MCAT Milesdown Biology
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Nuceloid Region
DNA region in prokaryotes
Bacteria DO NOT have nucleus!!
Nucleolus
Makes ribosomes, sits in the nucleus, no membrane
recall ribosomes are important for synthesizing 1º proteins from amino acids
both eukaryotes and prokaryotes have ribosomes —> necessary for cell function
Peroxisomes
Collect and break down material
waste products & toxins
Rough ER
Accepts mRNA to make proteins
rough bc studded w/ ribosomes
Smooth ER
Detox & makes lipids
Golgi apparatus
Modify/distribute proteins (only in eukaryotes)
packaging system of the cell
COPI & COPII
vesicles are used to transport materials and proteins to different parts of the cell, to know where they are going they need specialized coats
Coat protein complexes: I & II go in different directions
Both COPII & COPI operate on the cis face of the Golgi (the side facing the ER)
COPII:
ER —> Gogli (Anterograde)
delivers newly made proteins for processing and packaging
COPI:
Golgi —> ER (Retrograde)
returns mistakenly sent proteins or recycle machinery
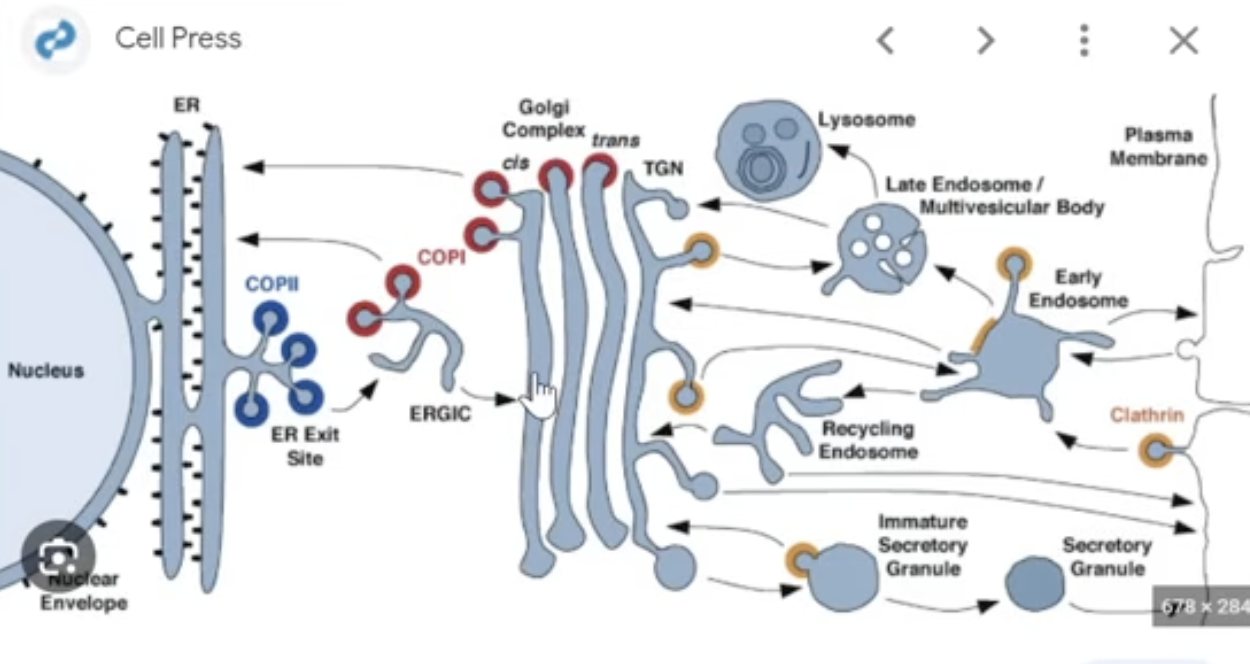
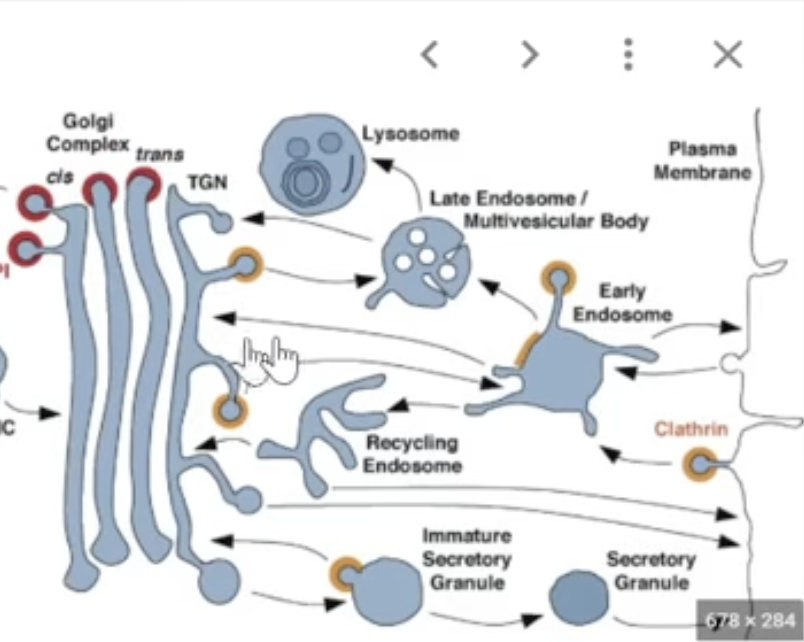
Cathrin
another coat protein — but handles endocytosis and trafficking from the Golgi to lysosomes or the membrane
moves between the gogli and the plasma membrane
destination: Lysosome (via endosomes) or inside cell
key function: handles endocytosis and Golgi sorting
Centrioles
9 groups of microtubules, pull chromosomes apart
two centrioles are stacked at a right angle to form a centrosome —> on polar ends of the cell and pull chromosomes apart during anaphase
Lysosomes
demo & recycling center
made by golgi
single membrane
plasmids
In prokaryotes, carry DNA not necessary for survival
can be used by biochemists to insert genes of interest
Obligate Aerobe
Requires O2
Obligate Anaerobe
Dies in O2
Facultative Anaerobe
toggles between aerobic and anaerobic
Aerotolerant Anaerobe
Does not use O2 but tolerates it
Gram +
purple, thick peptidoglycan/lipoteichoic acid cell wall
Gram -
pink-red, thin peptidoglycan cell wall & outer membrane
Eukaryotes
ETC in mitochondria
large ribosomes
reproduce via mitosis
Prokaryotes
ETC in cell membrane
small ribosomes
reproduction via binary fission
Plasmids carry DNA material, many have virulence factors
Episomes
plasmids that integrate into the genome
Prions
infectious proteins
trigger misfolding
alpha helical —> beta pleated sheets
lowers solubility
causes mad cow disease
Viroid
plant pathogen
Microfilaments
Actin Filaments (smallest)
Dynamic & flexible
Role in:
Cell shape and movement
Muscle contraction (with myosin)
Cytokinesis (cleavage furrow)
Endocytosis & pseudopodia
MCAT Buzzwords: Actin, myosin, lamellipodia, amoeboid movement
Microtubules
Hollow tubes of tubulin dimers
largest
Form:
Mitotic spindle (metaphase, anaphase)
Cilia/flagella (9+2 structure)
Intracellular highways for transport via kinesin and dynein
Centrioles/centrosomes
MCAT Buzzwords: Kinesin, dynein, colchicine, mitotic spindle, axoneme, 9+2
Intermediate Filaments
Sturdy, rope-like, most stable of the three
Structural reinforcement of the cell
Different cell types have different IFs:
Keratin (epithelial cells)
Lamin (nuclear envelope)
Desmin (muscle)
MCAT Buzzwords: Keratin, vimentin, lamin, desmosomes, nuclear lamina
Epithelia
thin tissue forming the outer layer of a body’s surface and lining the alimentary canal and other hollow structures
Parenchyma
functional parts of the organ
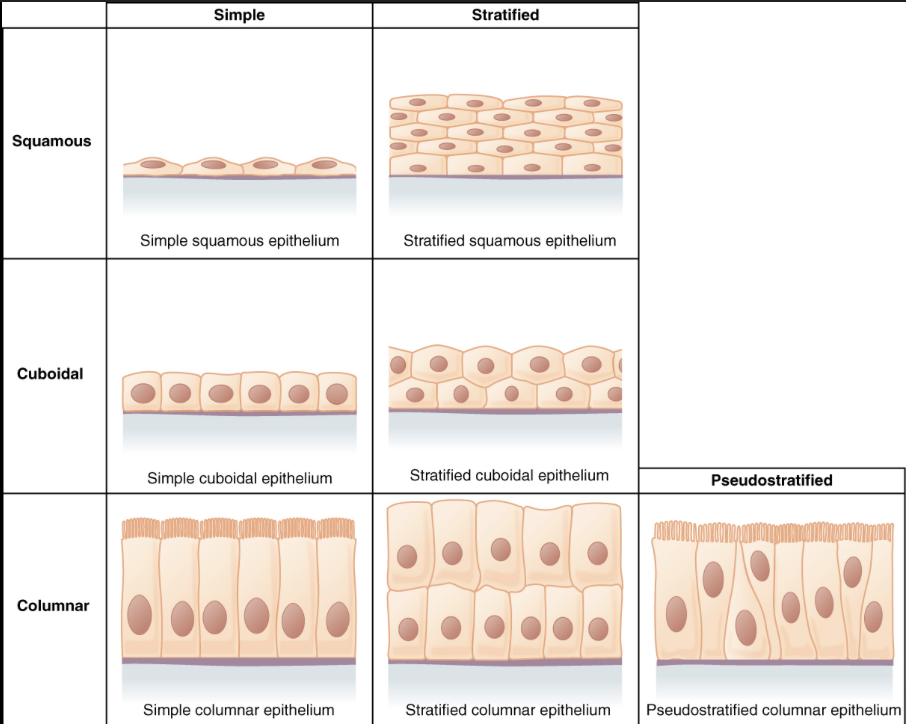
different types of epithelium
Simple —> one layer
Stratified —> multiple layers
Pseudostratified —> one layer but looks like multiple
Cuboidal —> cube shaped
Columnar —> long and narrow
Squamous —> flat, scale like
Connective Tissue
Stroma (support, ECM)
bone, cartilage, tendon, blood
Genetic Recombination
how bacteria get new DNA
Transformation
gets genetic info from environment
Conjugation
transfer of genetic info via conjugation bridge (bacteria “sex”)
F+ —> F- or Hfr —> recipient
antibiotic properties can be transferred via this way
Transduction
transfer using bacteriophage
Transposons
genetic info that can insert/remove itself
jumping genes that can move around
Capsid
protein coat around a virus
envelope
some viruses have lipid envelope
Virion
individual virus particle
Bacteriophage
bacteria virus; tall sheath injects DNA/RNA
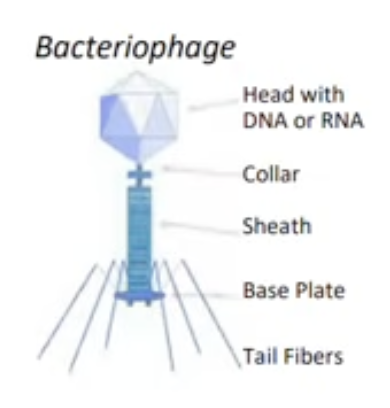
Viral Genome
may be DNA or RNA
may be single or double stranded
if single stranded…
positive sense: RNA can be translated into host cell
negative sense: RNA replicase must synthesize a complimentary strand, which can then be translated
Retrovirus
single stranded RNA
reverse transcriptase needed to make DNA before becoming transcribed to RNA again and making proteins
Lytic Cycle
Virions made until cell lyses
Lysogenic Cycle
virus integrates genome as provirus or prophage
goes dormant until stress activates it —> goes to lytic cycle
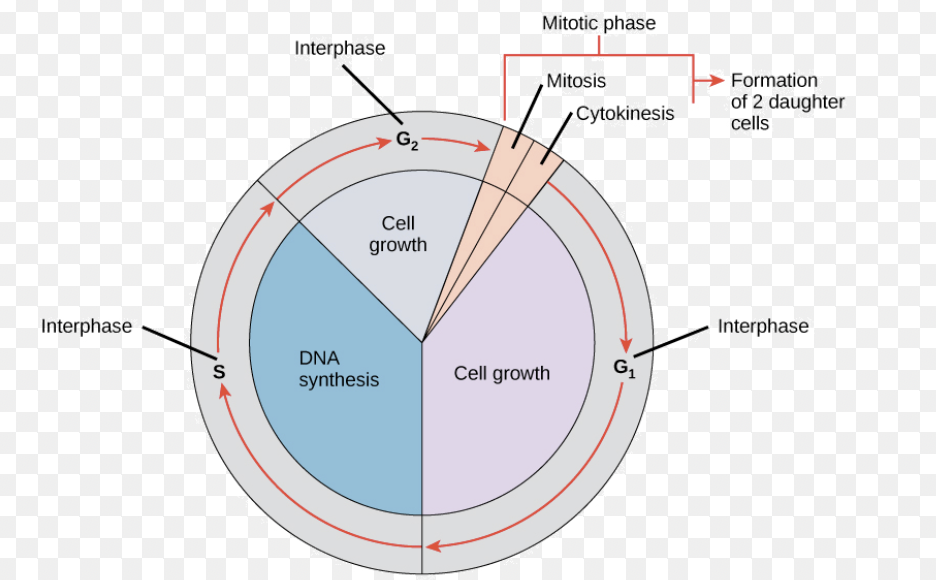
Cell Cycle: G1
Make mRNA and proteins to prep for mitosis
Cell Cycle: G0
A cell will enter G0 if it does NOT need to divide
enters after G1 if mitosis is not necessary
G1 checkpoint
Cell decides if it should divide; P53 is in charge
Cell Cycle: S
DNA is replicated
Cell Cycle: G2
Cell growth, makes organelles
G2 checkpoint
Check cell size & organelles
Cell Cycle: M
mitosis & cytokinesis
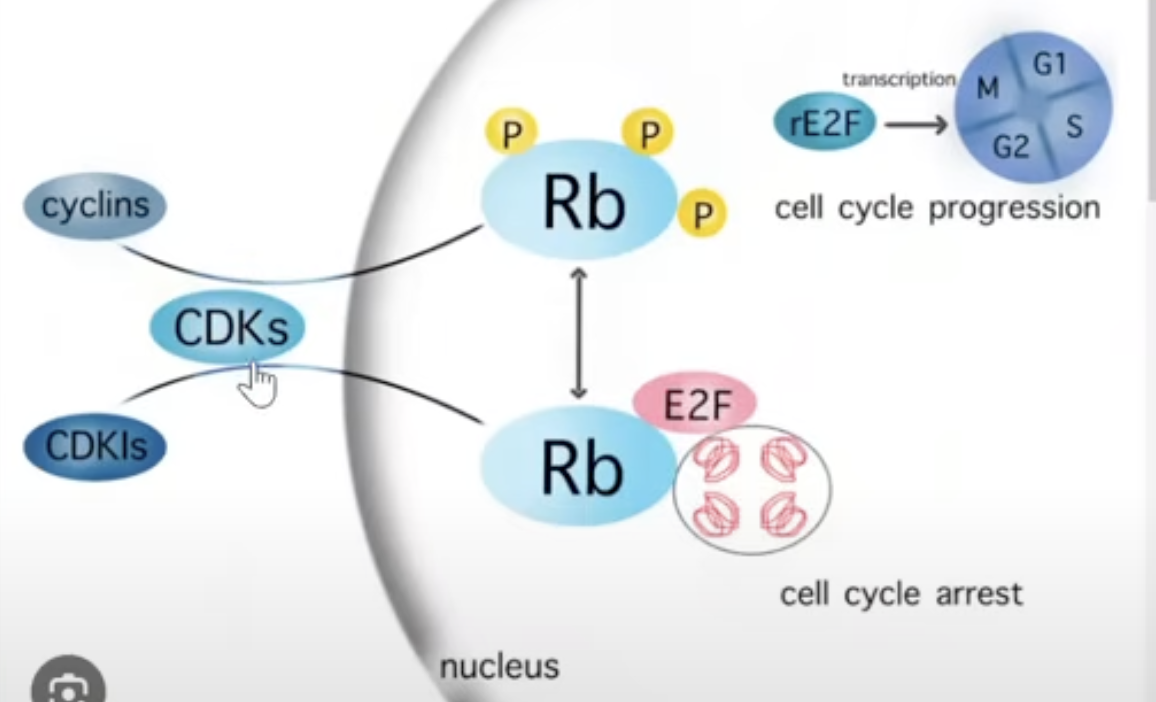
Positive Growth Signals
CDK + Cyclin create a complex
complex phosphorylates Rb to Rb+P
Rb changes shape, releases E2F
E2F releasing causes cell division to continue
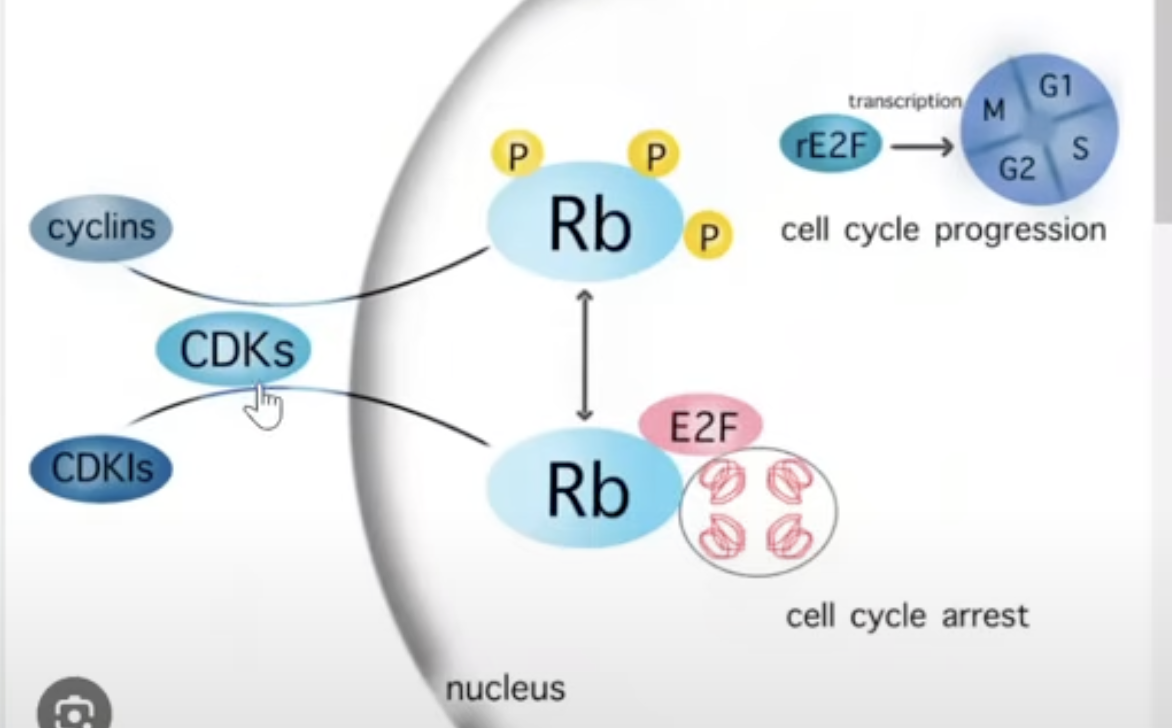
Negative Growth Signals
CDK inhibitors block phosphorylation of Rb
So, E2F stays attached
Cell cycle halts
Sex Chromosomes
Sex determined by 23rd pair of chromosomes
XX = female
XY = male
X-linked disorders
males express, females can be carriers
Y chromosome
little genetic information
SRY gene = “sorry you’re a male”
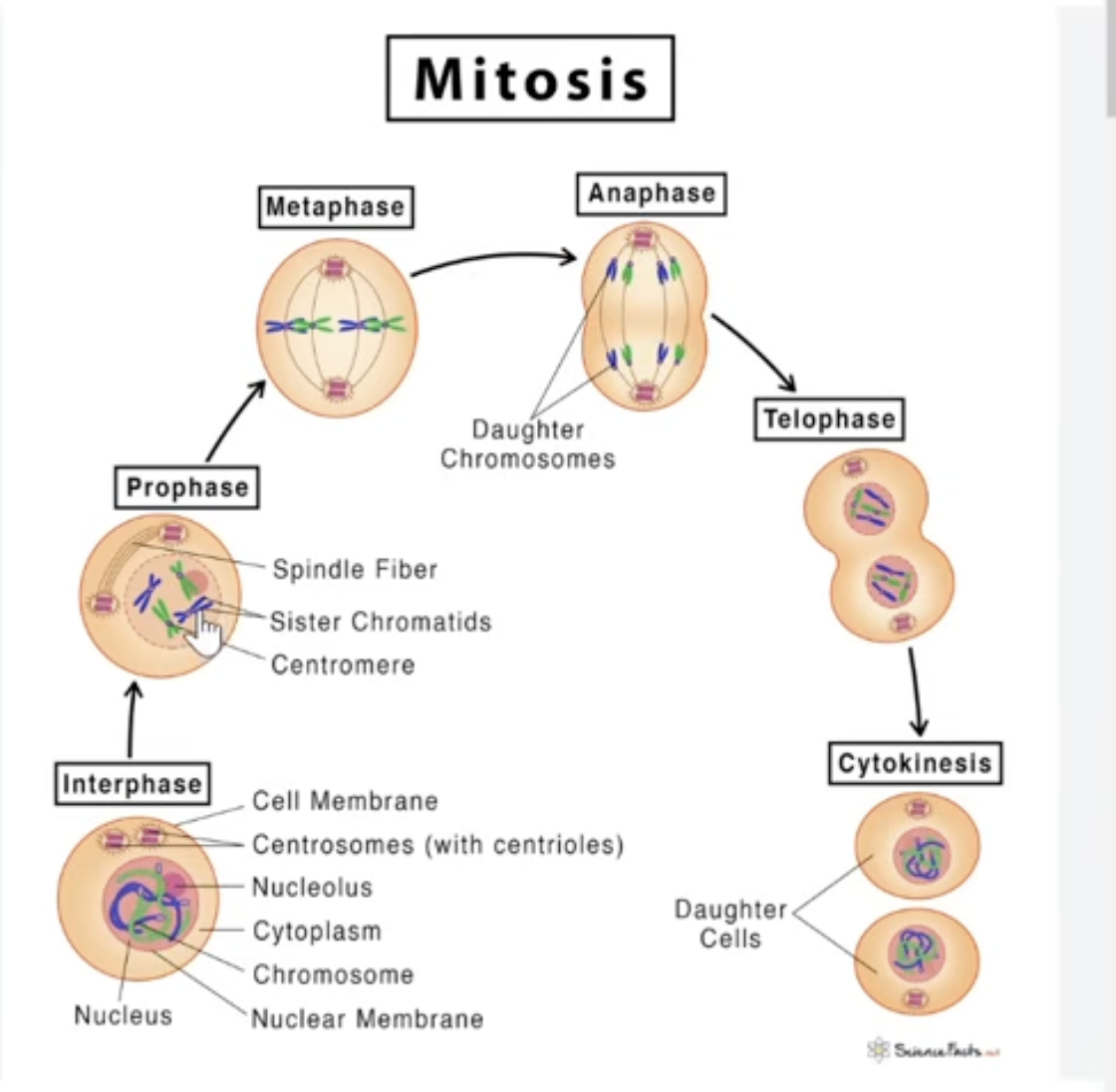
Mitosis
PMAT
ploidy of 2n throughout
Prophase: DNA condenses, centrioles migrate to opposite poles & microtubules form, nuclear envelope disappears
Metaphase: “meet in the middle”, chromosomes meet in the middle
Anaphase: “apart”, sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles
Telophase: chromosomes decondense, nuclear membrane forms, cytokinesis occurs (cytoplasm splits)
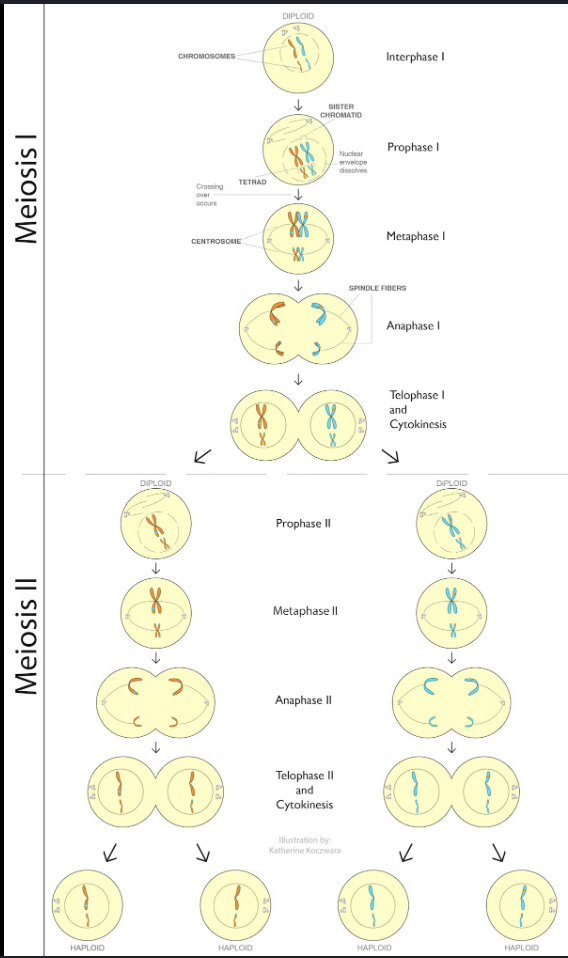
Meiosis
PMAT 2x
Prophase I: chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane dissolves, homologous chromosomes form bivalents, crossing over occurs
Metaphase I: spindle fibers from opposing centrosomes connect to bivalents (at centromeres) and align them along the middle of the cell
Anaphase I: homologous pairs move to opposite poles of the cell, this is disjunction and it accounts for the Law of Segregation
Telophase I: chromosomes decondense, nuclear membrane MAY reform, cell divides (cytokinesis), forms two haploid daughter cells of unequal sizes
Prophase II: chromosomes condense, nuclear membrane dissolves, centrosomes move to opposite poles (perpendicular to before)
Metaphase II: spindle fibers from opposing centromeres attach to chromosomes (at centromere) and align them along the cell equator
Anaphase II: spindle fibers contract and separate the sister chromatids, chromatids (now called chromosomes) move to opposite poles
Telophase II: chromosomes decondense, nuclear membrane forms, cells divide (cytokinesis) to form four haploid daughter cells
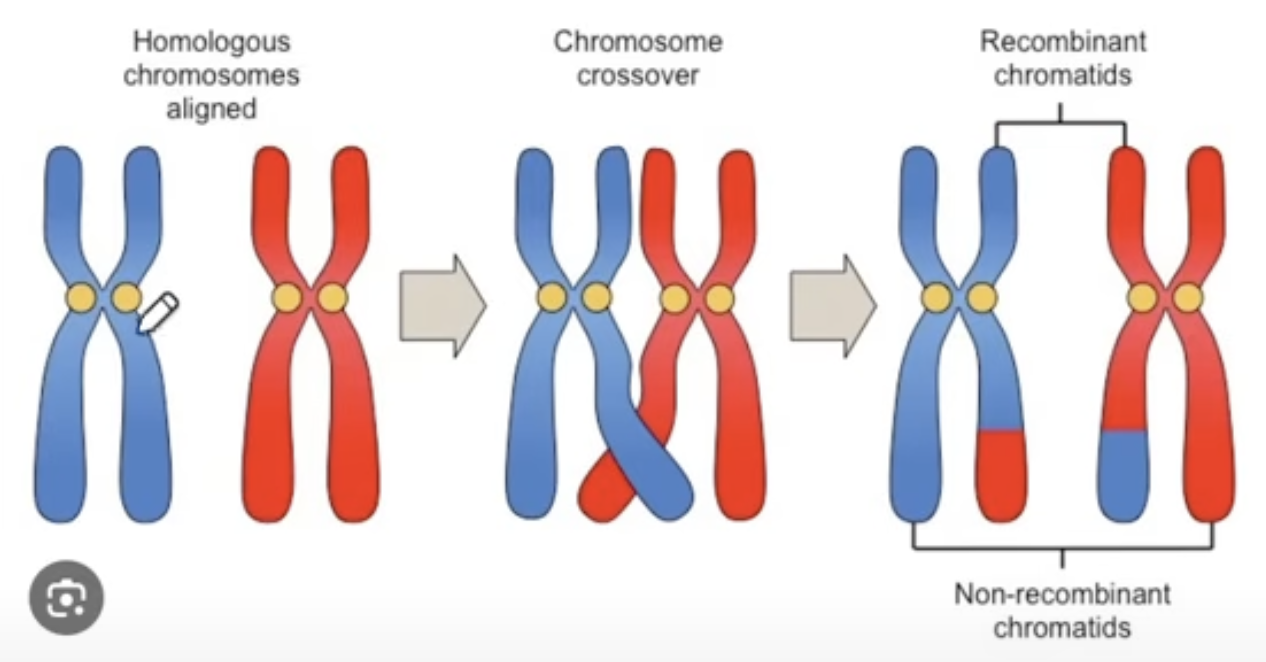
crossing over
exchange of genetic material to form new chromosomes that are genetically unique
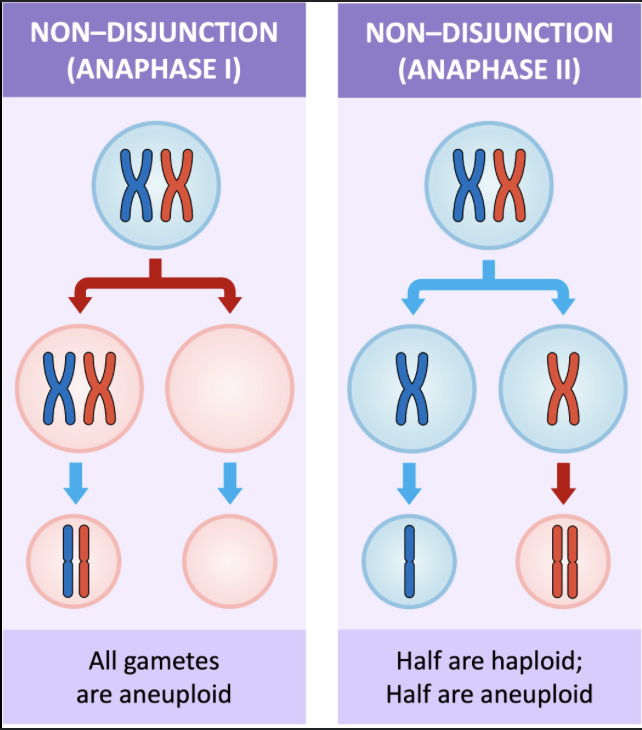
Nondisjunction
when sister chromatids/homologous pairs don’t separate properly during anaphase, results in aneuploidy
Law of Segregation
simply disjunction —> normal separation of chromosomes