English H: Romeo and Juliet Acts 1-5 Test
1/301
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
302 Terms
Dramatic Poetry
The most complex form of dramatic poetry is the full length verse play in which multiple speakers are given different voices
The language and format of dramatic poetry resemble what?
Poetry
The _____ and dialogue of dramatic poetry do not attempt to duplicate ______.
language, reality
Chorus
A group of characters who summarize the plot and comment on the action for the audience
Monologue
A long, uninterrupted speech made by one character
Aside
Words spoken onstage for the audience, not to be heard by other characters on stage
Prologue
The prologue serves as exposition introducing material before the first scene begins
Sonnet
A highly structured 14 line poem
Shakespeare used what poem form in his plays?
Sonnet
Rhyme scheme of sonnet
ABAB CDCD EFEF GG (rhyming couplet)
5 Act structure
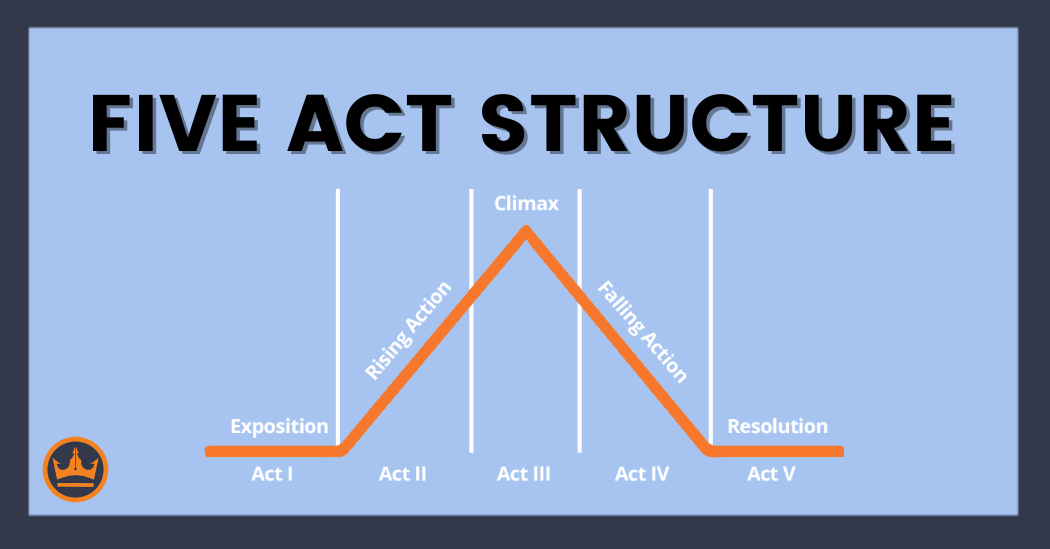
Tragedy
A genre of story in which a hero is brought down by his/her own flaws, usually by ordinary human flaws
Elements of Tragedy
Tragedy
Tragic hero
Reversal (downfall)
Hamartia
Catharsis
Characteristics
Purpose
Tragic Hero
The term hero is derived from a Greek word that means a person who faces adversity, or demonstrates courage in the face of danger
When the hero experiences a ______, he becomes a tragic hero.
downfall
Downfall
Descent to a lower position or standing, ruin or failure
_____ refresh to the downfall as the reversal.
Aristotle
The reversal usually occurs in Act _____ and moves towards the ______.
4, denouement
At the downfall point in the play, the hero’s Fortune shifts from _____ to _____.
good, bad
Hammartia
The tragic flaw or error that reverses a protagonist’s fortune from good to bad
Catharsis
A cleansing or purification brought about by great sadness, fear, or piety
One characteristic of a tragic hero is that the tragic hero has a ______ (hamartia) that leads leads to his downfall.
flaw
A tragic hero experiences a reversal of ______ or fortune.
fate
A tragic hero exhibits the trait of _____ often.
hubris
A tragic hero is always ______ and admired, talented and/or ______ character who loses his status.
respected, powerful
The tragic hero’s pain and ______ inspires sadness and pity in the audience.
suffering
The purpose of the tragic hero is to evoke ____, ____, and fear in the audience or reader.
sadness, pity
The purpose of the tragic hero in literature is to provoke an emotional ______ in the audience or reader.
Catharsis
The purpose of the tragic hero in literature is to provide a ____ ______ to the audience or reader.
cautionary tale
Through the tragic hero telling the audience of a cautionary tale makes the audience learn to avoid the ____ ____ which leads to the character’s demise.
tragic flaw
Literary Devices
Pun
Oxymoron
Apostrophe
Conceit
Allusion
Metonymy
Synecdoche
Pun
A play on words that have two meanings
Oxymoron
A contradiction that is nevertheless true
Apostrophe
Addressing something/someone dead or inanimate as if it can respond
Conceit
A fanciful metaphor, especially a highly elaborate or extended metaphor in which an unlikely far-fetched, or strained comparison is made between two things
Allusion
A reference to a literary work, mythology, history, or the Bible
An allusion is not _____, but for those who recognize allusions, it offers a _____ ______.
explained, deeper meaning
Metonymy
Substituting the name of an entity with something closely related to it
Example of a metonymy
The pen is mightier than the sword.
Sound Devices
End rhyme
Rhyme scheme
Rhyming couplet
Alliteration
Consonance
Assonance
Meter
Iambic pentameter
Blank verse
Synecdoche
A part of something is used to represent the whole
Example of a synecdoche
That brunette is staring at you. The puppy stole my heart. You have your nose in everybody else’s business.
End rhyme
Rhyme that occurs at the end of the lines as opposed to rhyming words within a line
Rhyme scheme
A set pattern of end rhyme
Shakesperean sonnet
ABABCDCDEFEFGG
Rhyming couplet
Two consecutive lines of end rhyme
A rhyming couplet usually joins a _____ or _____ and brings a scene, _____, sonnet, or _____ to a close.
thought, idea, soliloquy, act
The ____ at the end of a rhyming couplet closes out an act, sonnet, scene, or soliloquy to a close.
GG
Alliteration
Repetition of the initial consonant sound
Example of alliteration
Pout, pair, peal
Consonance
Repetition of the final consonant sound
Example of consonance
Pout, hat, tart
Assonance
Repetition of the vowel sound
Example of assonance
Pout, loud, now
Meter
A pattern of stressed and unstressed syllables that create a rhythm
Imabic pentameter
Five feet of unstressed followed by stressed syllables (heartbeat)
Example of Iambic Pentameter
I am a pirate with a wooden leg
Blank verse
Unrhymed iambic pentameter
Figurative language
Synecdoche
Metonymy
Personification
Metaphor
Simile
Hyperbole
Renaissance
Rebirth
Shakespeare contributed ______ poems to the Renaissance.
30,000
Sonnets are always ____ lines (like prologue) and are used to organize and ____ (cuatrine 4 lines).
14, unify
A rhyming couplet summarizes ______.
speech
“Star crossed lovers”
Fate over what happens to the relationship
In the prologue, we get ______ info.
background
Dramatic irony in the “star crossed lovers’” life
Shakespeare is warning
There’s more references to _____ and _____ than love (juxtaposition) in the ______.
hatred, violence, prologue
London
Very violent when Shakespeare was writing
Monologue is to _____ while a soliloquy is to _____ (alone).
others, yourself
Prose
When a servant speaks to show humbleness
Act 1 is all ______.
exposition
In Act 1, we know what happens when a character is introduced (______).
characterization
Act 1.2 shows _____ characterization of Capulet.
indirect
Capulet is _____ and ______.
protective, adoring
Capulet is a ______ father.
caring
Capulet had _____ feelings about Juliet because he was talking _____ (soliloquy).
genuine, alone
Capulet has ____ to prove.
nothing
Capulet wants to fight the _____, but is soft for _____ (juxtaposition).
Montonogues, Juliet
Lady Capulet is ____, ____, cold and direct.
terse, formal
Lady Capulet likes people to speak ______.
briefly
Lady Capulet is a _____ to the Nurse who is warm and ______.
foil, fuzzy
Lady Capulet is only going to settles with what she _____.
wants
The Nurse is the ____ _____.
comic
The Nurse is a ______ figure.
maternal
Common people (like the Nurse) are ______.
unrefined
The reason the Nurse is the comic relief is because why?
Common people are unrefined and she’s relatable to groundlings
Juliet is young and ______.
innocent
Juliet is relatable because why?
She’s obedient to the wish of marriage (people-pleaser)
Juliet is _____ and obedient.
submissive
“Endart”
Arrows, darts
Cupid is the Roman god of _____.
love
Cupid’s gold arrows cause what?
Love and passion
Cupid’s lead arrows cause what?
Hate and rejection
Rosaline is _____, which is why Romeo is so distrauight about losing her.
chastile (celabate?)
Act 1.5 story arc
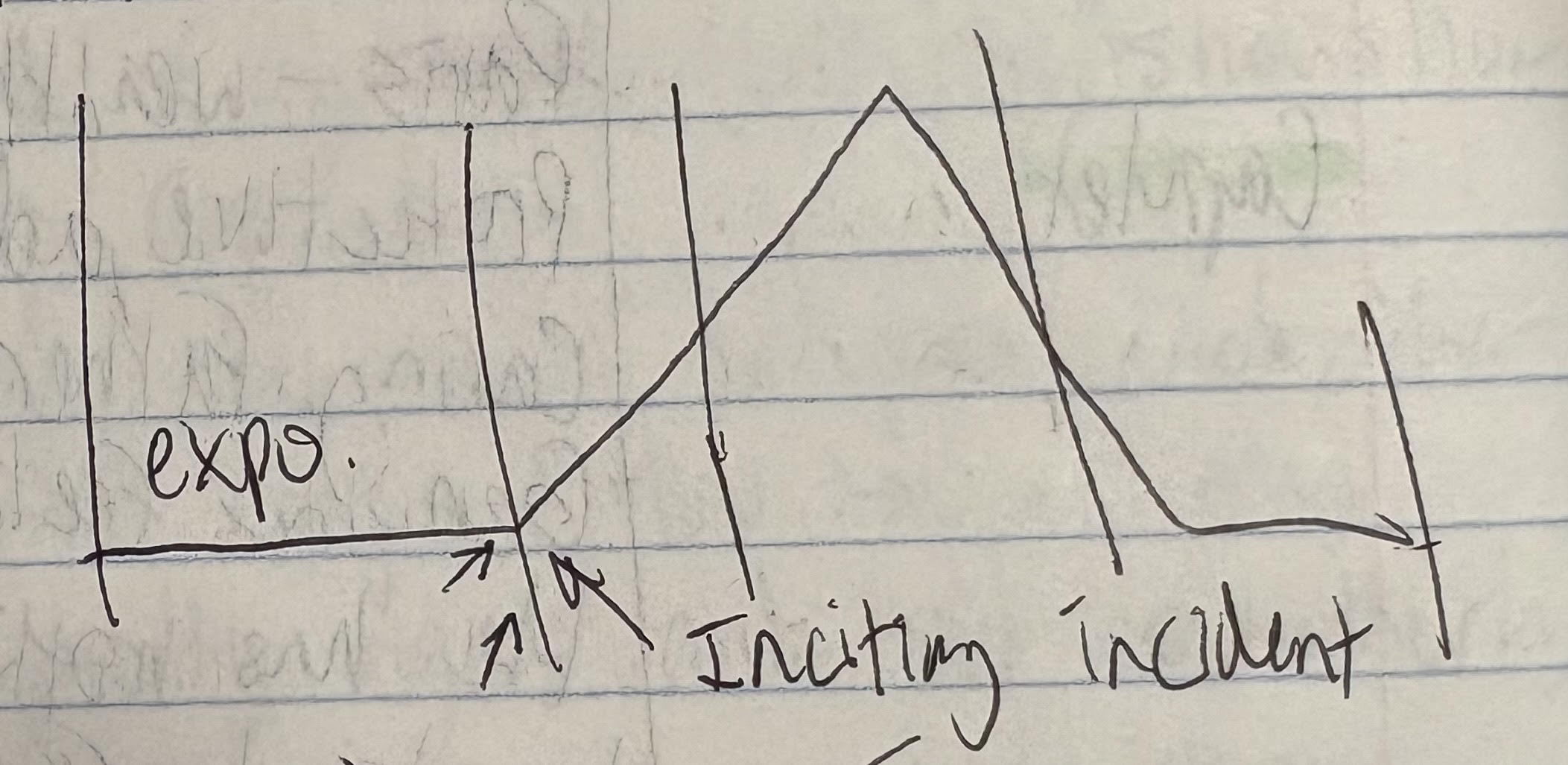
During the exposition, Romeo and _____ meet that sparks _____.
Juliet, love
What’s the inciting incident of Romeo and Juliet?
Tybalt gets mad at Romeo when he’s kicked out of the party
During Acts 1.3, 1.4, and 1.5 what are juxtaposed?
Scenes of love and hate
Gut feelings
The gut feelings Romeo and other characters have becomes a motif
A soliloquy is private _____, and reveals internal ______.
thoughts, conflict