Sexual Dysfunction, Gender Dysphoria, and Paraphilic Disorders
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Objectives
oAssess patients with sexual dysfunction.
o
oPlan nursing care for patients with sexual dysfunction.
o
oDescribe therapeutic interventions for patients with sexual dysfunction.
WHat are the phases of sexual response cycle
◦Phase 1: Desire- Desire phase – interest in sexual activity, including age, physical and emotional health, availability of sexual partner, and the context of an individual’s life
◦Phase 2: Excitement- Excitement phase – period of time during which sexual tension continues to increase from the preceding level of sexual desire
◦Phase 3: Orgasm- Orgasm phase – attained only at high levels of sexual tension
◦Phase 4: Resolution- sexual tension developed in prior phases subsides to baseline levels and sexual stimulation has ceased
What are the types of sexual dysfunction
Involves the disturbance in the desire, excitement, or orgasm phases of the sexual response cycle or pain during sexual intercourse
Female sexual interest/arousal disorder
Male hypoactive sexual desire disorders
Erectile disorder
Female orgasmic disorder
Delayed ejaculation
Premature ejaculation
Genito-pelvic pain/penetration disorder
Asexuality – may not have a desire for sexual relations
What are the risk factors for sexual dysfunction
Biological
◦Aging
Cognitive
◦Misinformation or ignorance
◦Unconscious guilt and anxiety
◦Anxiety related to performance
◦Poor communication between partners
◦Unacknowledged or unidentified sexual orientation
Epidemiology- More common in women than men
Comorbidity
Psychiatric, depressive, and personality disorders
Obesity and sedentary lifestyle
Etiology
Biological factors
Psychological factors
What general assessment do we do
General Assessment
◦Setting—private and without distractions
◦Notetaking kept to a minimum
◦Interview free from personal biases and judgmental attitudes
◦Good eye contact, relaxed posture, and friendly facial expressions facilitate patient’s comfort and communicate openness and receptivity on the part of the nurse
Self-Assessment
Discomfort, embarrassment
What diagnosis are there for impaired sexual functioning
◦Major Depressive Disorder
◦Intimate Partner Abuse
◦Altered body function from medication
◦Process of Aging
Other Diagnoses:
Relationship problem
Situational or chronic low self-esteem
Negative self-image
Lack of knowledge of sexual functioning
Substance use
Urinary tract infection
Ineffective sexuality pattern
Lack of significant other
Conflicts with sexual orientation
Impaired relationship with significant other
Knowledge deficit about alternative responses to illness
What outcomes do we want
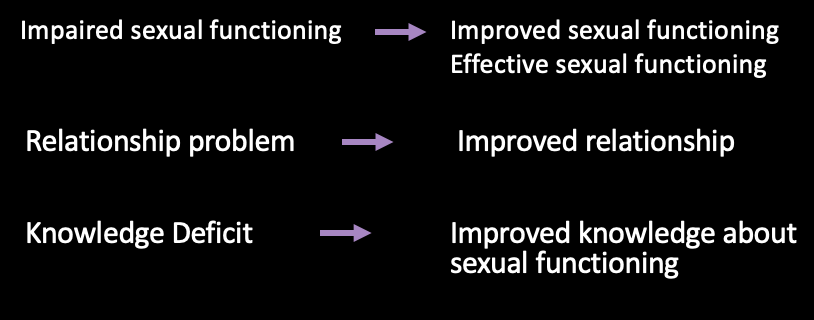
Refer to Table 20.4
What planning and implementation do we do
Planning
Implementation
◦Facilitate discussion about sexuality (Nonjudgmental)
◦Health Teaching and Health Promotion
Evaluation
What tx are there for sexual dysfunction?
Treatment Modalities
◦Pharmacotherapy
◦Psychological
◦Sensate focus
◦Behavioral therapy
◦Systematic desensitization
◦Masturbation training
What is gender dysphoria
Gender identity
◦Sense of “maleness” or “femaleness”
◦Not usually established until a child is 3 years old
Gender dysphoria
◦Feelings of unease about incongruent maleness or femaleness
Expressions of desire to be the opposite sex.
a sense of unease that a person may have because of a mismatch between their biological sex and their gender identity. This sense of unease or dissatisfaction may be so intense it can lead to depression and anxiety and have a harmful impact on daily life.
What are the RF for gender dysphoria
Epidemiology
◦Once considered a fairly rare condition, has increased
Comorbidity
◦May also have anxiety, disruptive and impulse-control problems, and depressive disorders
Risk Factors
◦Biological factors – hormones, genetics
◦Cognitive factors:
◦absence of same-sex role models
Internally melding
What are the treatments for gender dysphoria
Treatment Modalities:
Pharmacological interventions - Hormones
Surgical interventions - Sex reassignment surgery
Children: Optimize psychological adjustment and well-being; supportive family therapy
Adolescents and adults: Individual and family therapy; coping skills to deal with harassment; long-term psychotherapy; thorough psychological examination before sex reassignment
What are Paraphilic Disorders
Acts or sexual stimuli that are outside of what society considers normal, but are required for some individuals to experience desire, arousal, and orgasm
◦Intensity of sexual drive
◦Symptoms last at least 6 months
◦Small segment actually commit sexual offenses
Paraphilic disorder exists when recurrent, intense sexually arousing fantasies, sexual urges, or behaviors currently cause distress or impairment
to the individual or whose satisfaction has entailed personal harm, or risk of harm, to others generally involving: non-human objects,
the suffering or humiliation of oneself or one’s partner, children, or non-consenting persons.
Compelling urge to get physical with your partner that is an aberration from what is expected of a person, that is to say usual genital arousal for a phenotypically normal, physically of age and consenting human counterpart, is referred to as Paraphilia or sexual perversion. This condition lives up to the standards of a disabling problem when it hampers the overall health of a person, leads to psychological setback or victimization of another individual (read more for healthy sexual life).
Psychological impacts of going through such a condition
1. The perpetrator of the variation may or may not see this as a condition: The person suffering from this condition may or may not treat it as a problem. In both ways, it is harmful. Knowing it as a problem and not seeking treatment or assistance can be harmful for oneself and others. Not realizing that you are subject to a serious sexual condition might propel you to commit wrong to non- consensual partners while being confident about your ways.
2. Social ostracization kills them: Coming in the open with a sexual fantasy that is not acceptable to the society can leave you with varied reactions. People might be incited to attack you for being unusual or they might isolate you. The latter is a probable outcome. Rarely does society guide you towards betterment in such cases. Social ostracization can result in deep rooted hatred for the world at large.
3. Perpetual humiliation can push them more into Paraphilia: Humiliation for being different from the rest can make a person feel shame. Shame and constant regret cannot help an instance of sexual perversion. It can make a man or woman more obstinate. In such a situation a person would strongly cling to his or her condition feeling extremely dejected.
4. 'To be or not to be' haunts people suffering from Paraphilia: Many times a sufferer is not able to understand what is wrong in having objectionable sexual behavioral tendencies and fantasies. As long as your fantasies are limited to your own mental domain or are performed on a consensual partner, there are no complications. The minute an obnoxious sexual urge is performed leading to personal or public harm, a threatening hitch arises.
5. Problems in expressing oneself can make a person suicidal: To adhere to societal norms a person might keep his desires on a leash. This kind of compromising over a long span of time will make a person depressive and may also prompt him to commit suicide.
What is Exhibitionistic disorder
Exhibitionistic disorder is the illegal and intentional display of one’s genitals in a public place.
What is Fetishistic disorder
is an intense sexual attraction to either inanimate objects or to body parts not traditionally viewed as sexual, coupled with clinically significant distress or impairment.
What is Frotteuristic disorder
Frotteuristic disorder is a condition defined as recurrent and intense sexual arousal from touching or rubbing against a nonconsenting person, as manifested by fantasies, urges, or behaviors, or by rubbing against non-consenting people for sexual stimulation.
What is Sexual sadism disorder & Sexual masochism disorder
Sexual sadism is infliction of physical or psychologic suffering (eg, humiliation, terror) on another person to stimulate sexual excitement and orgasm.
Sexual masochism is intentional participation in an activity that involves being humiliated, beaten, bound, or otherwise abused to experience sexual excitement.
What is Transvestic disorder
Transvestic disorder is when sexual satisfaction is achieved by dressing in the clothing of the opposite gender.
What is Voyeuristic disorder
Voyeuristic disorder is characterized by seeking sexual arousal through viewing, usually secretly, other people in intimate situations.
What is Pedophilic disorder
WHat is Telephone scatologia disorder
What is Necrophilic disorder
What is Zoophilic disorder
What is Coprophilic disorder
Coprophilic disorder s the paraphilia involving sexual arousal and pleasure from feces.
What is Klismaphilic disorder
Klismaphilia is a sexual disorder under the group of paraphilias where sexual gratification is obtained by the use of enemas.
What is Urophilic disorder
What is Hypoxyphilia
hypoxyphilia disorder is sexual fantasy involving arousal obtained by reduction of oxygen flow to the brain. It is a paraphilia
usually involving one person alone (i.e., autoerotic asphyxia) but occasionally involving sexual partners. Is an erotic asphyxia that can result in death or loss of consciousness.
What are risk factors for sexual disorders
Epidemiology
◦Men more than women (mostly Caucasian)
Comorbidity
◦Personality disorders commonly co-occur with sexual offending behaviors
Risk Factors
◦Biological – head trauma, abnormal levels of androgens
◦Cognitive
◦Psychoanalytic theories
◦Learning theories
Cognitive theories
What assessment do you do for sexual disorders
General Assessment
◦Assess potential for self-harm or harm to others
◦Differentiate between victims and active agents
◦Focus of assessment on the presenting problem
◦Elicit patient’s perception of the impact of sexual disorder on current illness
Self-Assessment – comfort level, non-judgmental, hostility
What are the risks for these disorders
Nursing diagnosis
ØRisk for suicide
ØRisk for violence
ØImpaired impulse control
ØProblematic sexuality behavior
Outcomes identification
Risk for suicide —→ Decreased suicide risk
Planning
Focus on safety and crisis intervention
What implementation do you do for sexual disorders
Implementation
◦Health teaching and health promotion
◦Teamwork and safety
Evaluation
What meds do you give for sexual disorders
Treatment Modalities
◦Pharmacological interventions
◦Antiandrogens
◦Antidepressants
◦Psychotherapy – cognitive behavioral therapy