Lab Exam 2- Lab F- Banana Oil (Fischer Esterification)
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
what is a Fischer esterification?
an acid-catalyzed equilibrium reaction between carboxylic acid and an alcohol in tithe presence of a strong acid catalyst (H2SO4) to produce ester and water as a by product
explain how the Fischer esterification is reversible
the ester can react with the acid and water to go back to the starting materials
how do we prevent the reaction from reversing?
it is necessary to push the equilibrium by either removing water as it forms or by using excess of one of the reagents
why do we reflux the reaction?
to increase the rate of the reaction
what is the reaction temperature during a reflux?
the boiling point of the solvent
how can you adjust the temperature fo the reaction without needing to worry about equilibrating an external bath?
by choosing the proper solvent
in the lab how were we able to drive the equilibrium reaction to the product side and attain a good yield of ester?
using an excess of glacial acetic acid and refluxing for 50 minutes
what is done in order to remove all of the excess acetic acid?
extraction by washing the organic layer with sodium bicarbonate to convert acetic acid into sodium acetate salt, moving all of the acetic acid into the aqueous layer where sodium acetate has greater solubility
what makes acetic acid easy to remove?
the fact that it is a carboxylic acid and can be easily deprotonated
what is left in the organic layer after the removal of the acetic acid?
isopentyl alcohol, isopentyl acetate, and a trace amount of water
what is extracted after removing the acetic acid and how?
washing the organic layer with saturated brine solution is used to draw water out of the organic layer
what is done after both extractions?
the organic layer is dried even more with a drying agent (anhydrous CaCl2) and the salt is then separated from the organic solution by gravity filtration
what is left in the organic solution after all of the extractions and the drying? how are they separated?
isopentyl alcohol and isopentyl acetate; by a simple distillation
pH of the aqueous layer after the separatory funnel was washed with sodium bicarbonate should be?
neutral; ph = 7
during the simple distillation what material is collected into a vial?
the material that boils between 125-138ºC
what does it mean for the Fischer esterification to be an acid catalyzed reaction?
the acid is regenerated and is never consumed
why is glacial acetic acid named "glacial"?
because at freezing point it forms crystals
what is glacial acetic acid's boiling point?
117-118º C which is very high
what is the purpose of a reflux?
to heat a reaction mixture at its boiling temperature (the boiling point of the solvent used in the reaction) to form the product, without losing any material inside the reaction flask
what are the advantages of a reflux?
maintains a constant temperature in the reaction flask and the reaction is able to reach equilibrium with minimal evaporation
what are purification techniques for solids?
recrystallization, TLC, extraction
what is a purification technique for liquids?
simple distillation
what is the purpose of a simple distillation?
- to separate liquids boiling below 50ºC at 1 atm from: non-volatile impurities or another liquid that boils at least 25ºC higher than the first
what happens during a simple distillation?
a liquid is vaporized by boiling, then condensed back to a liquid (distillate), and collected in a receiving flask
if a volatile compound is being distilled, what can you do to the receiver to minimize loss of vaporization?
the receiver can be chilled
why don't you want to distill too dryness?
leaving a small amount of residue will prevent overheating and breaking the flask, and also prevent formation of pyrolytic tars that are difficult to wash out
vacuum distillation is used for
compounds that either boil at too high temperature, or that decompose near their boiling points; under vacuum compounds can be distilled at temperatures lower than their atmospheric boiling points because the pressure is different
fractional distillation is used to
separate liquid mixtures that are soluble in each other, and that boil at less than 25 ºC from each other at 1 atm
how does a fractional distillation work?
a fractioning column is inserted between the distillation flask and the distilling head, providing a larger surface area over which a number of separate liquid-vapor equilibria can occur ; many vaporizations and condensations take place before the distillate is collected
what is the name for a fractioning column?
vigreux columns
what is the efficiency of a fractioning column expressed by?
by a number of theoretical plates
what is one theoretical plate equivalent to?
one simple distillation cycle
what is the efficiency reported as?
HETP : Height of a column that is equivalent to one theoretical plate
the lower the HETP
the more efficient the column
the larger the molecular weight
the higher the boiling point
the greater the intermolecular interactions
the higher the boiling point; (h-bonding, polarizing)
vapor pressure =
atmospheric pressure
the Clausius Clapeyron equation
measures vapor pressures at different temperatures
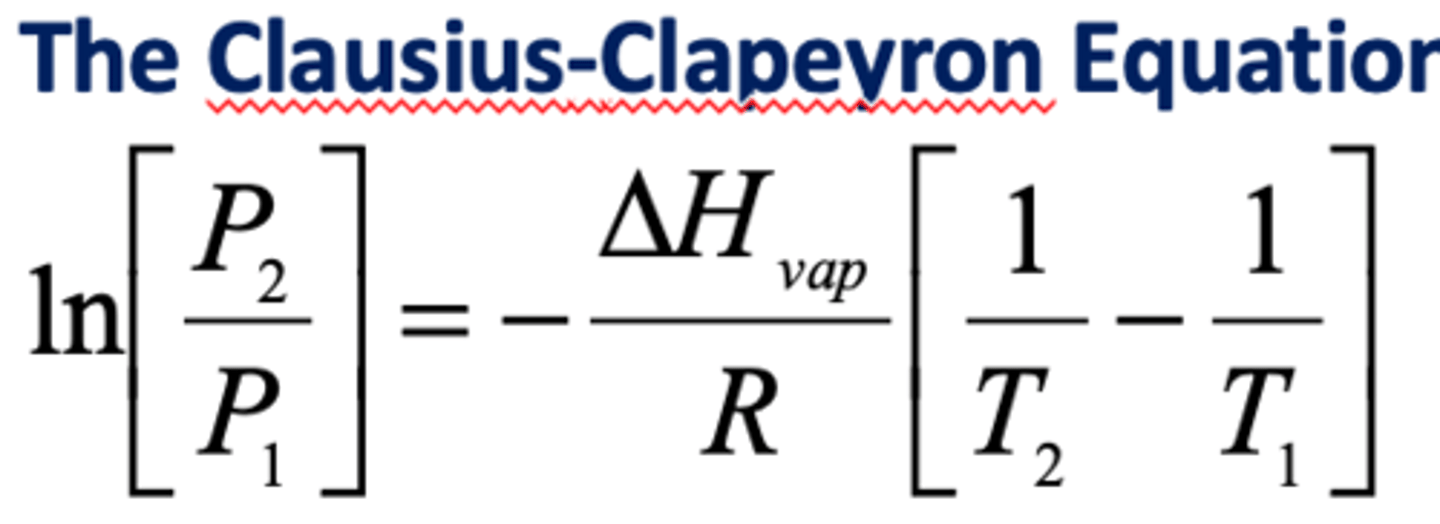
normal boiling point
defined as the temperature at which a liquid's vapor pressure equals 1 atm
vapor pressure of water at 25ºC
24 mmHg
vapor pressure of water at 50ºC
92 mmHg
vapor pressure of water at 100ºC
1 atm or 760 mmHg
why should you make sure joints are tight?
loose joints will cause product to escape
where should a thermometer be posited?

what is a variac?
a variable voltage transformer; it provides a voltage-adjusted source of alternating current; the heating mantle is connected to it
where do you plug heating mantles?
into the varian outlets under the hood
varian settings are set based on
boiling point; the higher the boiling point, the greater the voltage required
how do you avoid bumps?
using boiling stones; filling distillation flask to only 1/2 - 1/3 full
how do you pour liquids into the distillation flask? why?
using a funnel, to prevent the liquid from contaminating the ground glass joints
how does water from the condenser flow?
from bottom to top; it flows up
why do you wash first with water?
to drain the sulfuric acid
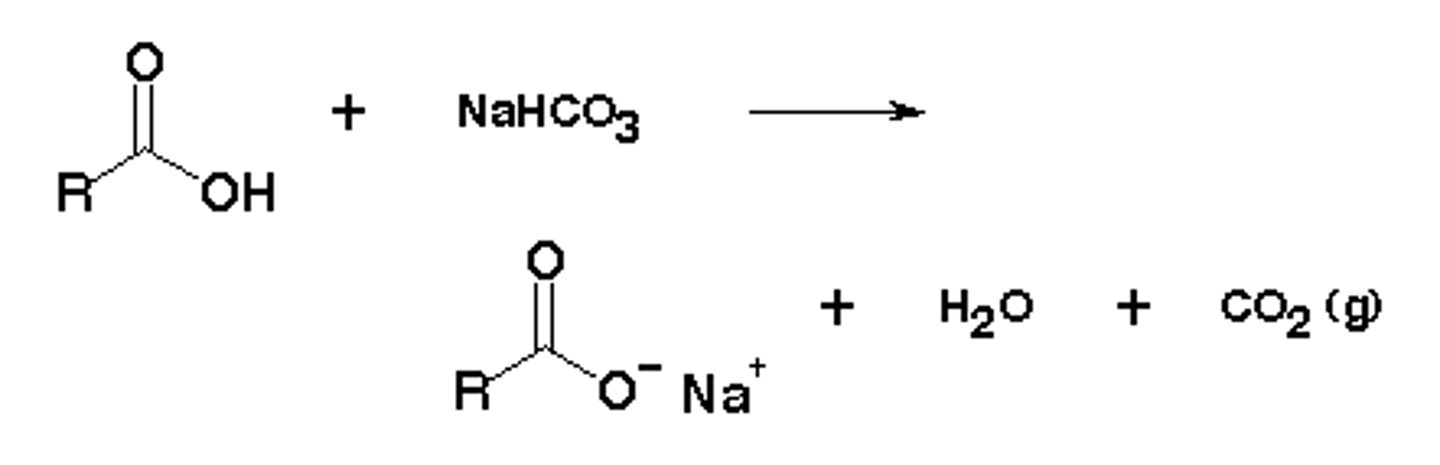
why do you wash with sodium bicarbonate?
to deprotonate glacial acetic acid
what is the equation of acetic acid with NaHCO3?
why do we use brine?
to draw water out of the organic layer as a first step in the drying process
what is brine ?
a saturated salt solution
why do we do a simple distillation?
because since we only have a small amount of isopentyl alcohol to remove anyways from the product, since we started with excess acetic acid, this task can be accomplished by simple distillation; the material that distills will be mostly isopentyl acetate which may be contaminated with a small amount of isopentyl alcohol, but because there is only very little of this contaminant, the amount of isopentyl acetate lost in this case is most likely less than what would be lost with a fractional distillation
why don't we do a fractional distillation?
because the difference between the boiling points of the liquids we are trying to separate is too small and in doing a fractional distillation we would lose a large amount of material to column holdup and the vapor pressure in a fractional distillation with a sufficient number of theoretical plates to obtain pure separation
what is the order of washing the extraction?
water, sodium bicarbonate, brine, then anhydrous CaCl2
anhydrous CaCl2 pellets and gravity filter paper are disposed of into
the biohazard box
low boiling distillate is disposed of into
C, H, and O non-halogenated waste container
where do boiling stones go?
the biohazard box