Organic Chemistry - Reaction Types
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
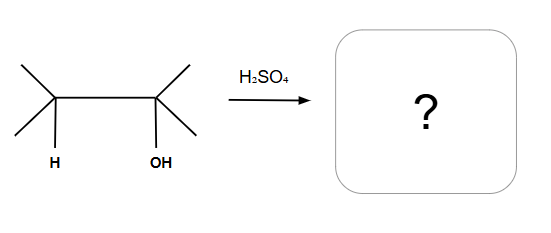
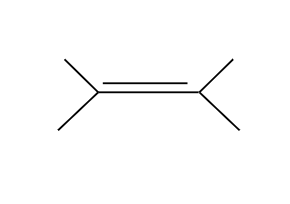
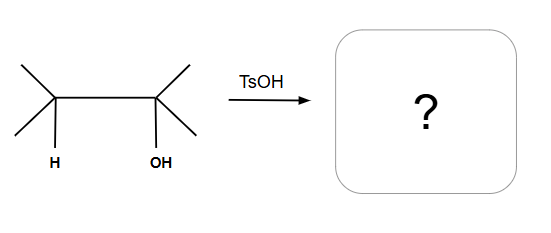
Dehydration Reactions
Tertiary and Secondary alcohols undergo E1
Can have alkyl and halide shifts
Methyl and primary alcohols undergo E2
POCl3 is always E2
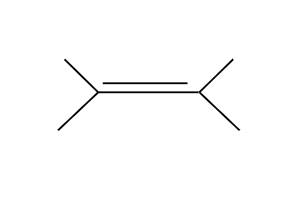
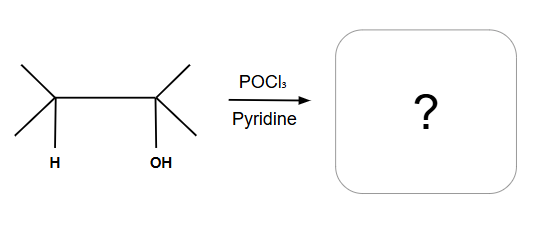
ALWAYS E2
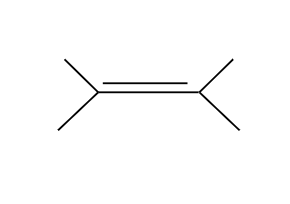
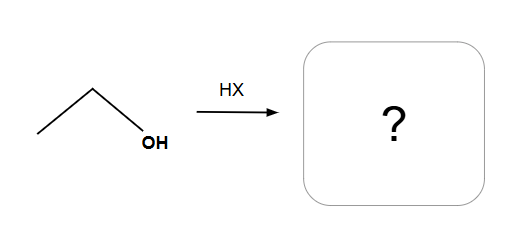
Tertiary and Secondary alcohols undergo SN1
Methyl and primary alcohols undergo SN2
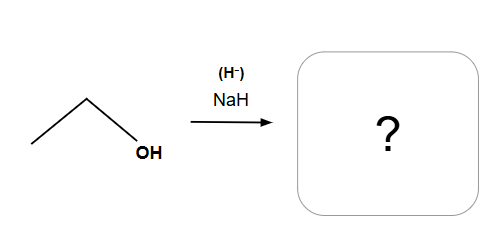
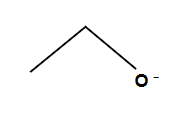
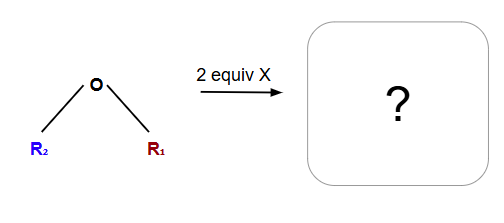
Alkoxide formation for ether synthesis
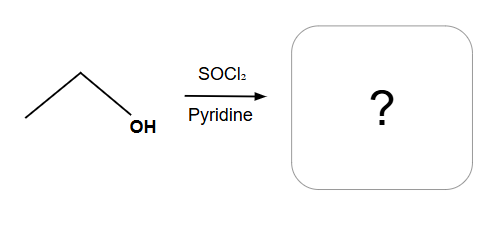
Always SN2
Only work with methyl and primary alcohols
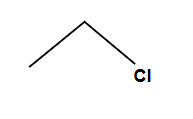
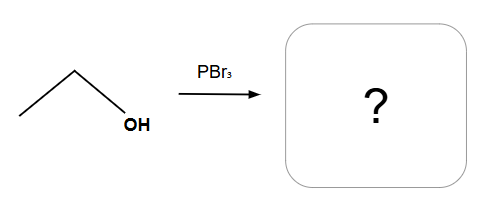
Always SN2
Only work with methyl and primary alcohols
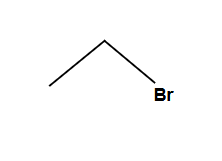
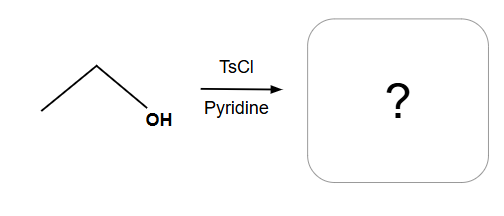
No stereochemical change
Creates good LG
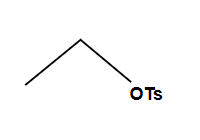
SN1 if R is secondary or tertiary
SN2 if R is primary
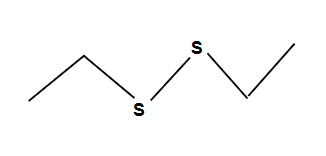
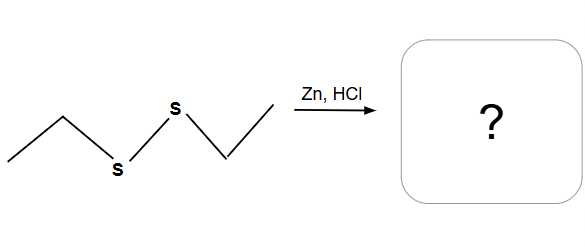
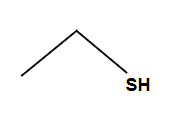

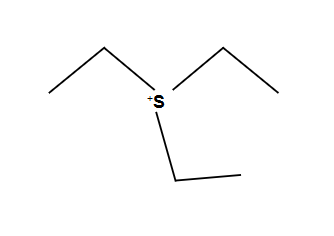
Epoxide Rule with opticality
Optically inactive reactants product optically inactive products
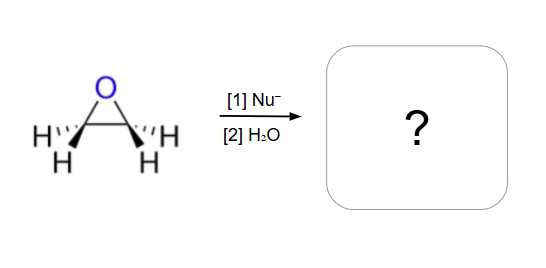
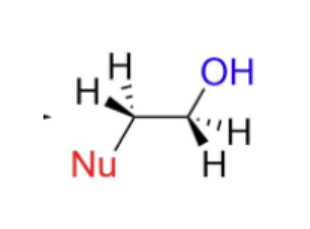
In an unsymmetrical epoxide, the nucleophile attacks the LESS substituted carbon

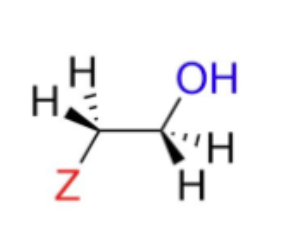
In an unsymmetrical epoxide, the nucleophile attacks the MORE substituted carbon
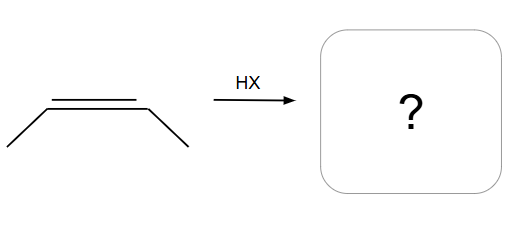
Follows Markovnikov’s Rule
Always SN1
Addition is Syn and Anti
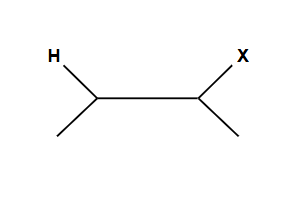
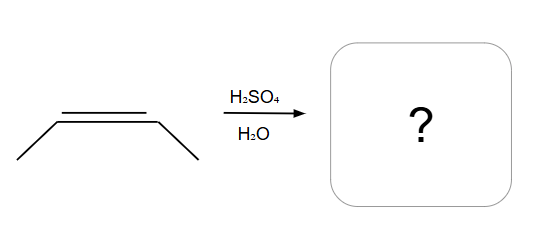
Follows Markovnikov’s Rule
Always SN1
Addition is Syn and Anti
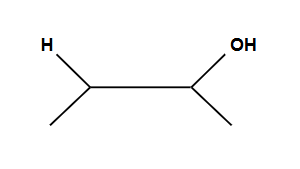
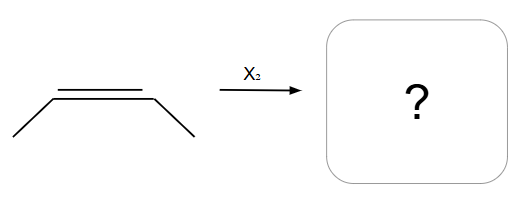
Creates an ring that is then opened by the second halogen
NO POSSIBLE CARBOCATION
Addition is Anti ONLY
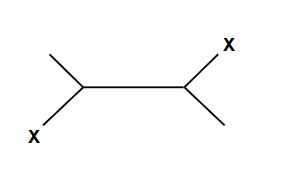
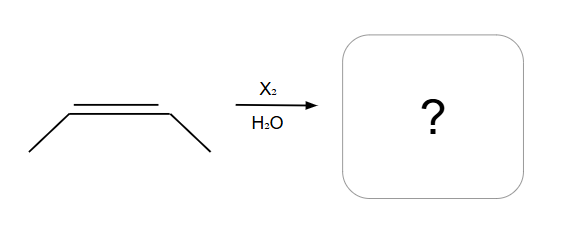
Creates an ring that is then opened by water
NO POSSIBLE CARBOCATION
Addition is Anti ONLY
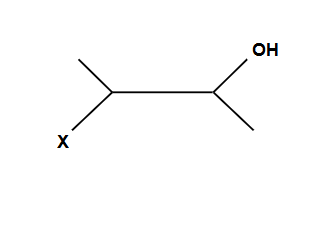
Creates an ring that is then opened by water
NO POSSIBLE CARBOCATION
Addition is Anti ONLY
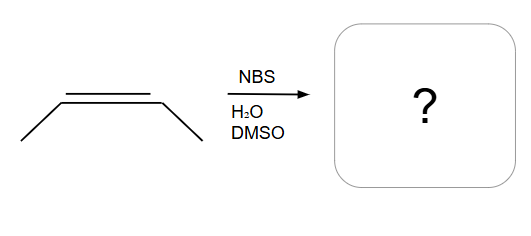
Another way of adding X2/H2O
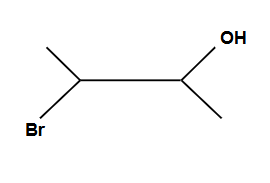
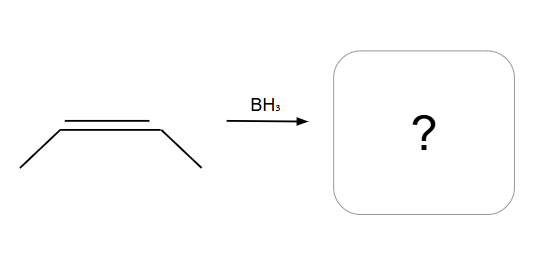
Addition is Syn ONLY
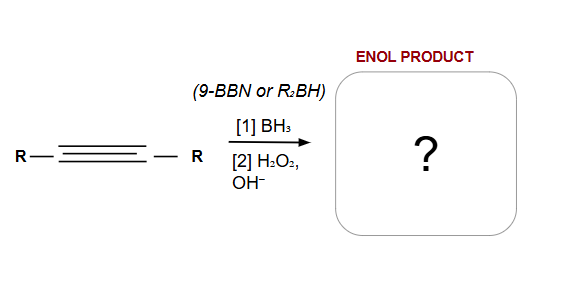
Anti-Markovnikov
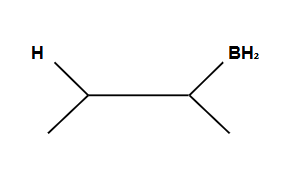

Addition is Syn ONLY
Anti-Markovnikov
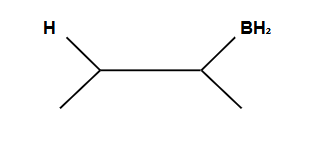
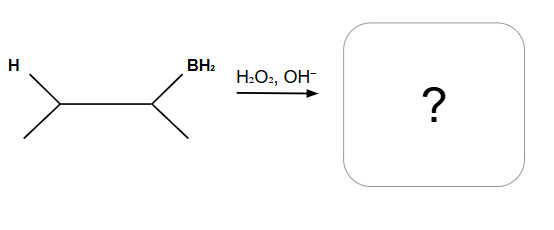
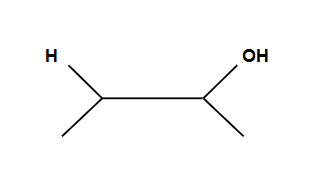
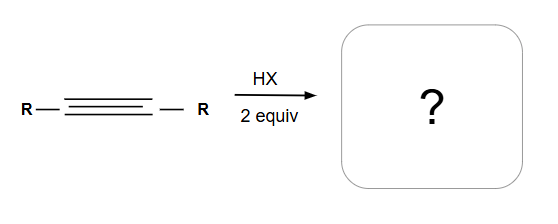
Markovnikov
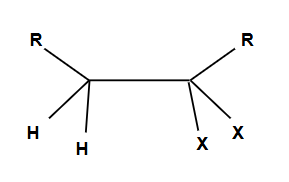

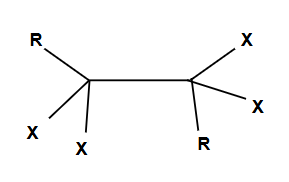
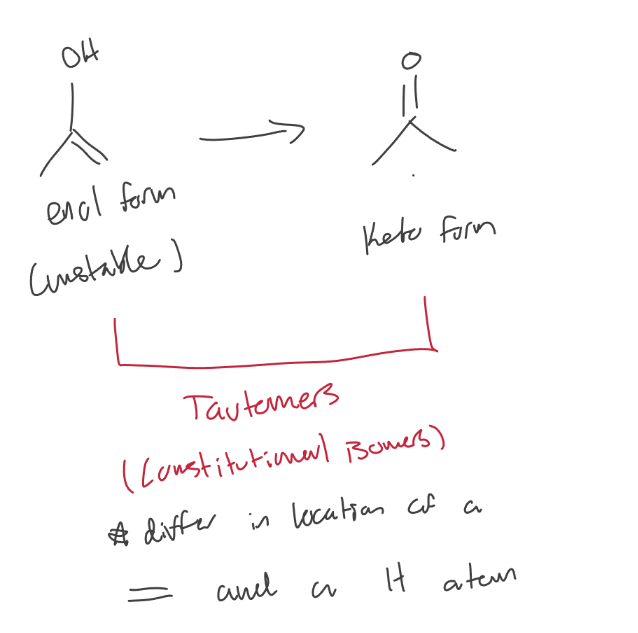
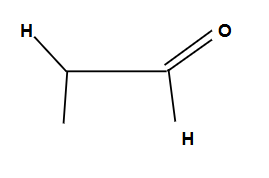
Tautomers
Enols shift to form ketones for more stability
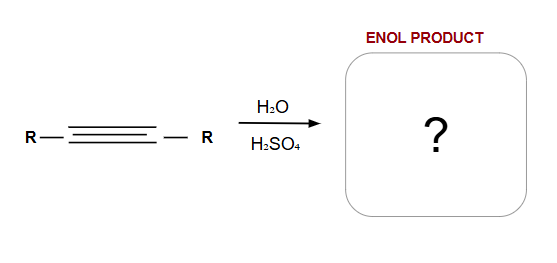
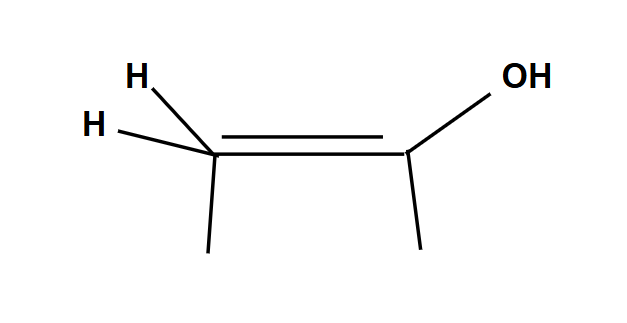
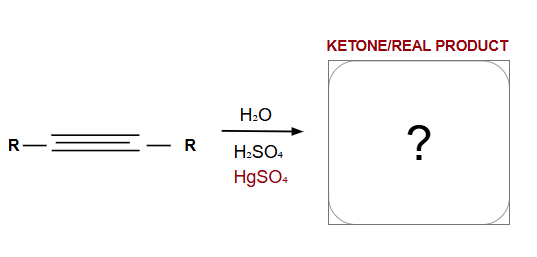
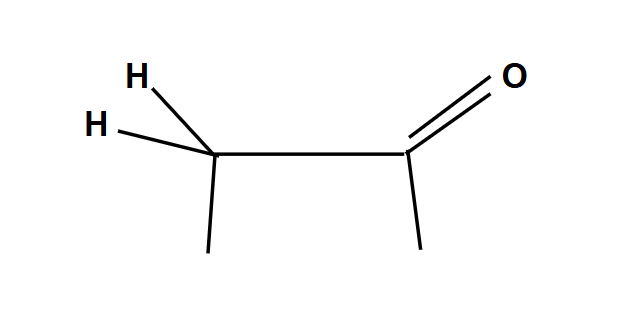
Anti-Markovnikov
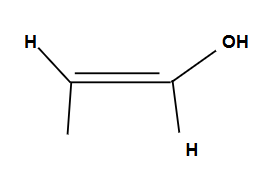
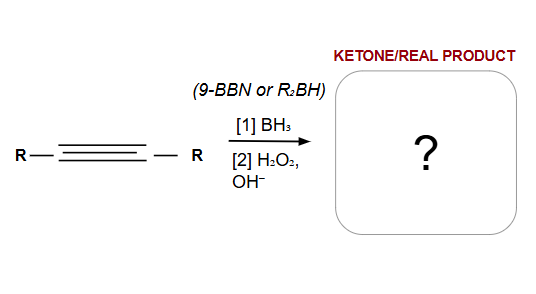
Anti-Markovnikov
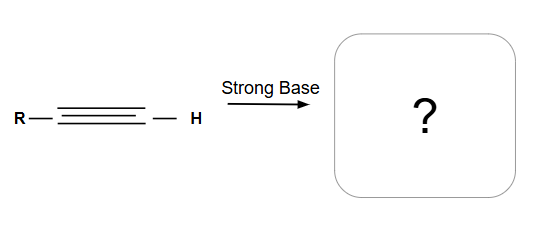
Acetylide anion
Reactions involving it:
Primary or methyl alkyl halide: SN2
Secondary or tertiary: E2
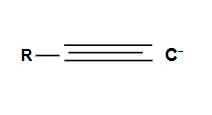
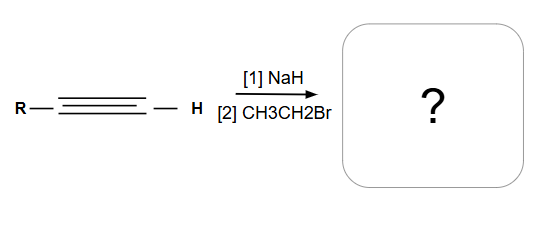
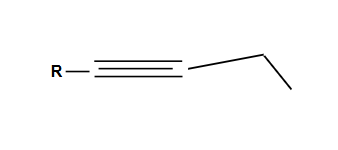
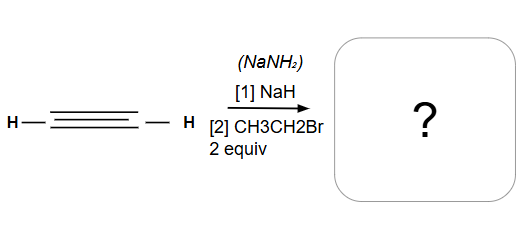
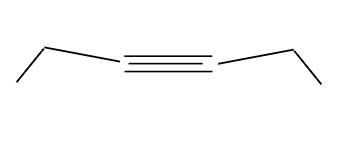
Formation of an internal alkyne