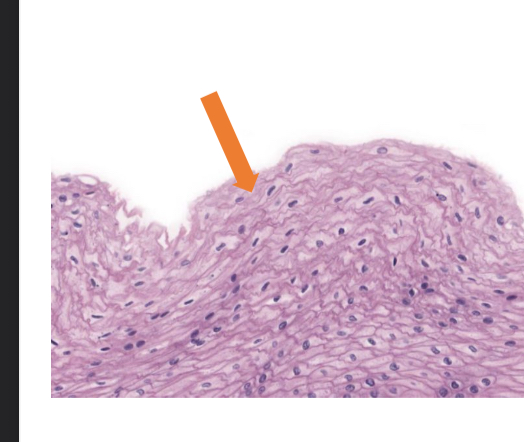
what tissue is this
stratified squamous epithelial
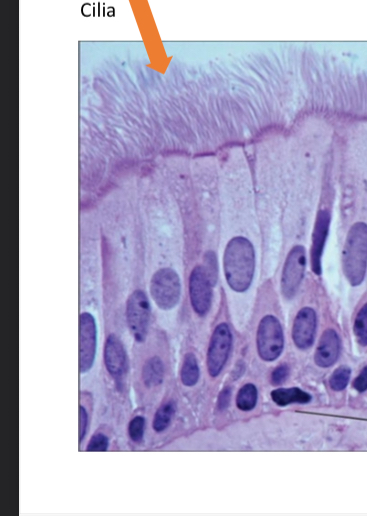
what tissue is this
psuedostratified columnar epithelial
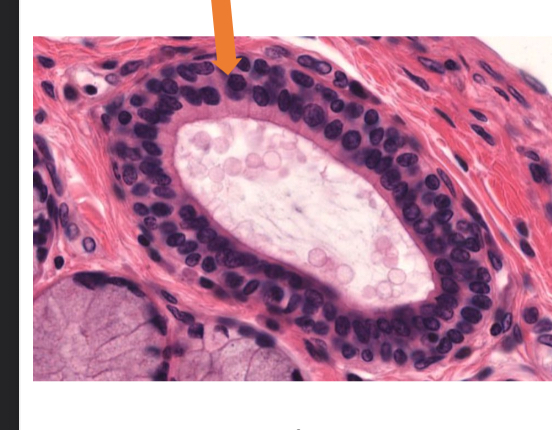
what tissue is this
stratified cuboidal epithelial
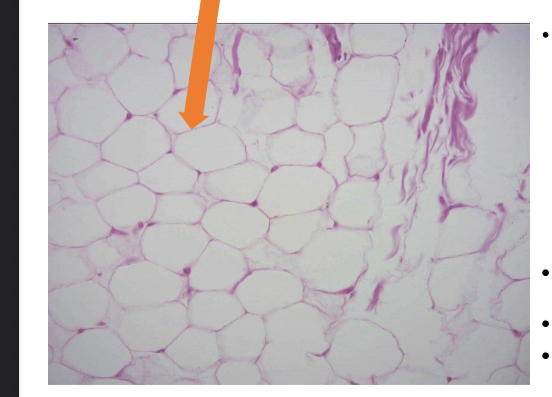
what tissue is this
adipose (connective tissue)
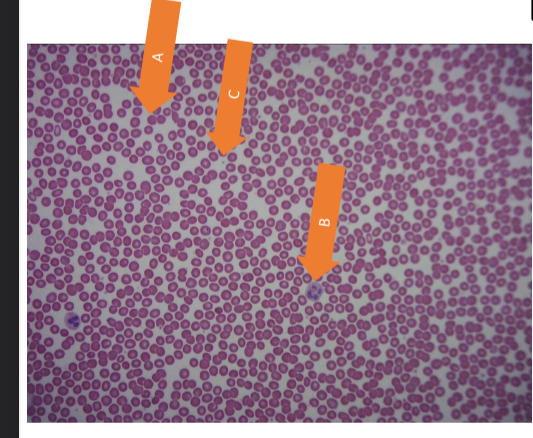
what tissue is this
blood (connective tissue)
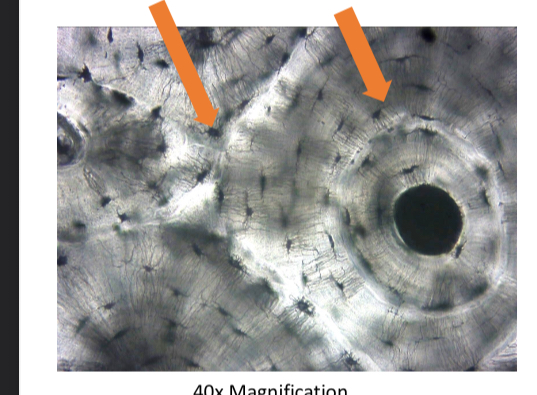
what tissue is this
compact bone (conective tissue)
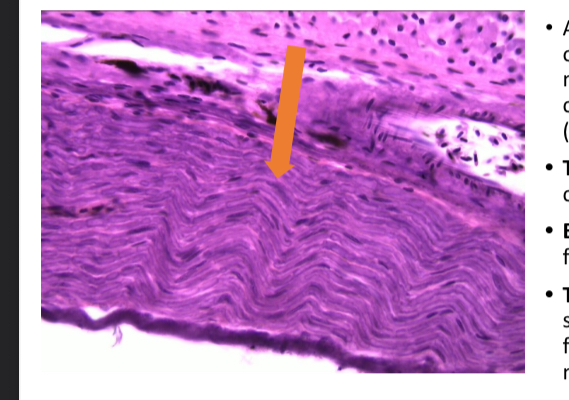
what tissue is this
dense regular connetive tissue
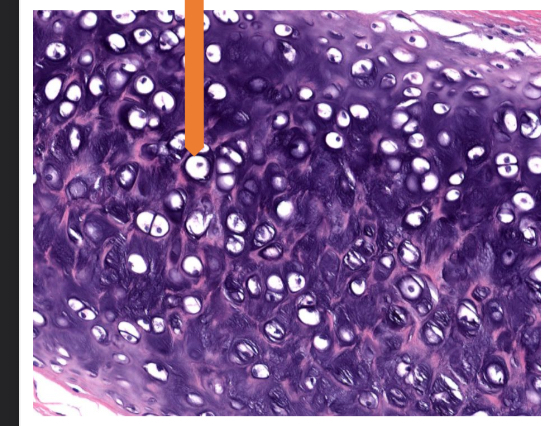
what tissue is this
elastic cartilage ( connective tissue)
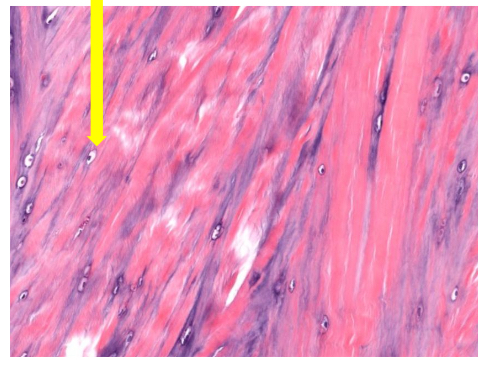
what tissue is this
fibrocartilage (connective tissue)
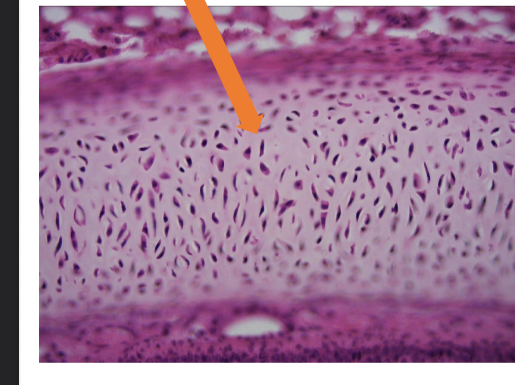
what tissue is this
hyaline cartilage (connective tissue)
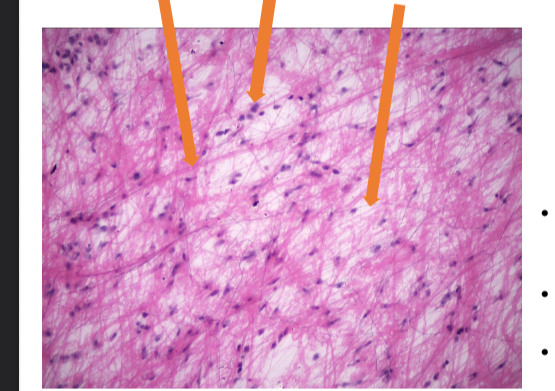
what tissue is this
loose connective tissue ( areolar)
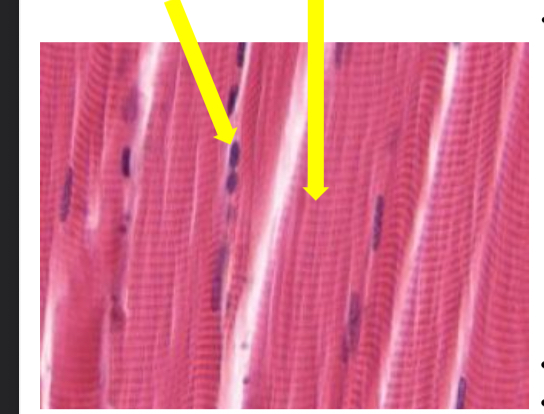
what tissue is this
skeletal muscle tissue
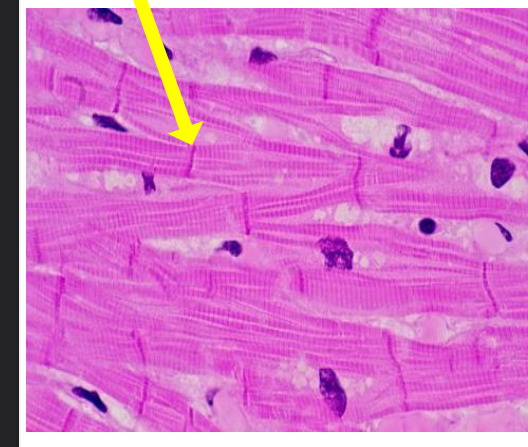
what tissue is this
cardiac muscle tissue
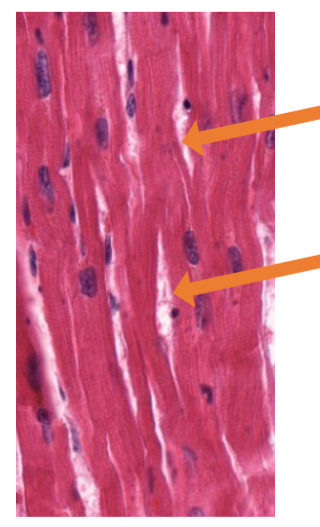
what tissue is this
cardiac muscle tissue
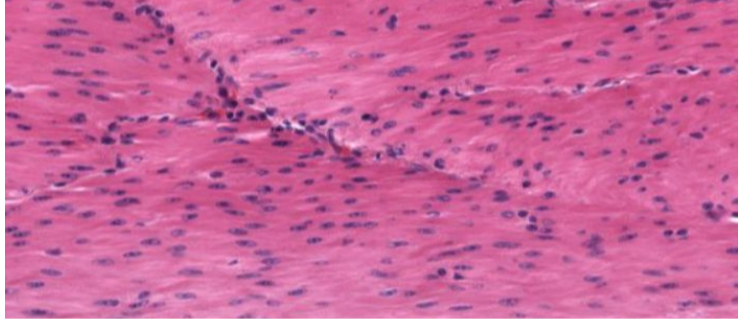
what tissue is this
smooth muscle tissue
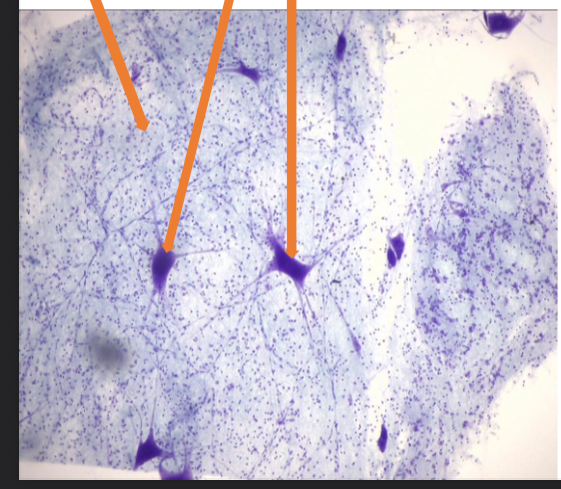
what tissue is this
nervous tissue