The Axial Skeleton: Structure and Function
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
162 Terms
Axial Skeleton
Divided into three parts: The Skull, The Vertebral Column, and Thoracic cage.
Skull
Composed of two sets of bones: cranium (8 bones) and facial bones (14 bones).
Cranium
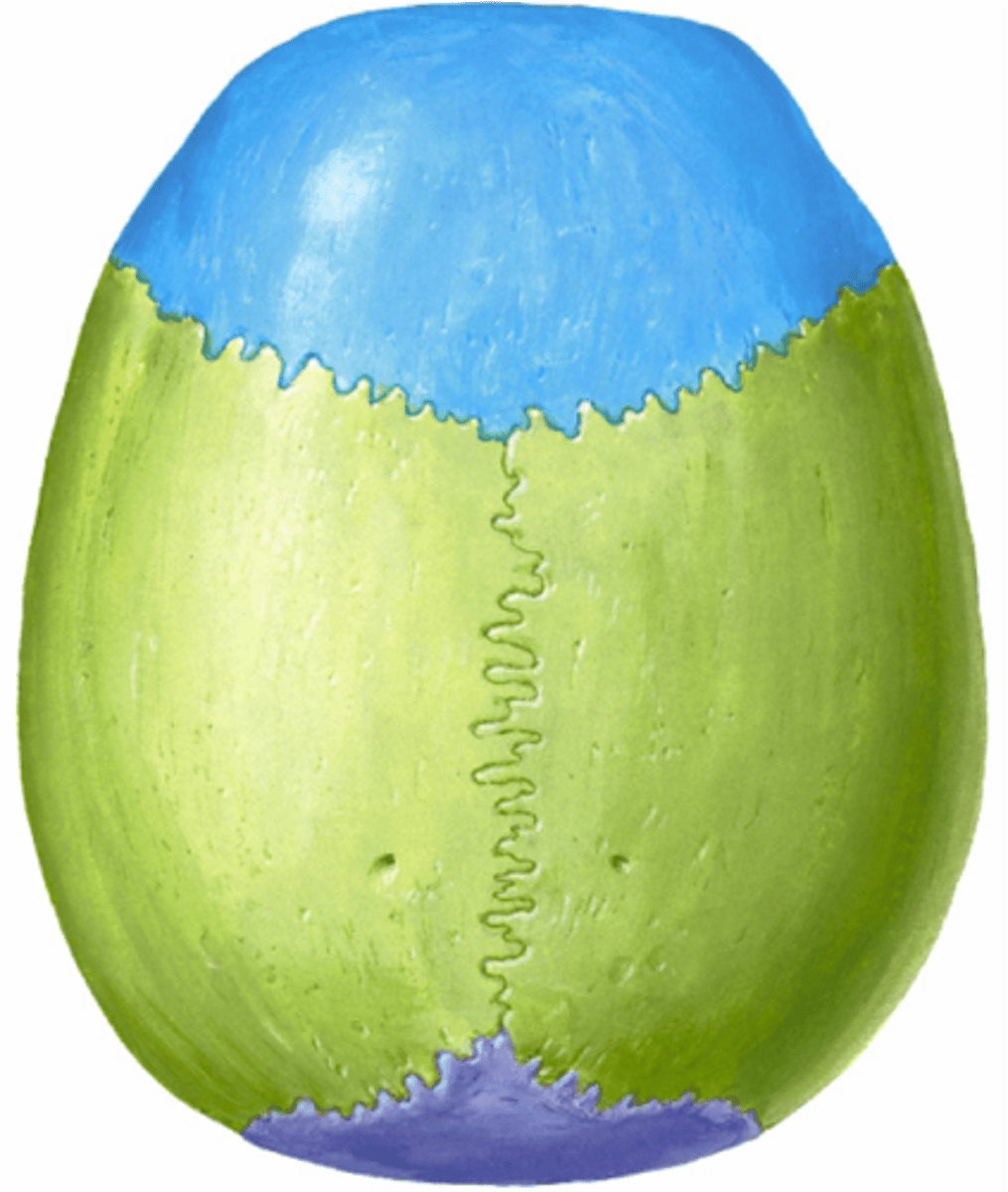
Divided into two major areas: cranial vault (calvaria) and cranial base.
Cranial Vault
Forms the superior, lateral, and posterior walls of the skull.

Cranial Base
Forms the bottom portion of the skull.
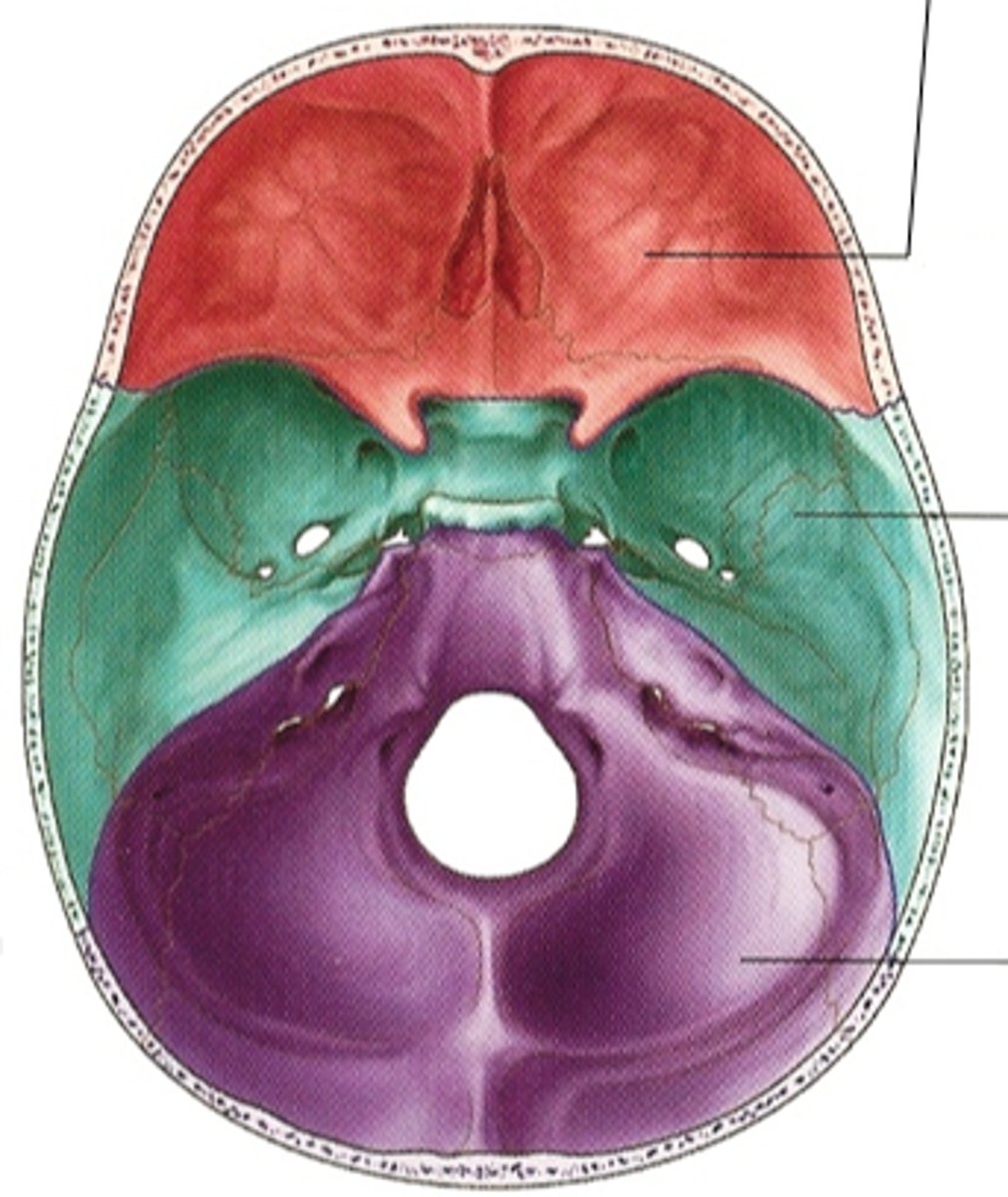
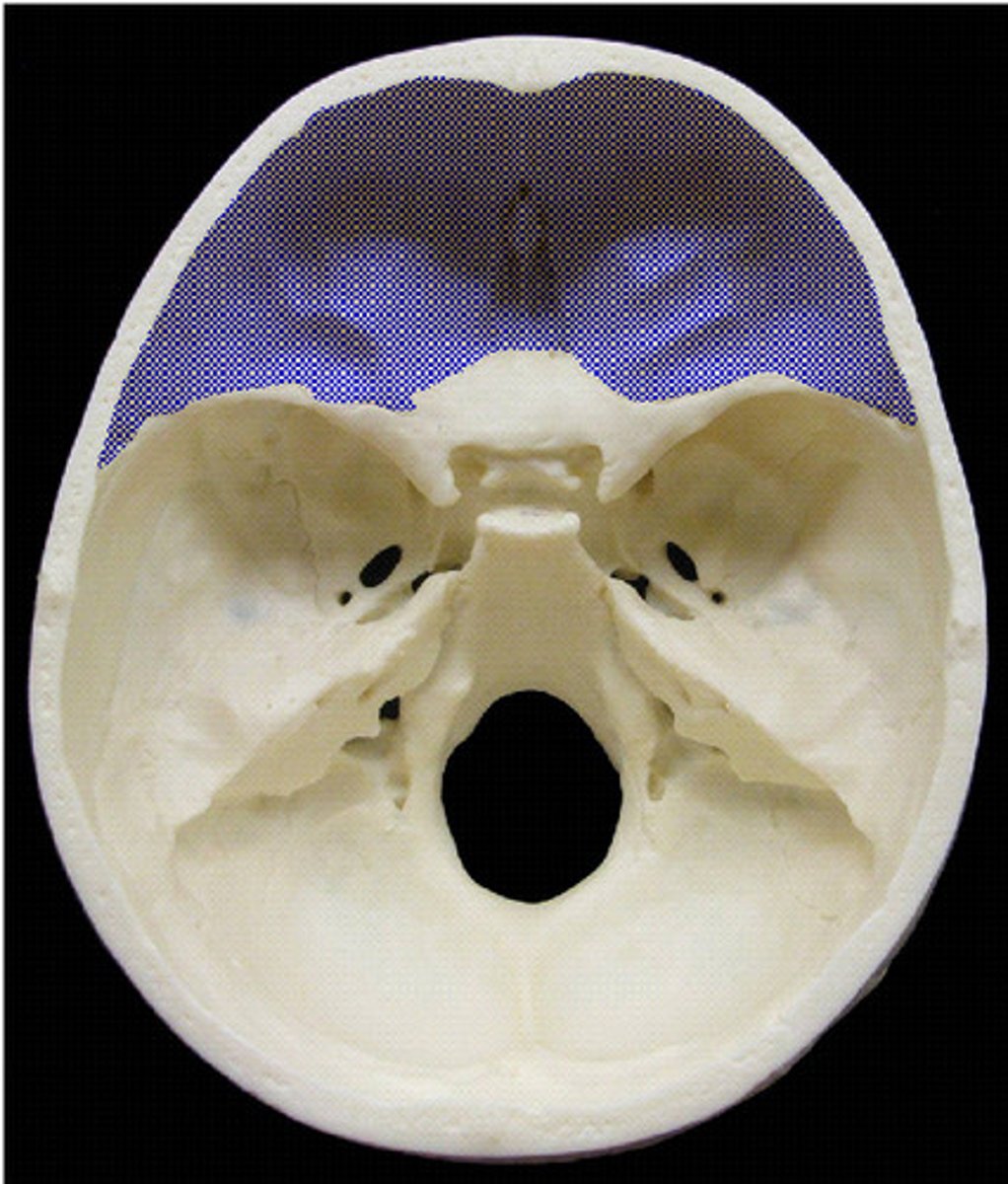
Cranial Fossae
Three distinct repressions in the cranial base: anterior, middle, and posterior.
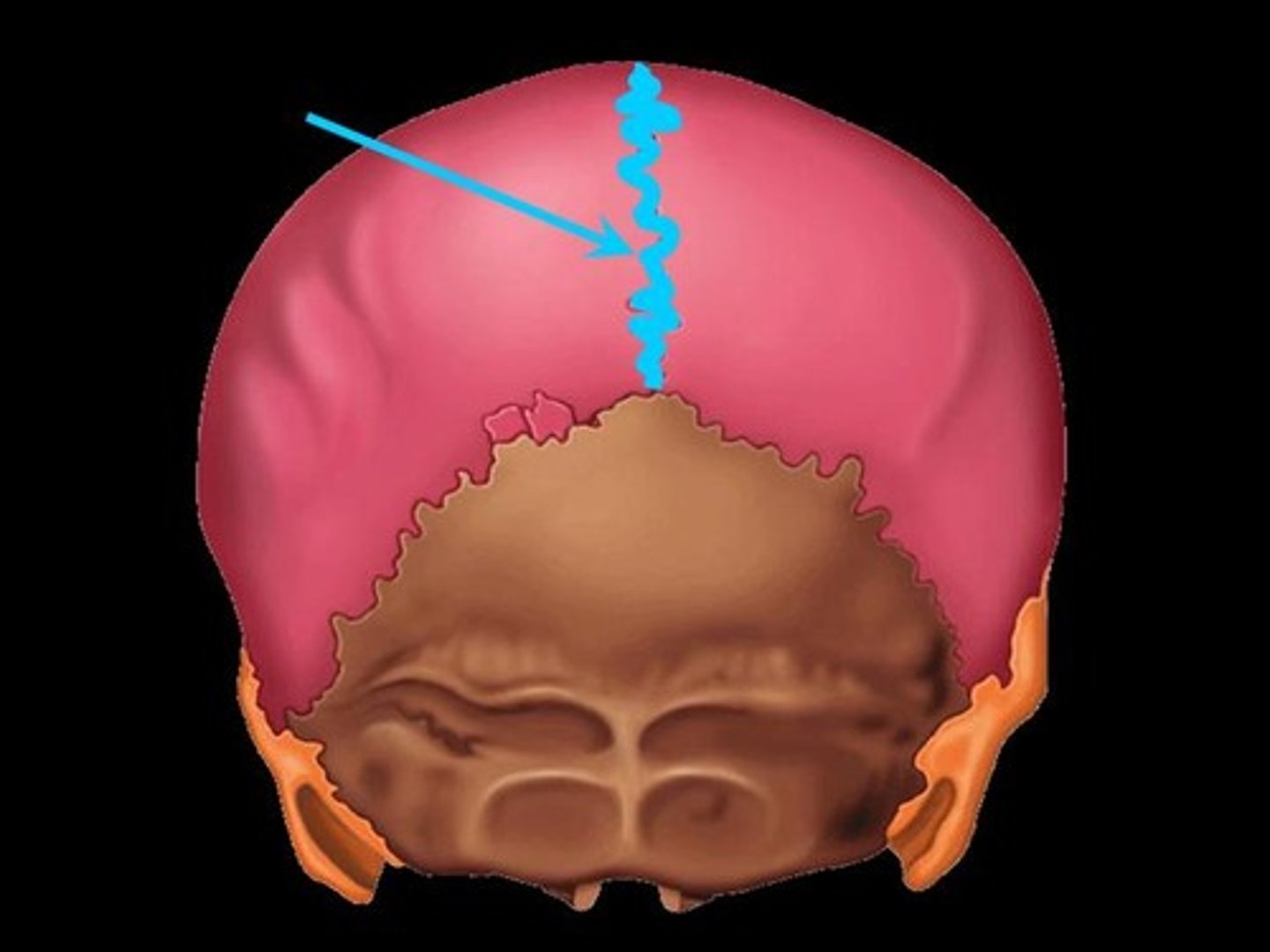
Sagittal Suture
Occurs where the left and right parietal bones meet superiorly in the midline of the cranium.
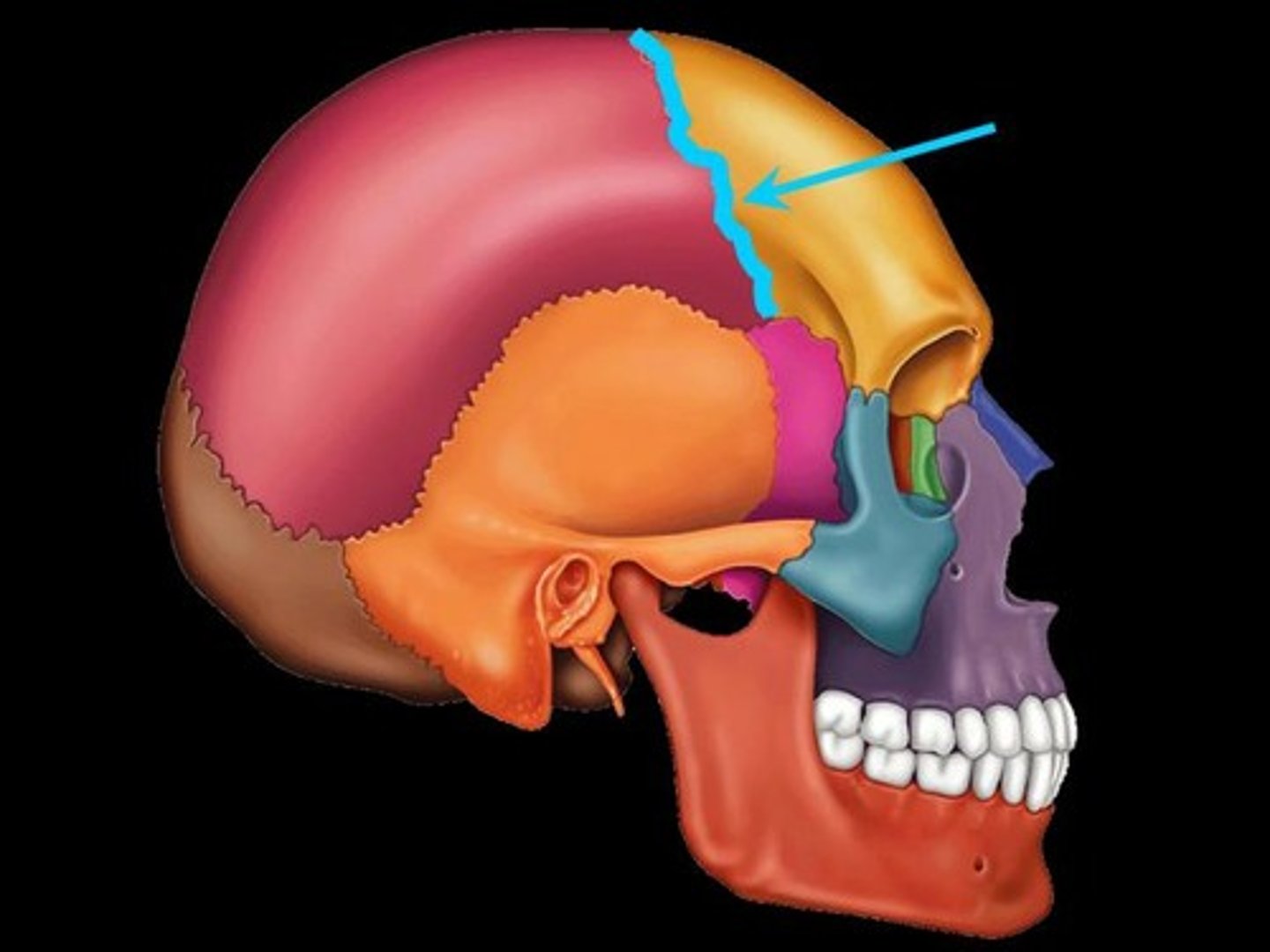
Coronal Suture
Running in the frontal plane where the parietal bones meet the frontal bone anteriorly.
Squamous Suture
Occurs where a parietal bone and temporal bone meet on the lateral aspect of the skull.
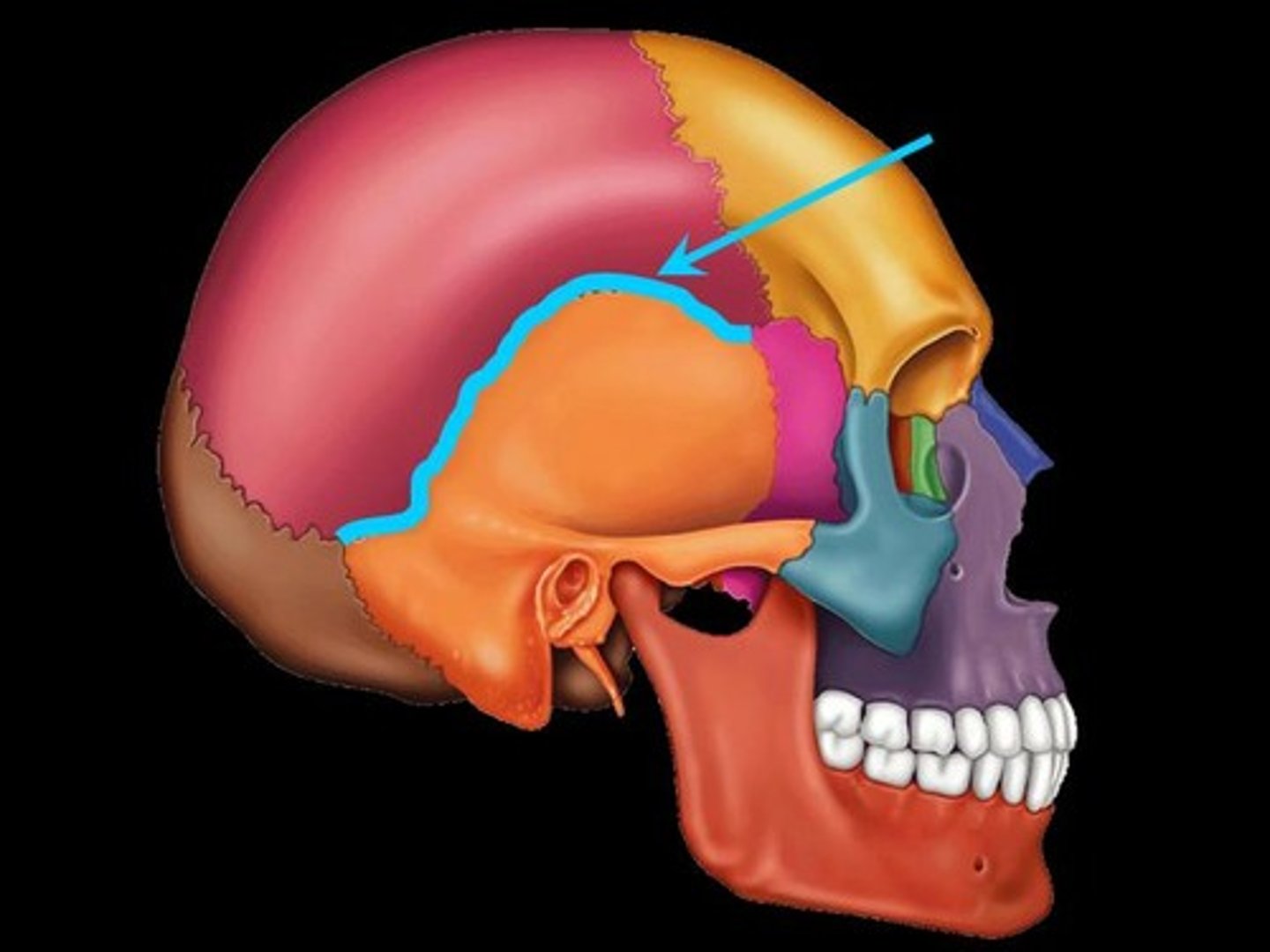
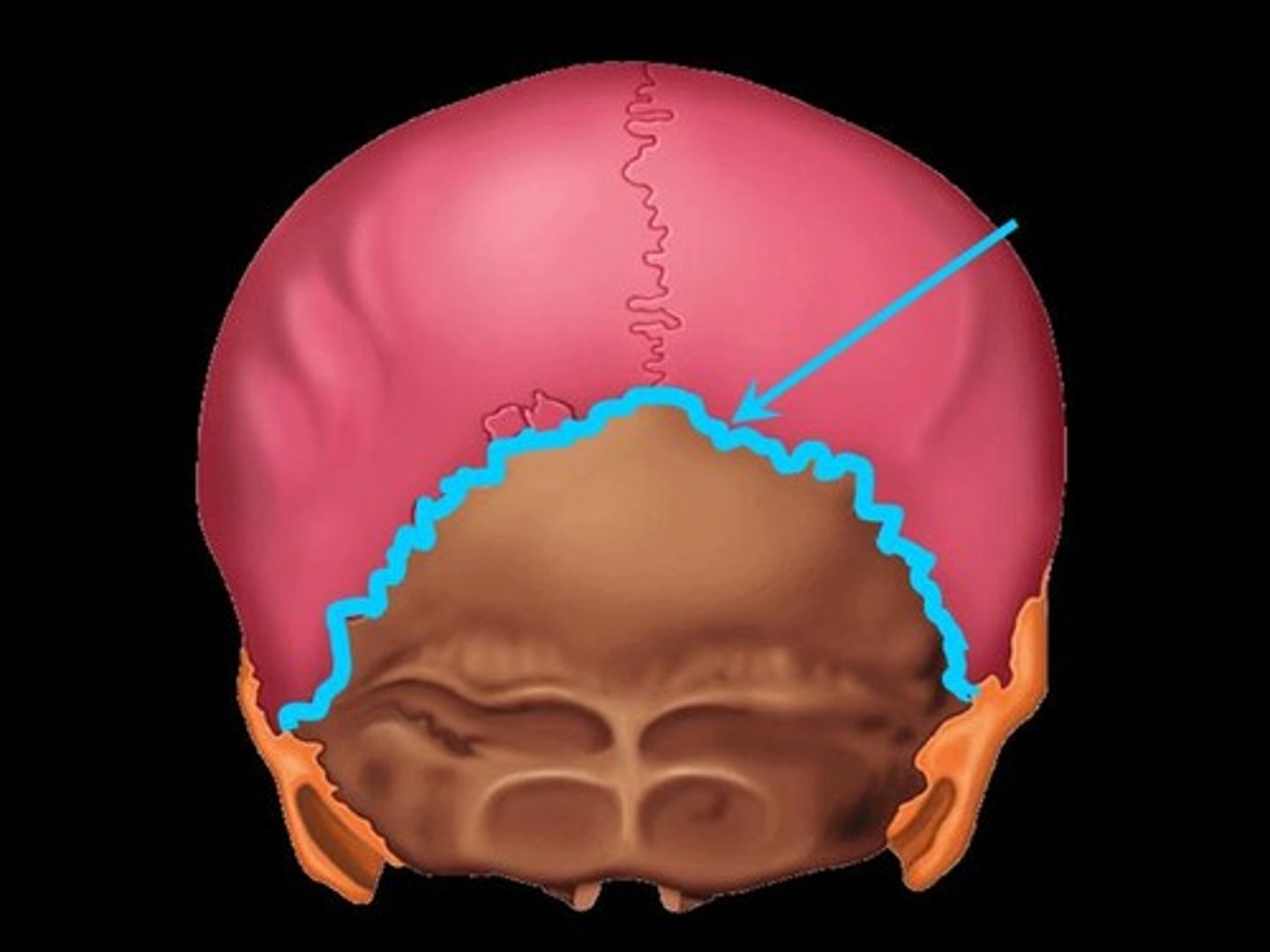
Lambdoid Suture
Occurs where the parietal bones meet the occipital bone posteriorly.
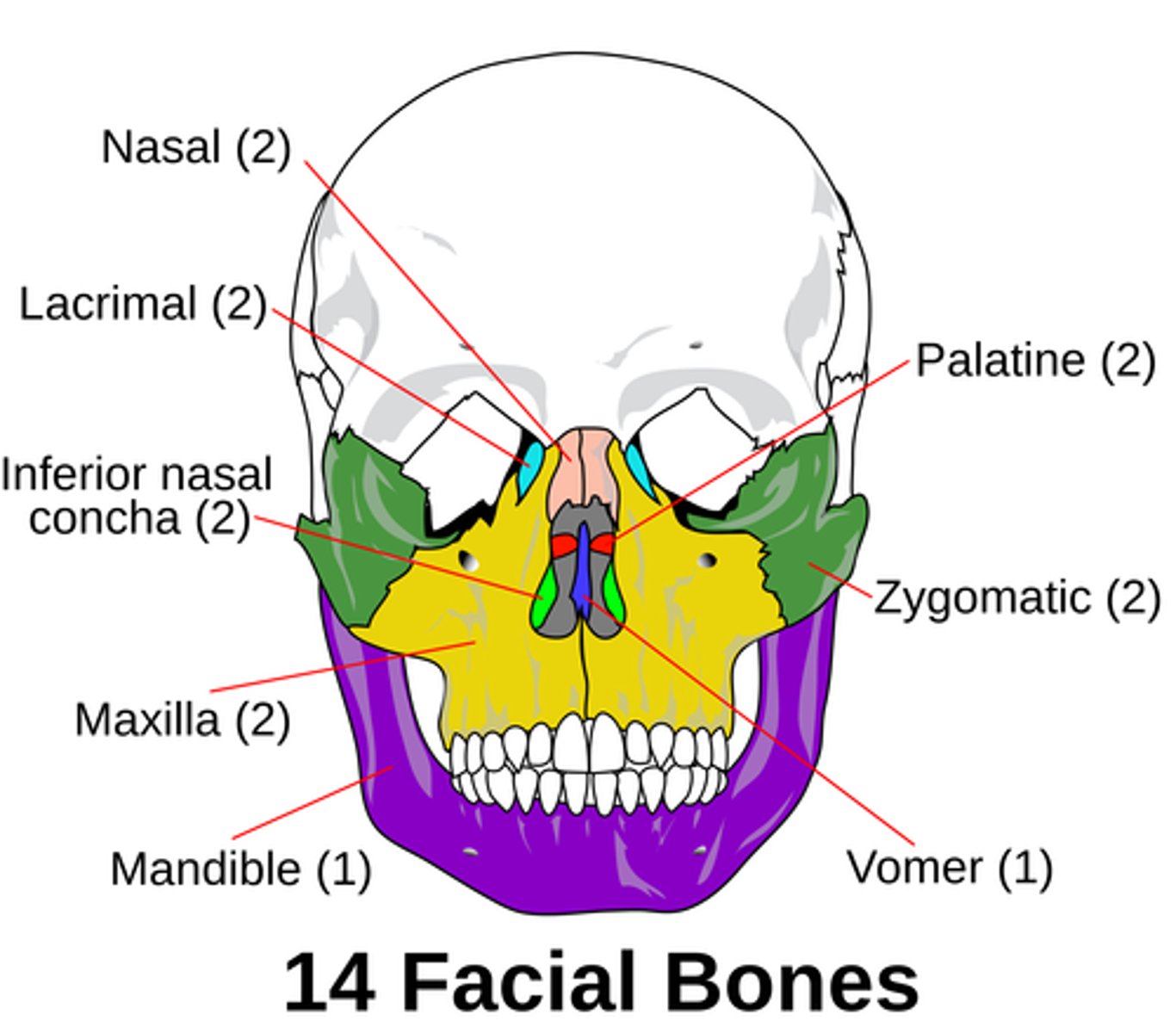
Facial Bones
Of the 14 bones composing the face, 12 are paired; only the mandible and vomer are single bones.
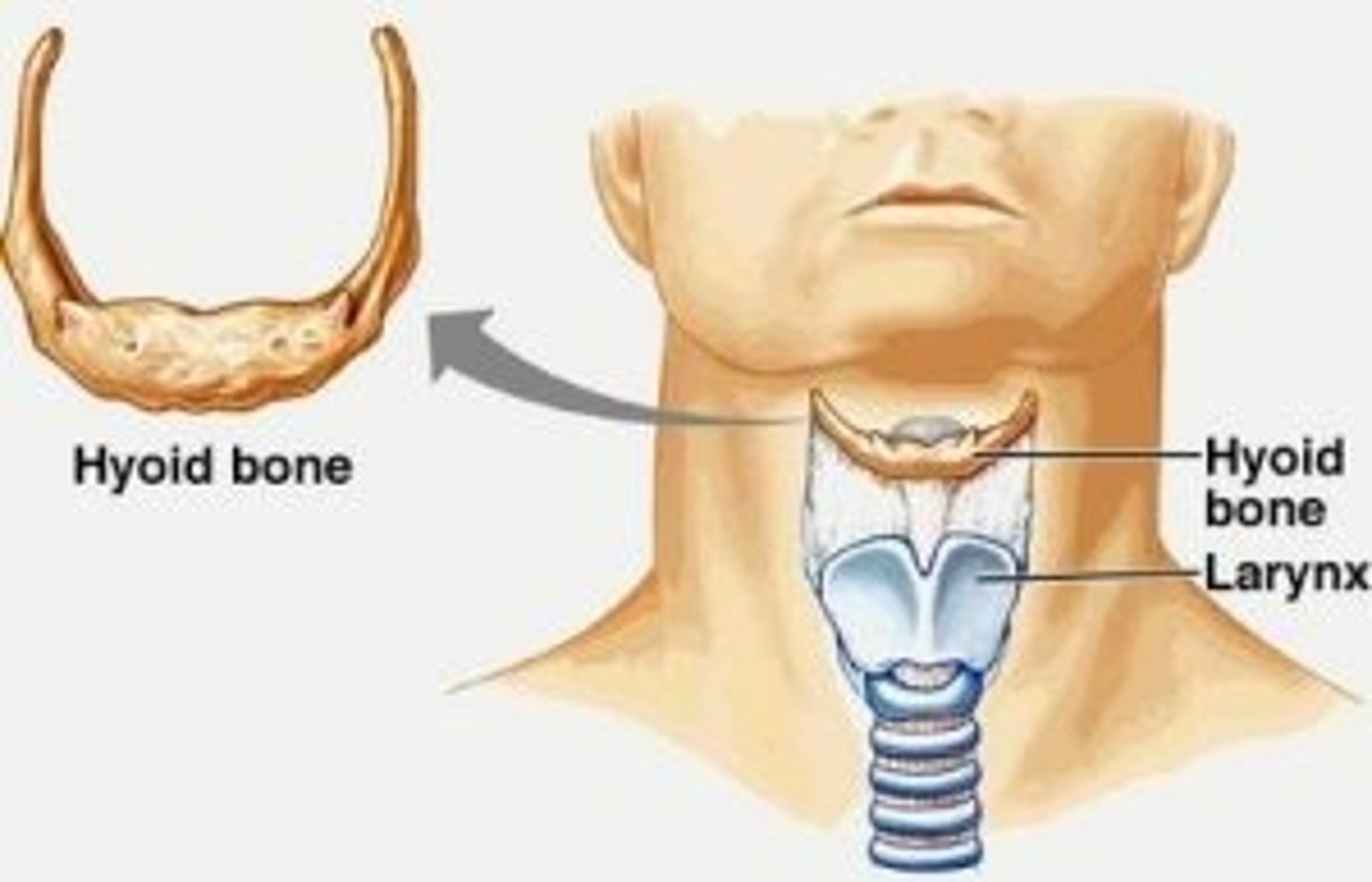
Hyoid Bone
Located in the throat above the larynx, serving as a point of attachment for tongue and neck muscles.
Paranasal Sinuses
Mucus-lined, air-filled cavities in five skull bones that lighten the skull and act as resonance chambers.
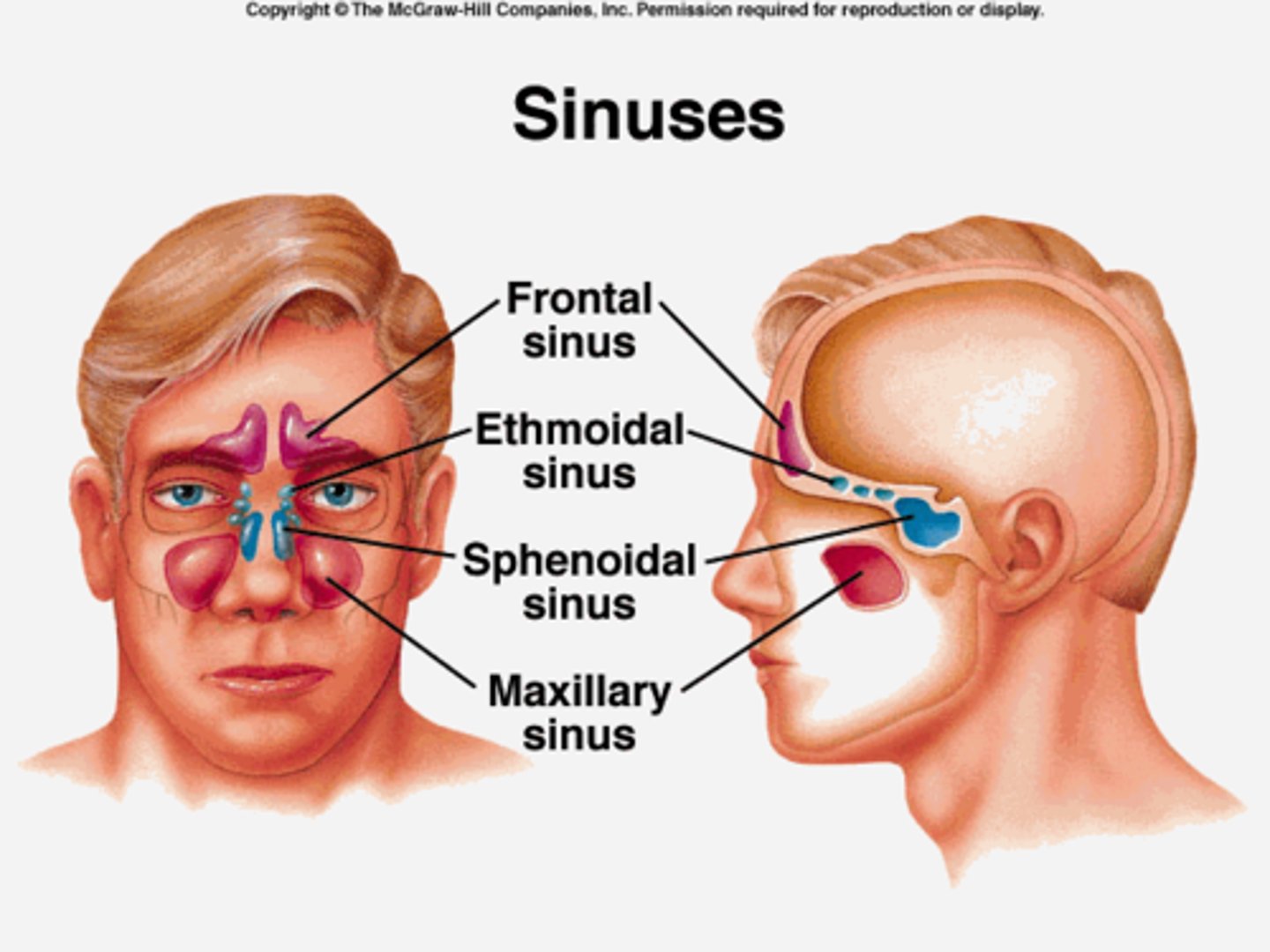
Maxillary Sinus
The largest of the sinuses found in the skull.
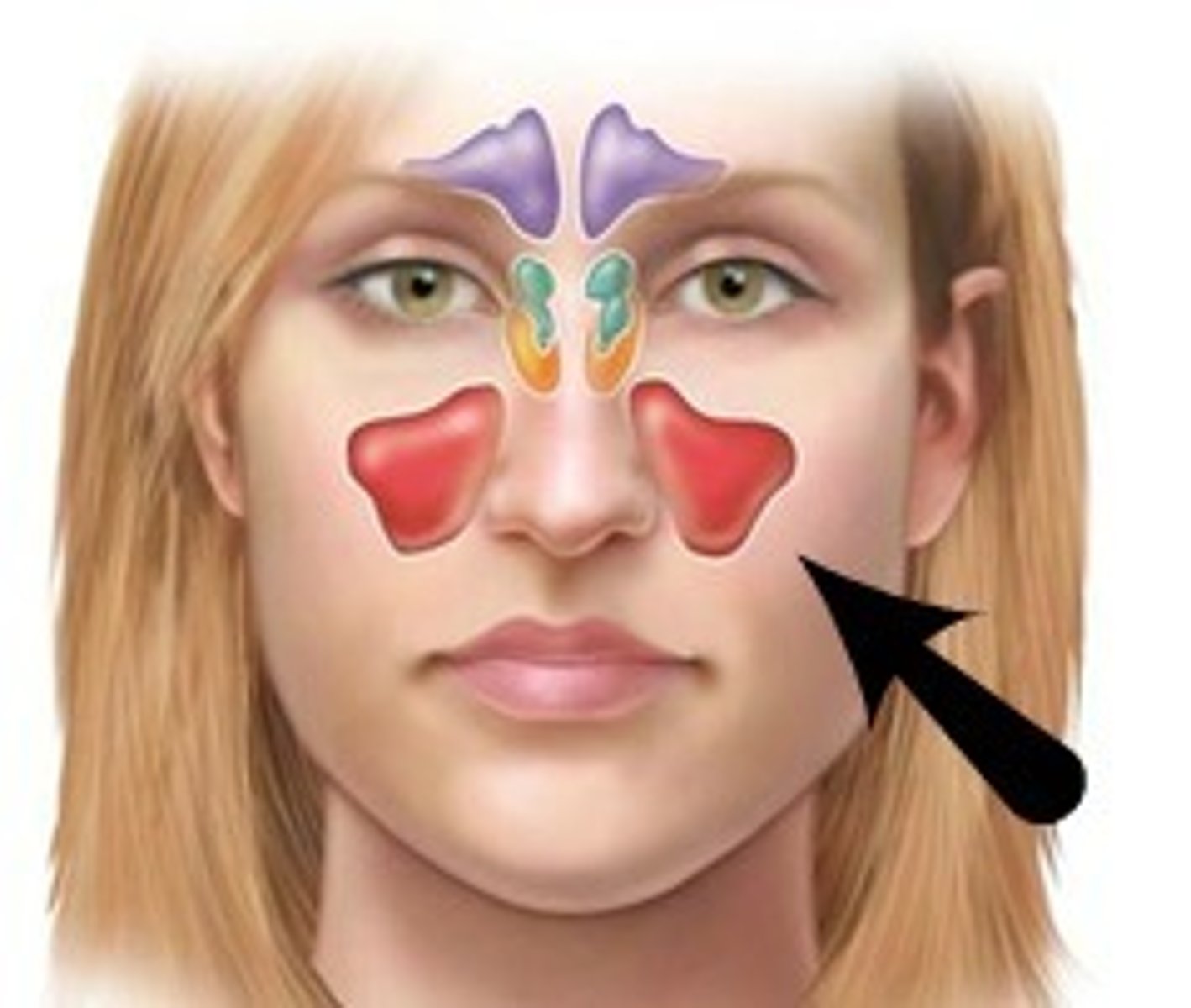
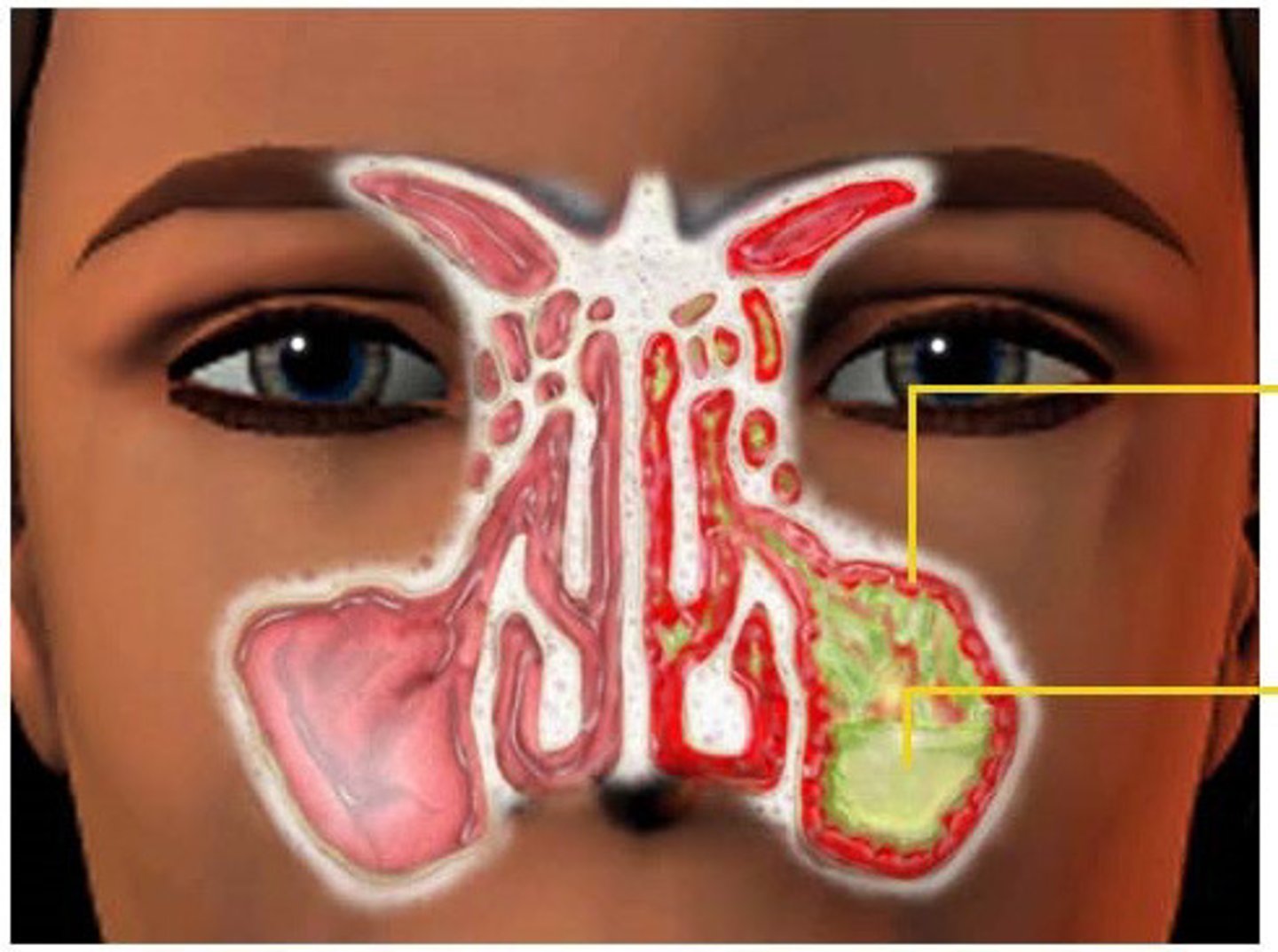
Sinusitis
Inflammation of the sinuses due to allergy or bacterial invasion.
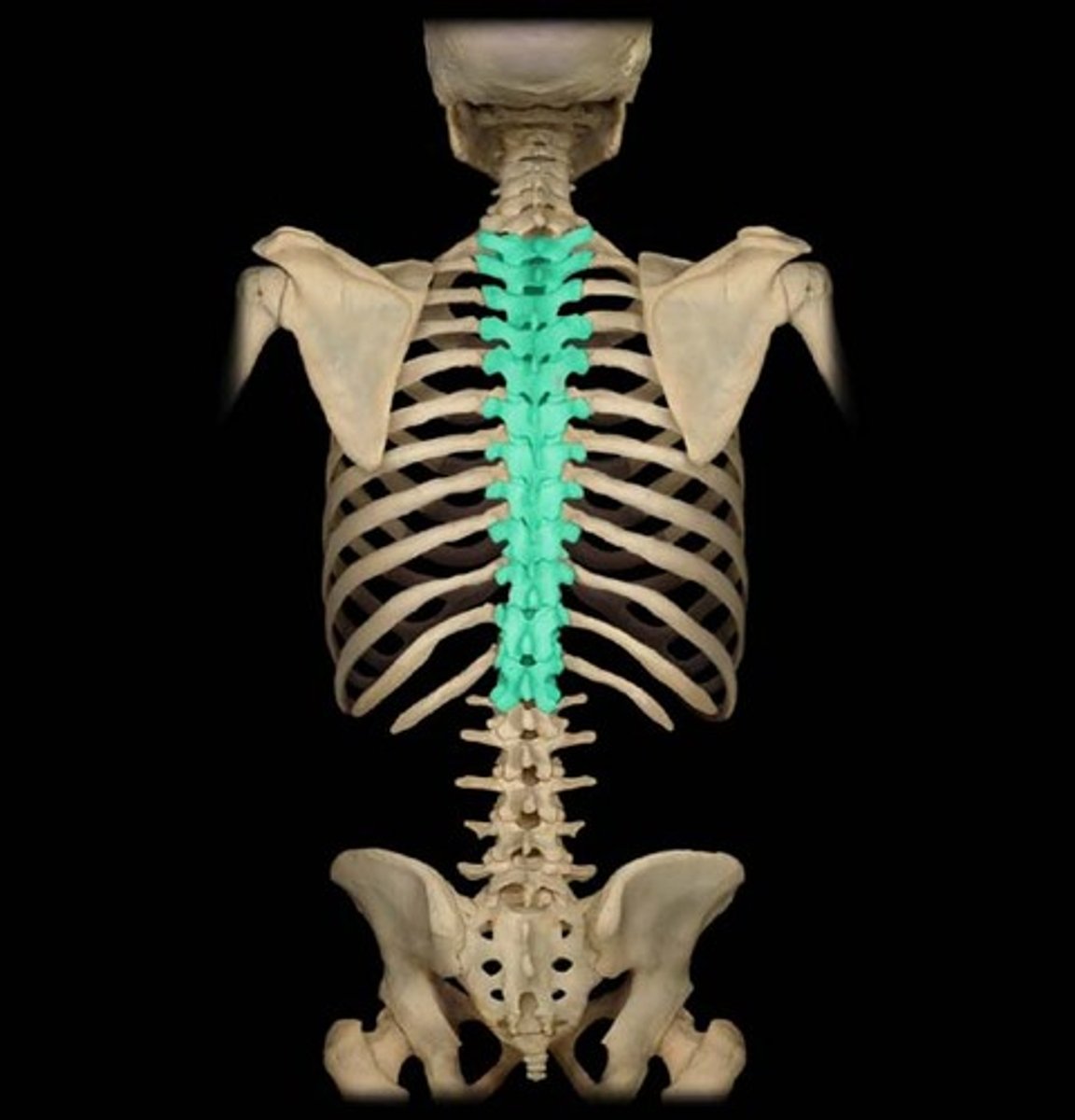
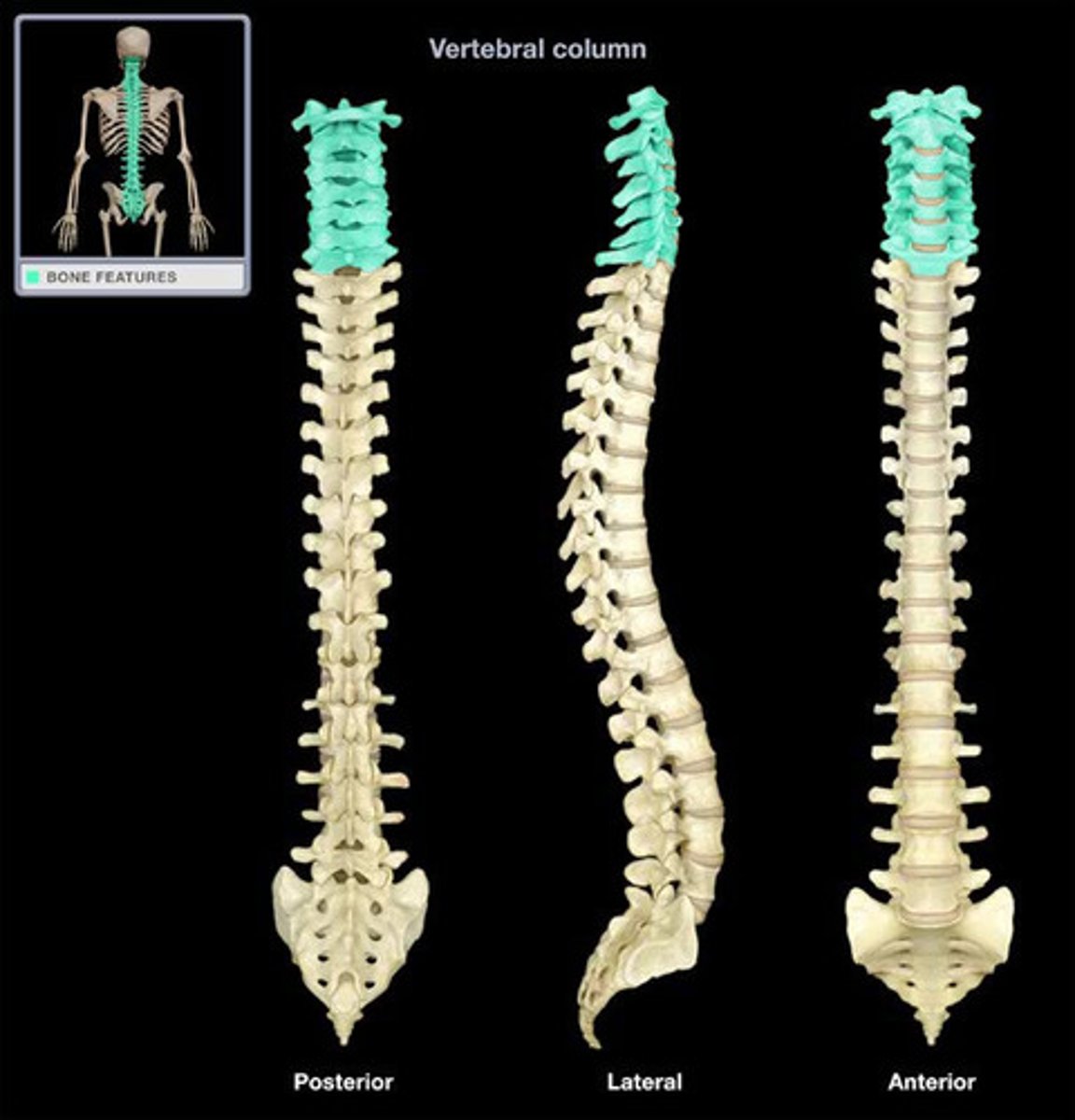
Vertebral Column
Extending from the skull to the pelvis, it forms the body's major axial support and protects the spinal cord.
Vertebrae
Composed of 24 bones in the vertebral column.
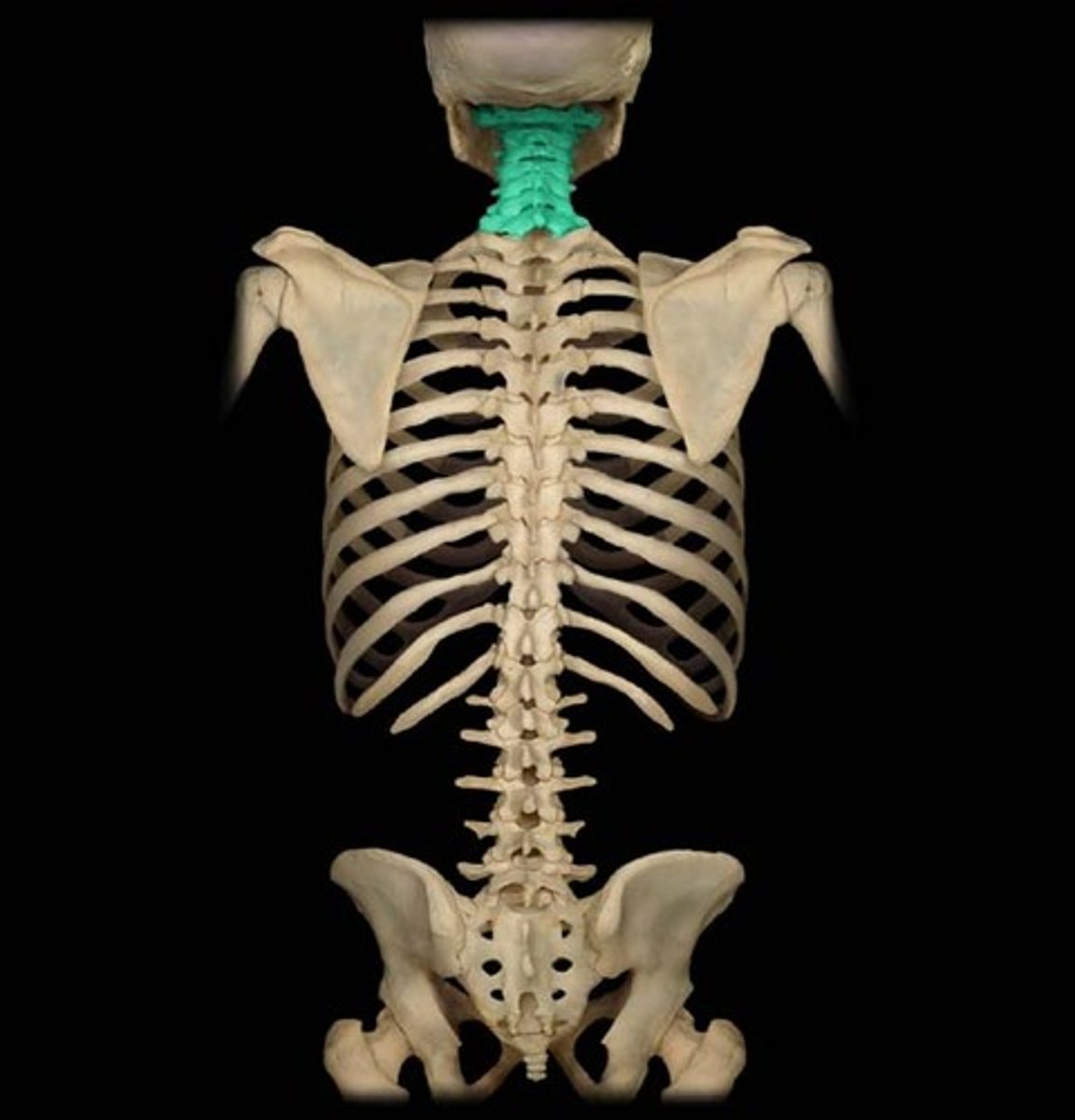
Cervical Vertebrae
Seven bones of the neck, labeled C1-C7.
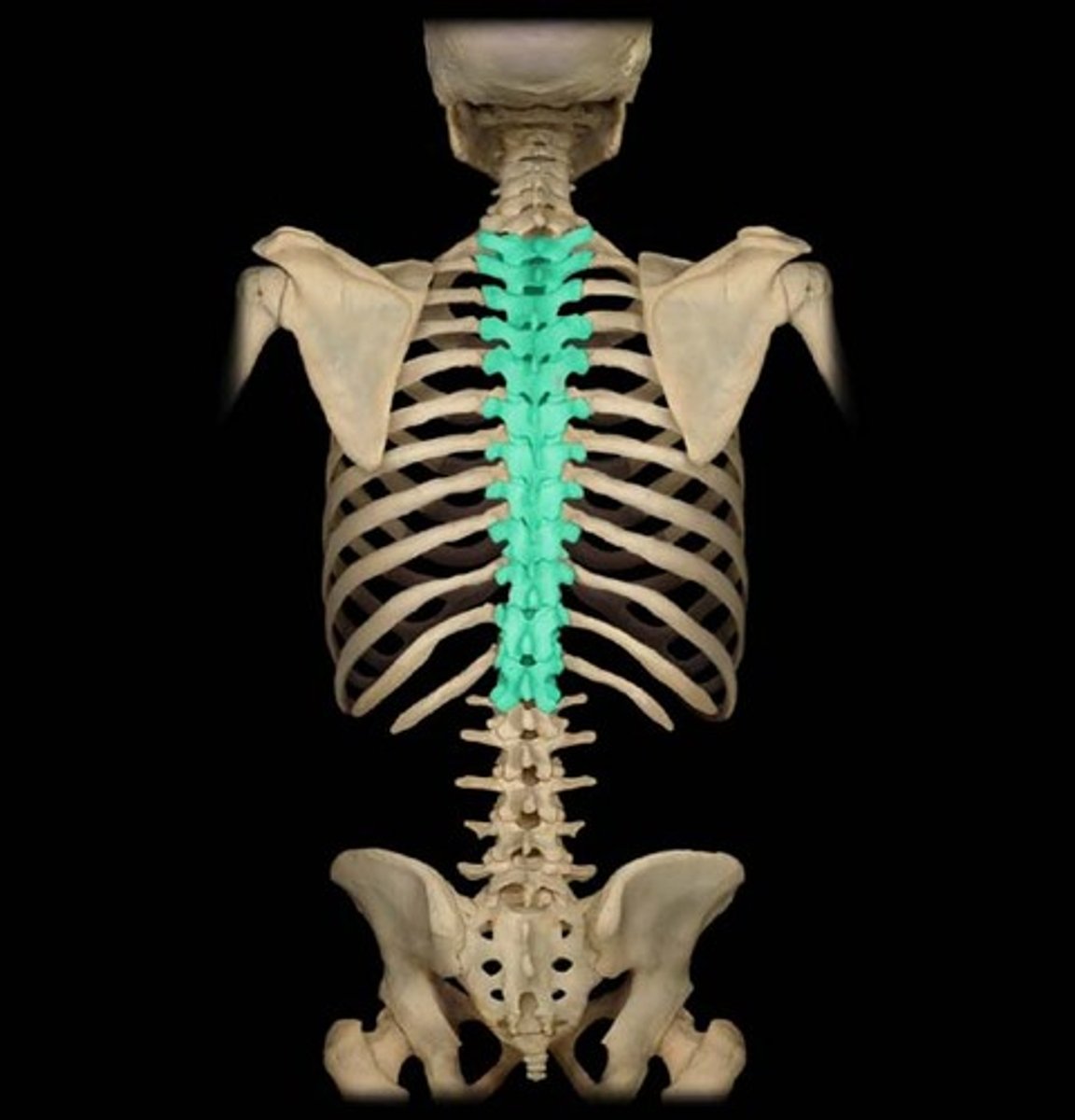
Thoracic Vertebrae
Twelve vertebrae located in the upper back.
Lumbar Vertebrae
Five vertebrae supporting the lower back.
Intervertebral Discs
Pads of fibrocartilage that cushion the vertebrae and absorb shocks.
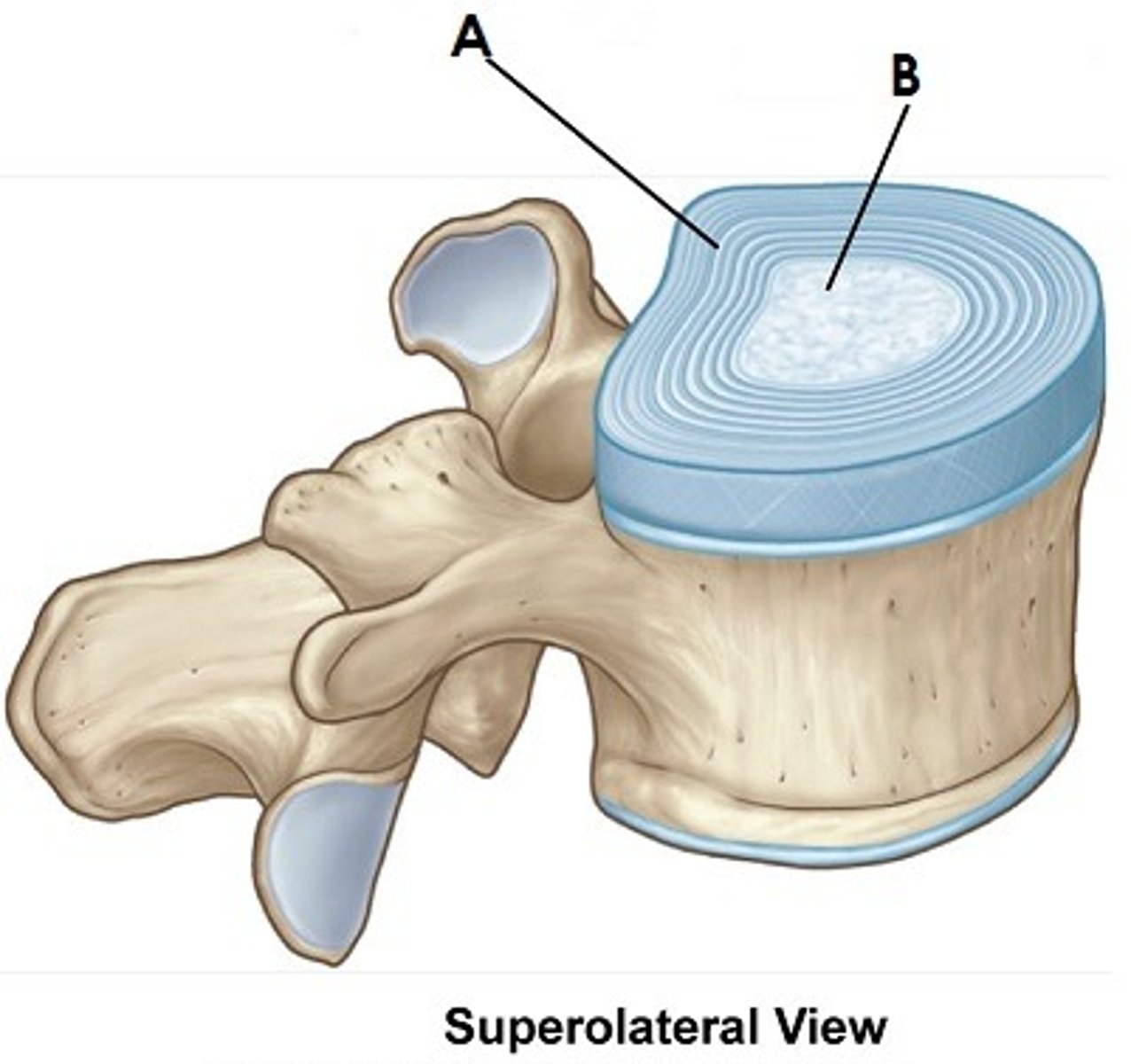
Nucleus Pulposus
Central gelatinous region of an intervertebral disc that behaves like a rubber ball.
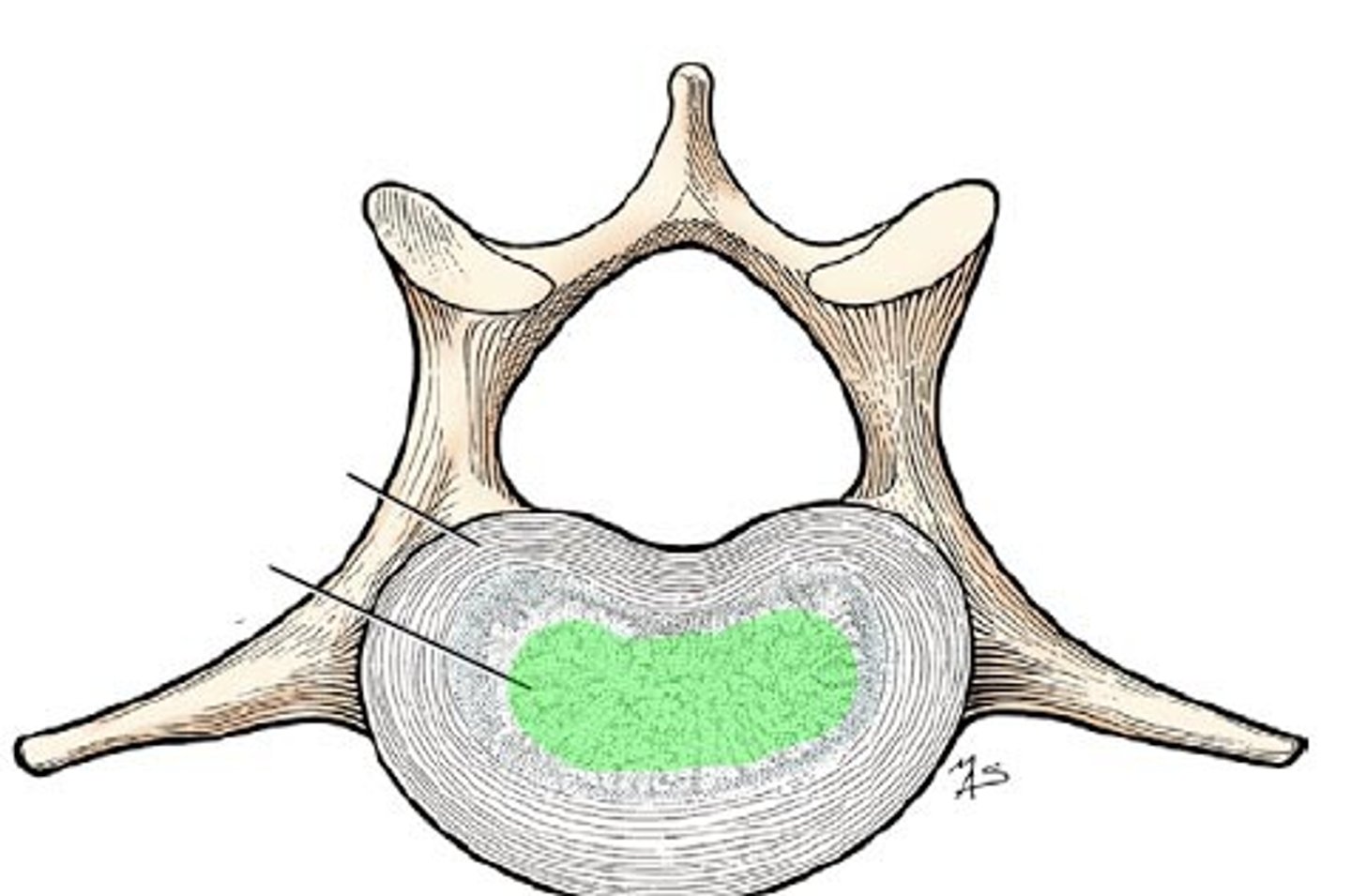
Annulus fibrosus
Stabilizes the disc and contains the nucleus pulposus.
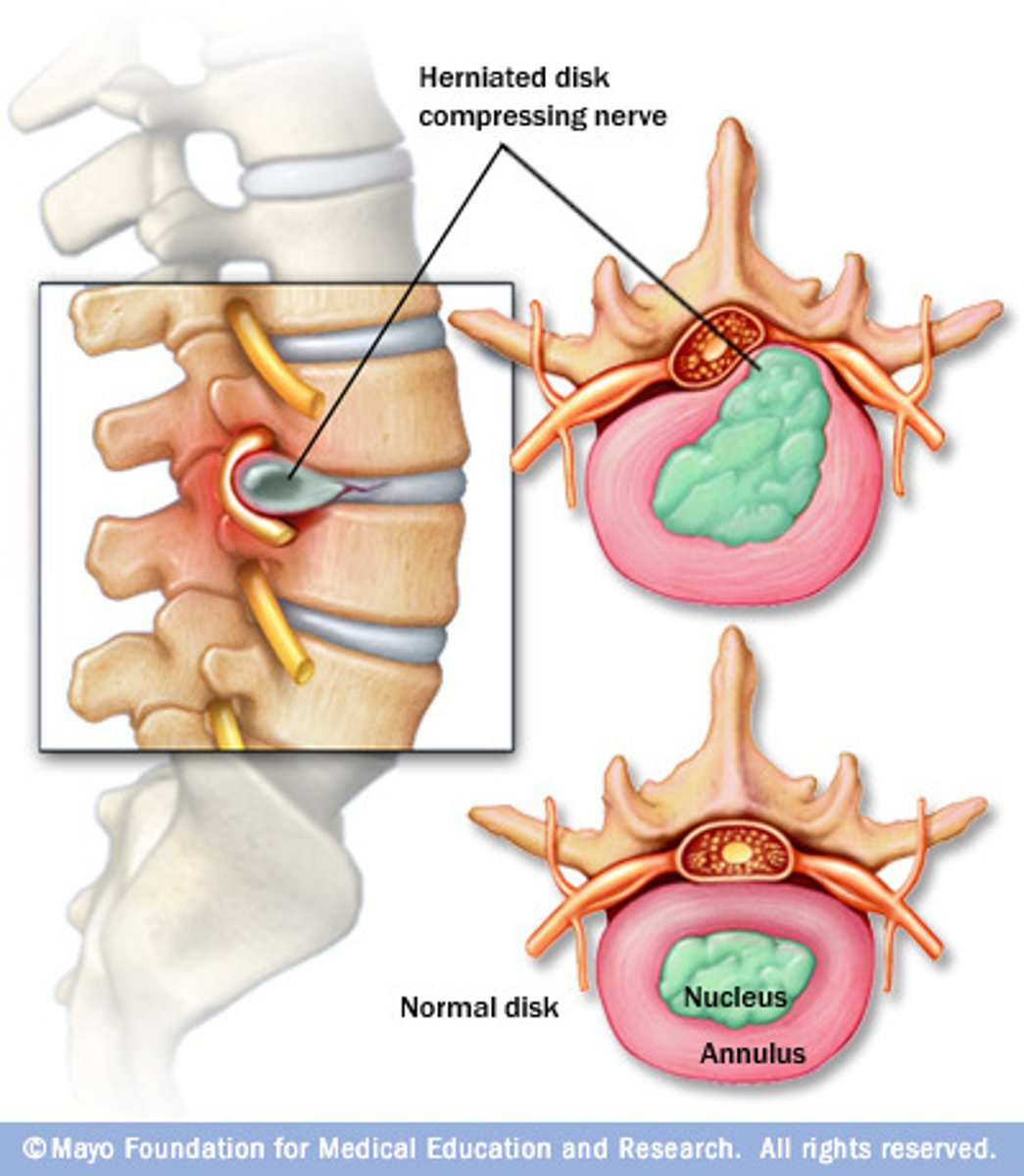
Herniated discs
A condition in which the annulus fibrosus commonly ruptures and the nucleus pulposus protrudes through it.
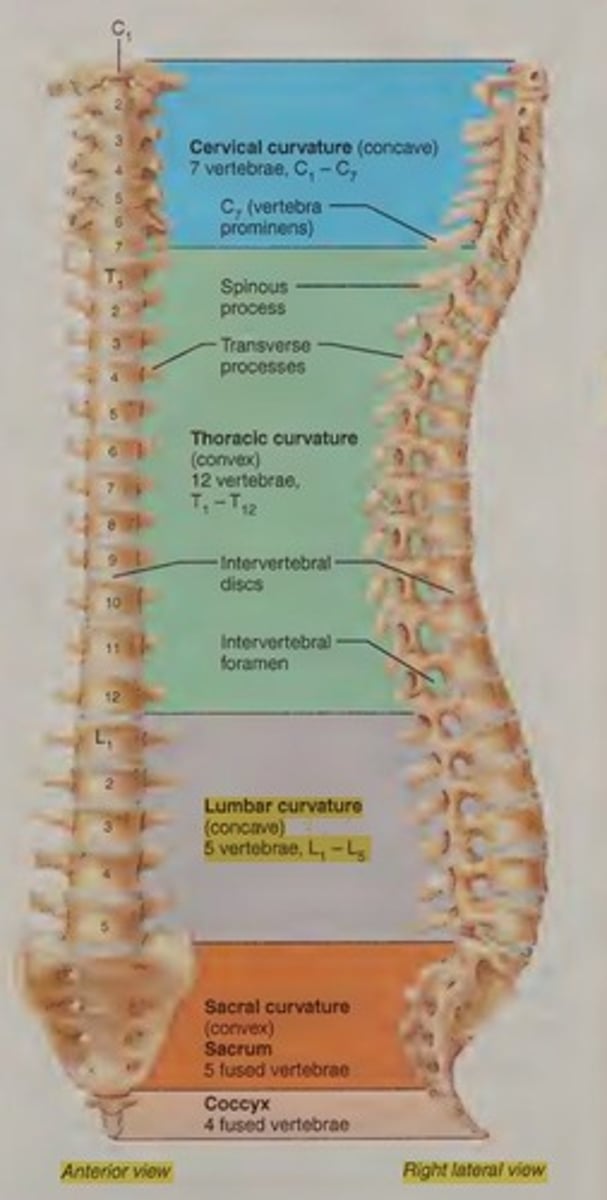
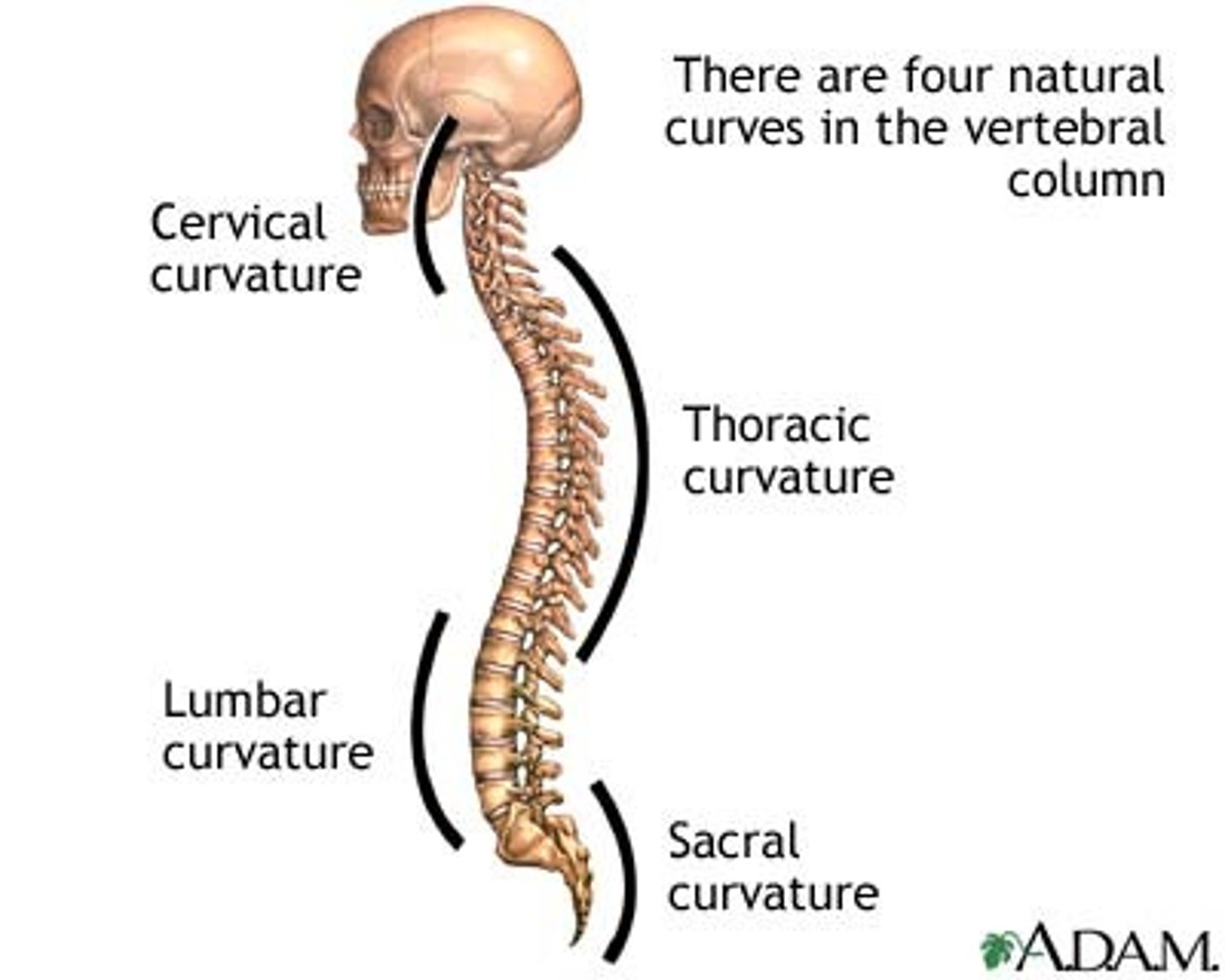
Primary curvatures
The thoracic and sacral curvatures of the spine that are present and well developed at birth.
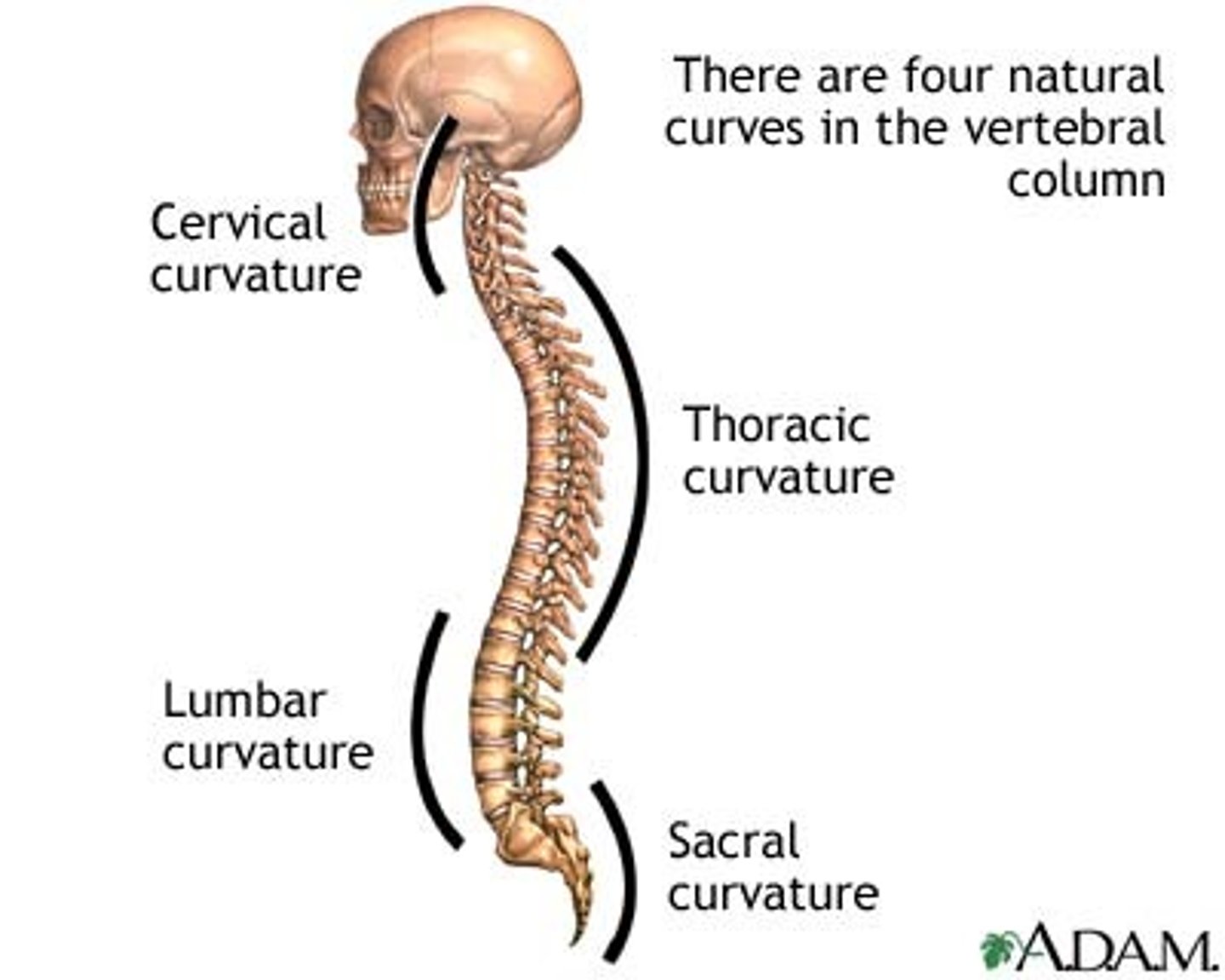
Secondary curvatures
Curvatures that are formed later, including the cervical curvature and lumbar curvature.
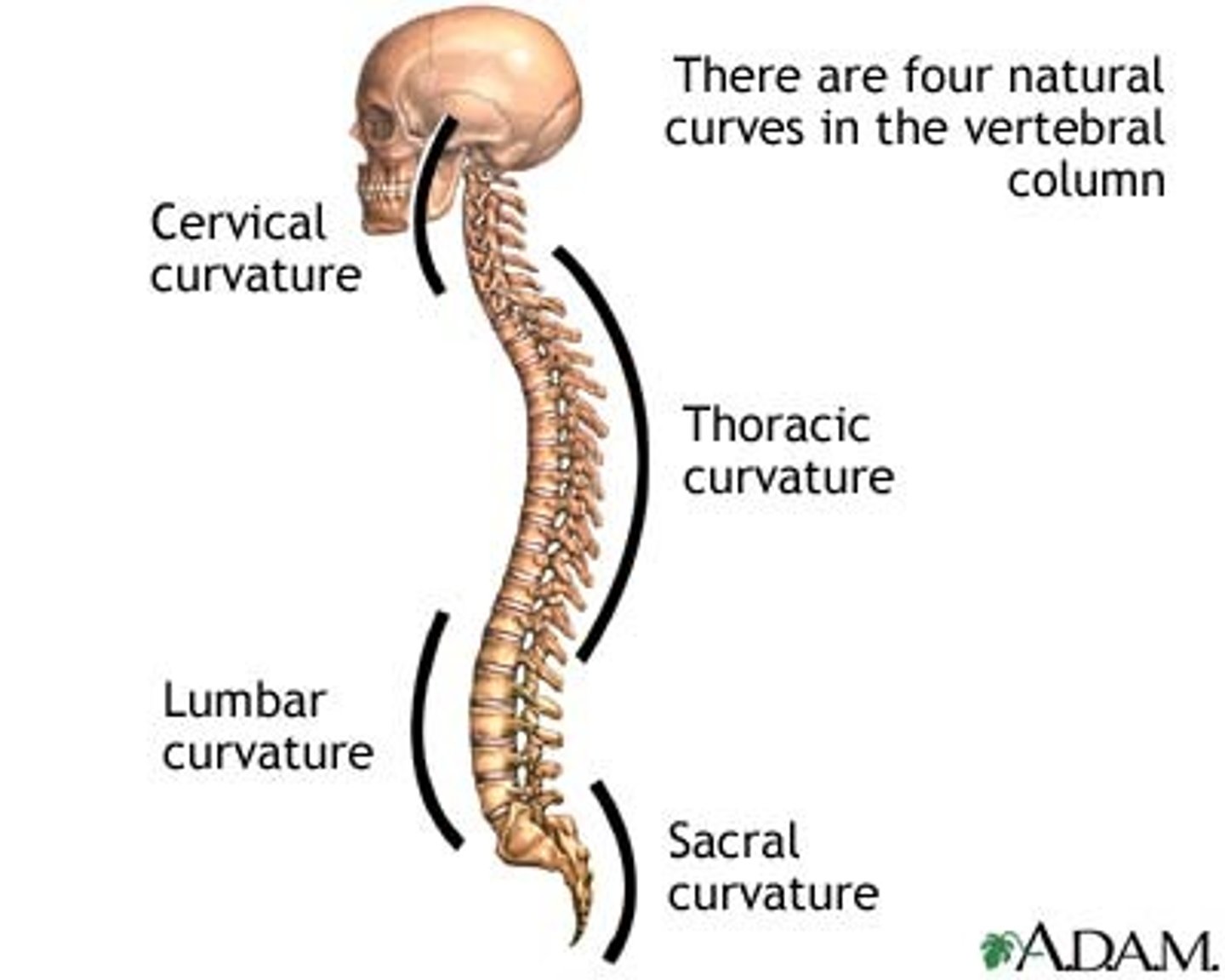
Cervical curvature
Becomes present when the baby begins to hold its head up independently.
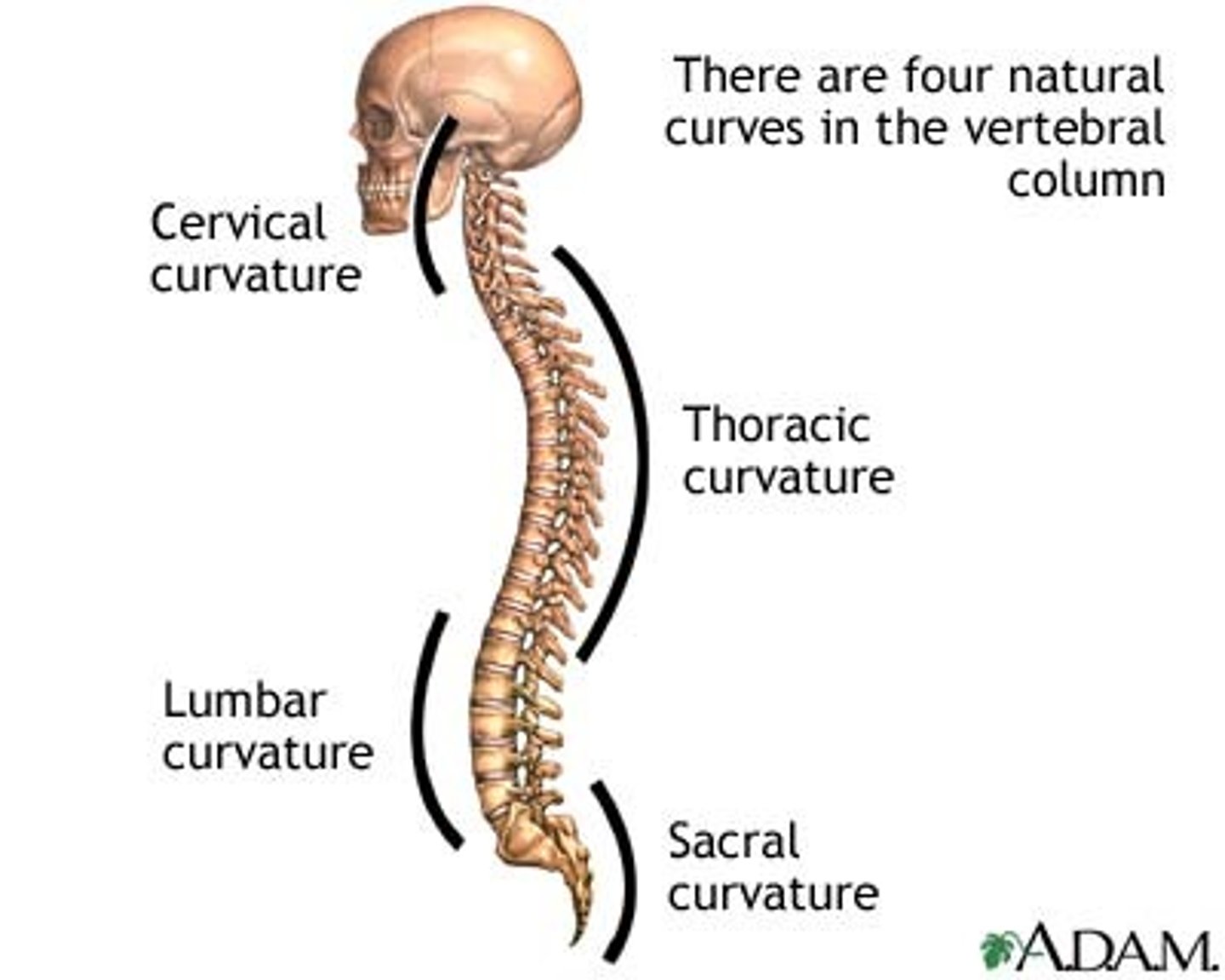
Lumbar curvature
Develops when the baby begins to walk.
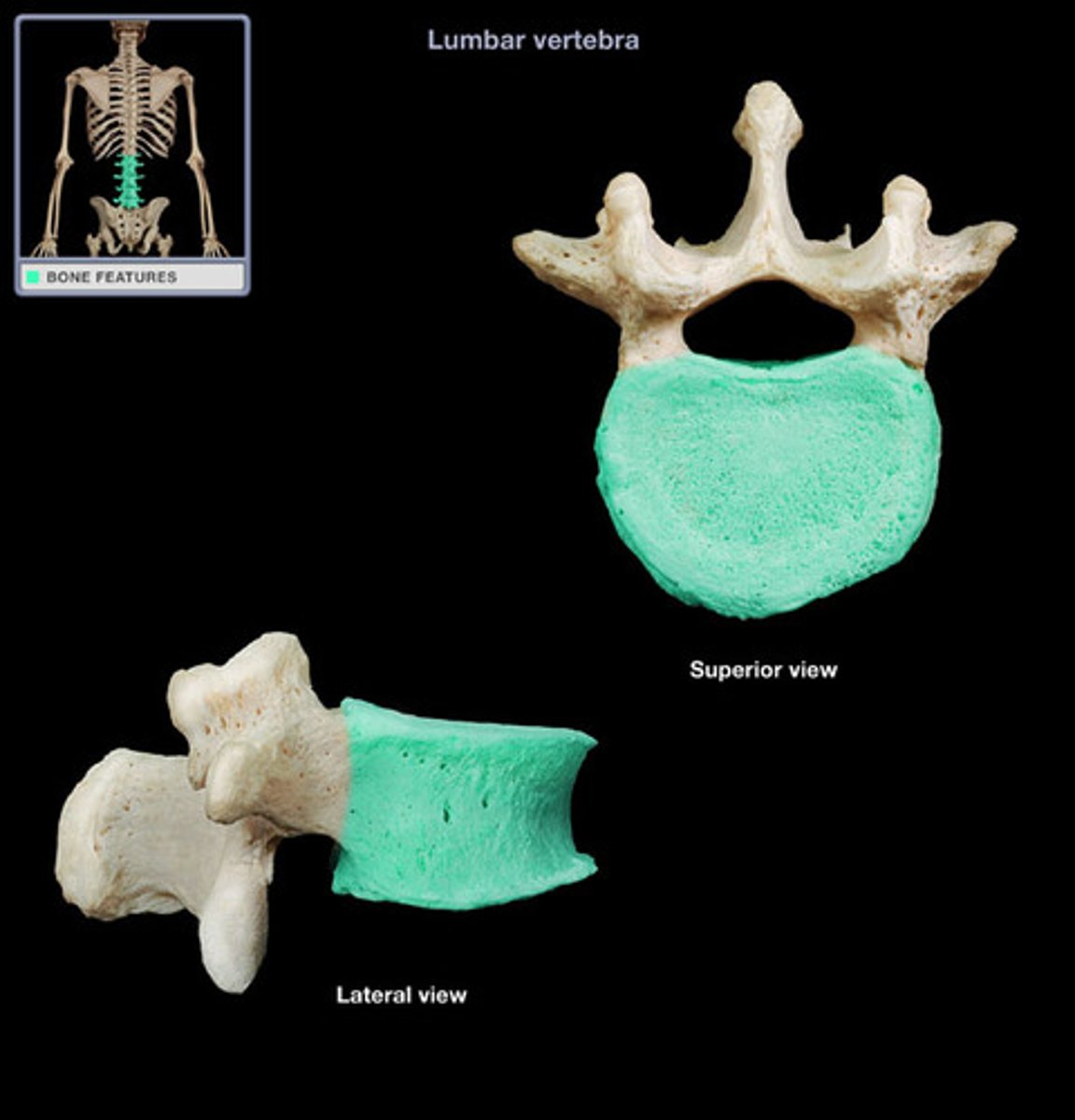
Body (centrum)
Rounded central weight-bearing portion of the vertebra, which faces anteriorly in the human vertebral column.
Vertebral arch
Composed of two pedicles and two laminae.
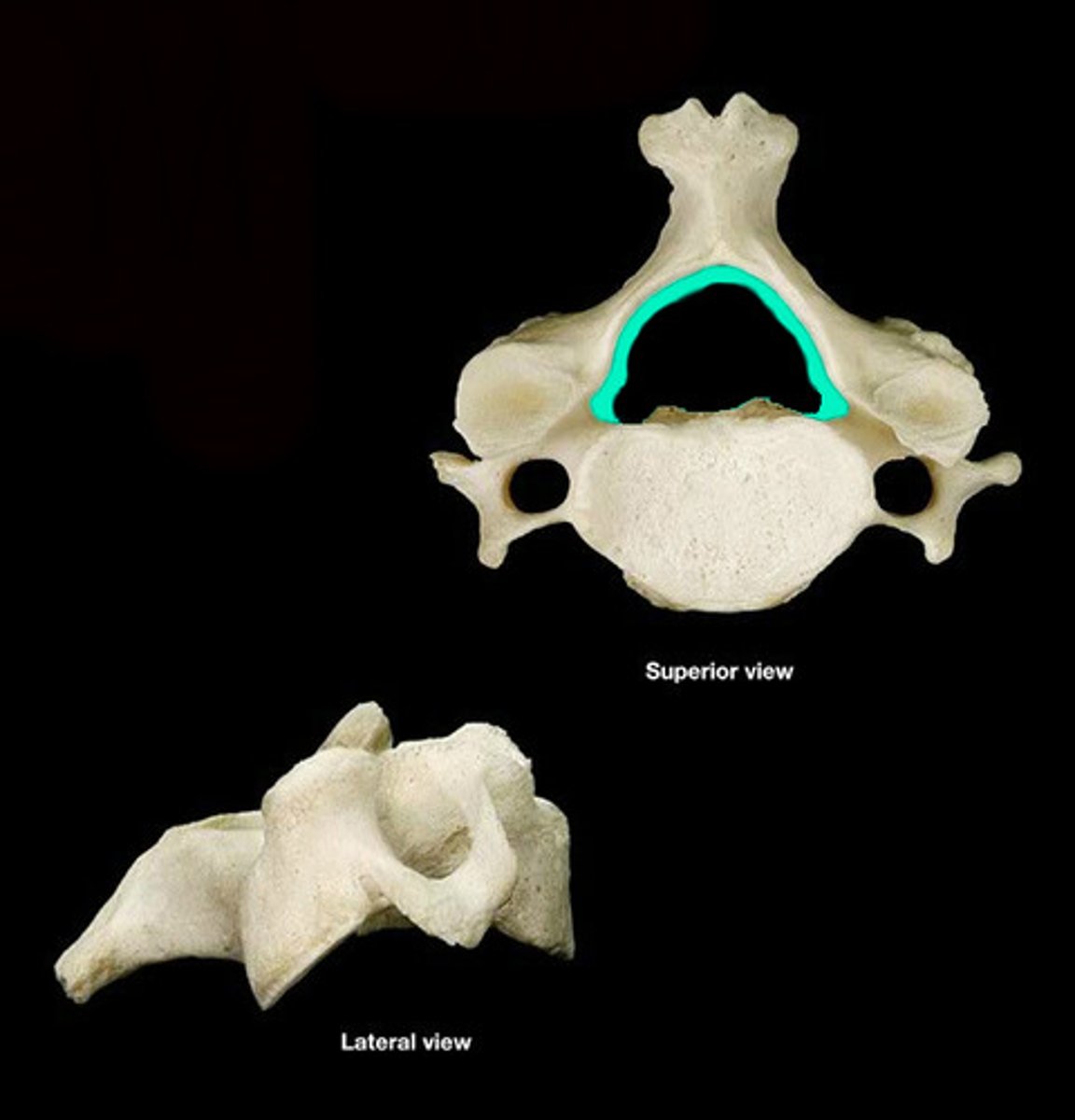
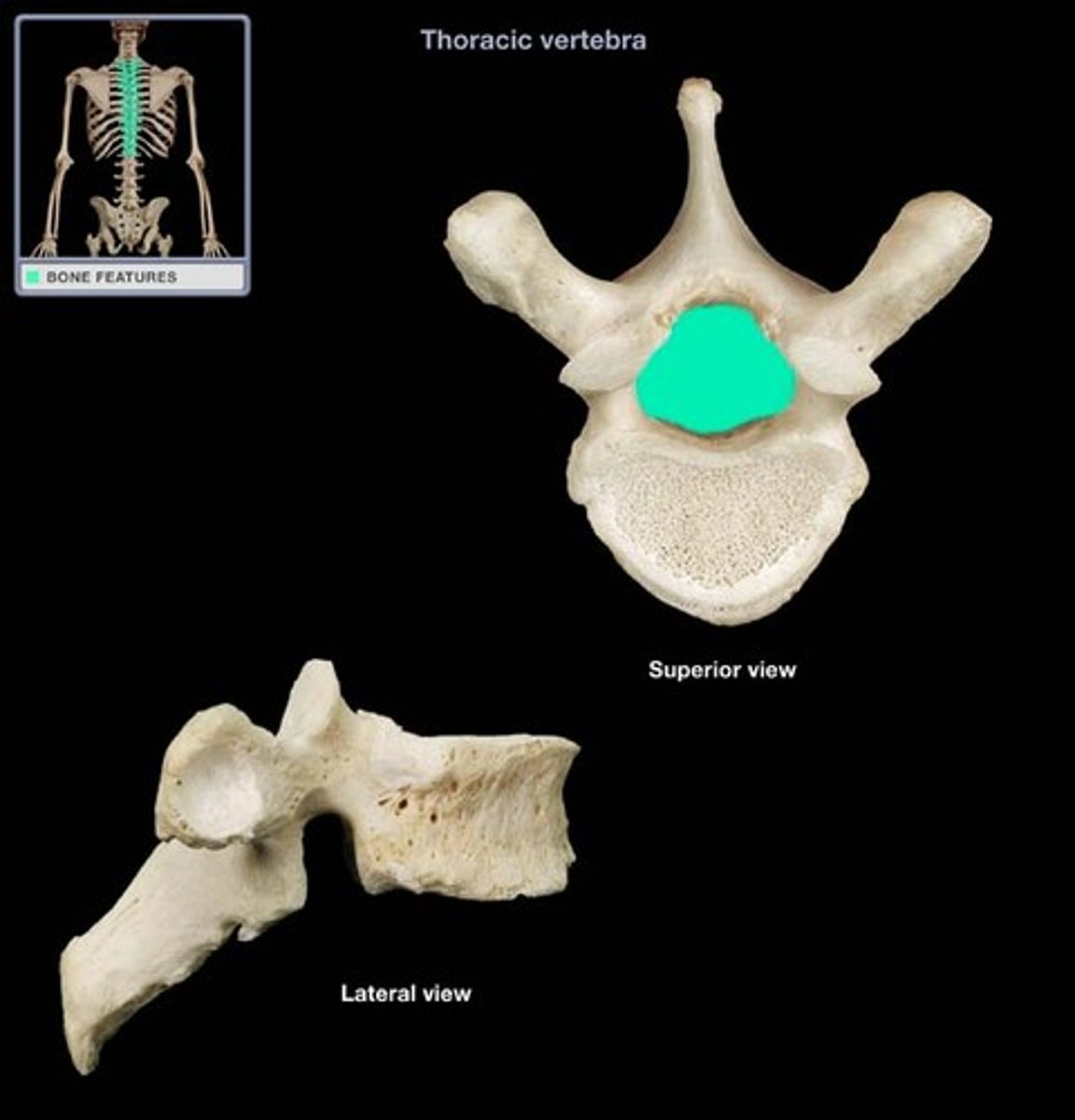
Vertebral foramen
Opening enclosed by the body and vertebral arch; a passageway for the spinal cord.
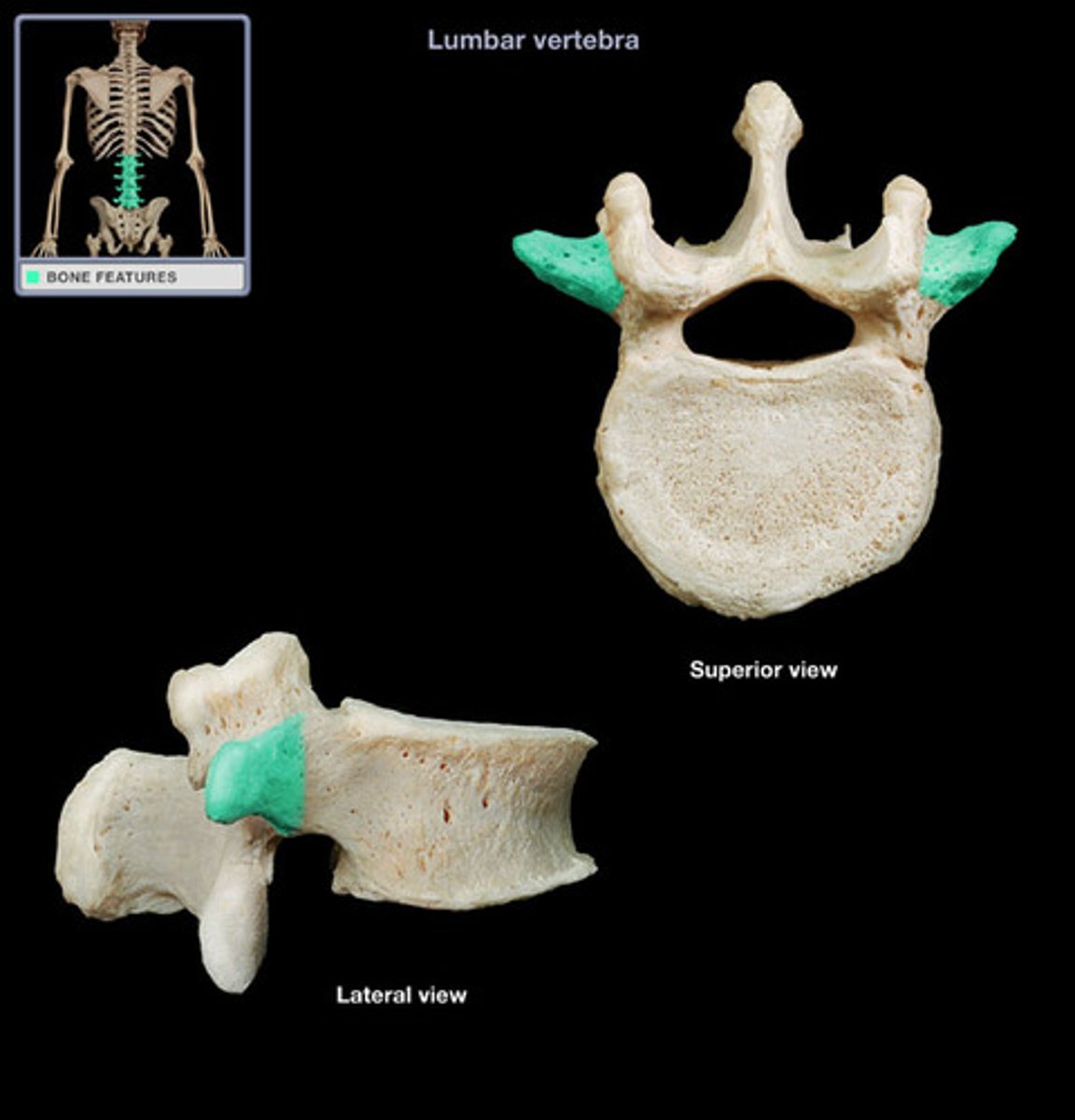
Transverse processes
Two lateral projections from the vertebral arch.
Spinous process
Single medial and posterior projection formed at the junction of the two laminae.
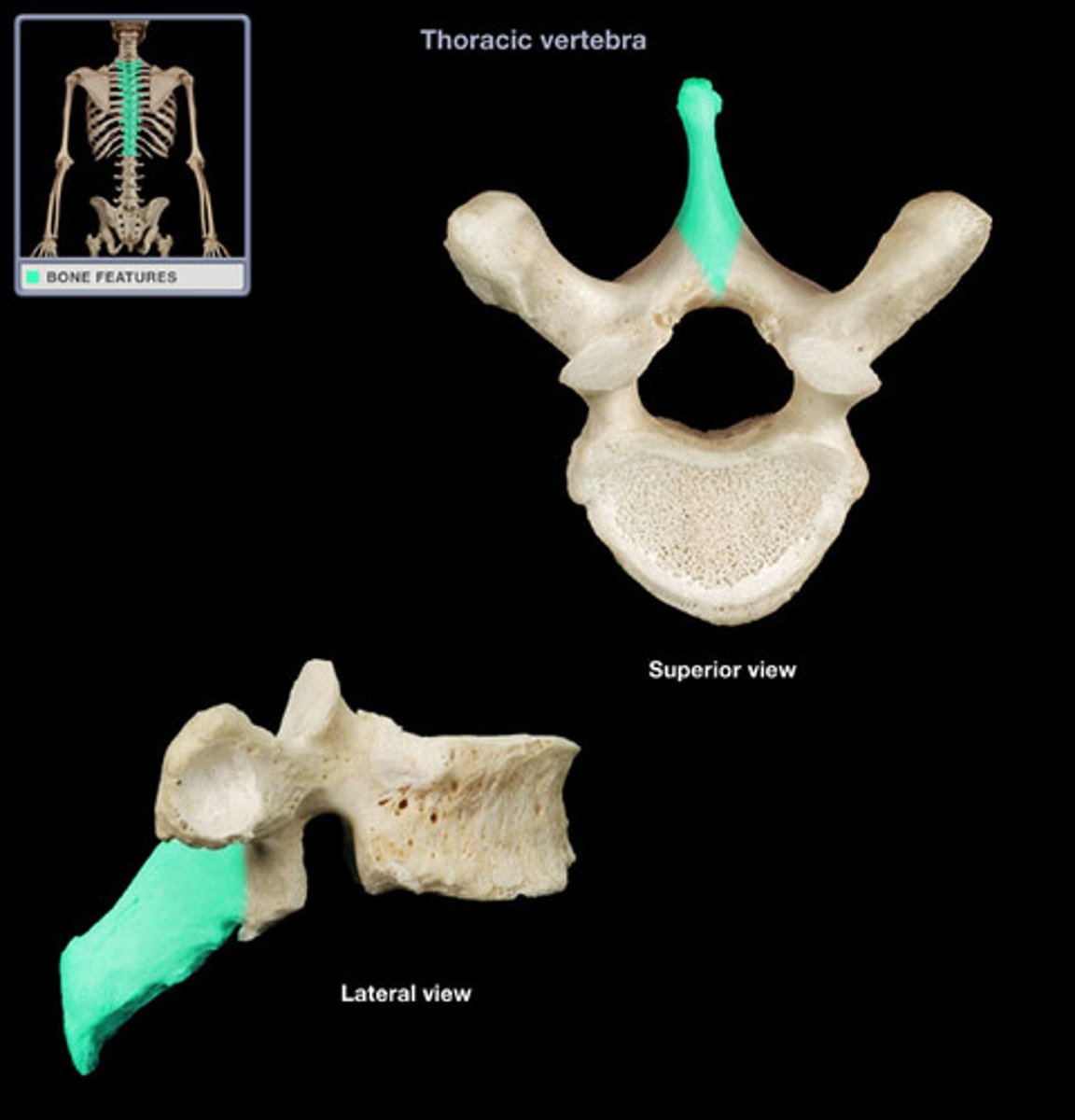
Superior and inferior articular process
Paired projections lateral to the vertebral foramen that enable articulation with adjacent vertebrae.
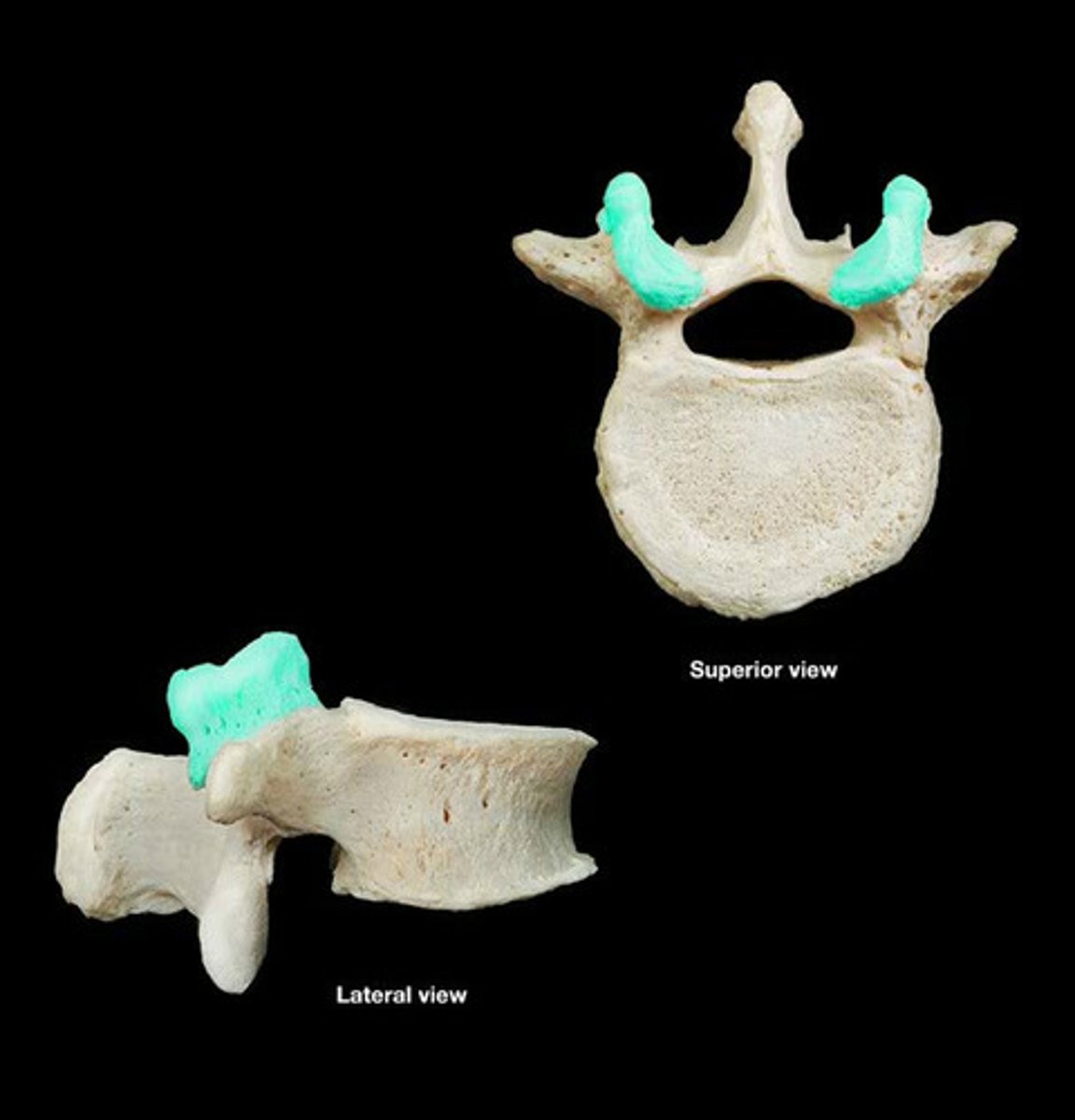
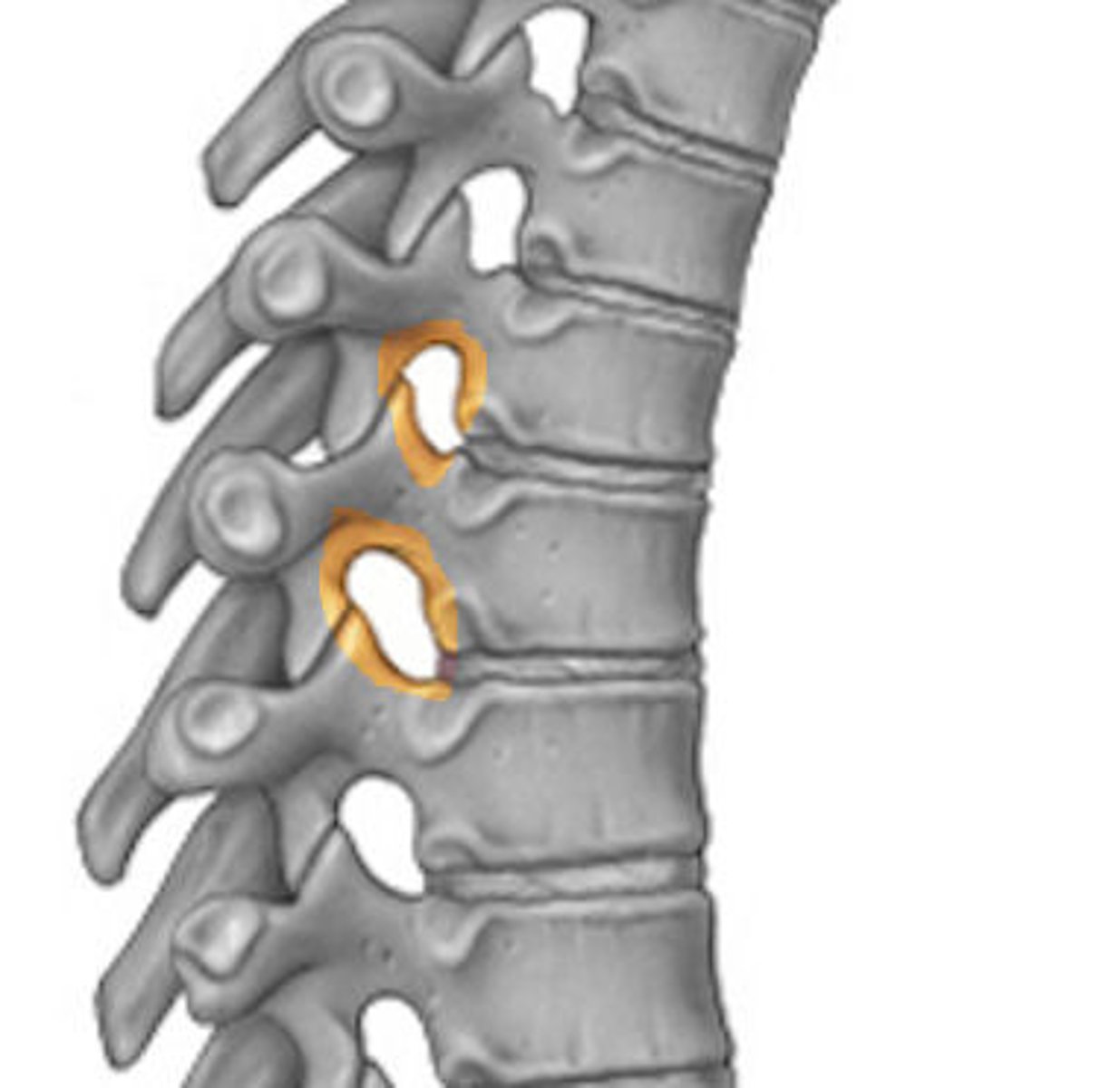
Intervertebral foramina
Openings created by notches on the inferior and superior surfaces of the right and left pedicles for spinal nerves to leave the spinal cord.
Atlas (C1)
Lacks a body, and its lateral process contains large concave depressions on their superior surfaces that receives the occipital condyles of the skull.
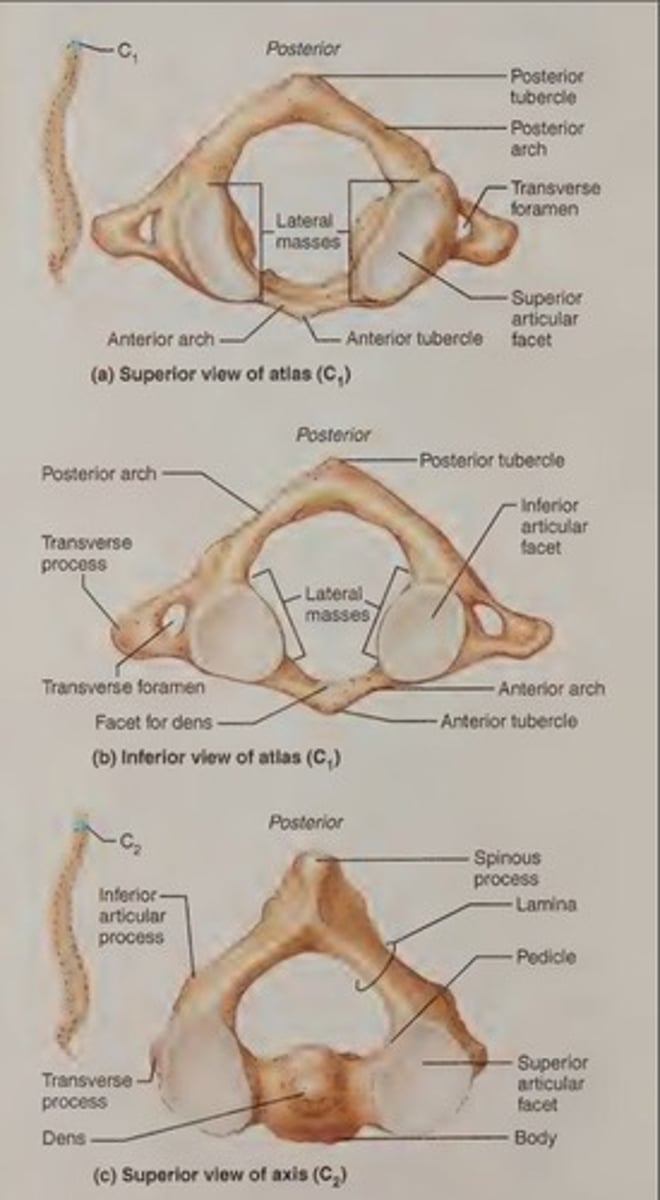
Axis (C2)
Acts as a pivot for the rotation of the atlas (and skull) above, bearing a large vertical process called the dens.
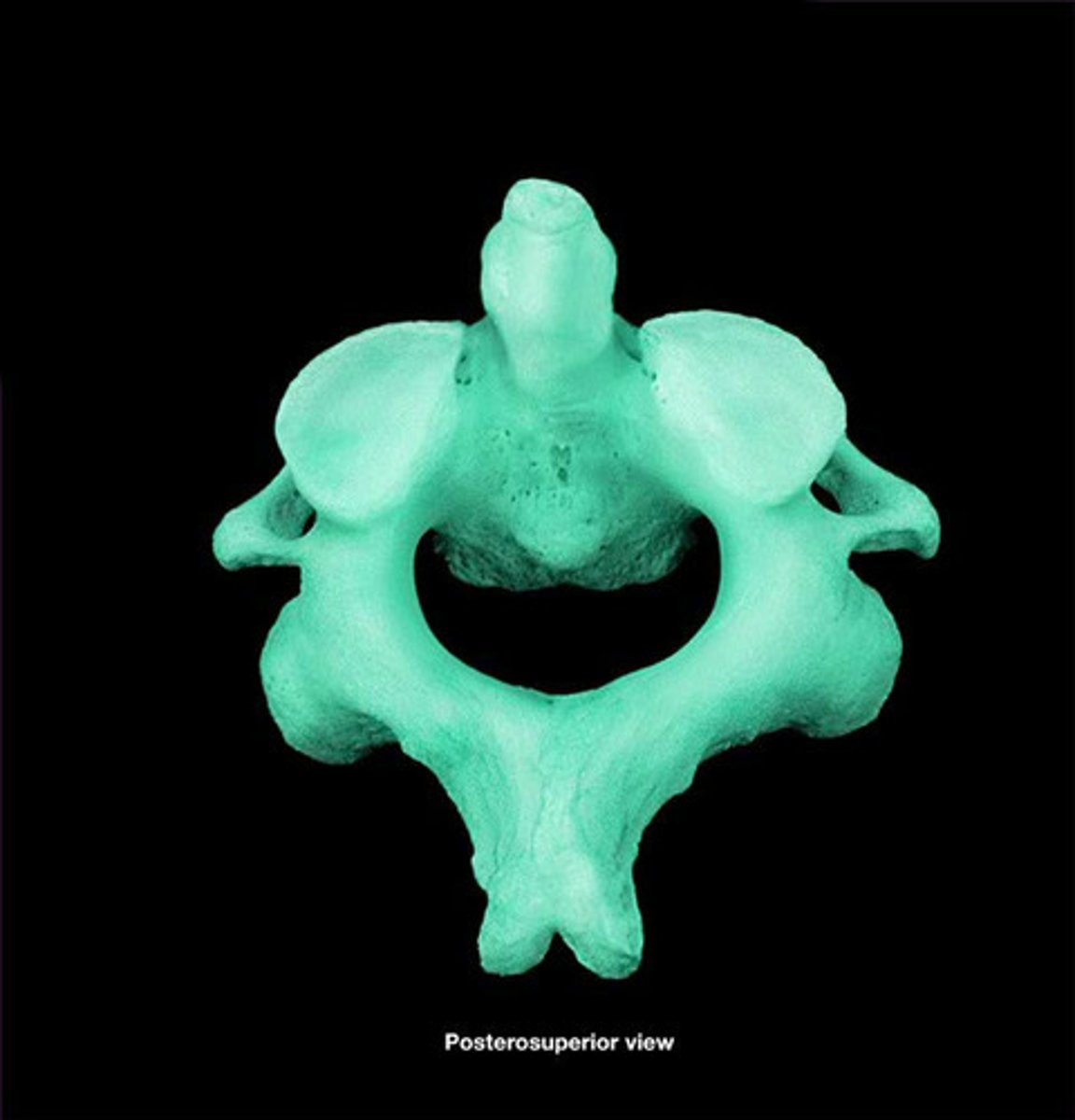
Vertebra prominens
The spinous process of C7, which is visible through the skin at the base of the neck and is the landmark for counting the vertebrae.
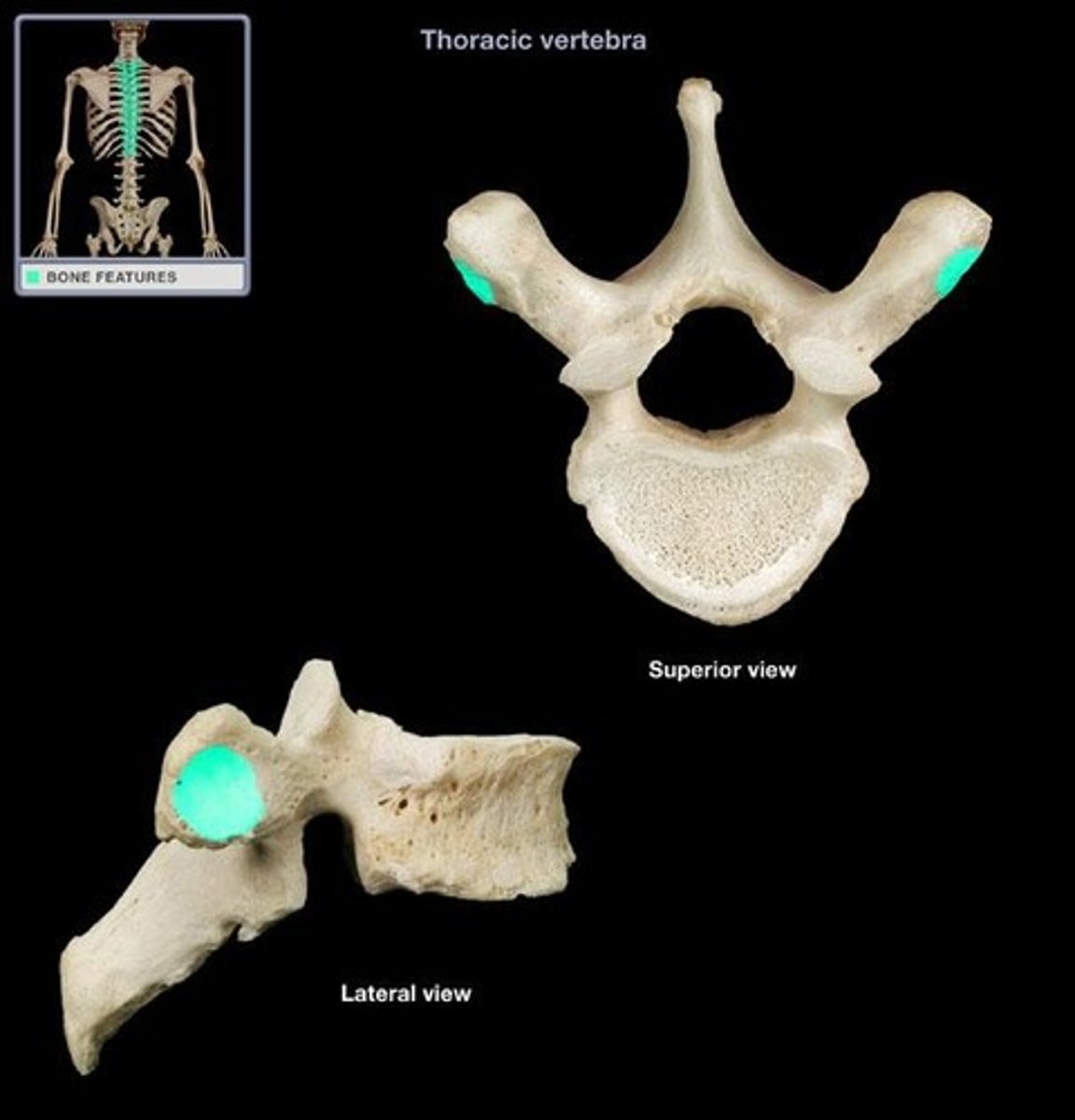
Costal facets
Two small articulating surfaces on each side of the thoracic vertebrae close to the origin of the vertebral arch that articulate with the heads of the corresponding ribs.
C3-C7 cervical vertebrae
Distinguished from the thoracic and lumbar vertebrae; they are the smallest, lightest vertebrae with a triangular vertebral foramen.
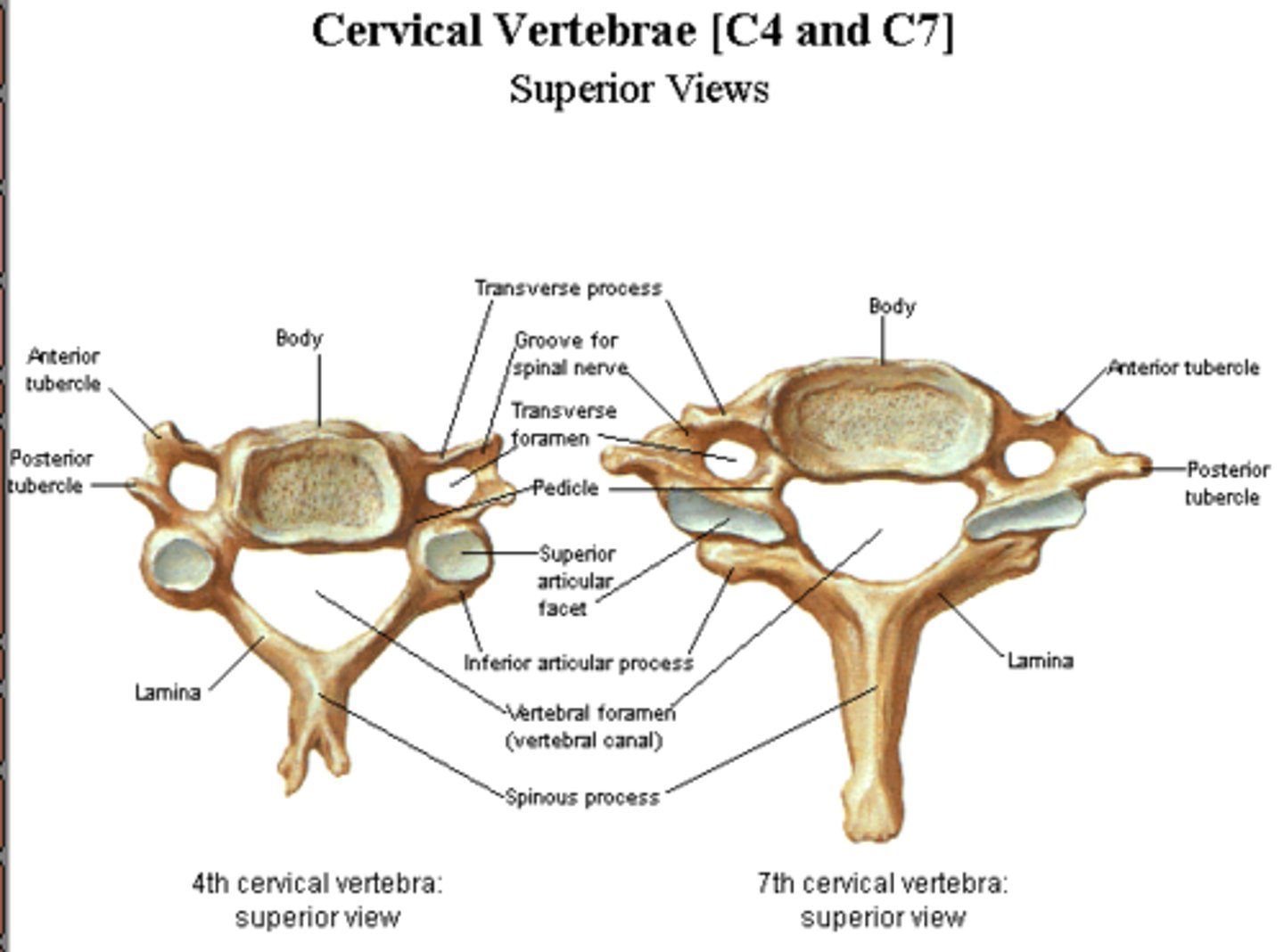
Bifurcated spinous process
The spinous process of the cervical vertebrae that is divided into two branches.
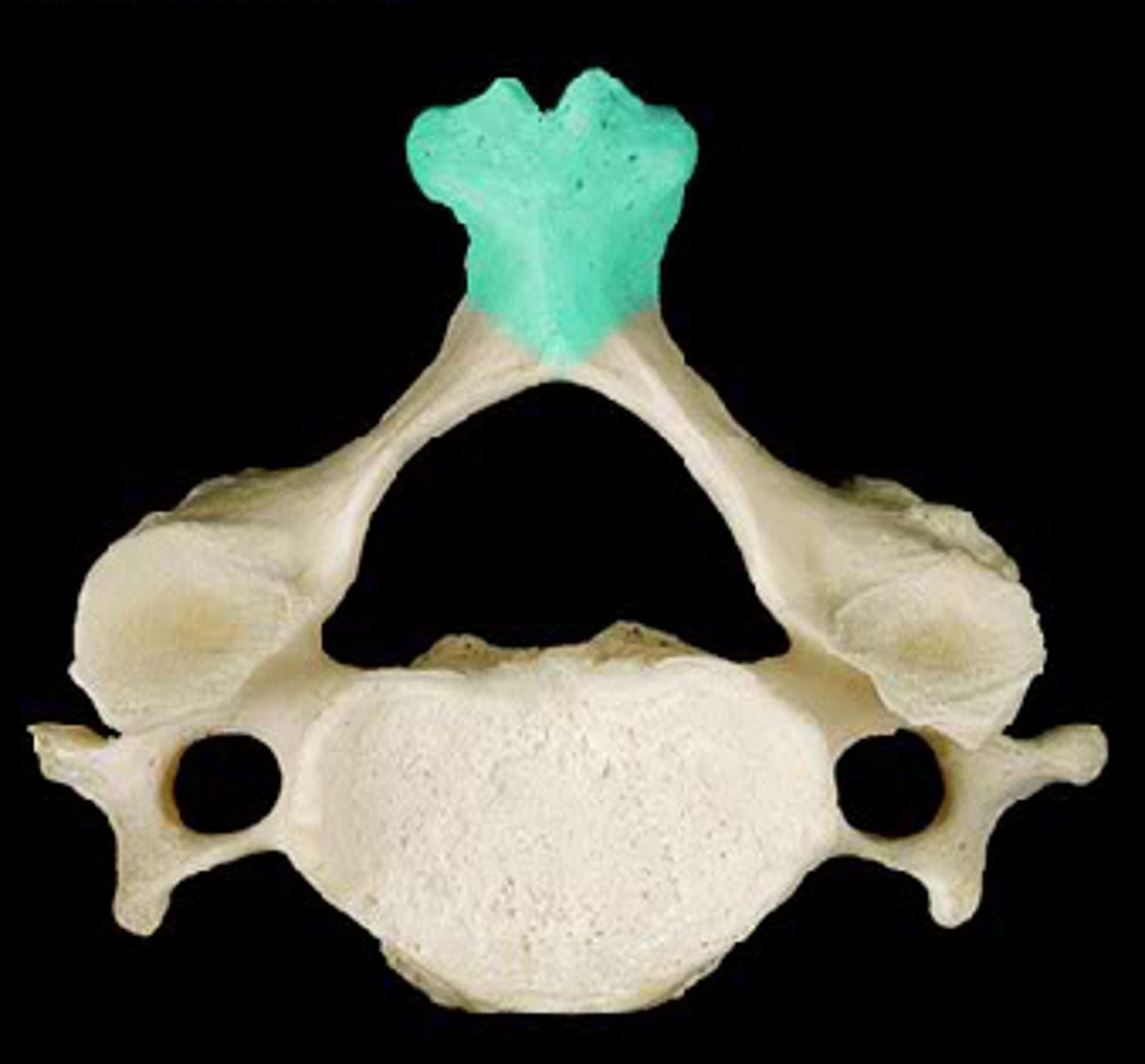
Vertebral arteries
Pass superiorly through the foramina in the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae on their way to the brain.
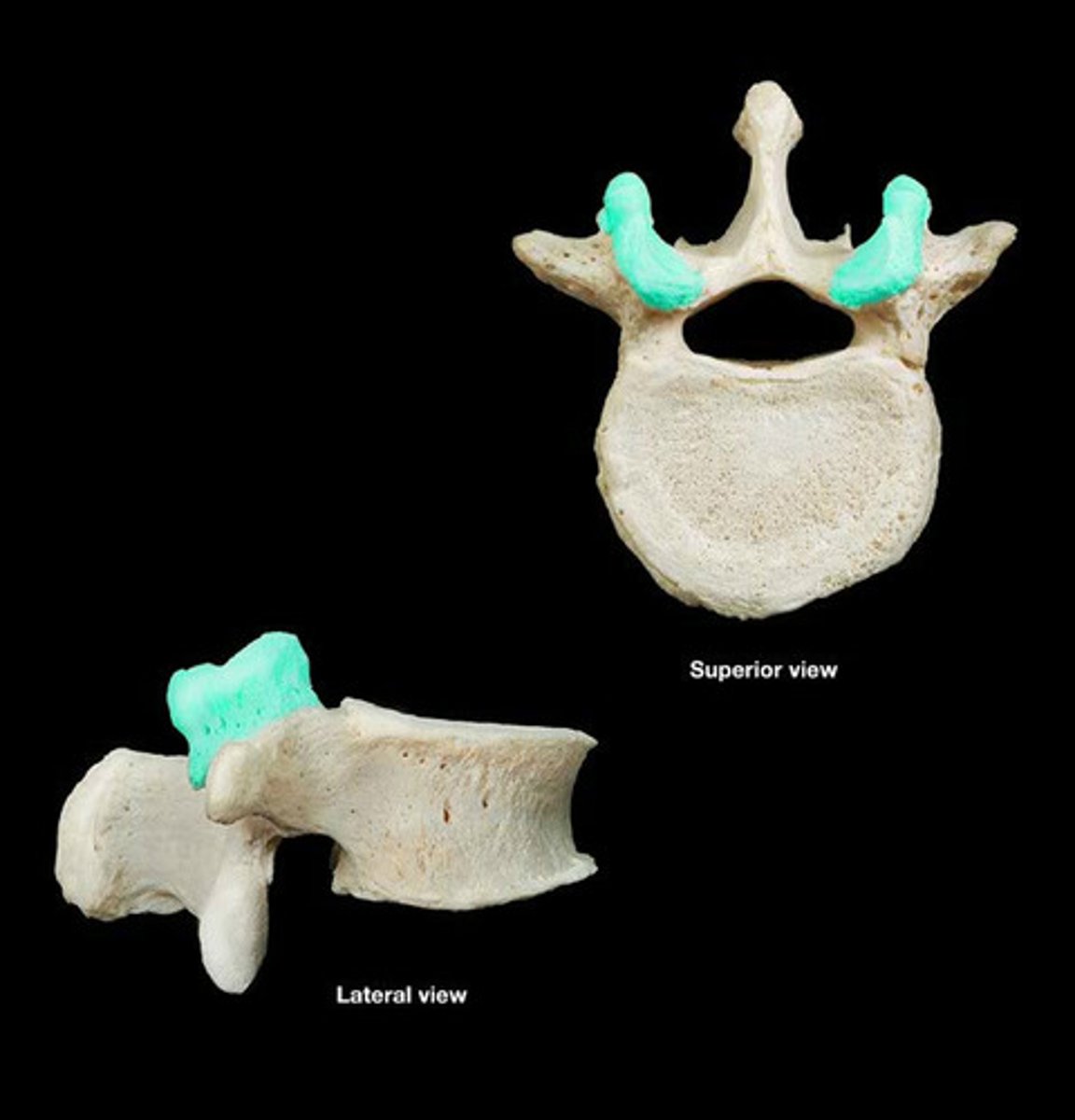
Superior articular facets
Facets on lumbar vertebrae that face posteromedial.
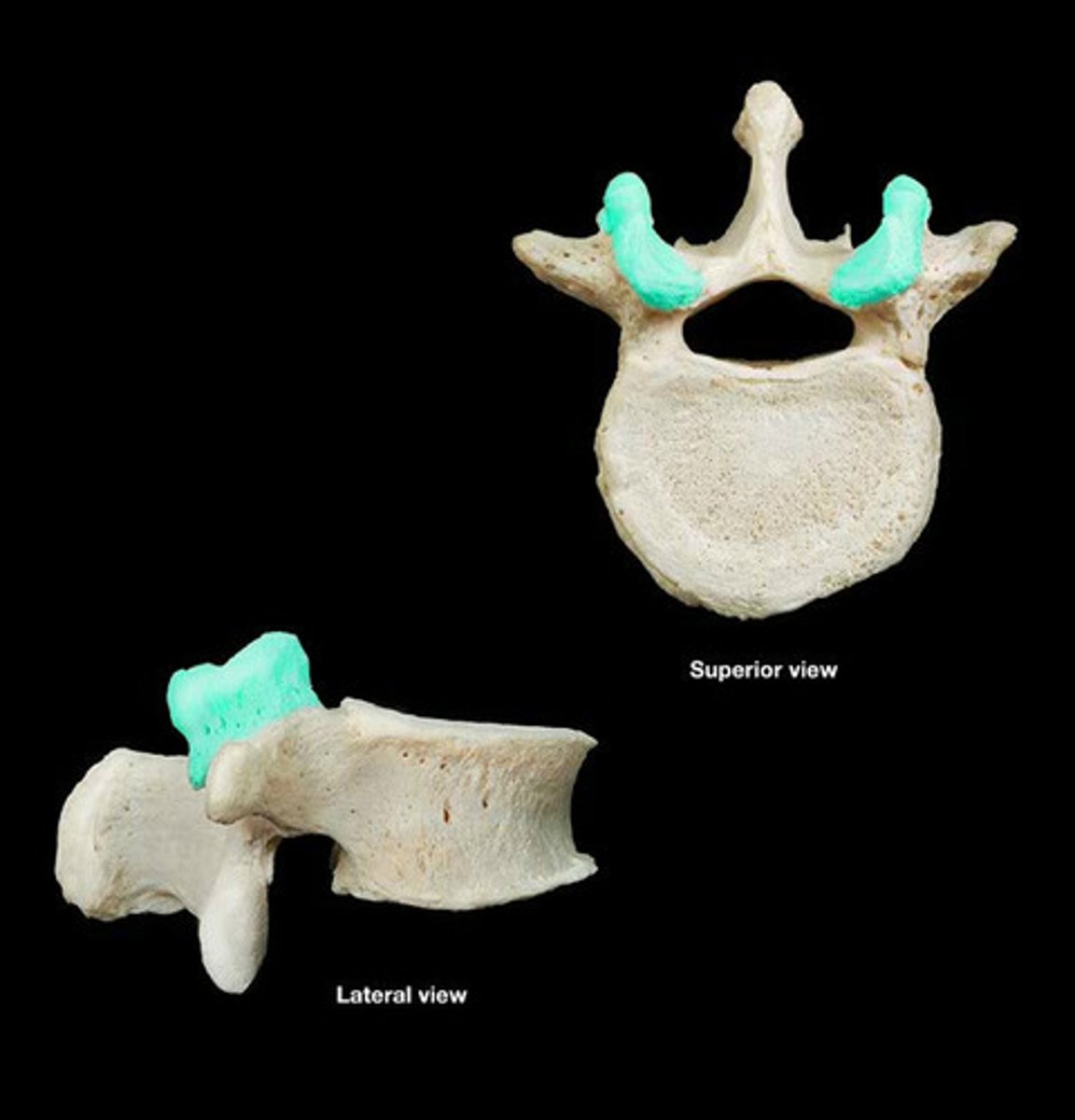
Inferior articular facets
Facets on lumbar vertebrae that are directed anterolaterally.
Spinal cord termination
The spinal cord ends at the superior edge of L2.
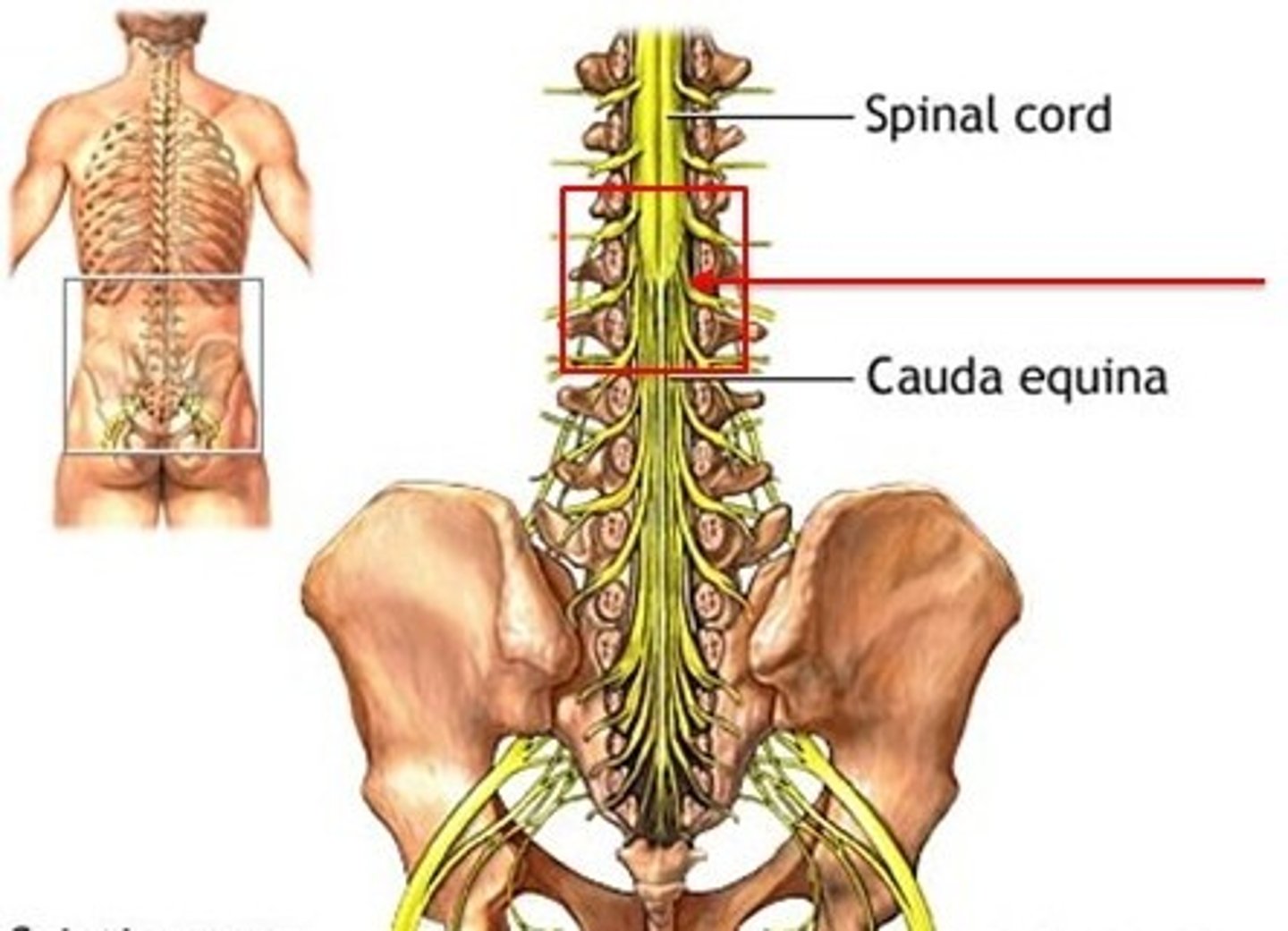
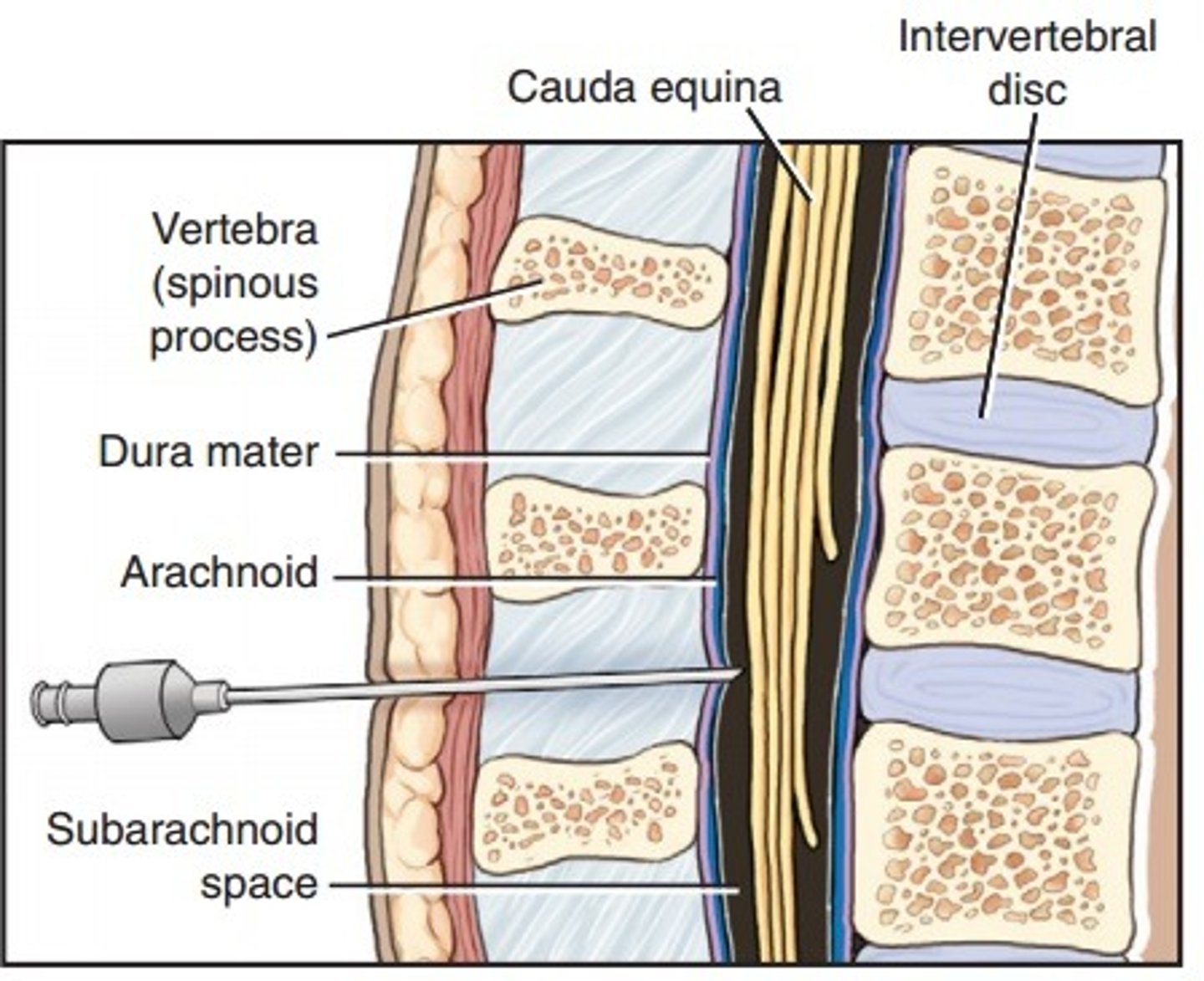
Cerebrospinal fluid
Fluid that fills the outer covering of the spinal cord, extending beyond L2.
Lumbar puncture
A procedure for examining cerebrospinal fluid, typically done between L3 and L4 or L4 and L5.
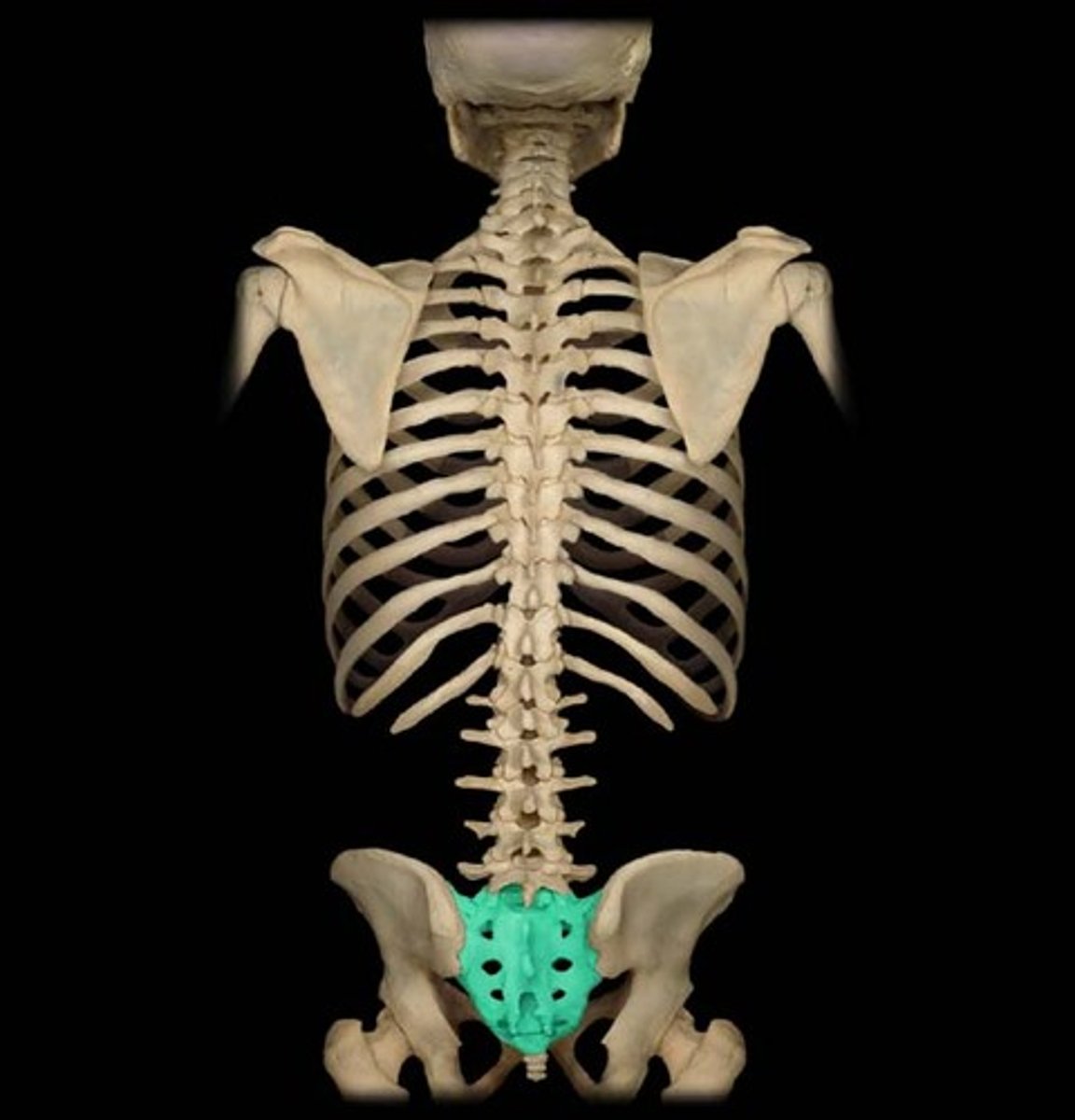
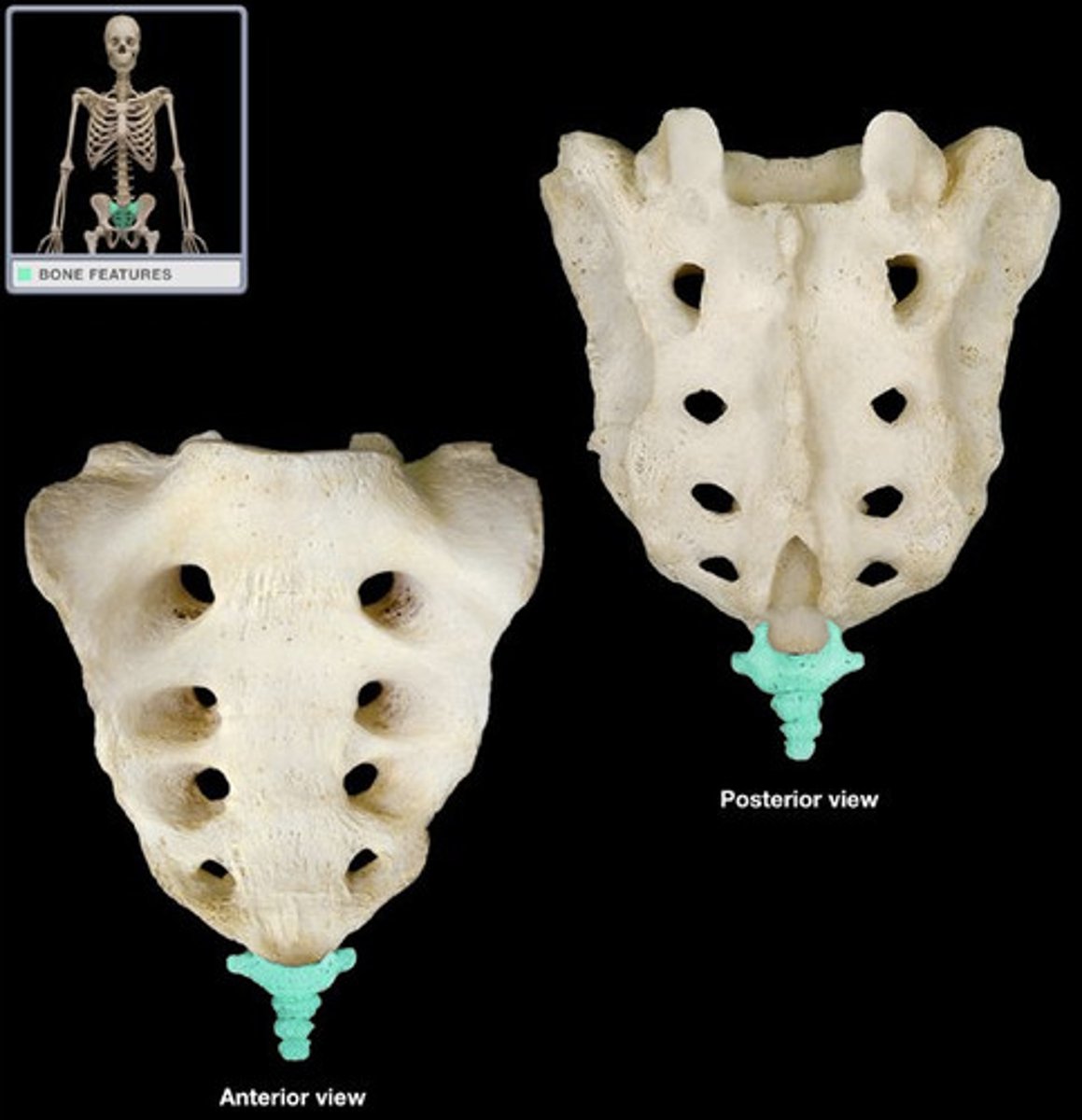
Sacrum
A composite bone formed from the fusion of five vertebrae.
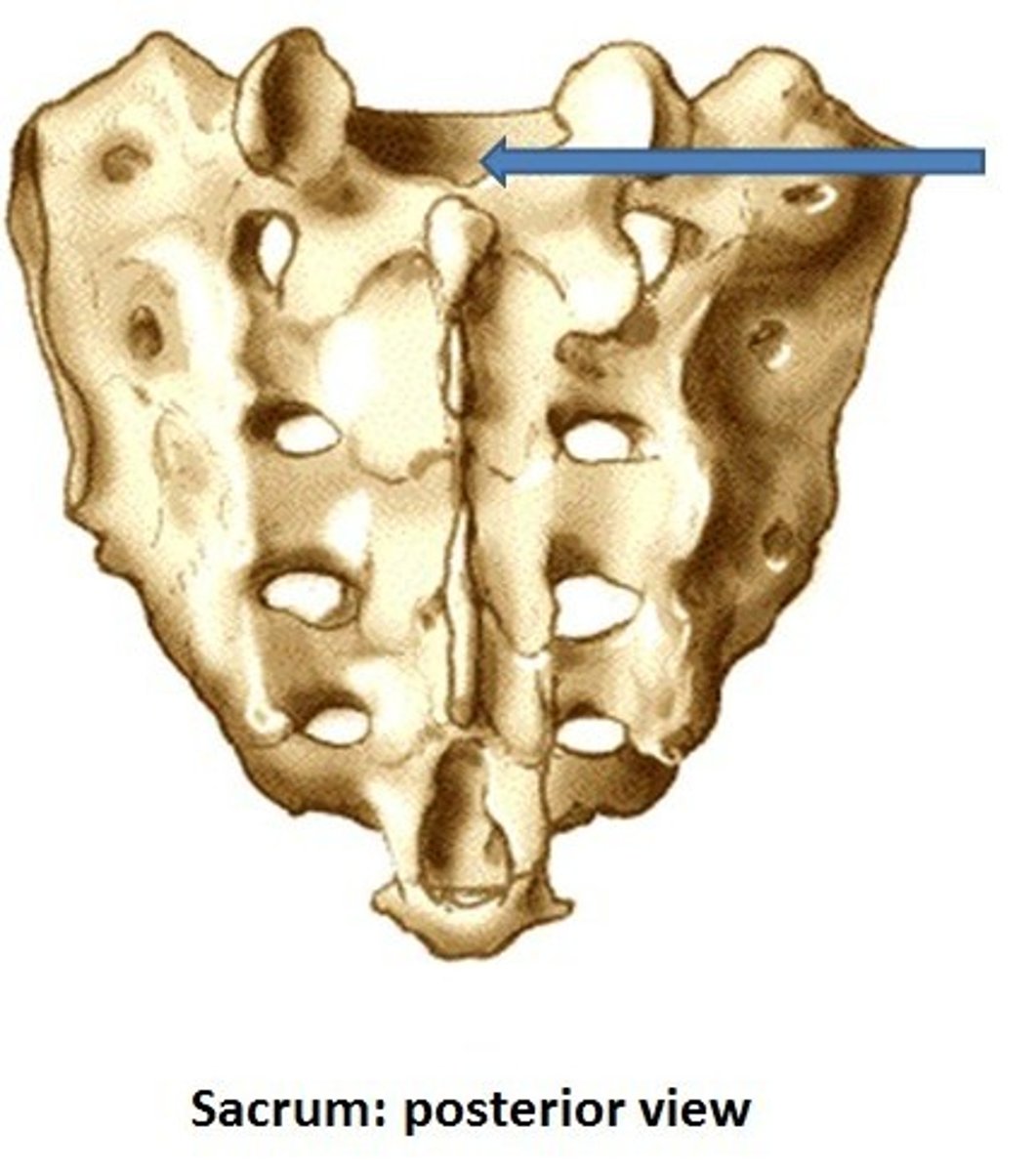
Median sacral crest
A remnant of the spinous processes of the fused vertebrae in the sacrum.
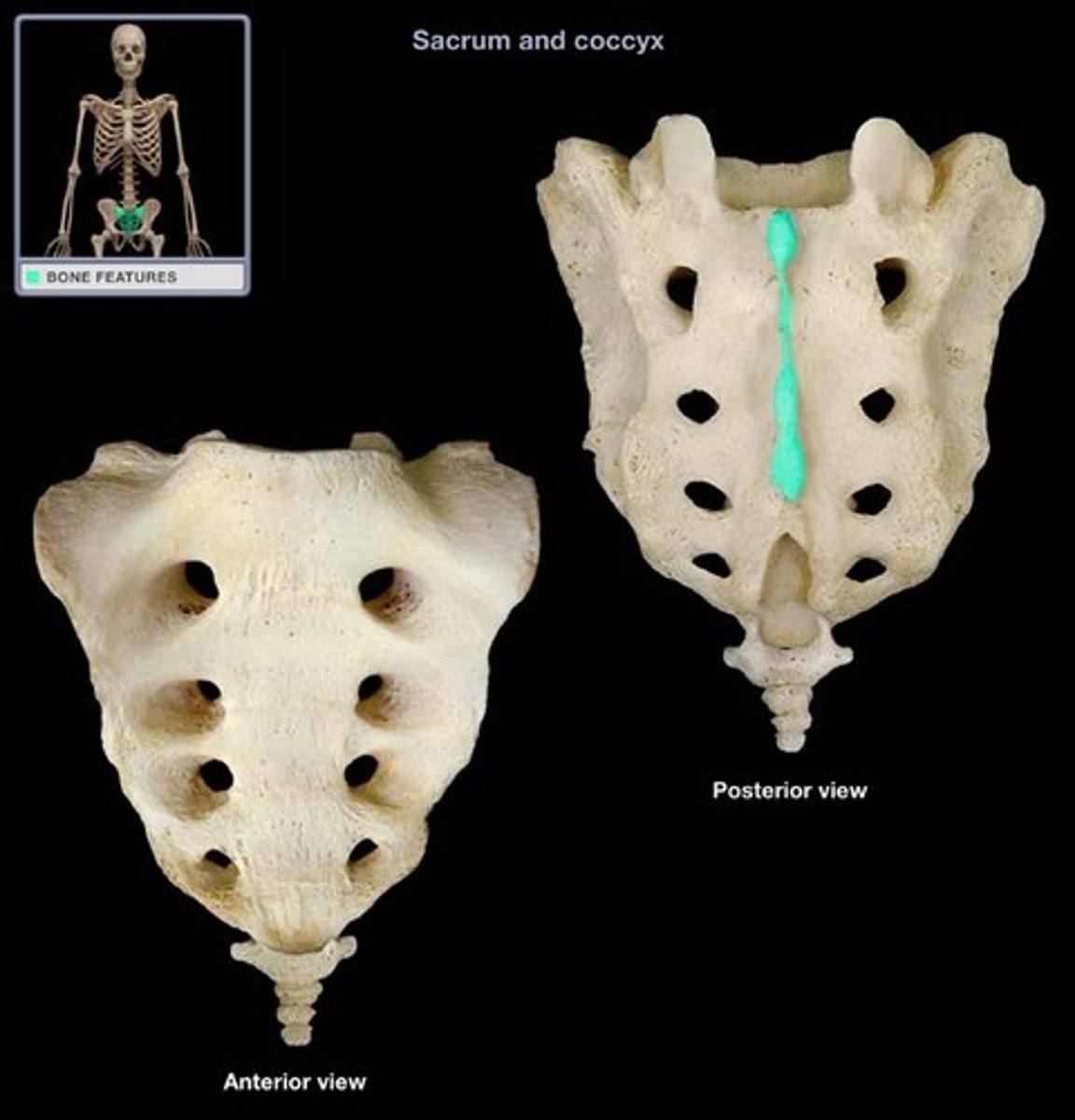
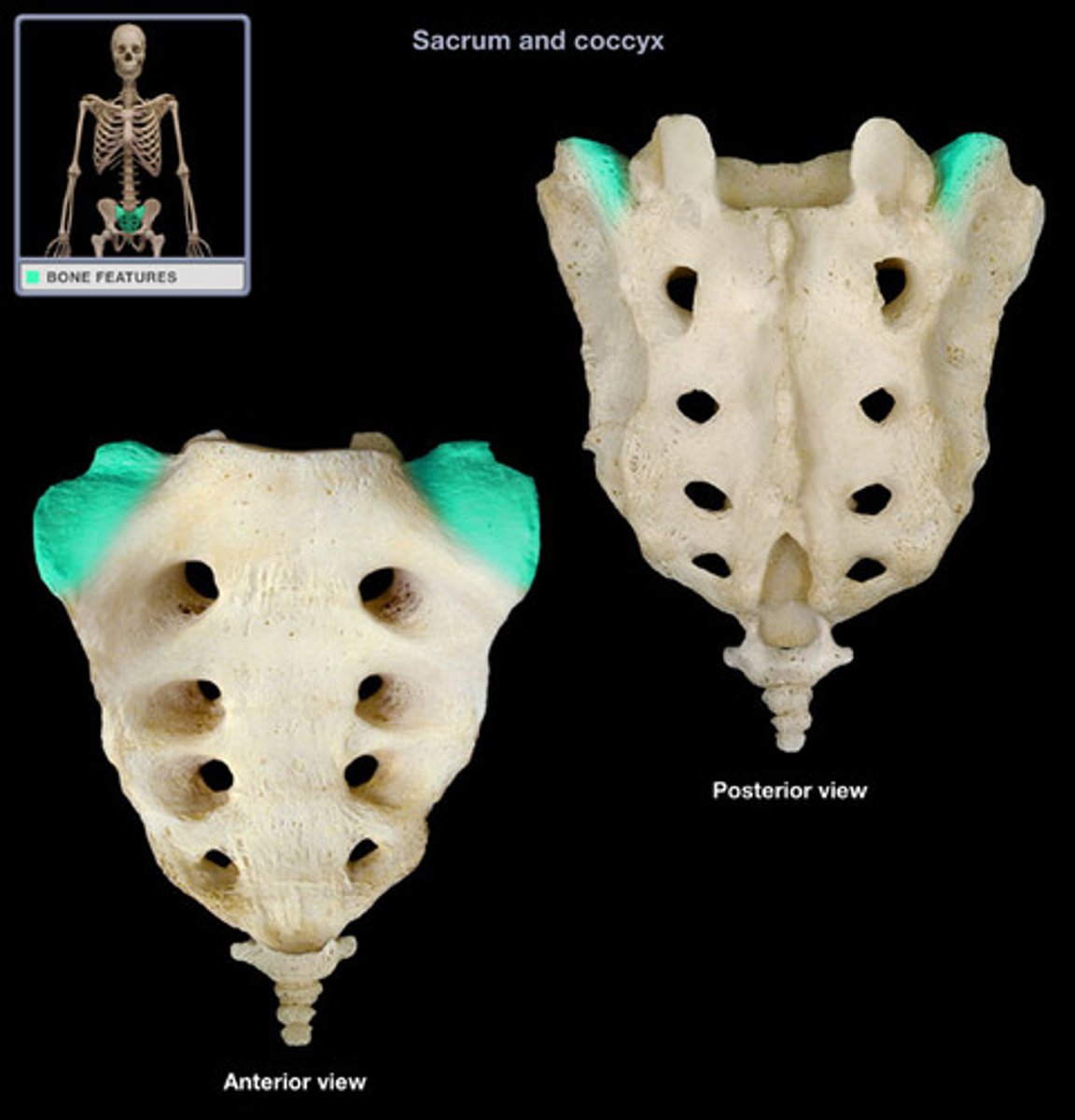
Alae
Winglike structures formed by the fusion of transverse processes that articulate laterally with the hip bones.
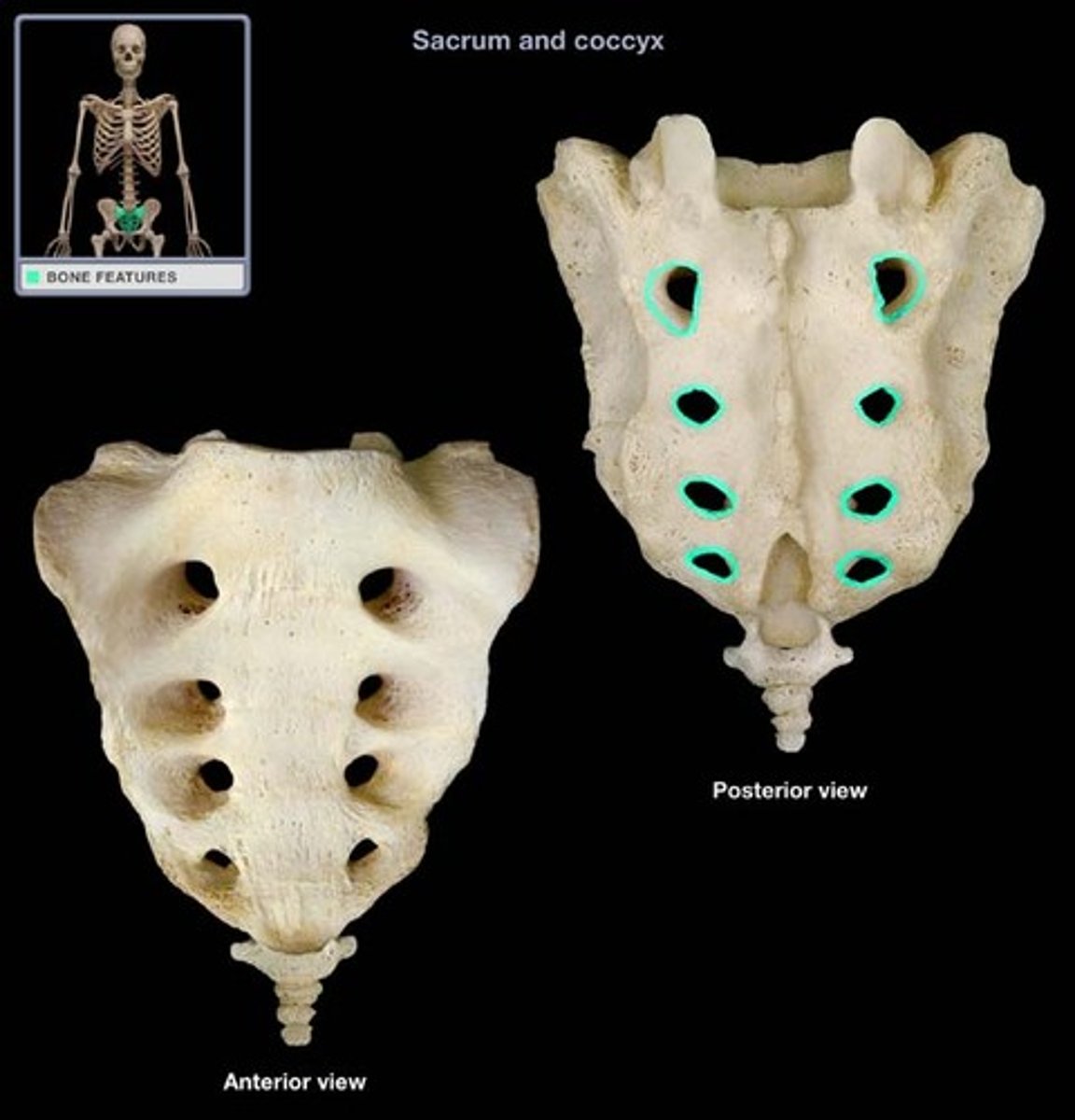
Sacral foramina
Openings that allow blood vessels and nerves to pass, located at either end of the ridges on the sacrum.
Sacral canal
The continuation of the vertebral canal inside the sacrum.
Sacral hiatus
An enlarged opening at the termination of the sacral canal near the coccyx.
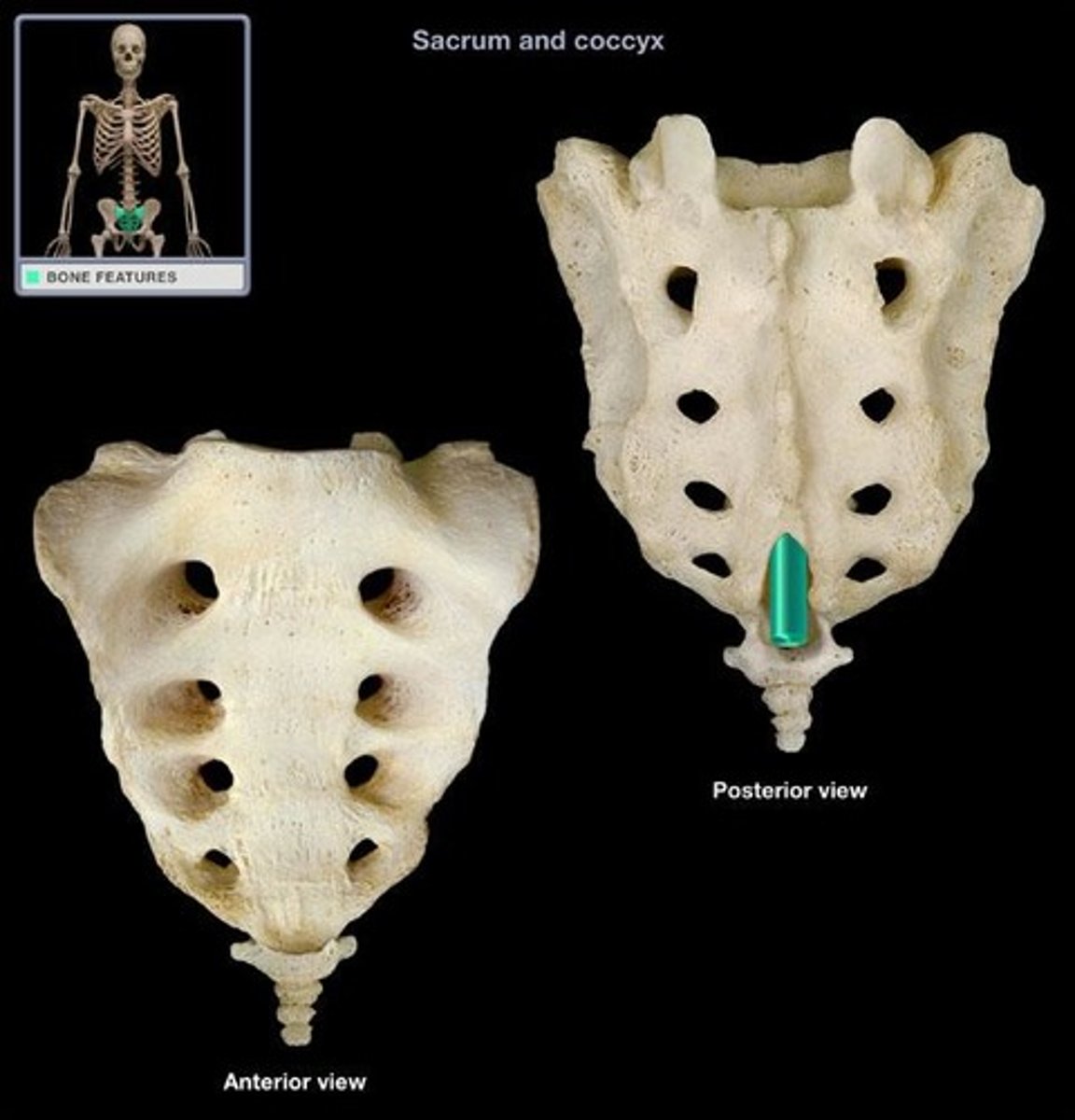
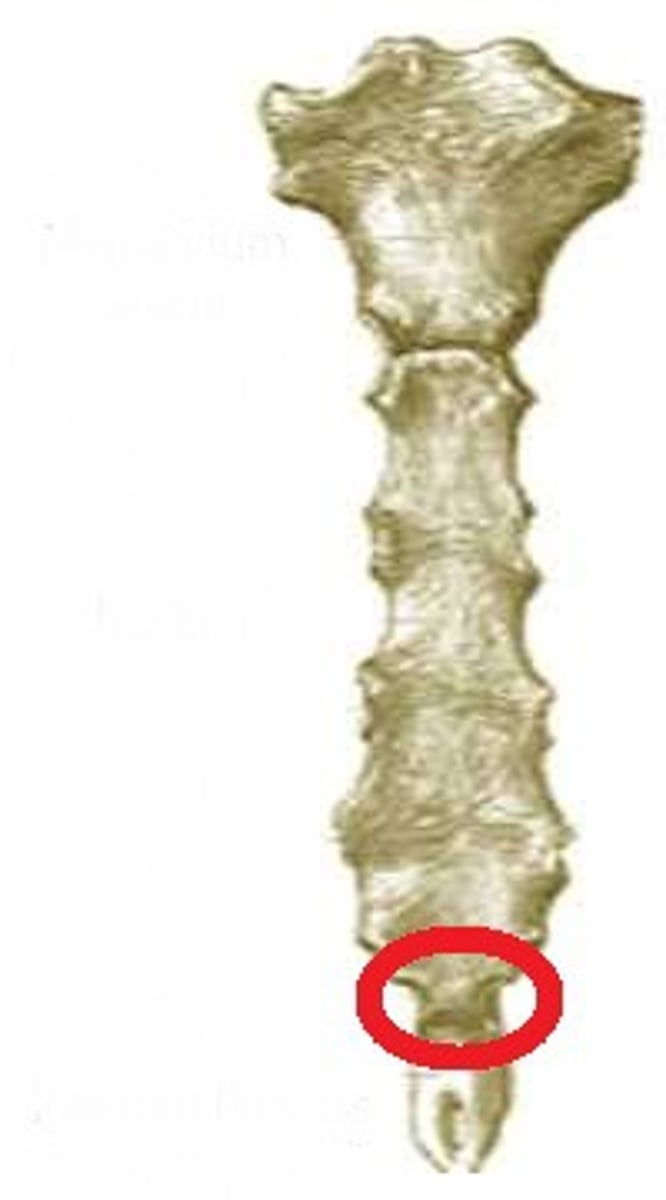
Coccyx
The human tailbone, formed from the fusion of three to five small irregularly shaped vertebrae.
Thoracic cage
The bony thorax composed of the sternum, ribs, thoracic vertebrae, and cartilages.
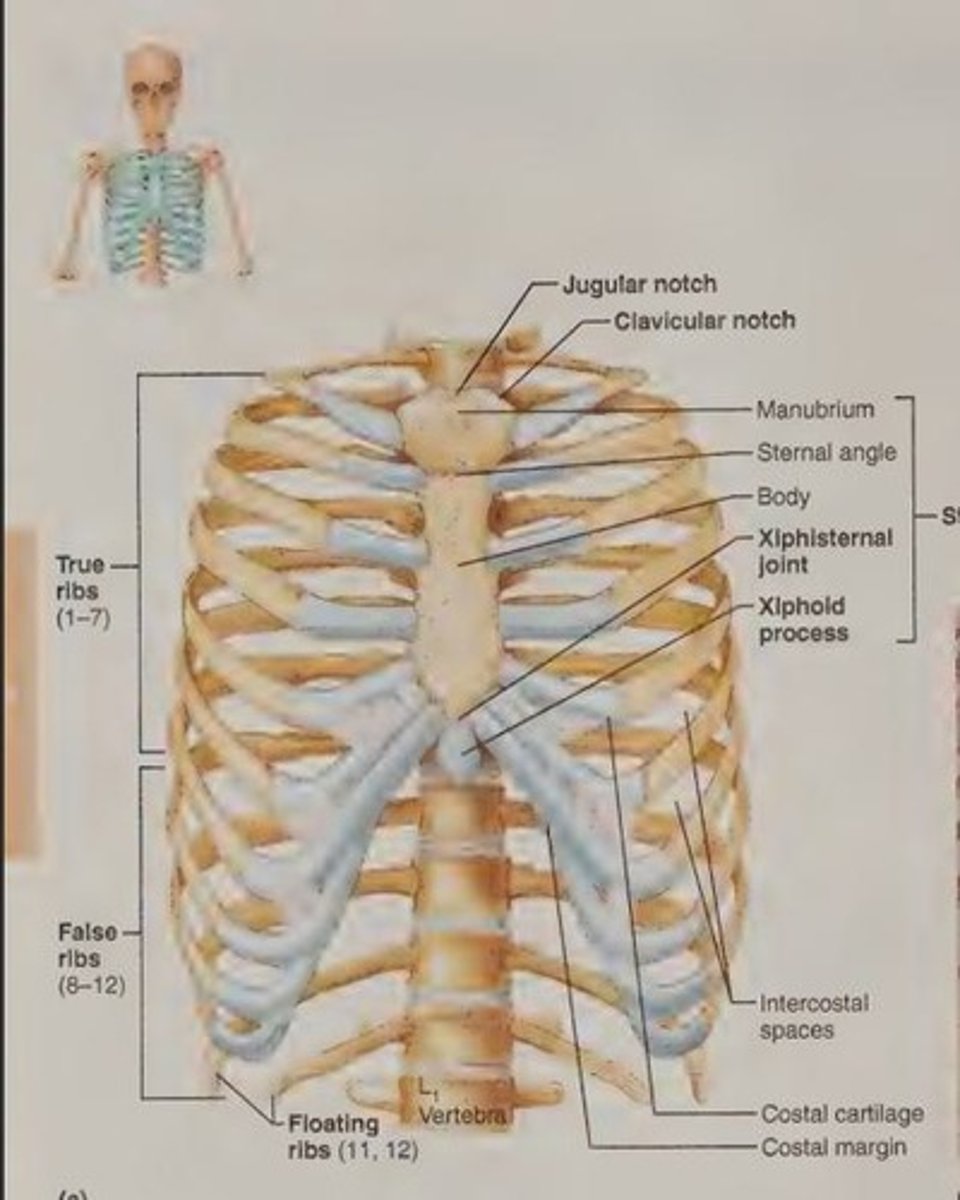
Sternum
A flat bone resulting from the fusion of three bones: the manubrium, body, and xiphoid process.
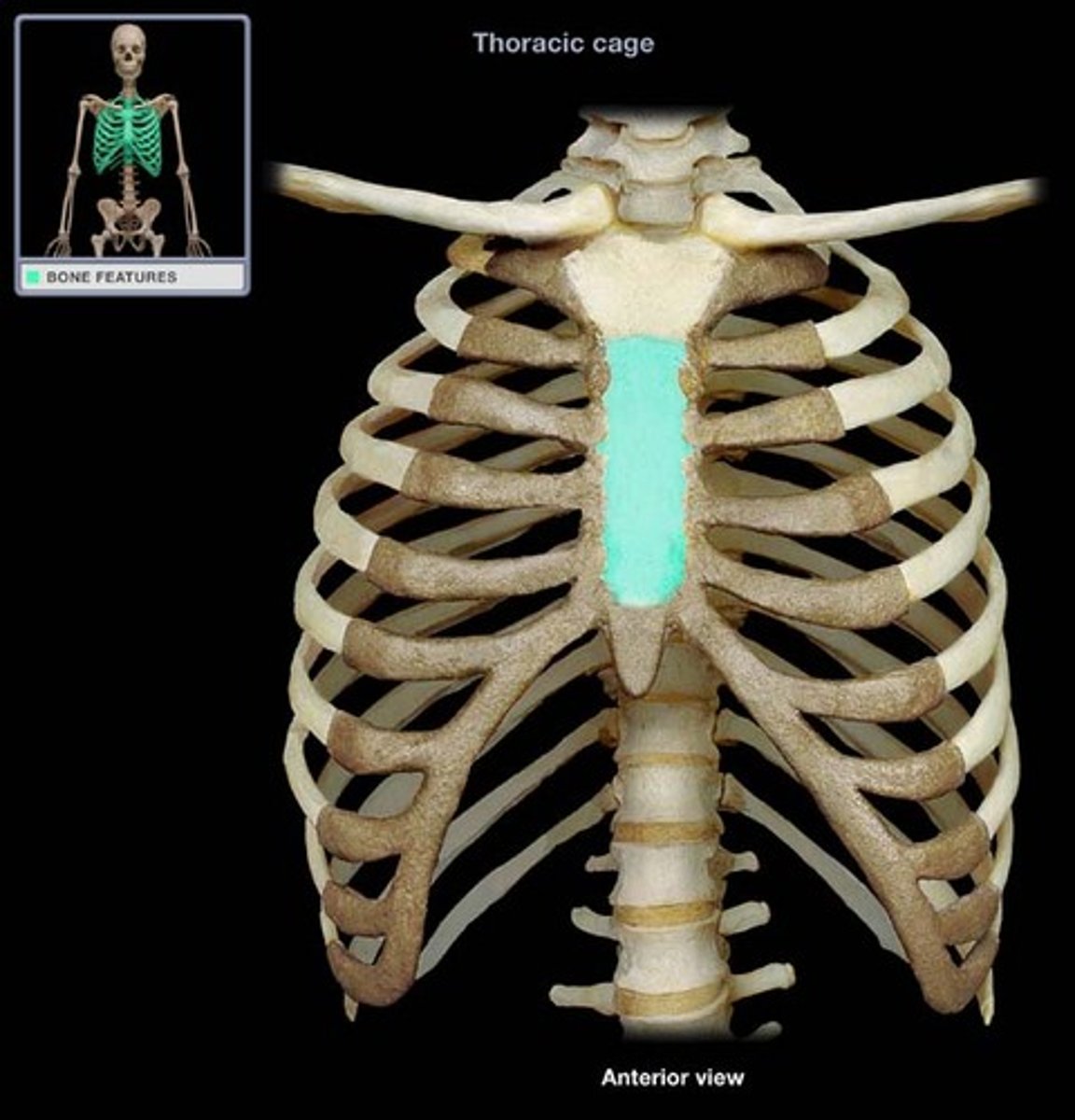
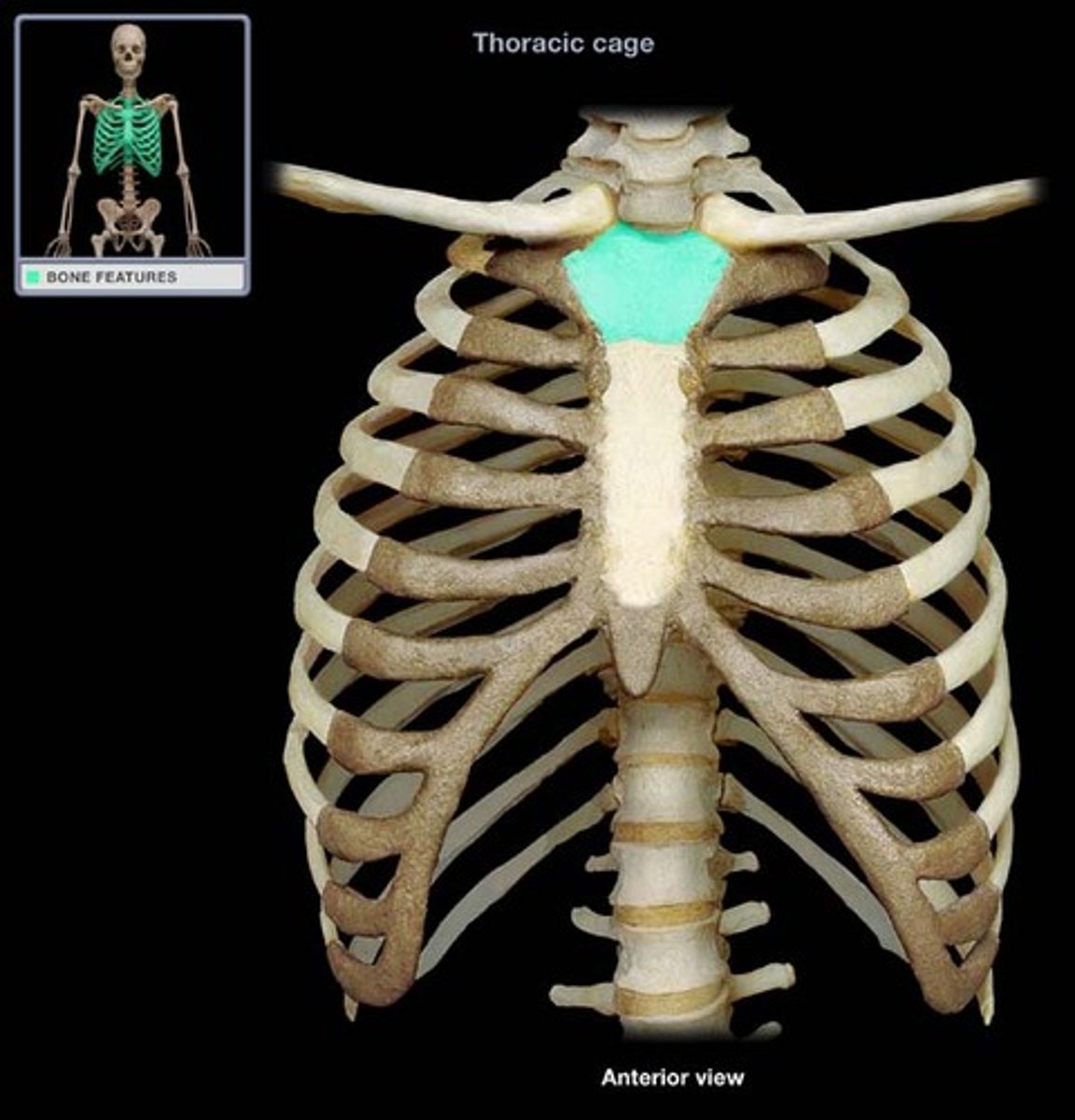
Manubrium
The superiormost part of the sternum that articulates with the clavicle.
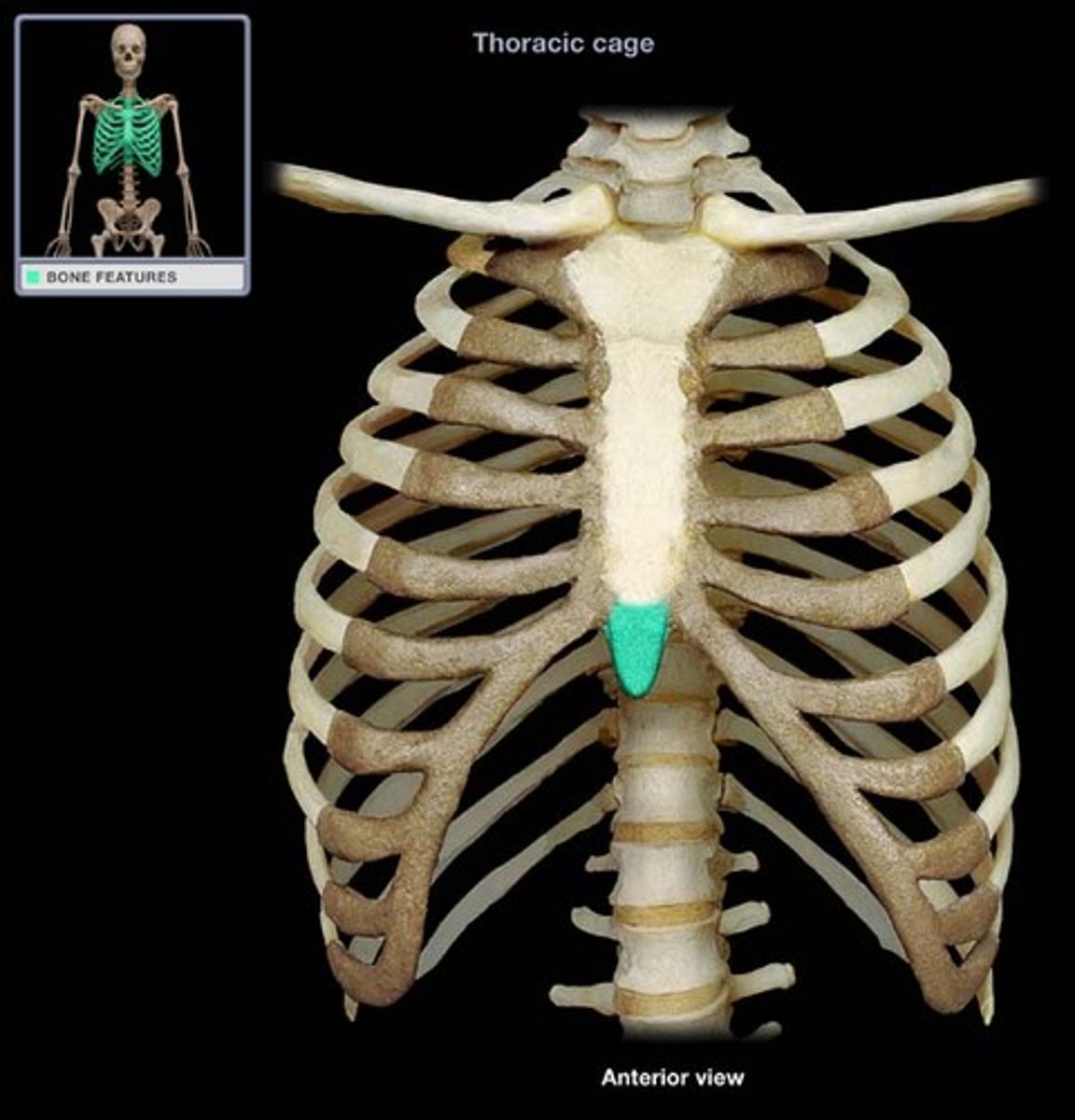
Xiphoid process
The inferior end of the sternum that lies at the level of the fifth intercostal space.
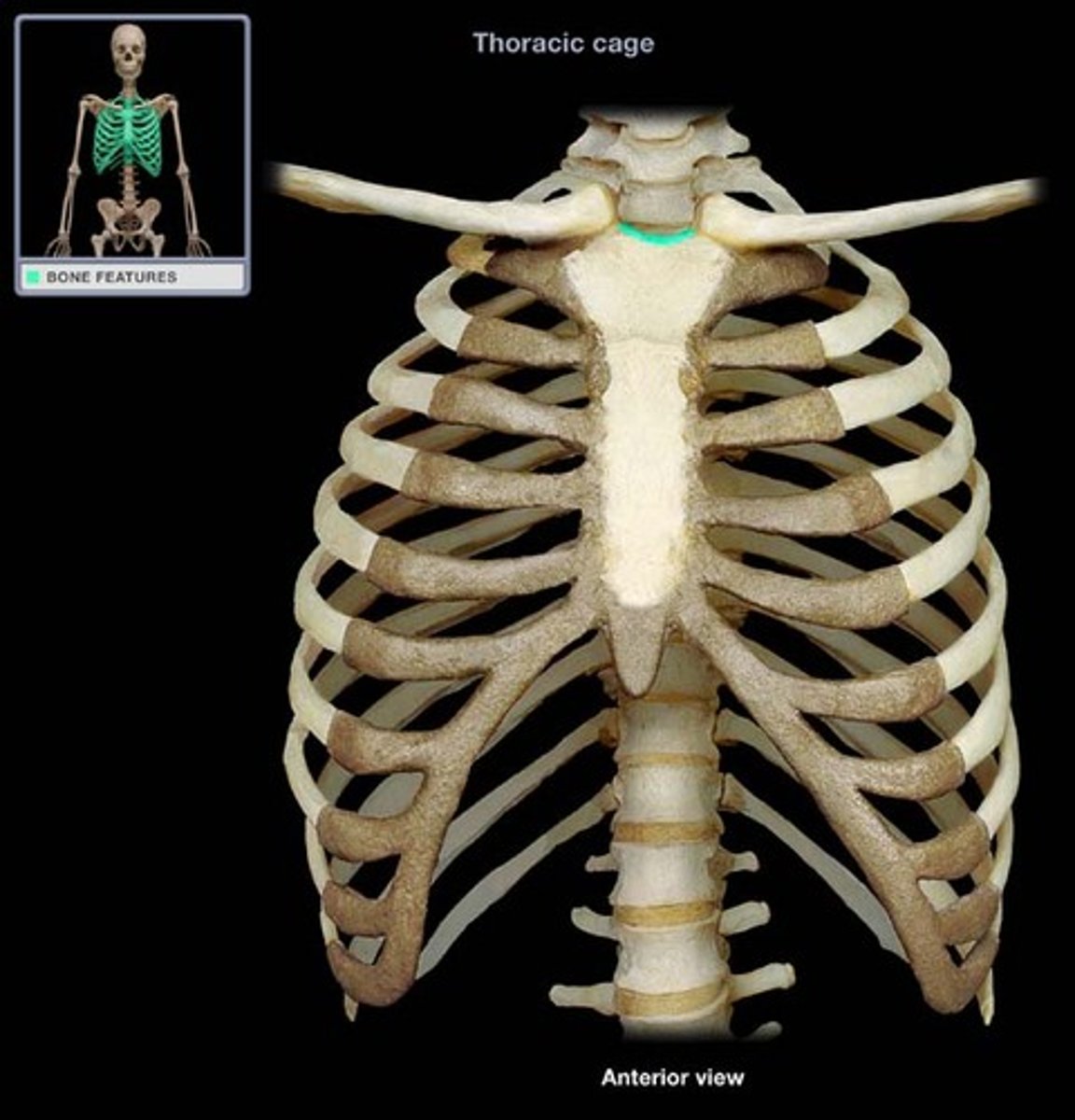
Jugular notch
The concave upper border of the manubrium, easily palpated and generally at the level of the disc between the second and third thoracic vertebrae.
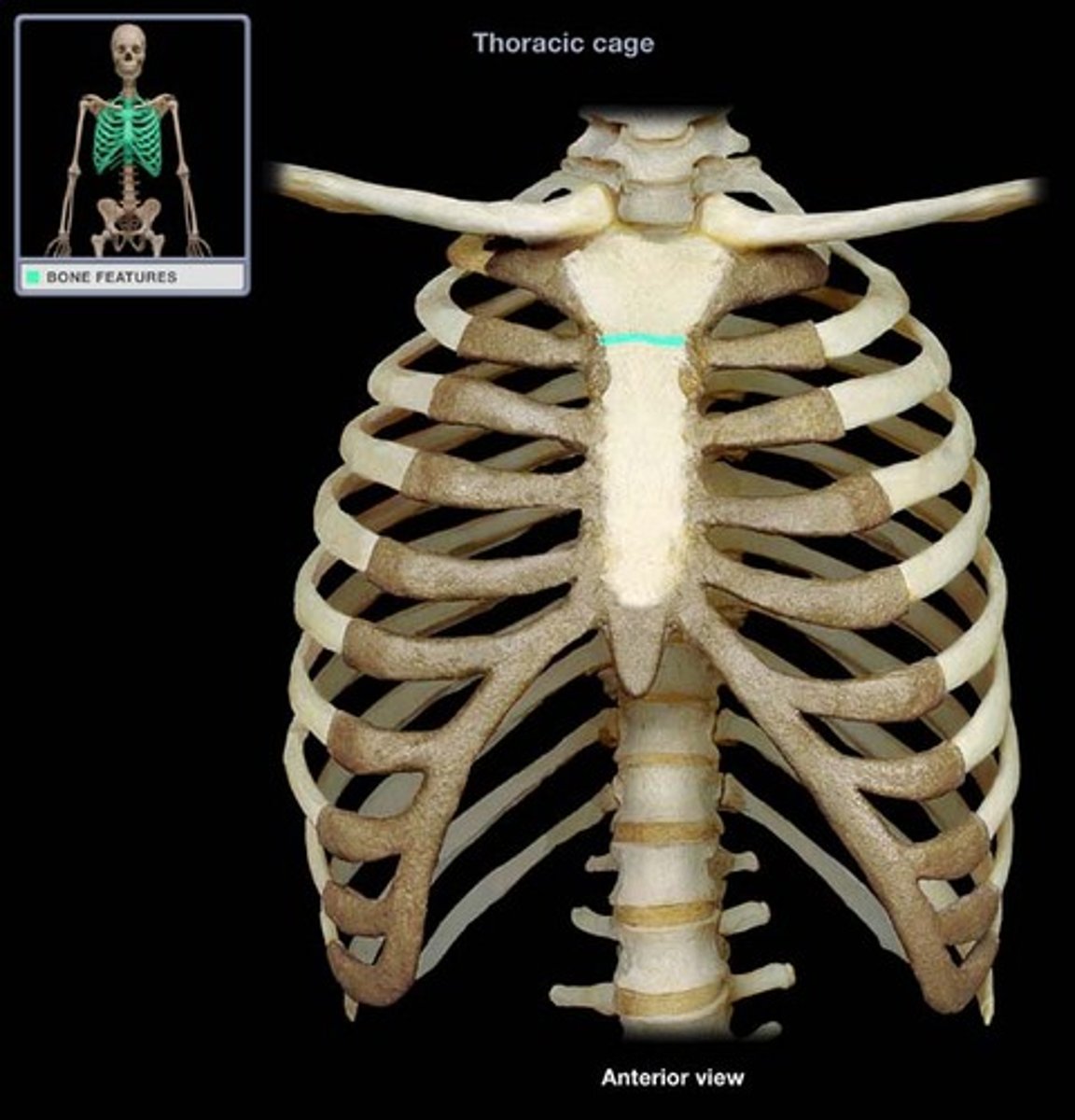
Sternal angle
The angle formed by the meeting of the manubrium and body of the sternum, serving as a reference point for counting ribs.
Xiphisternal joint
The point where the sternal body and xiphoid process fuse, located at the level of the ninth thoracic vertebra.
Ribs
The 12 pairs of ribs that form the walls of the thoracic cage, articulating posteriorly with the vertebral column.
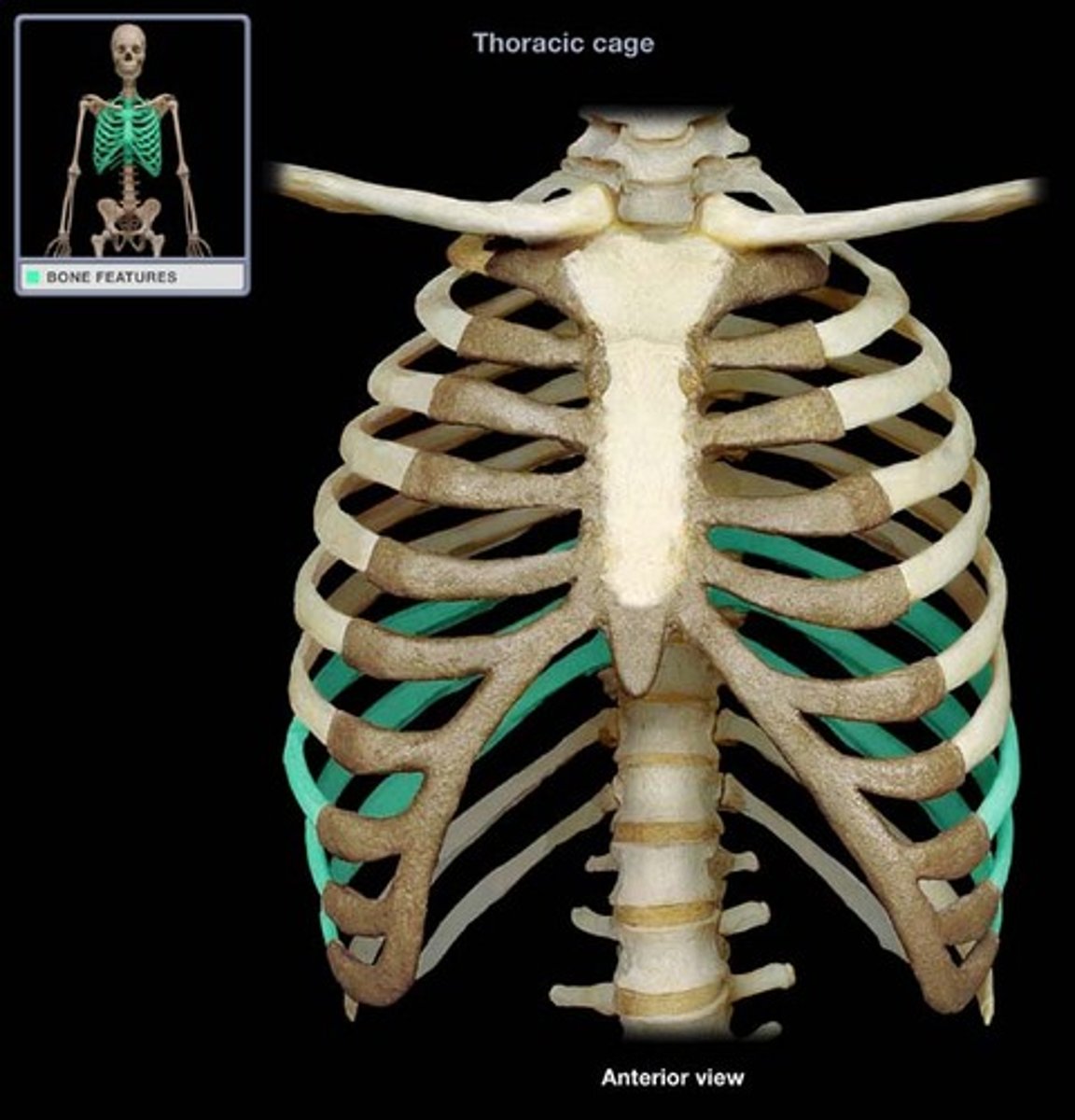
True ribs
The first seven pairs of ribs that attach directly to the sternum by their own costal cartilages.
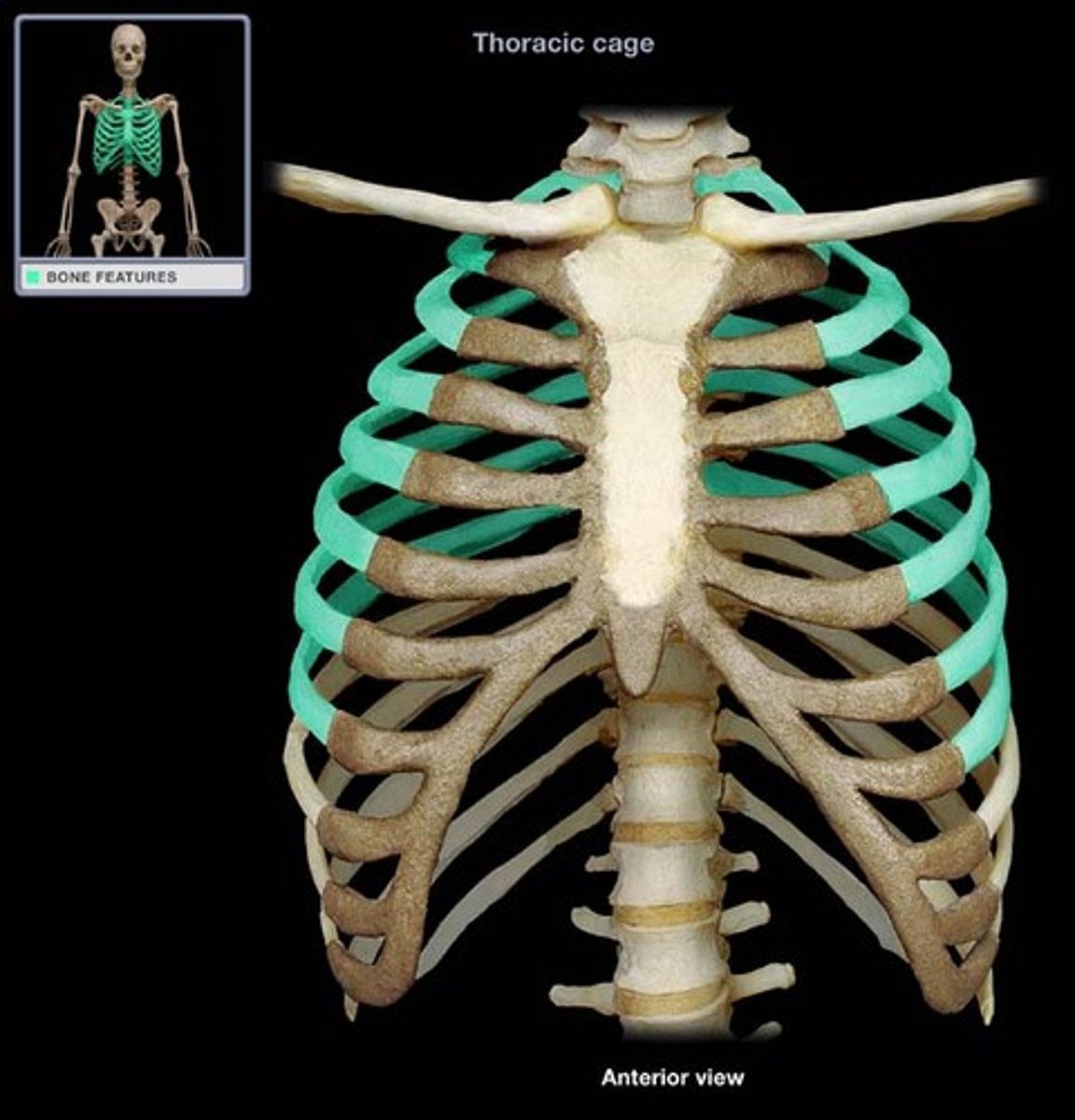
False ribs
The next five pairs of ribs that attach indirectly to the sternum or entirely lack a sternal attachment.
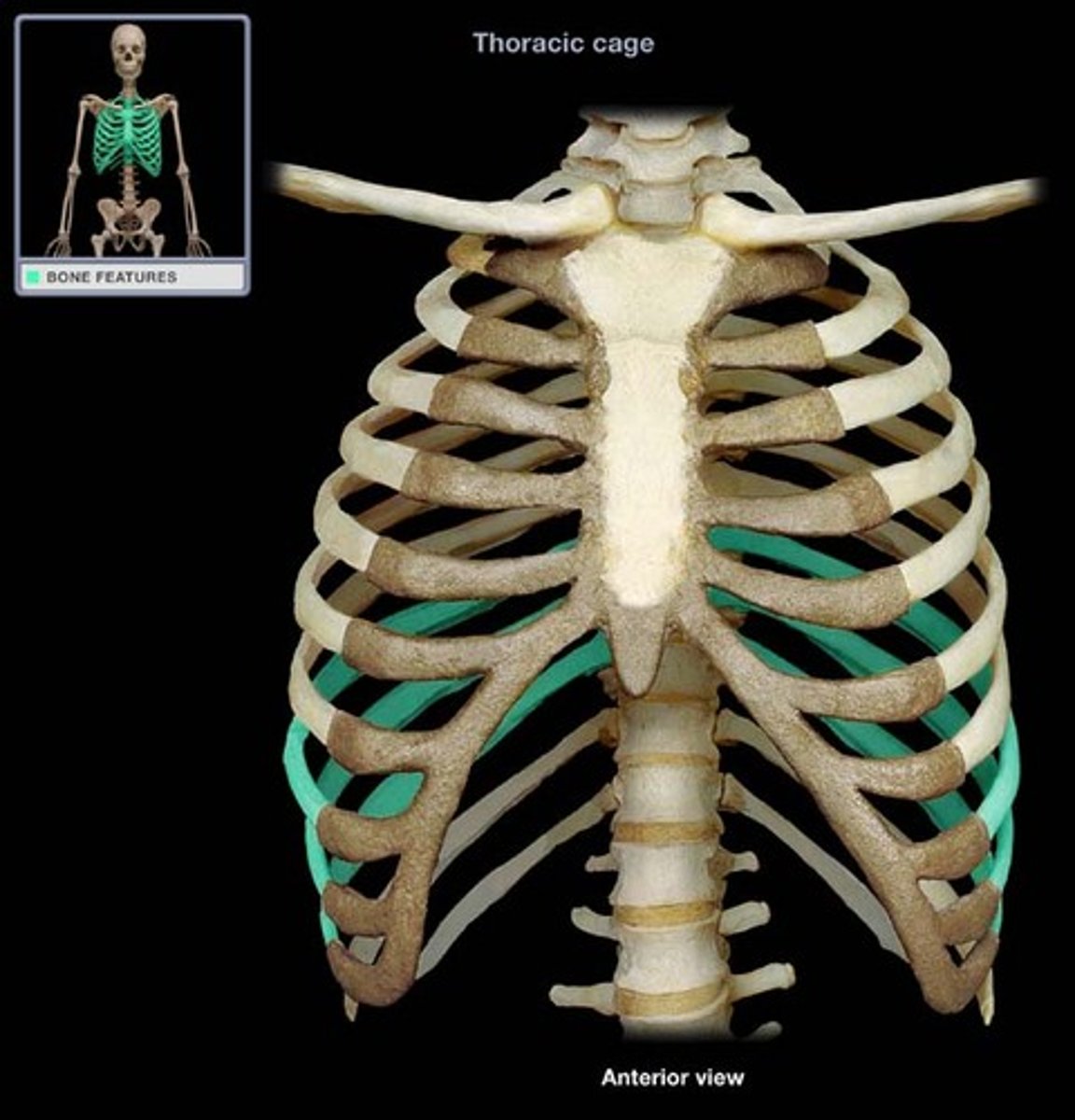
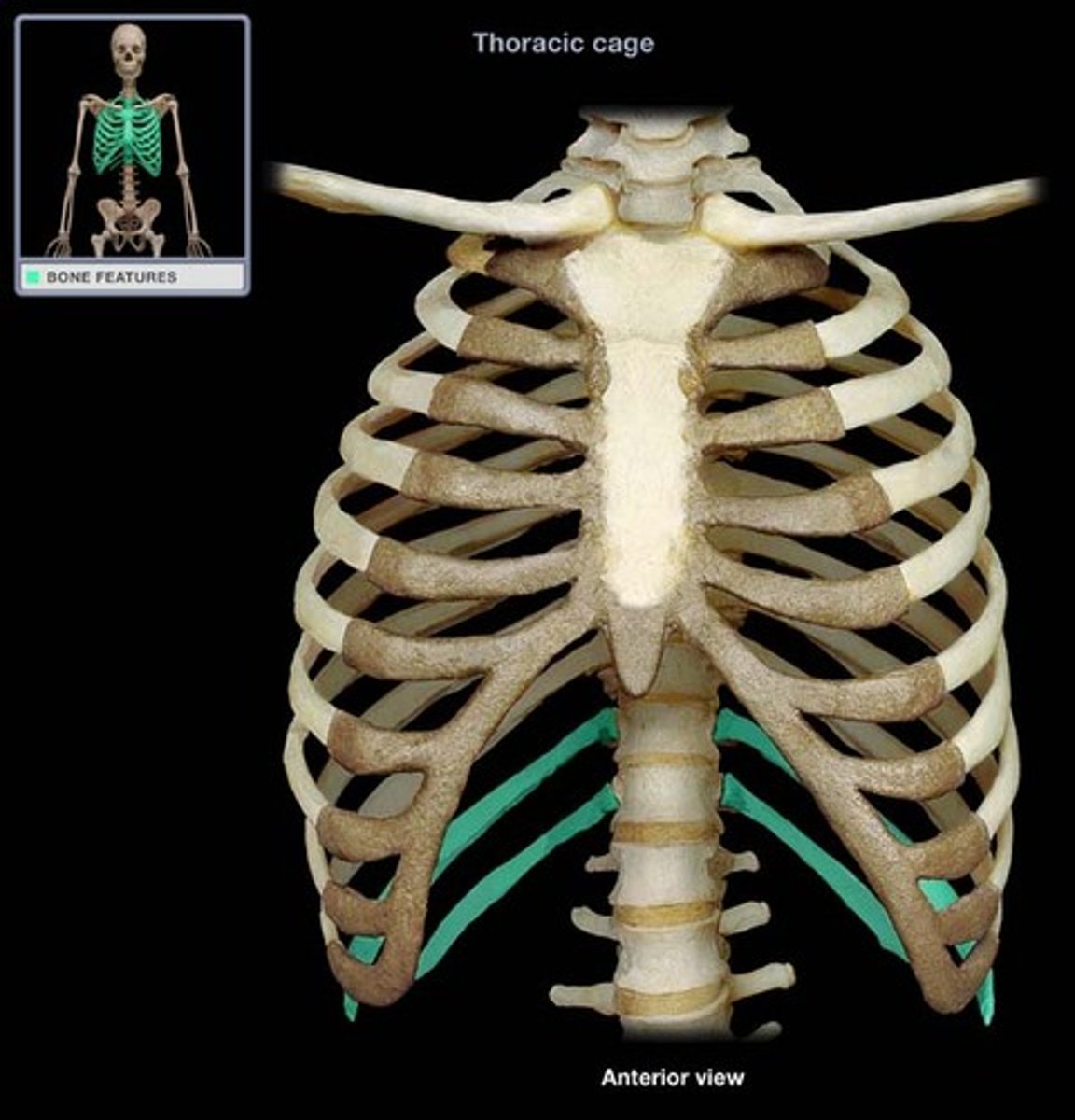
Vertebrochondral ribs
Ribs 8-10 that have indirect cartilage attachments to the sternum via the costal cartilage of rib 7.
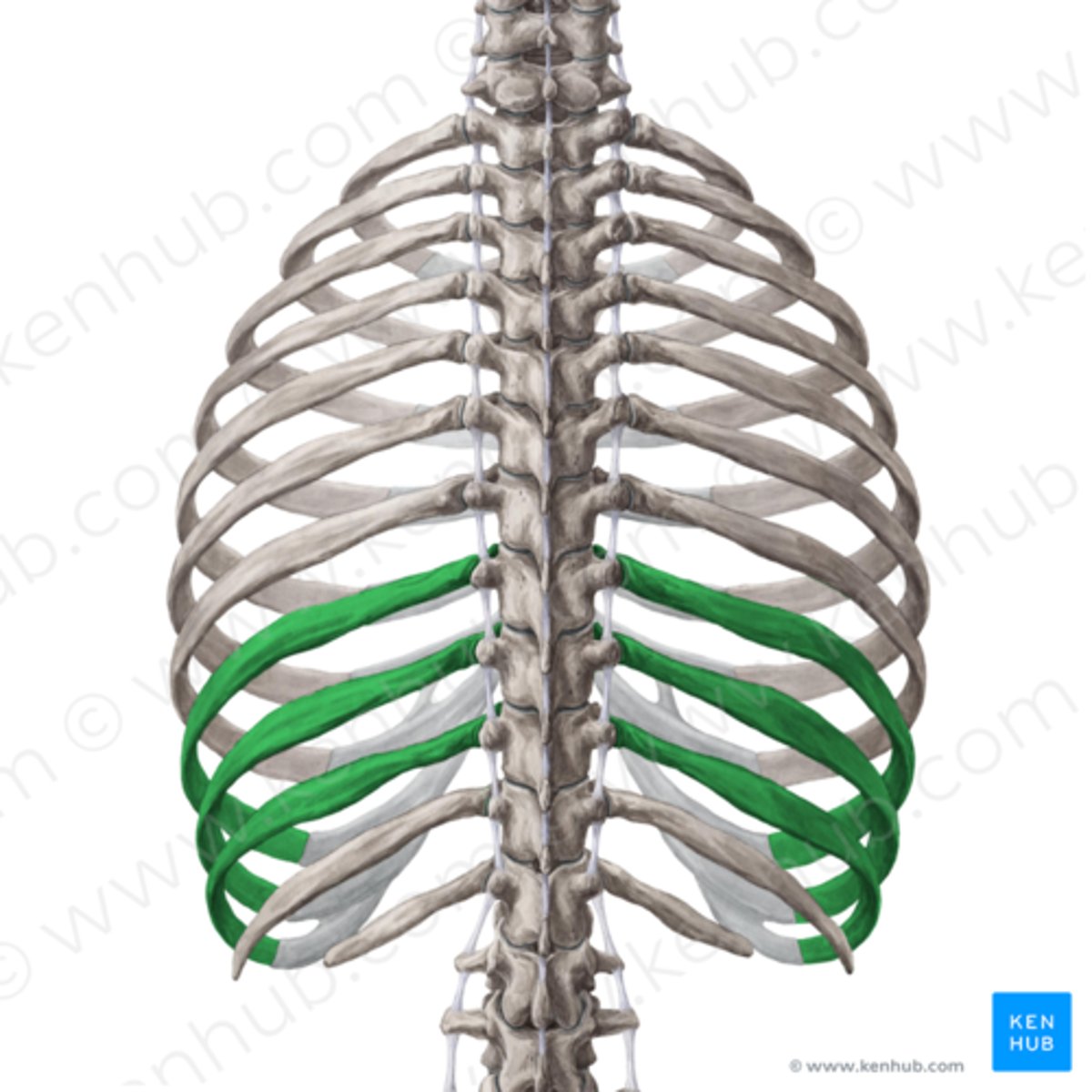
Floating ribs
The last two pairs of ribs that have no sternal attachment.
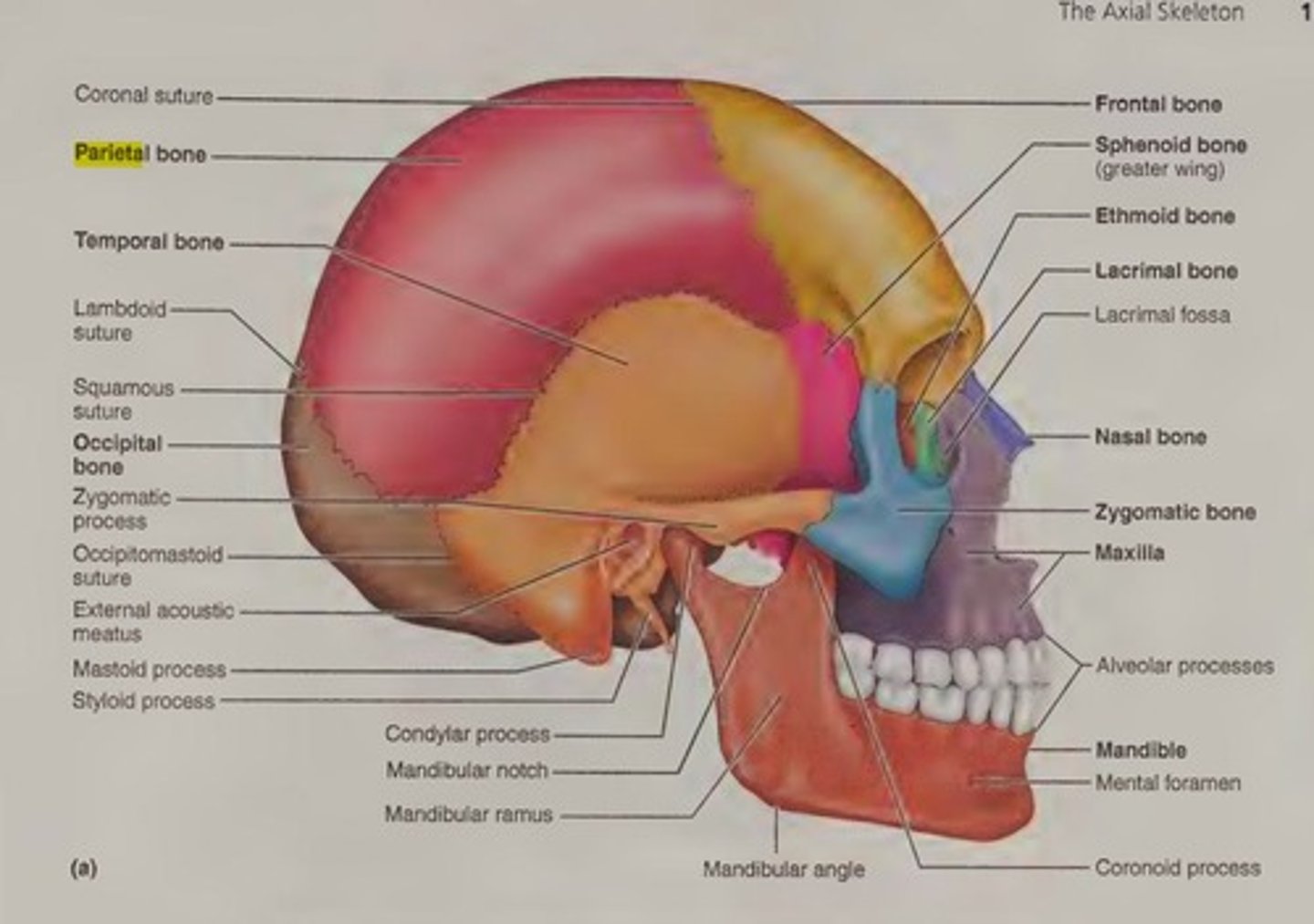
Parietal bone
A bone forming the central side and upper back part of each side of the skull.
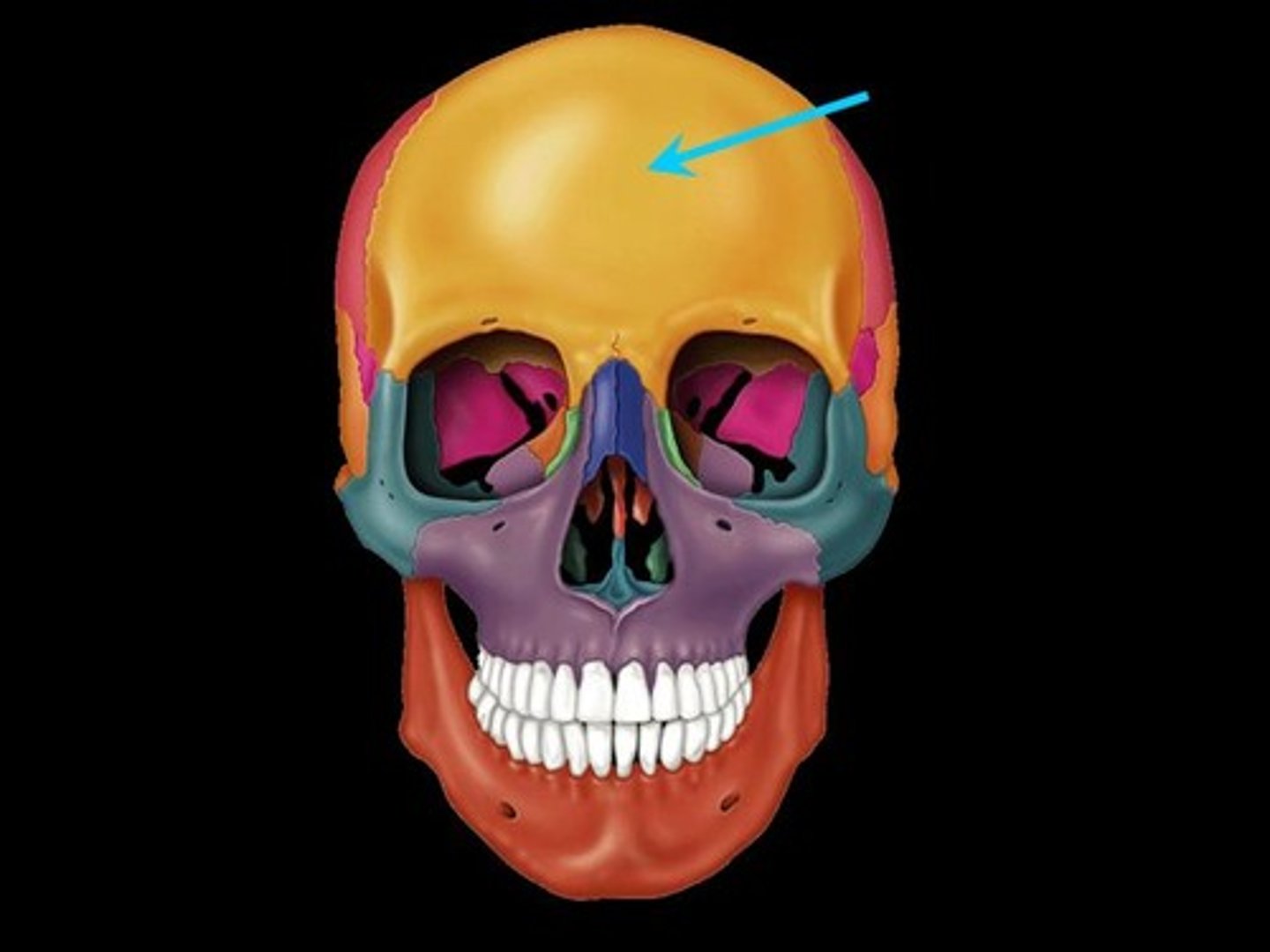
Frontal bone
A bone that forms the forehead and roofs over most of the orbits and nasal cavity, consisting of two halves at birth separated by a suture.
Temporal bone
Either of a pair of bones which form part of the side of the skull on each side and enclose the middle and inner ear.
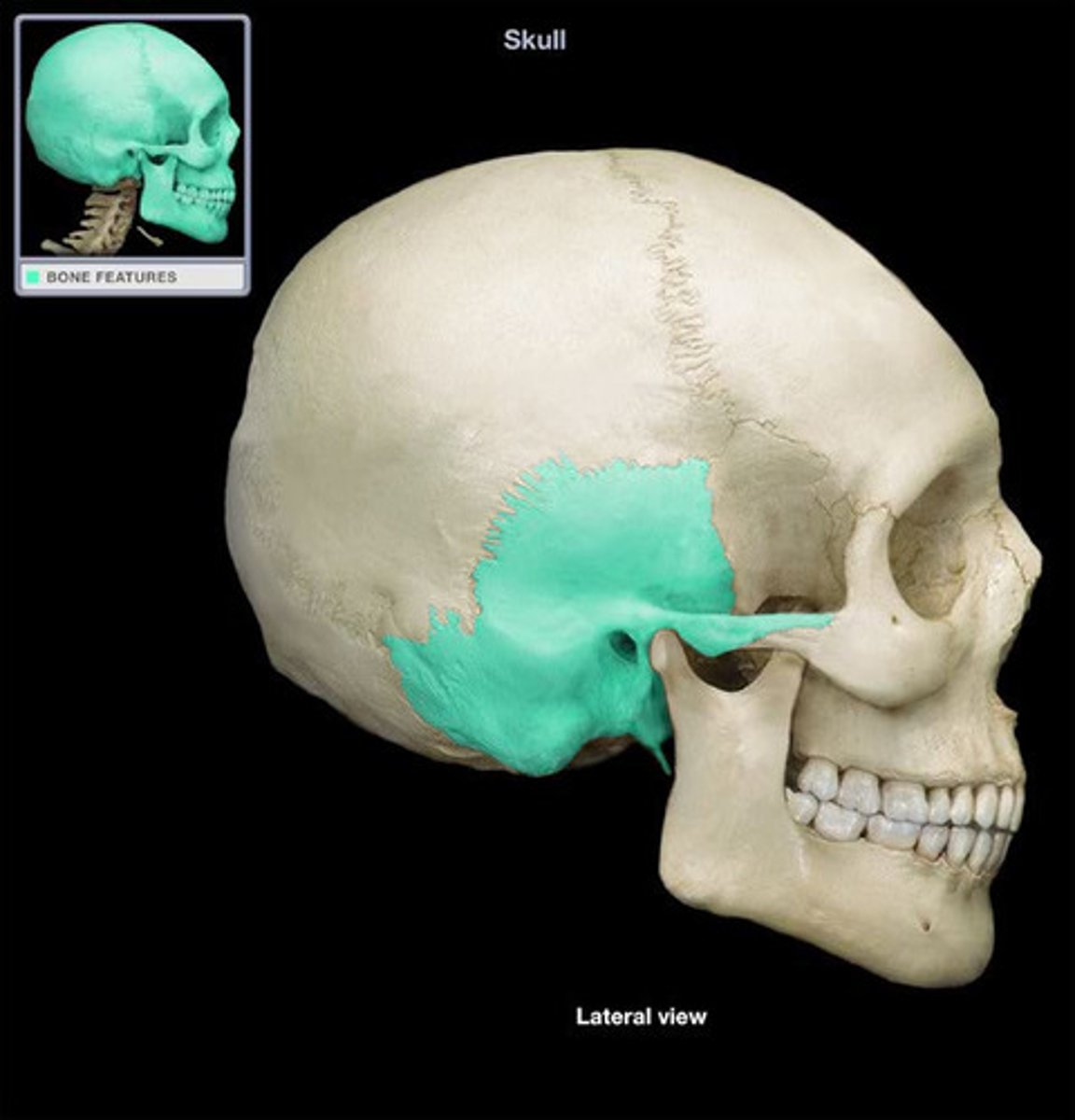
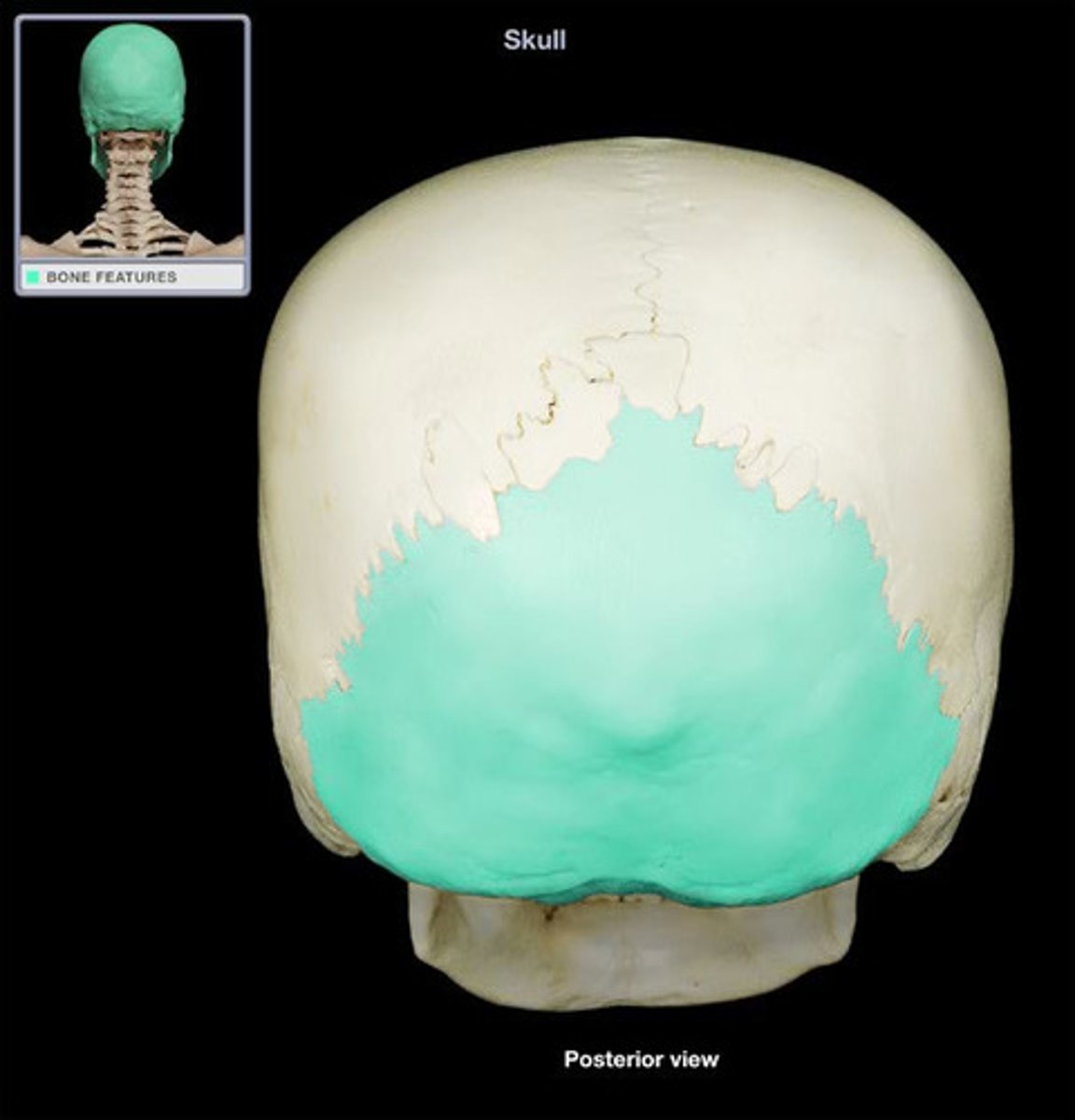
Occipital bone
The bone that forms the back and base of the skull, through which the spinal cord passes.
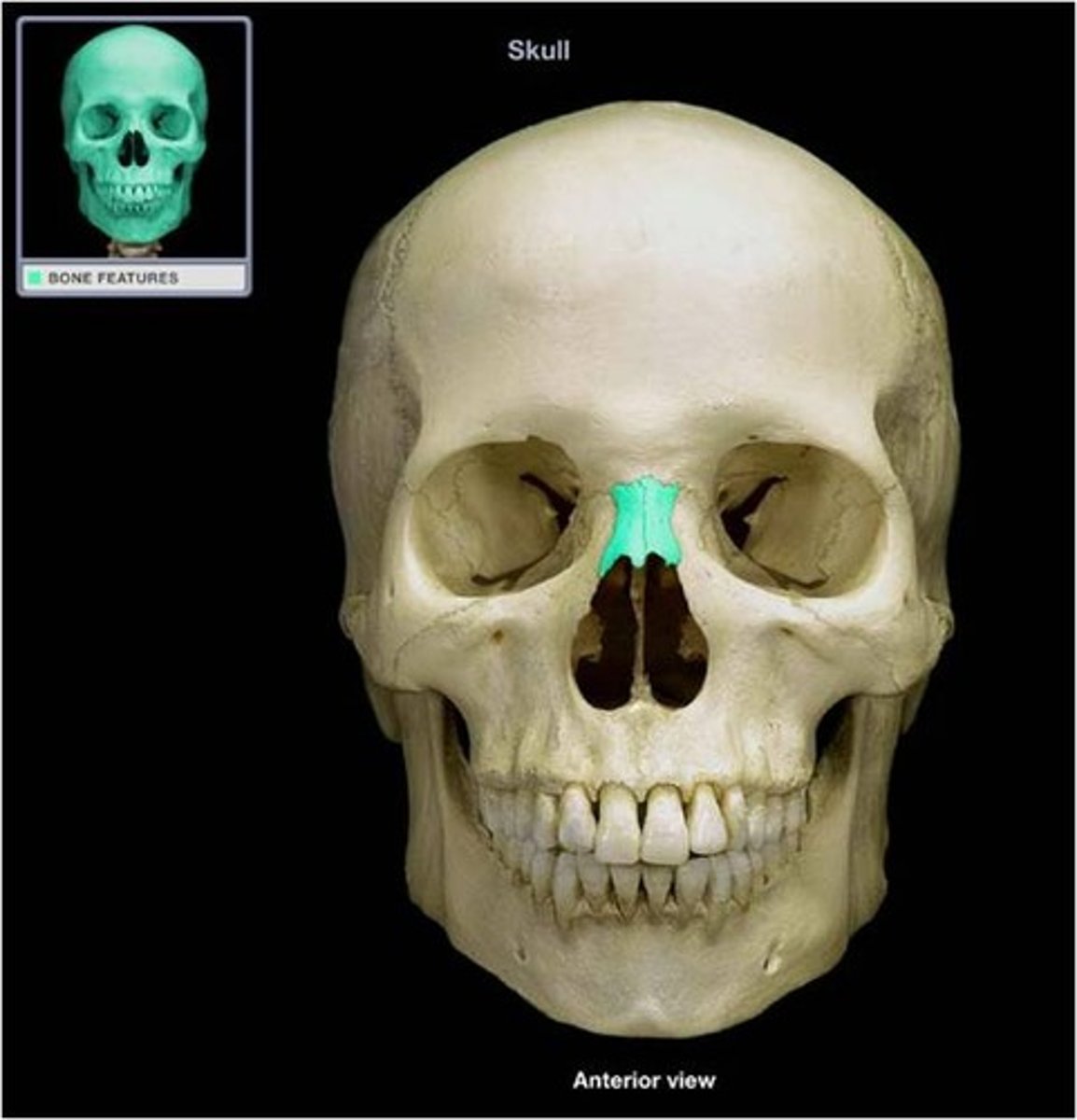
Nasal bone
Small rectangular bones forming the bridge of the nose.
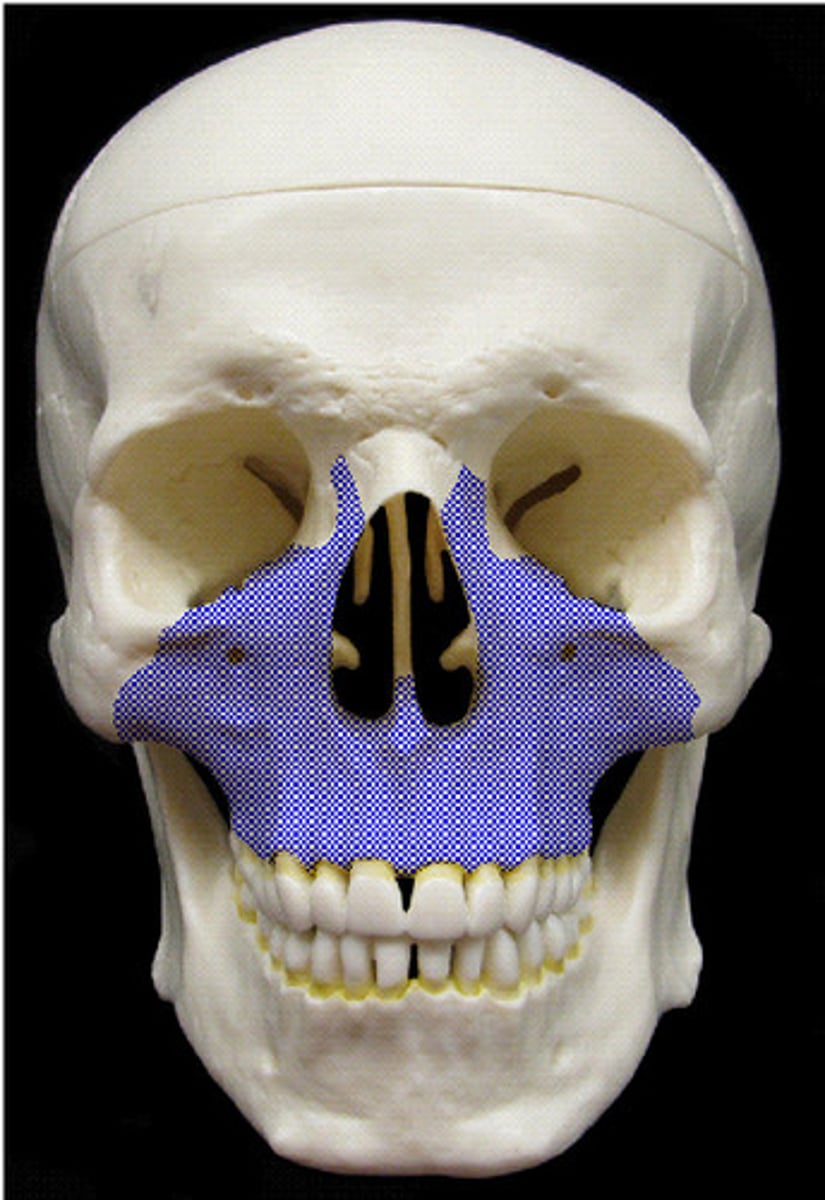
Maxilla
Keystone facial bones that articulate with all other facial bones except the mandible; they form the upper jaw and parts of the hard palate, orbits, and nasal cavity.
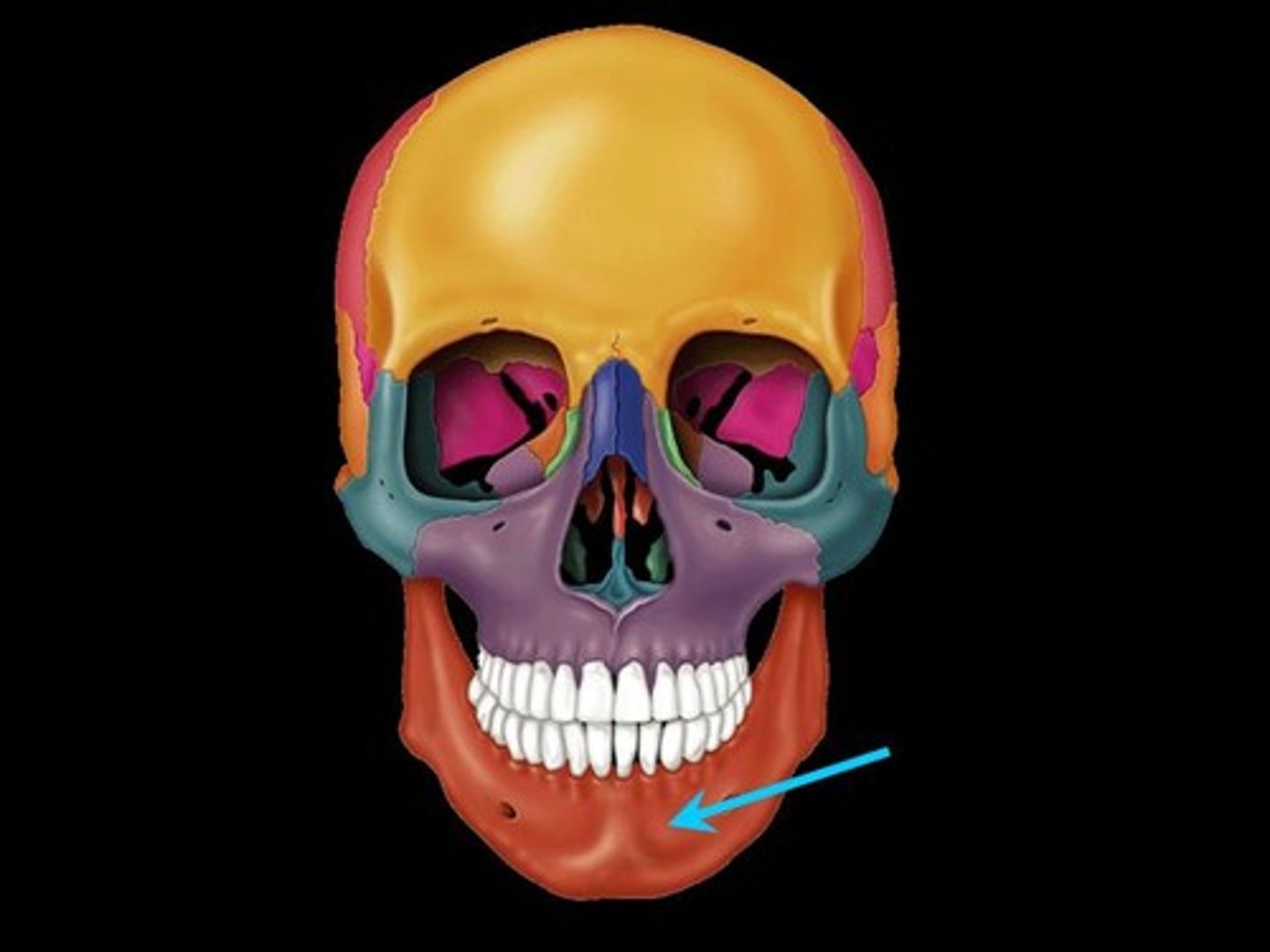
Mandible
The lower jawbone, which articulates with the temporal bone to form the only freely movable joints in the skull (the temporomandibular joint).
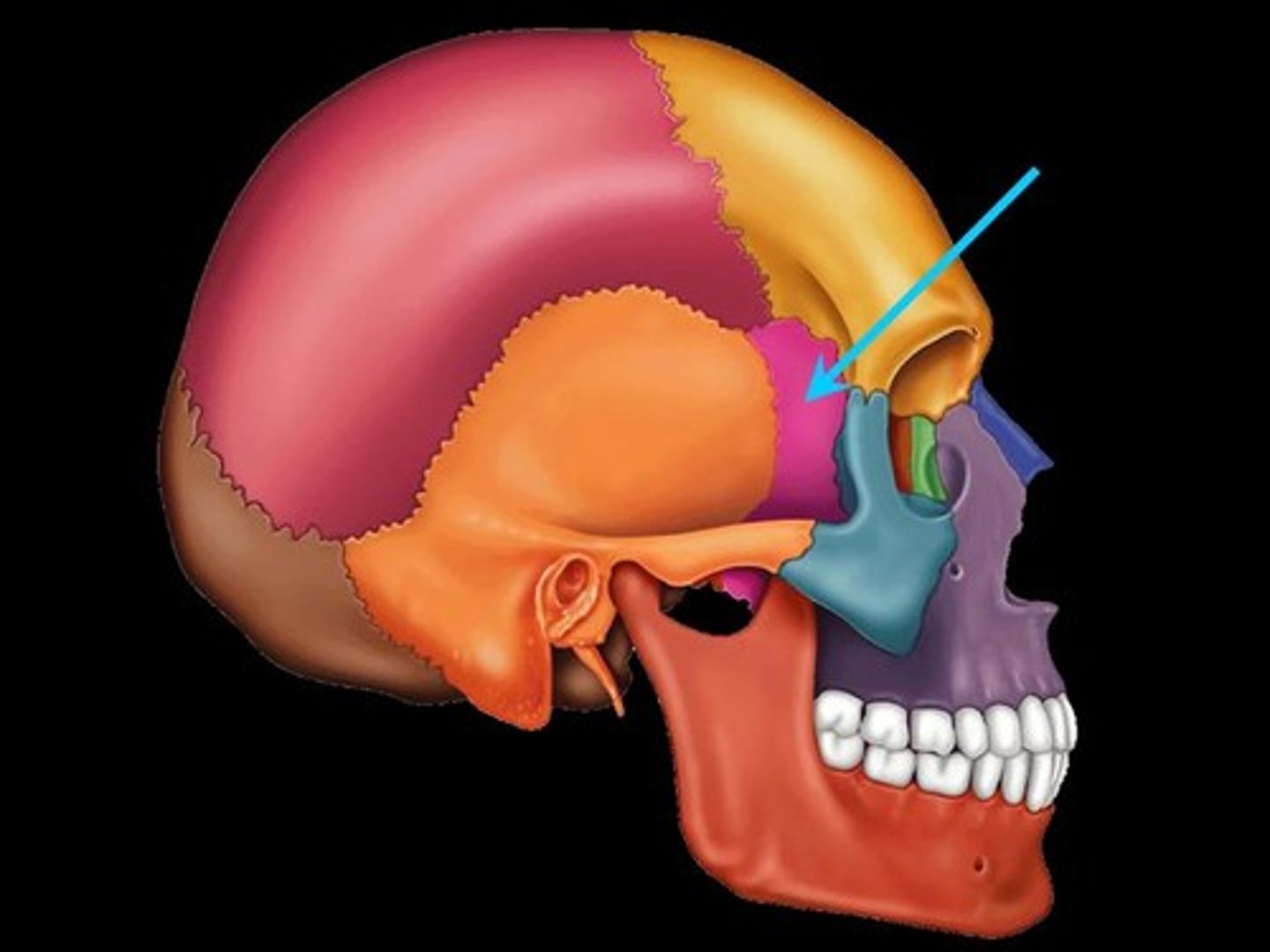
Sphenoid bone
A compound bone that forms the base of the cranium, behind the eye and below the front part of the brain, containing two pairs of broad lateral wings and a number of other projections, as well as two air-filled sinuses.
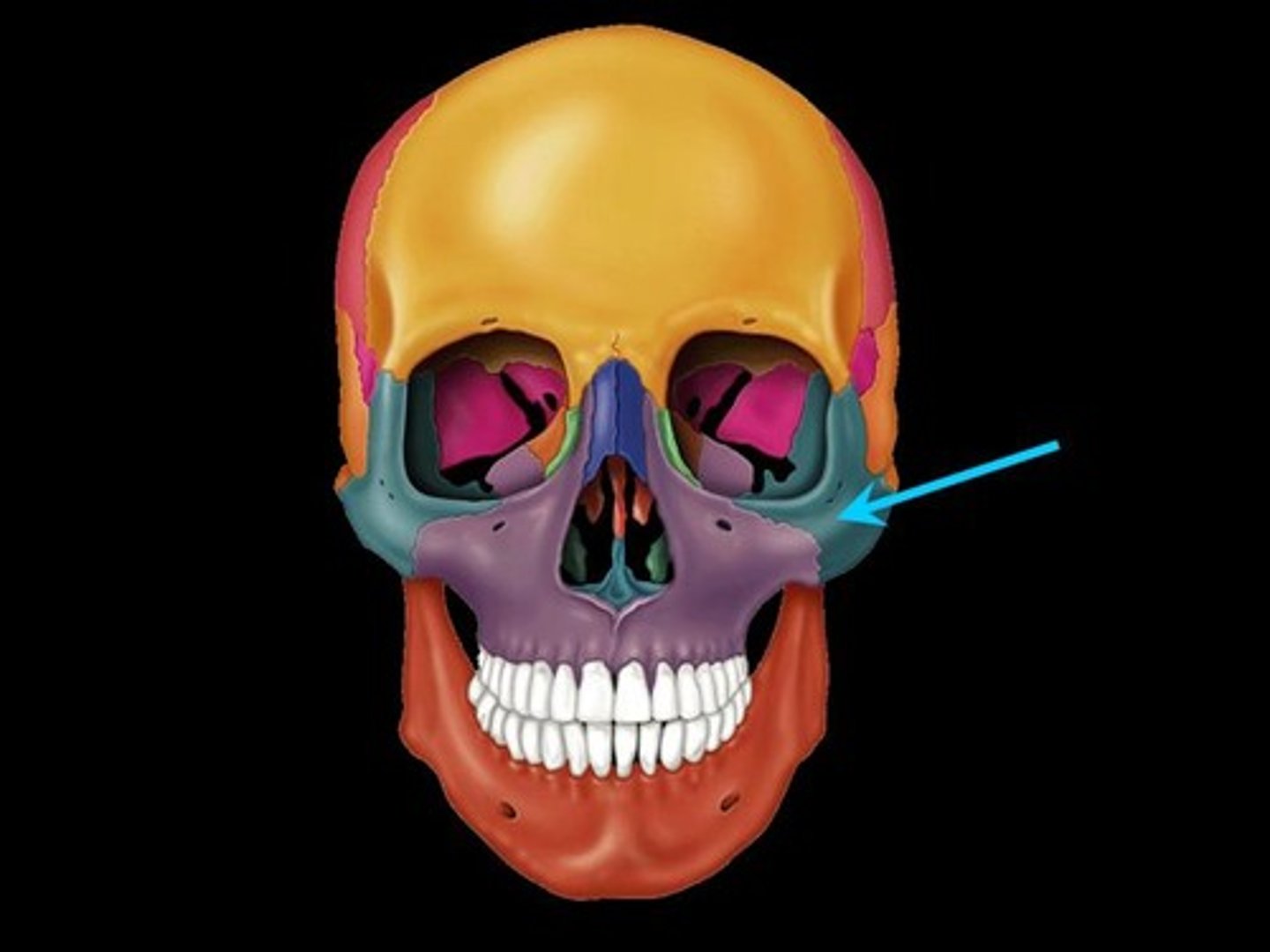
Zygomatic bone
The bone that forms the prominent part of the cheek and the outer side of the eye socket.
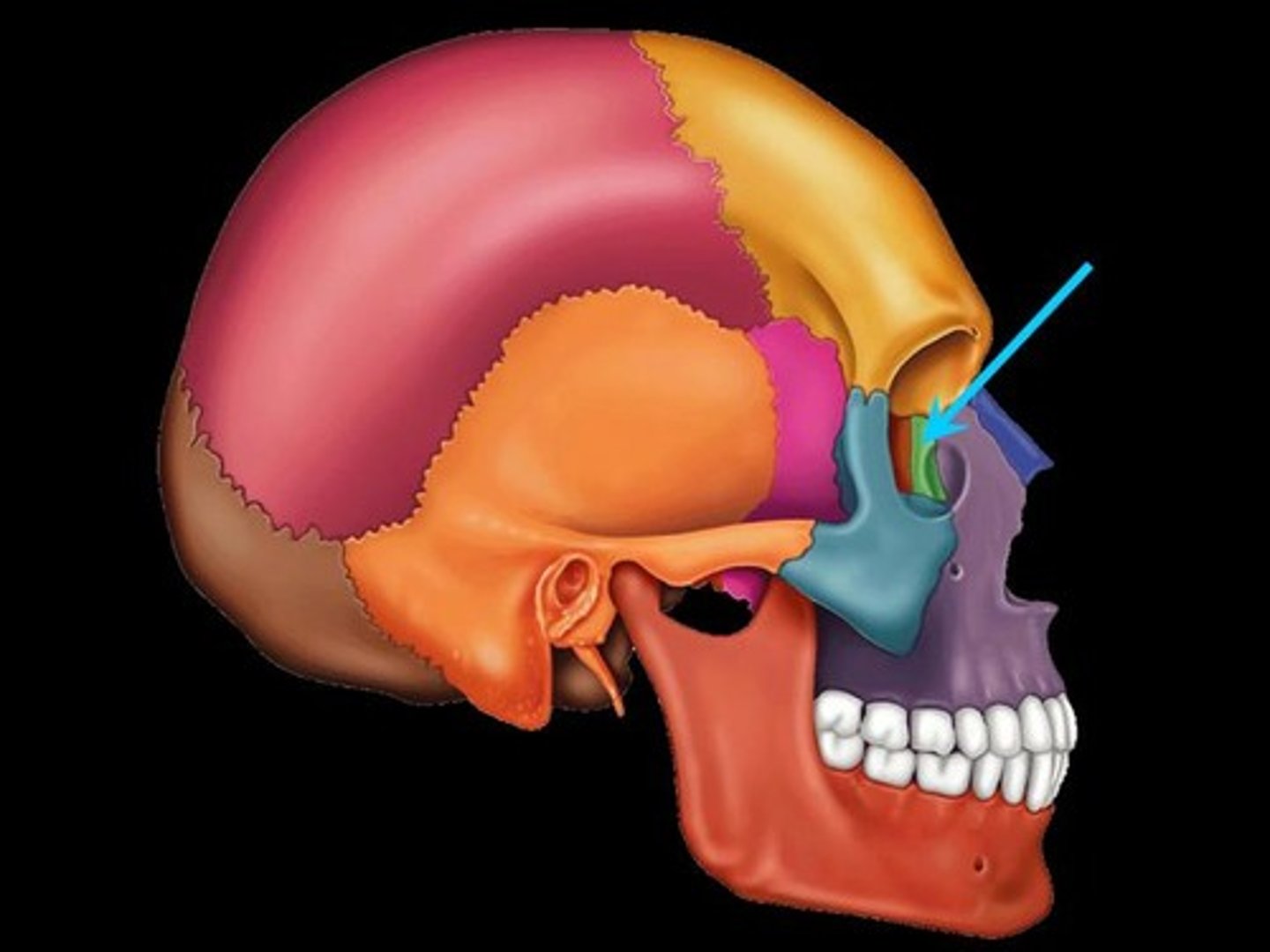
Lacrimal bone
Each forms part of the medial orbit in between the maxilla and ethmoid bone.
Ethmoid bone
A square bone at the root of the nose, forming part of the cranium, and having many perforations through which the olfactory nerves pass to the nose.
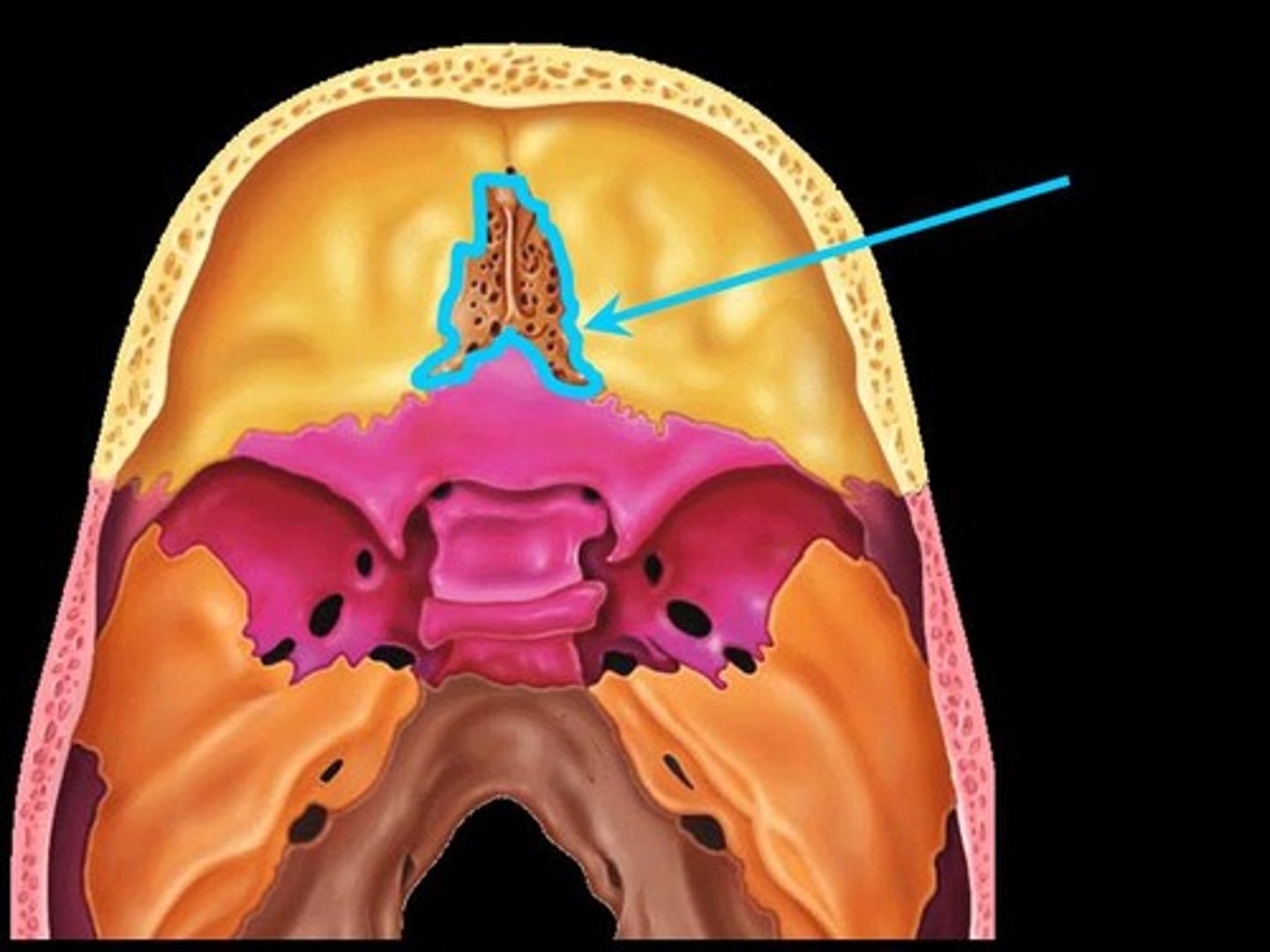
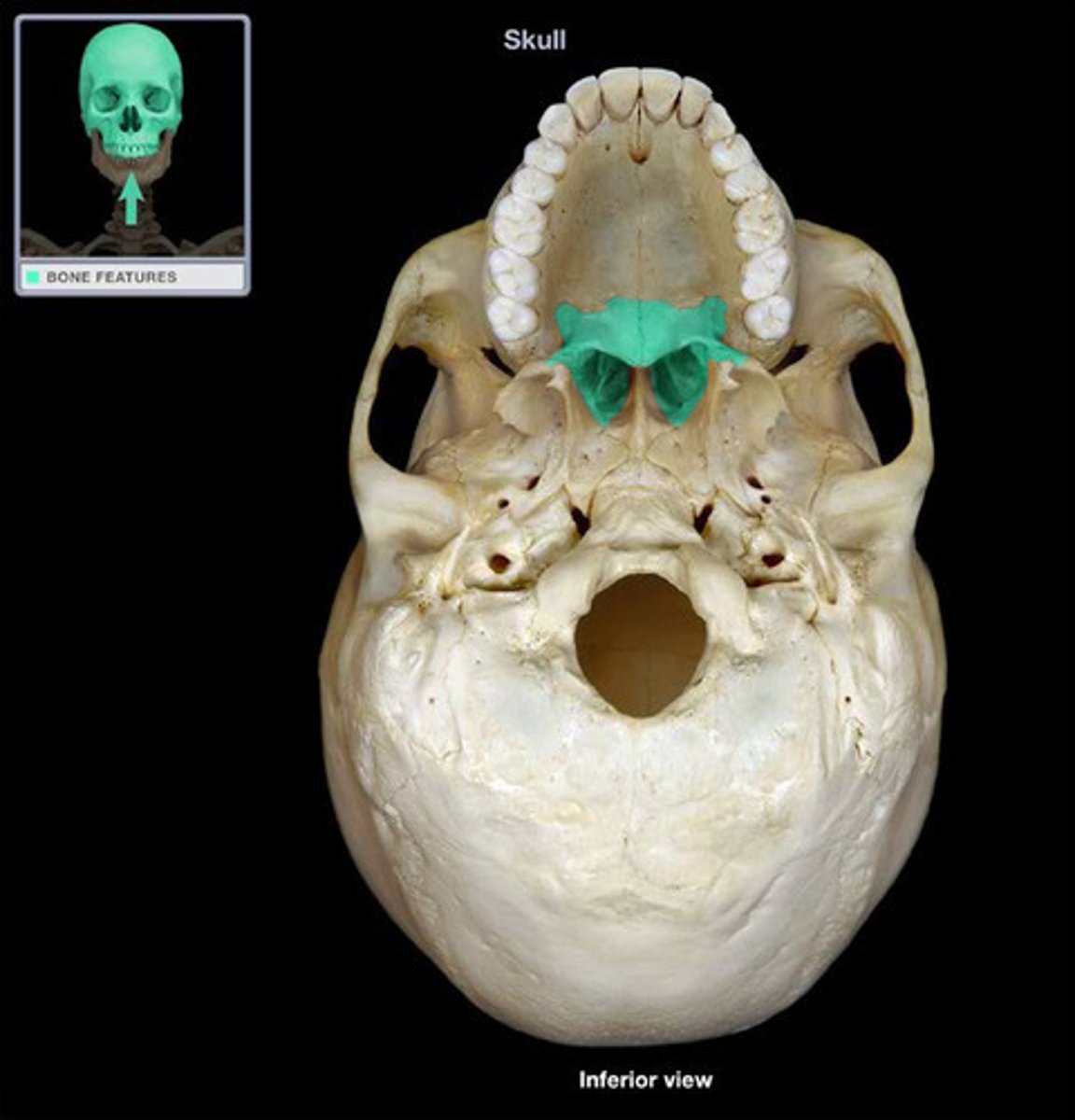
Palatine bone
Forms the posterior hard palate, a small part of the nasal cavity, and part of the orbit.
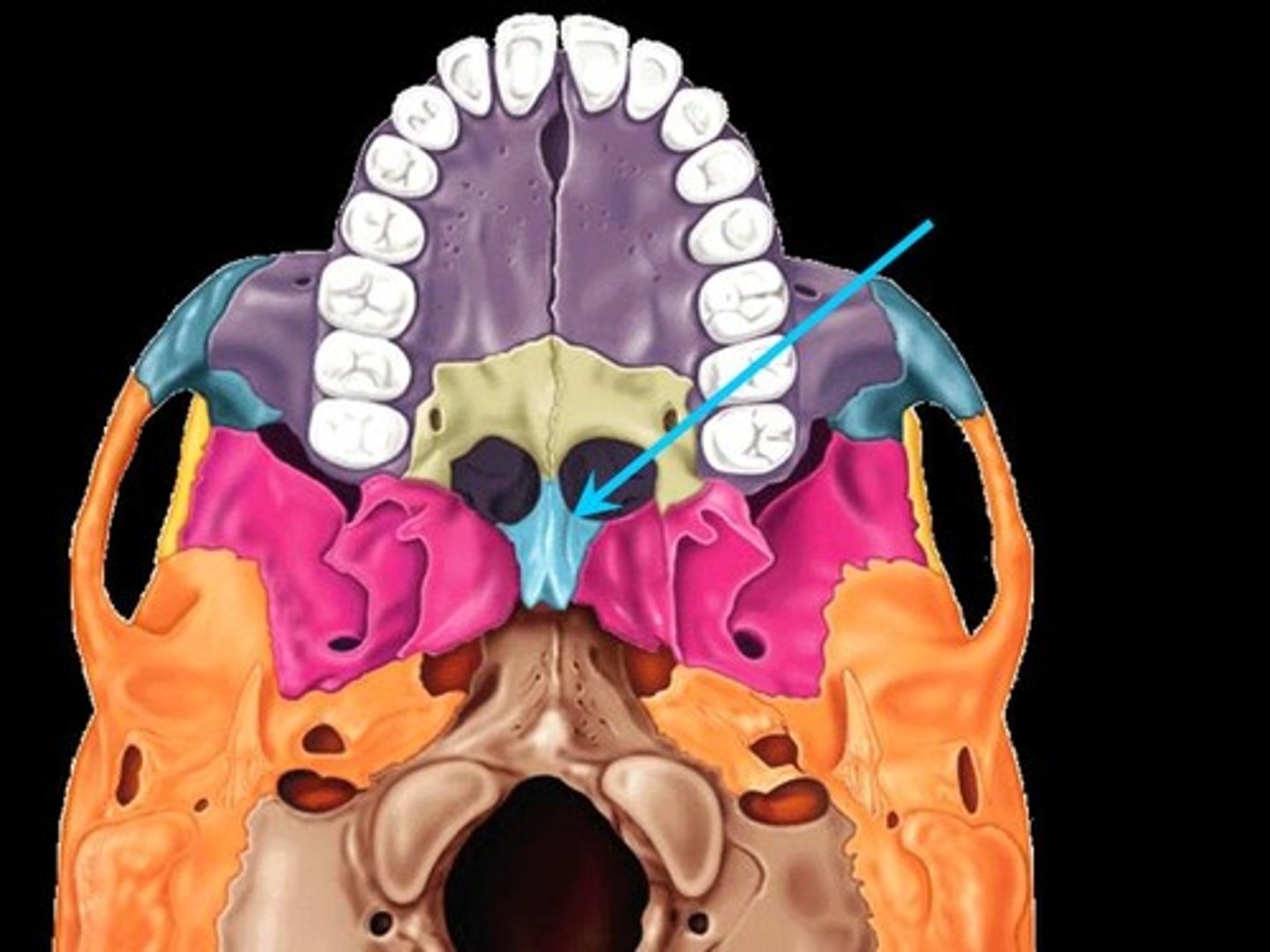
Vomer
A thin, blade-shaped bone that forms the inferior nasal septum.
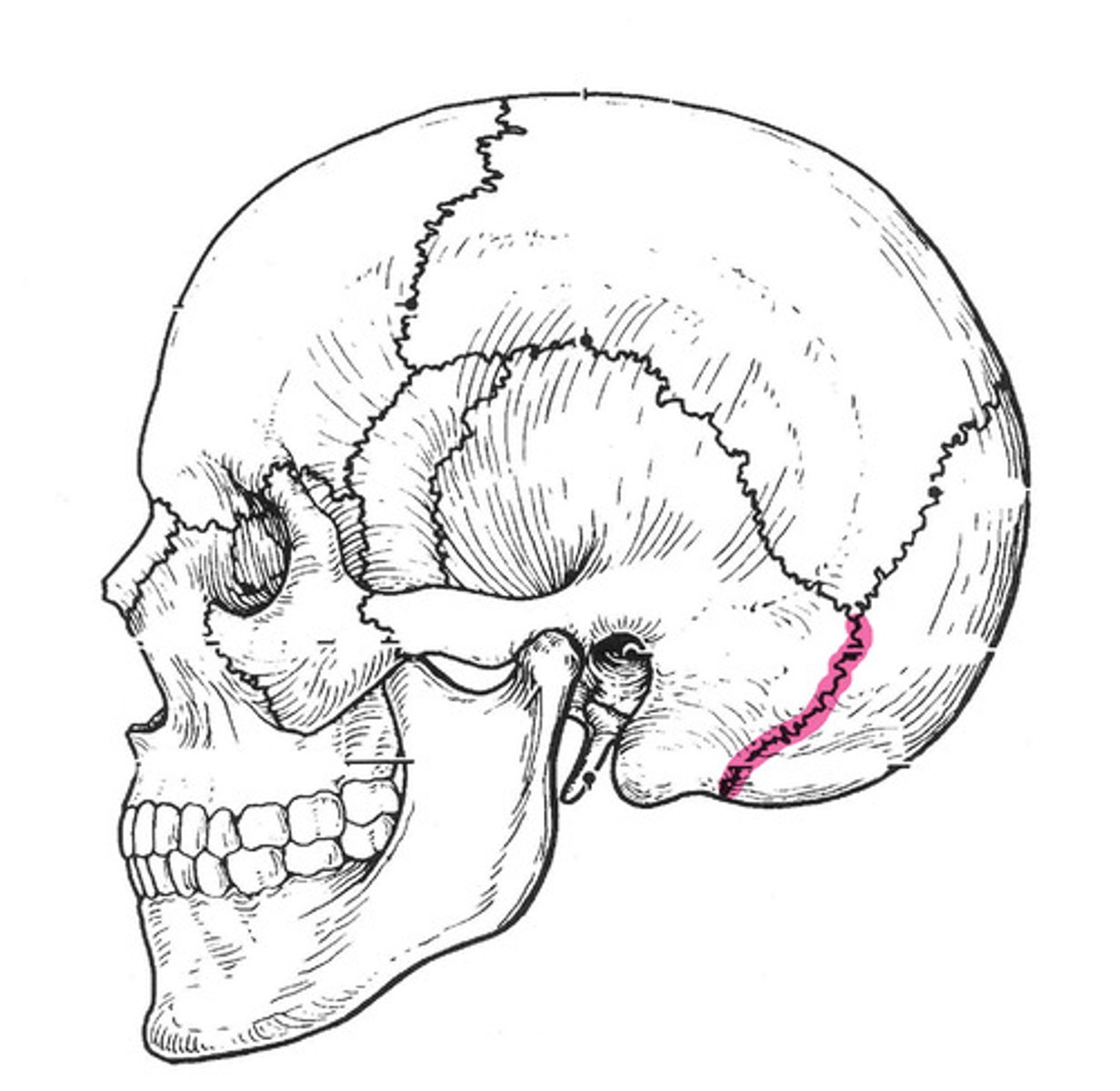
Occipitomastoid suture
The cranial suture between the occipital bone and the mastoid portion of the temporal bone.
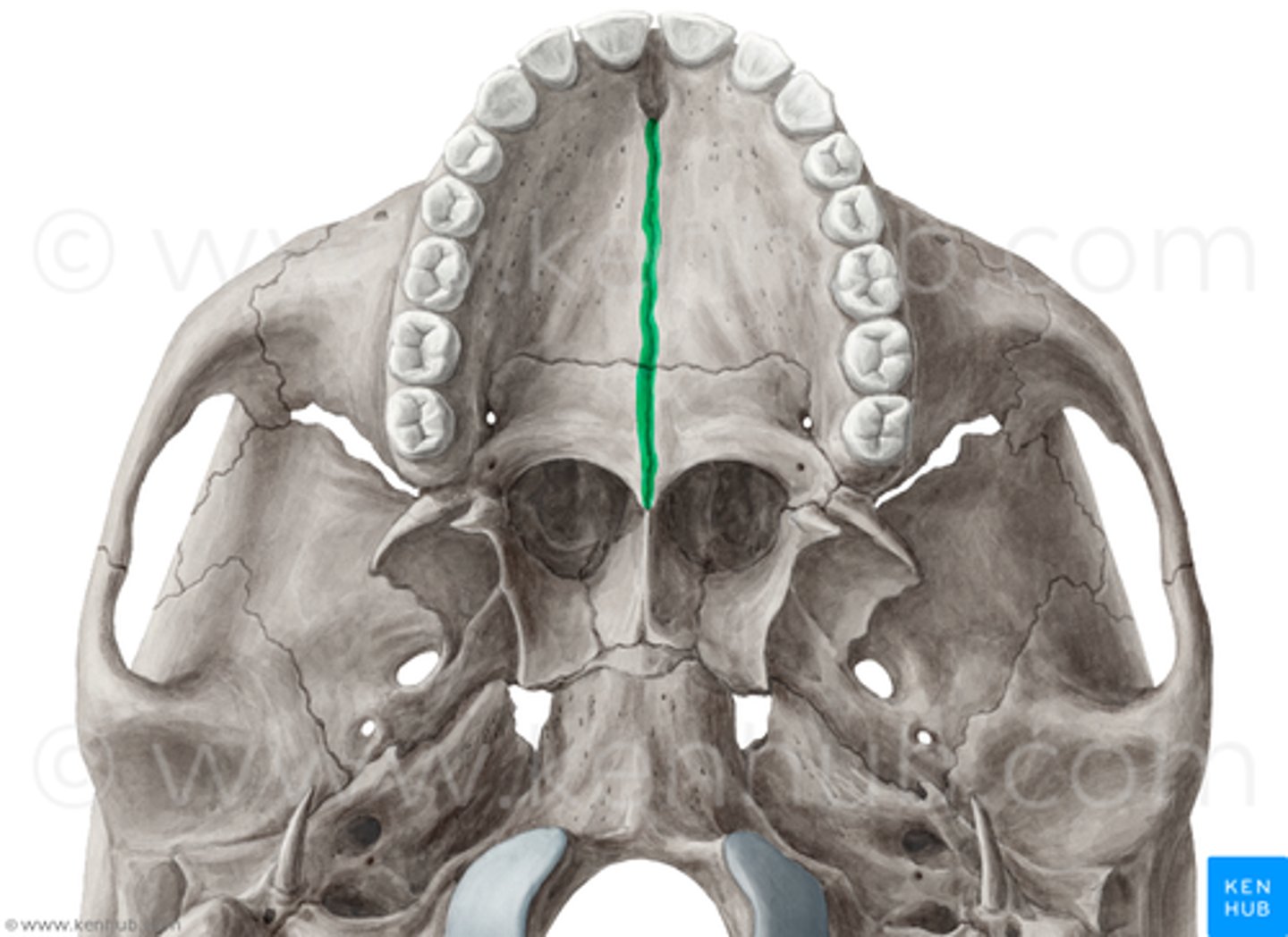
Median palatine suture
The median fusion point of the horizontal plates of the palatine bones.
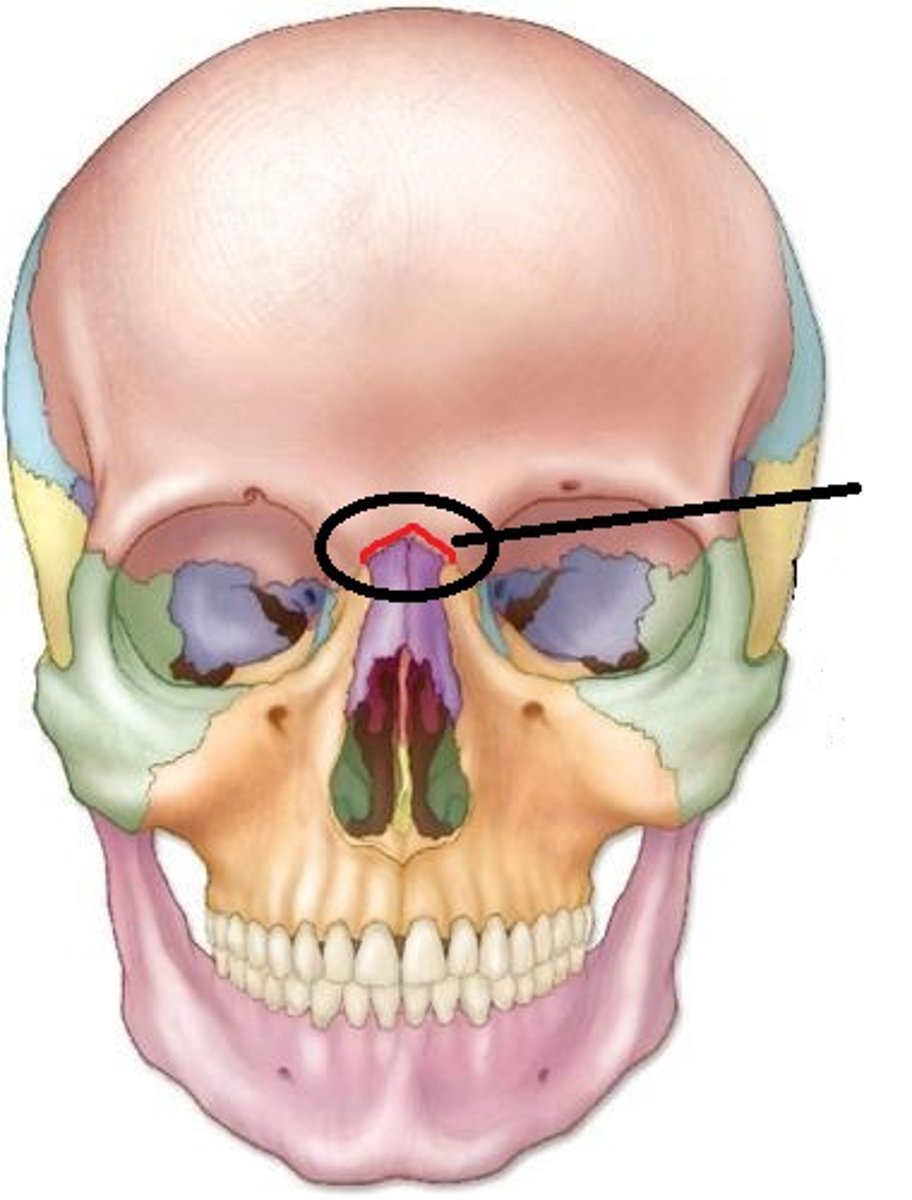
Frontonasal suture
A fibrous joint in the human skull that connects the frontal bone and the nasal bone.
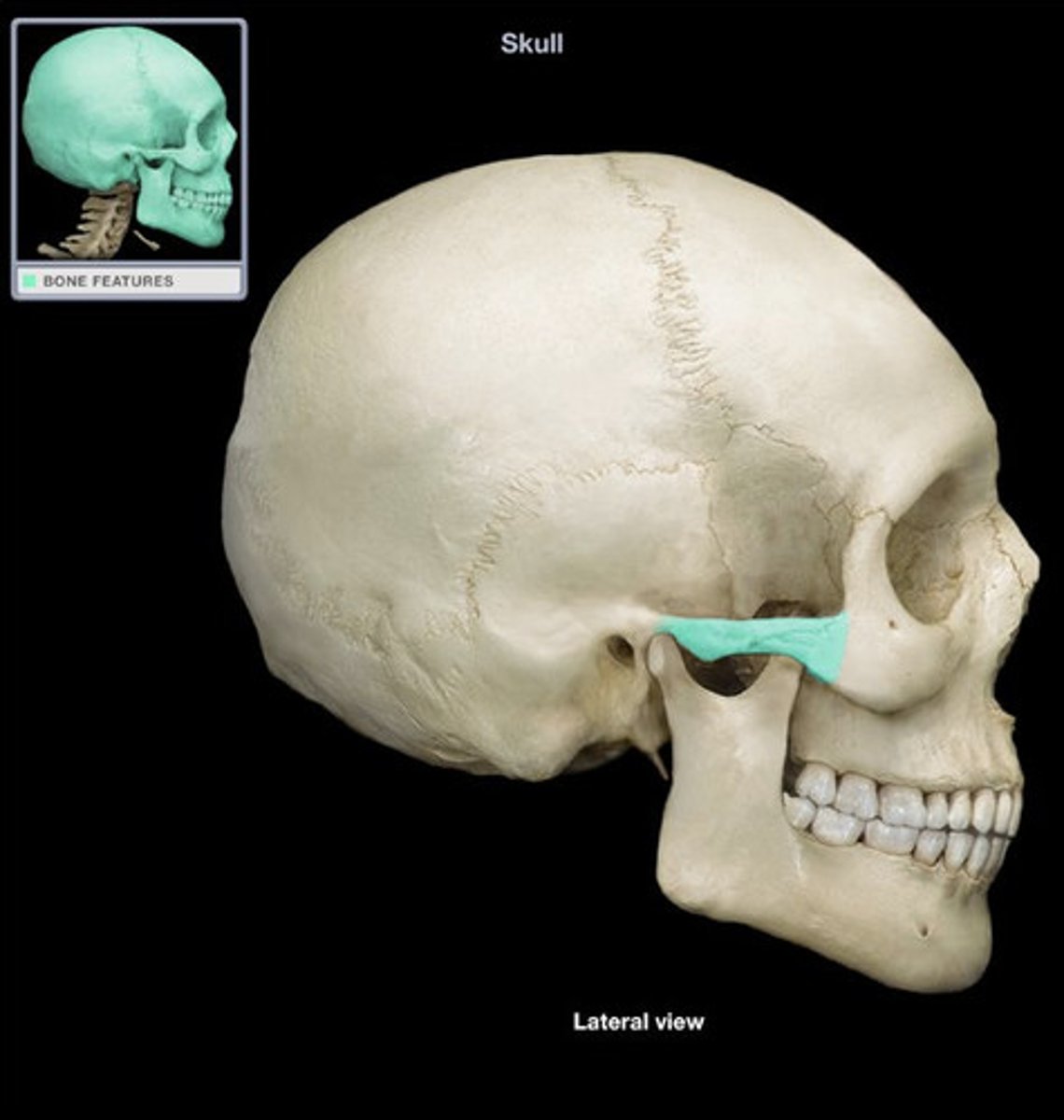
Zygomatic process
A bridgelike projection that articulates with the zygomatic bone to form the zygomatic arch.
External acoustic meatus
Canal leading to the middle ear and eardrum.
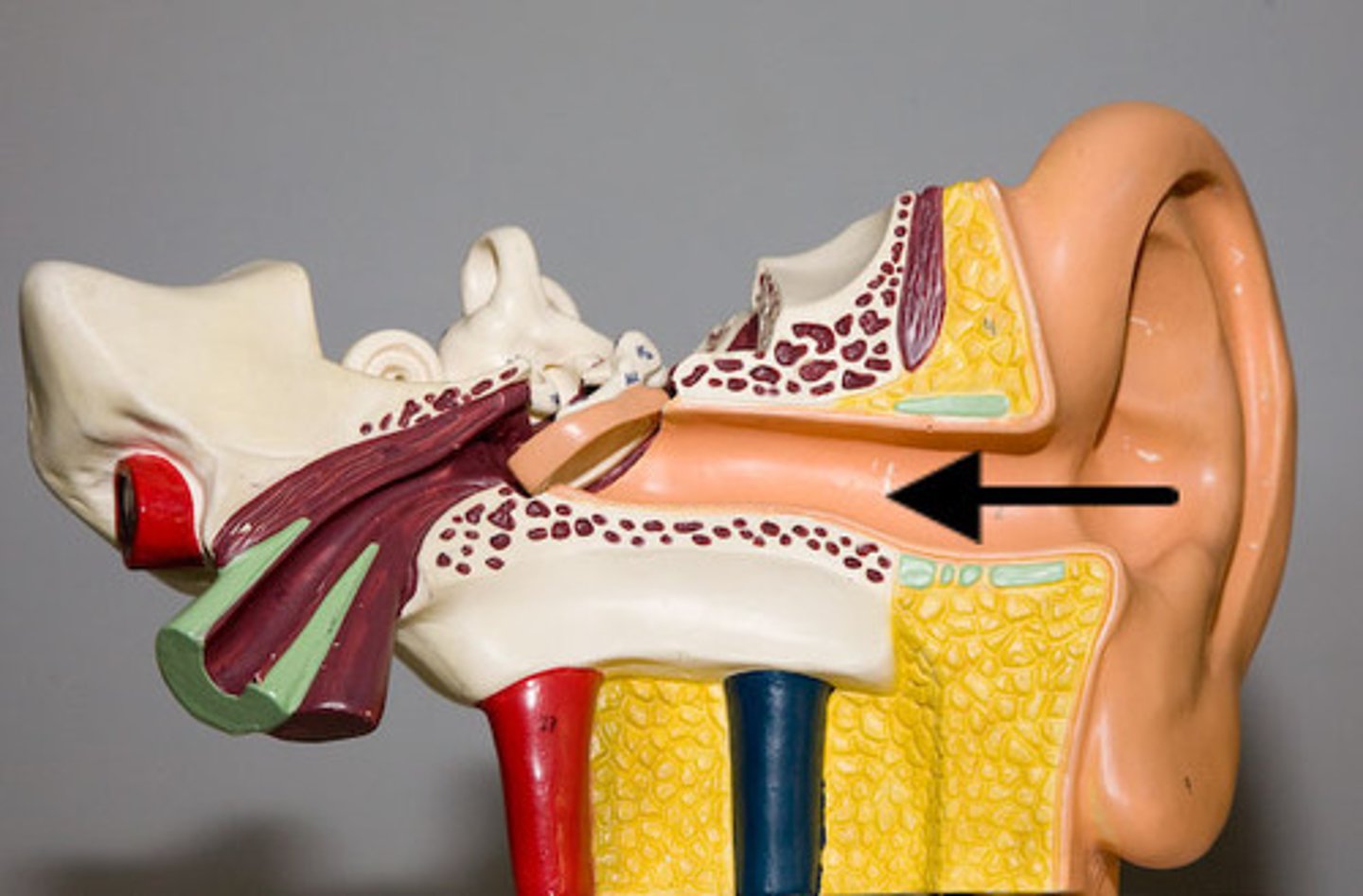
Mastoid process
Located posterior to the external acoustic meatus; serves as an attachment point for neck muscles.
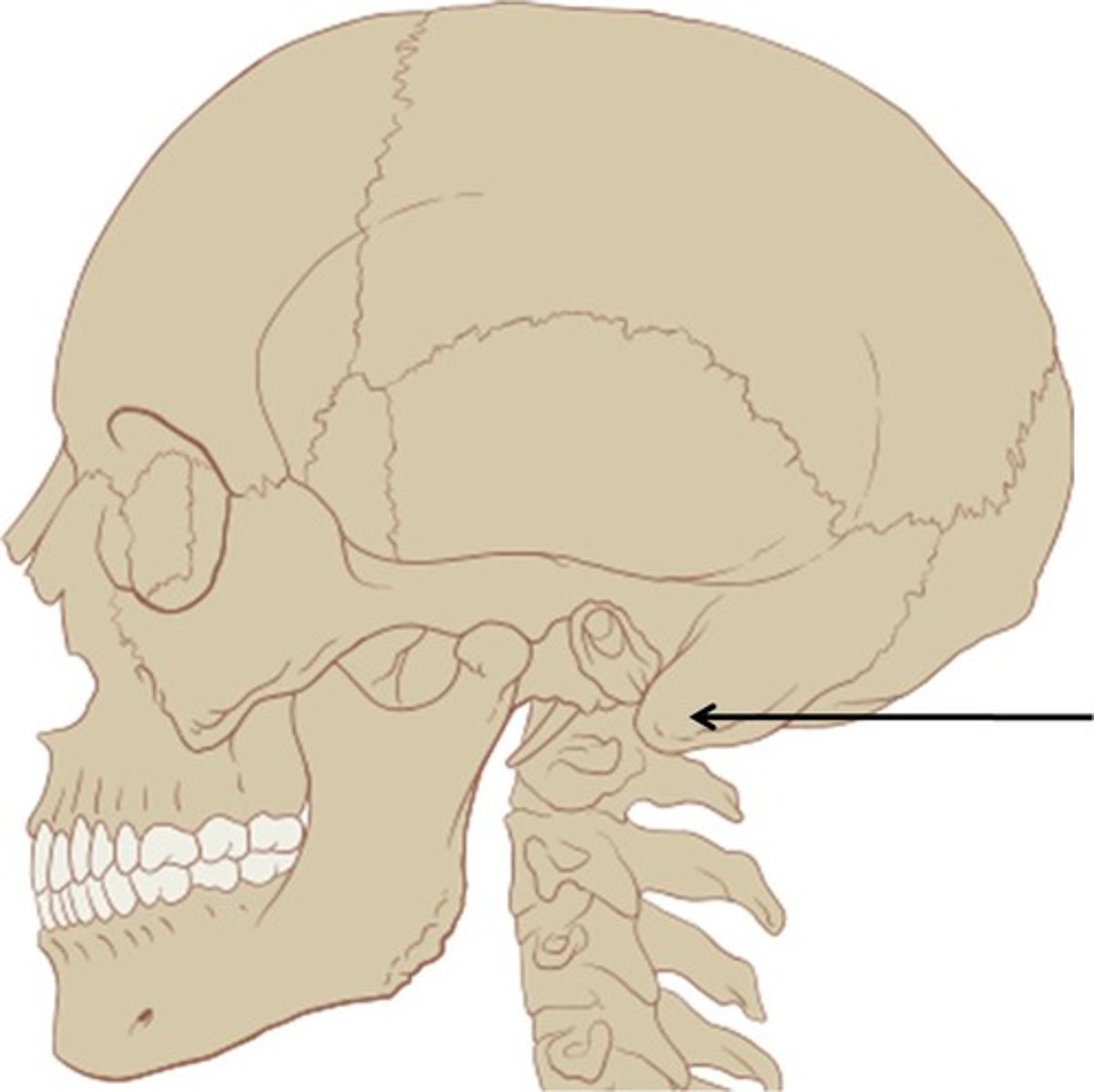
Styloid process
Needle-like projection that serves as an attachment point for ligaments and muscles of the neck.
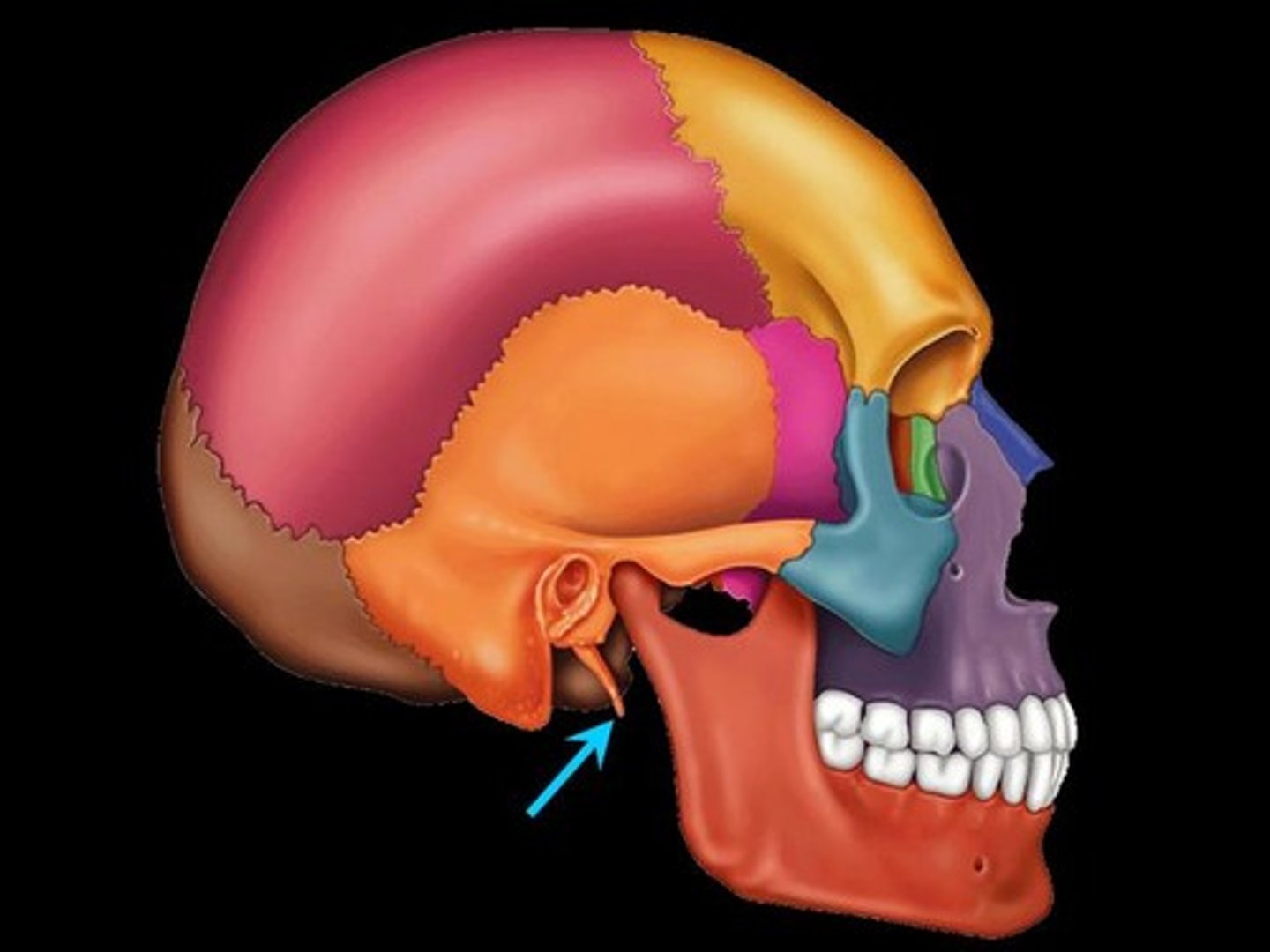
Mandibular condyle
The rounded, articular end of the condylar process on the ramus of the lower jawbone (mandible).
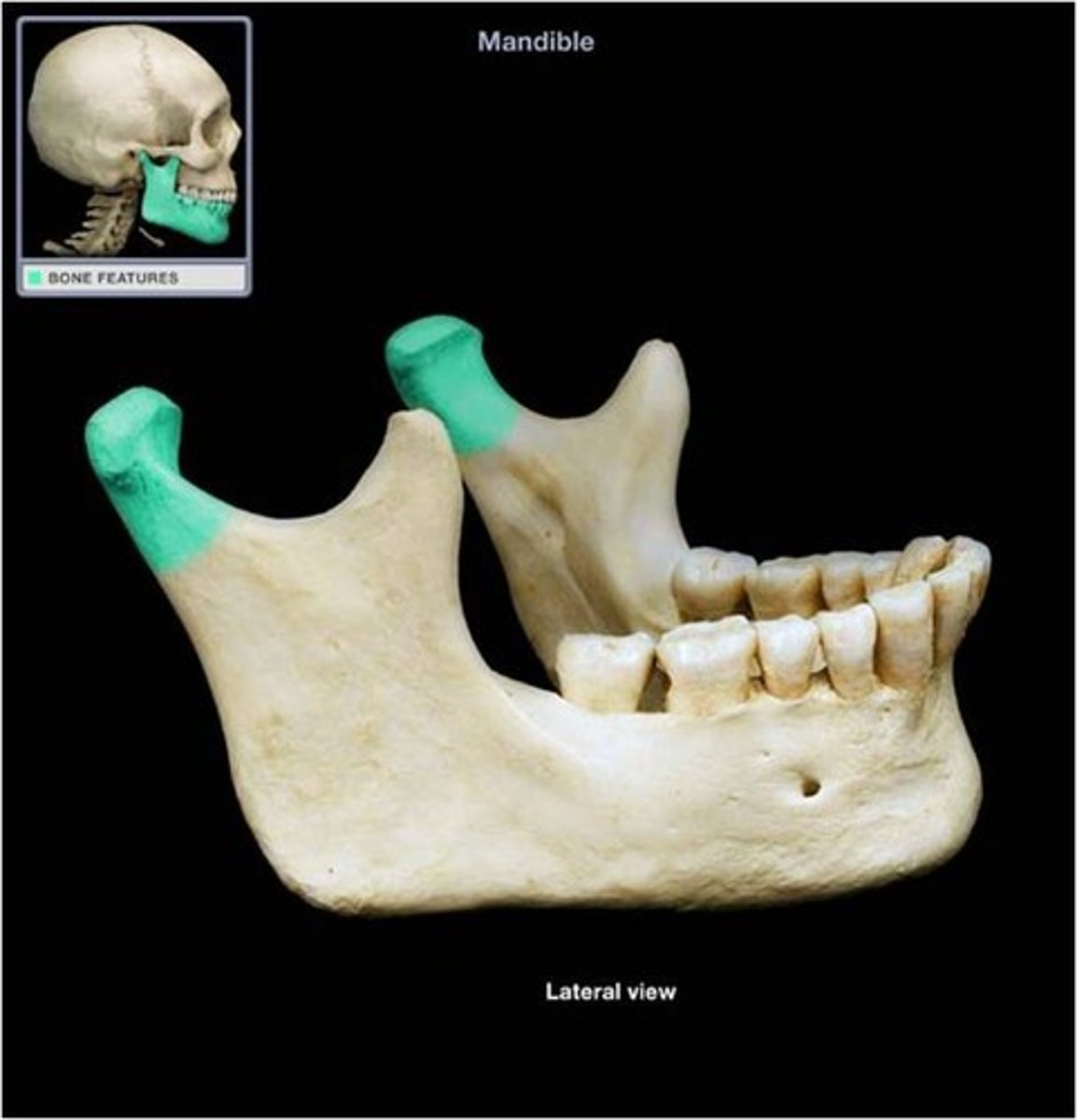
Mandibular notch
A U-shaped indentation or concave groove located on the superior border of the ramus of the mandible.
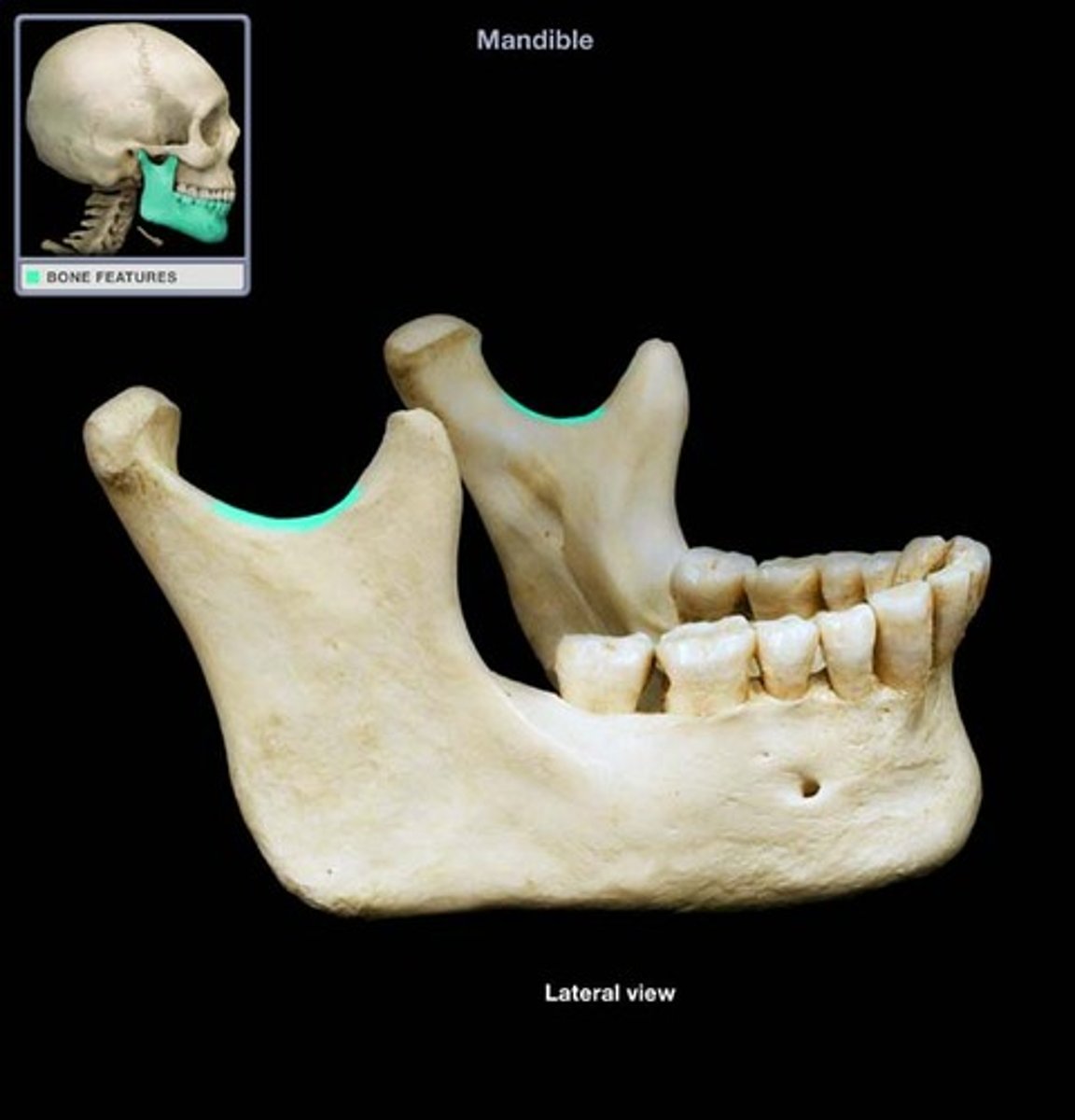
Mandibular ramus
Vertical extension of the body.
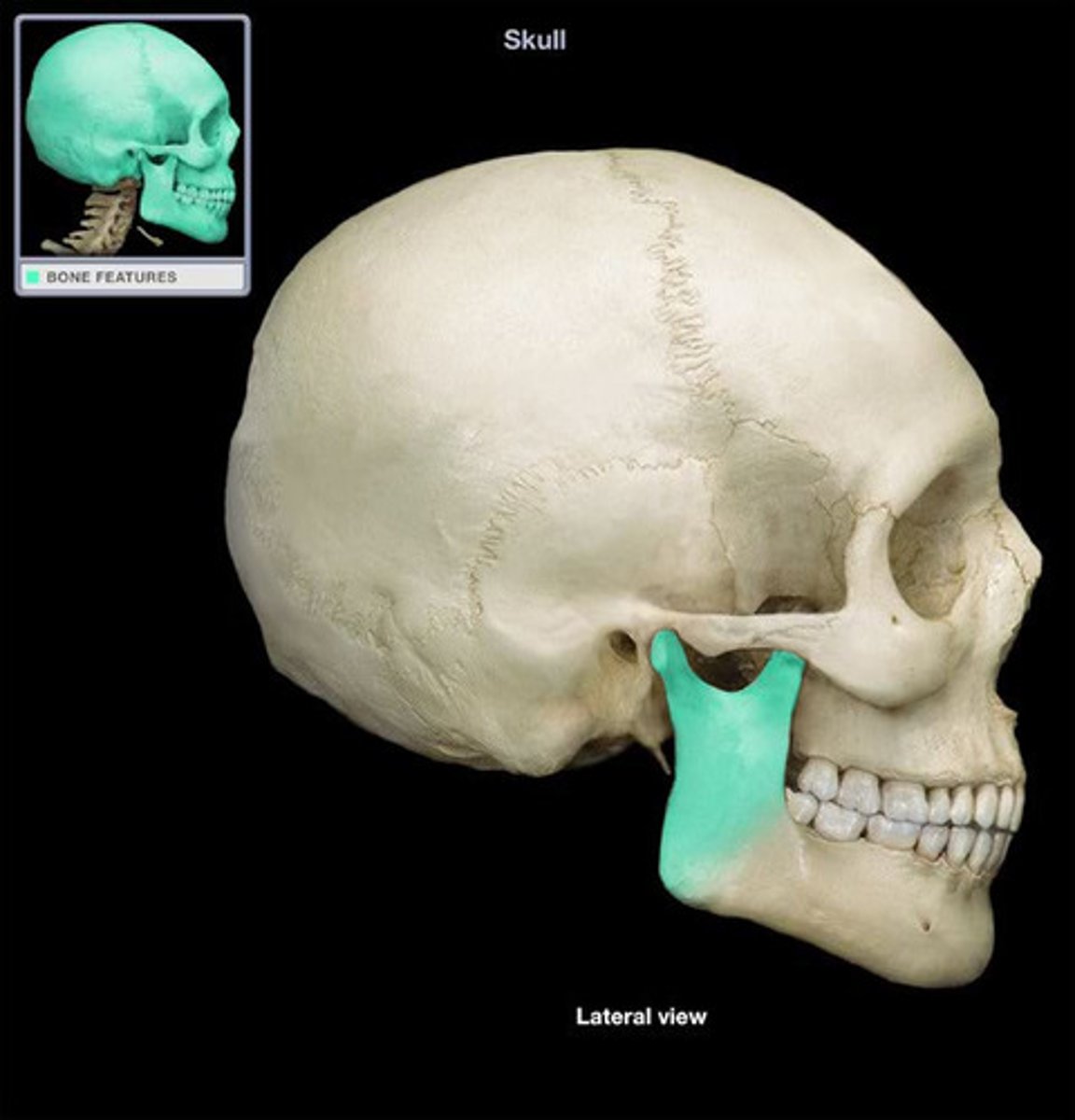
Mandibular angle
Posterior points where the ramus meets the body.
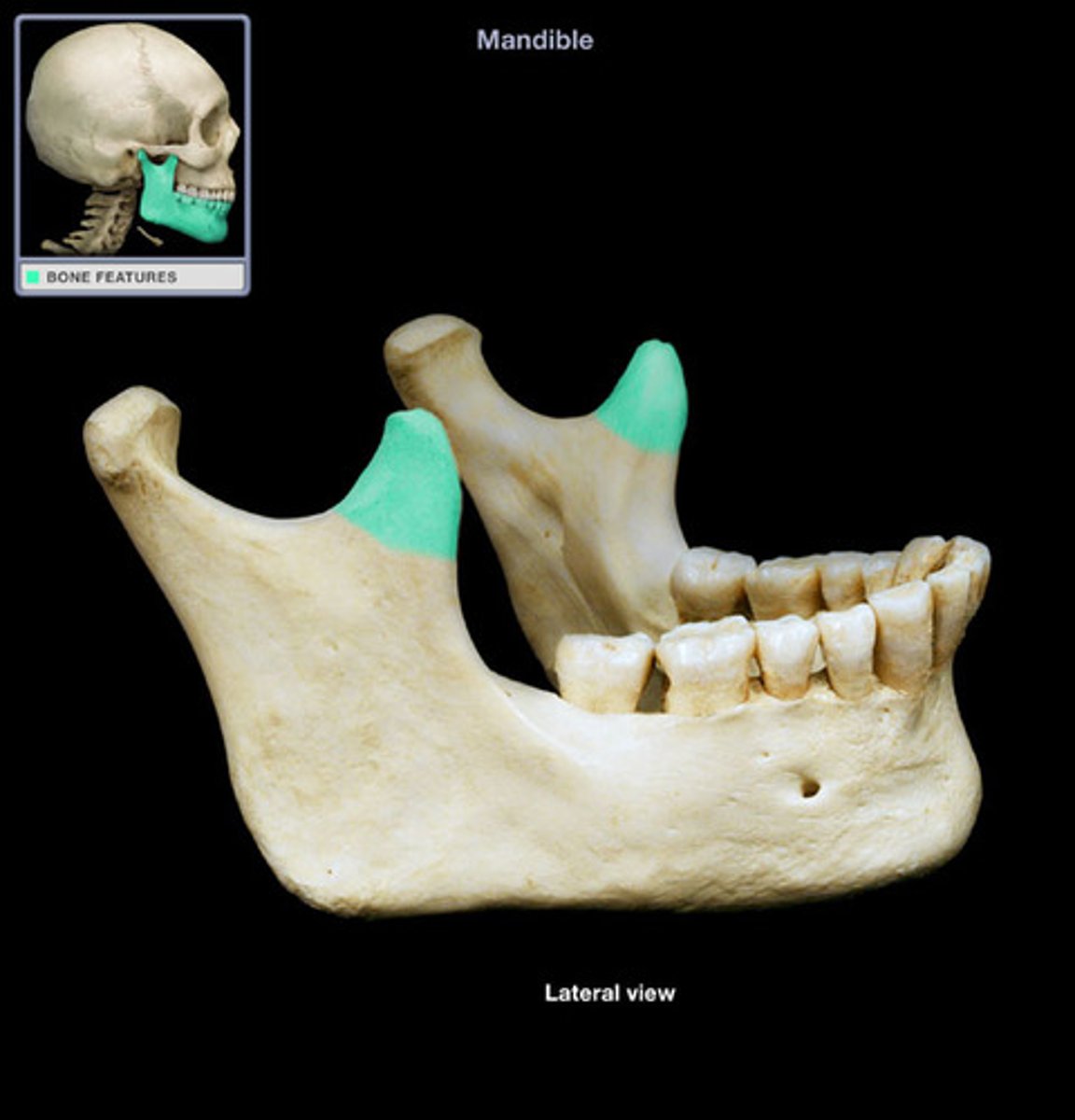
coronoid process
a flattened triangular projection above the angle of the jaw where the temporalis muscle is attached
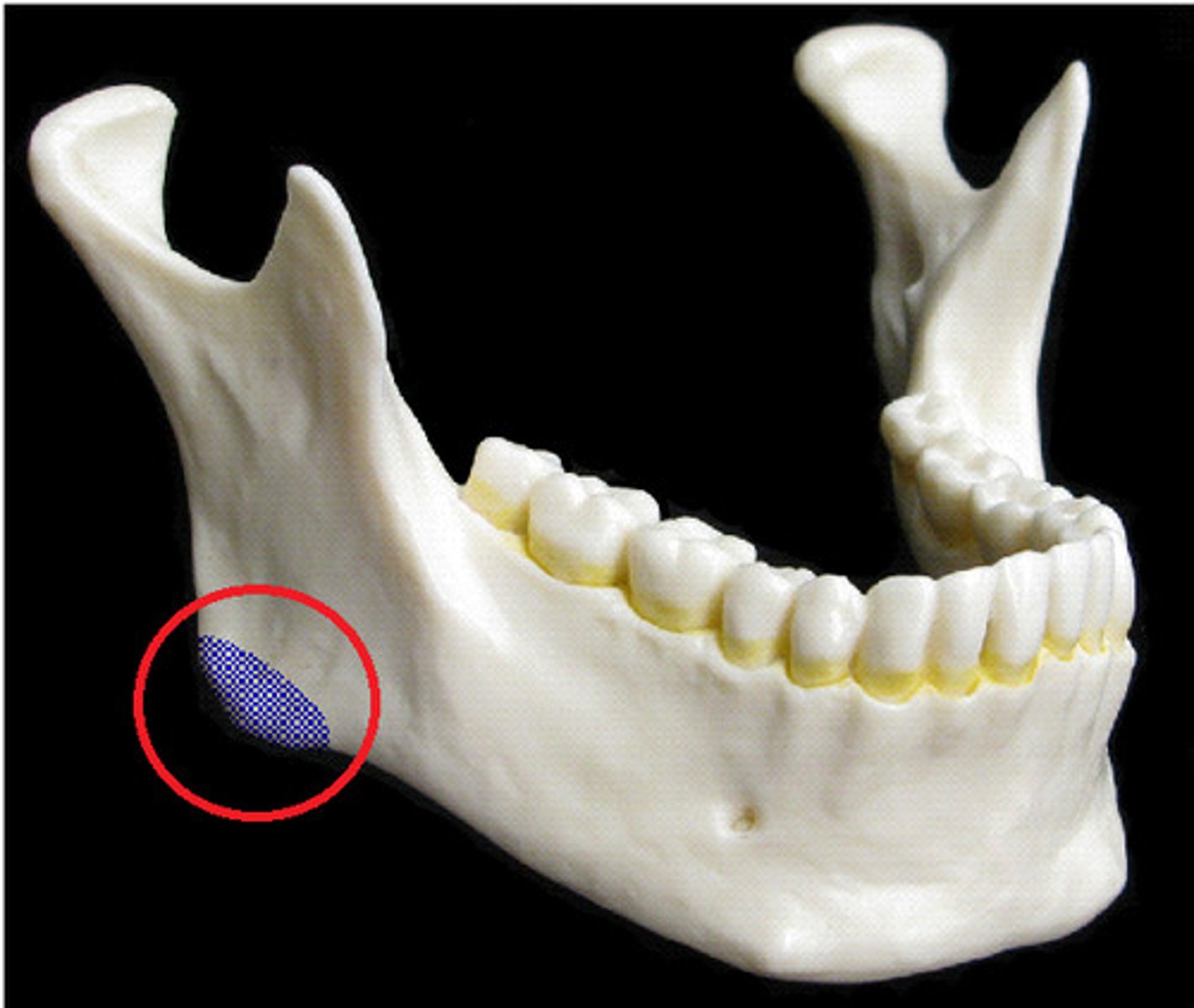
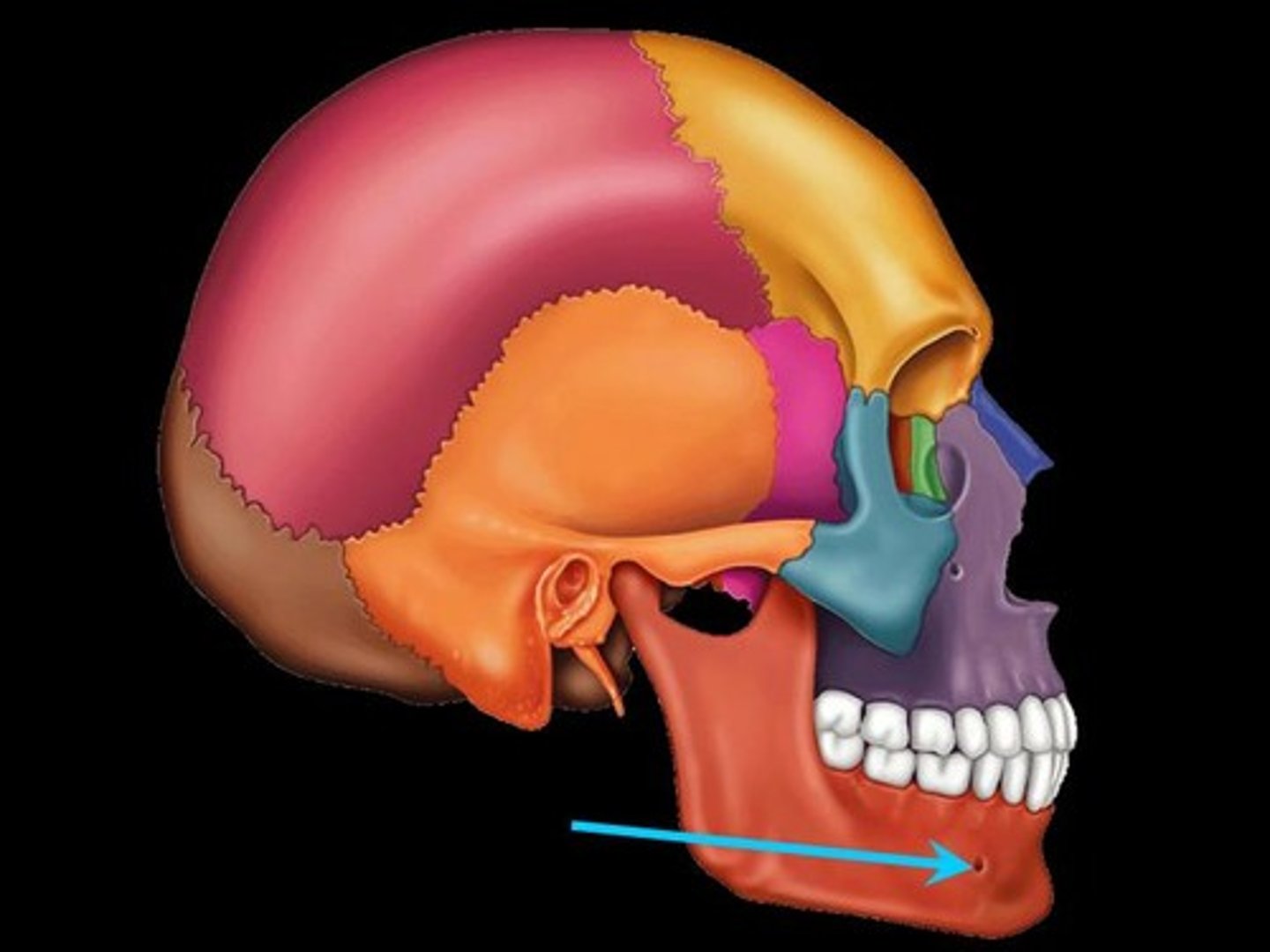
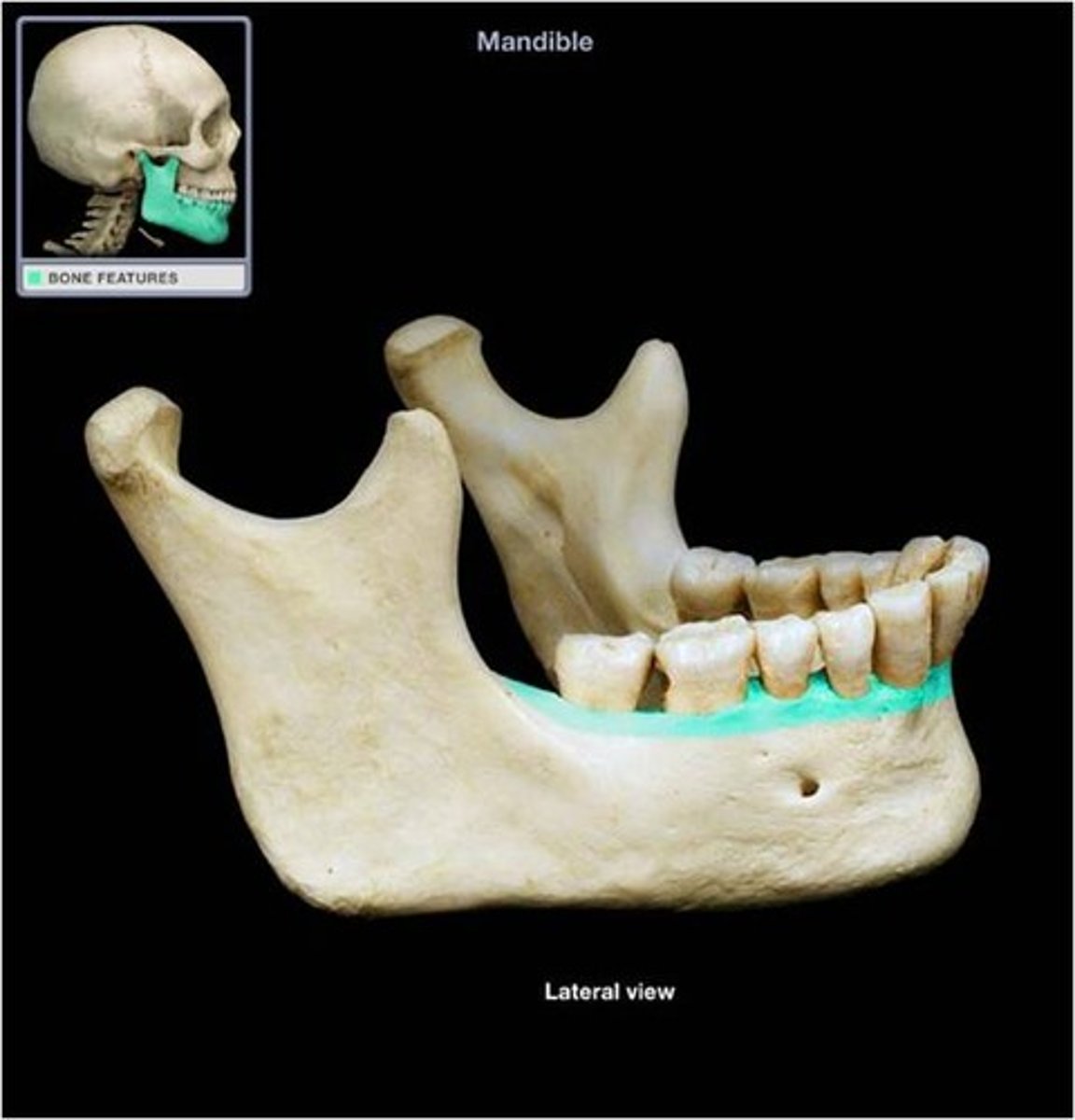
mental foramen
the opening through which the mental nerve exits the mandible
alveolar margins
the extreme edge of the bone that surrounds the teeth, forming the tooth sockets
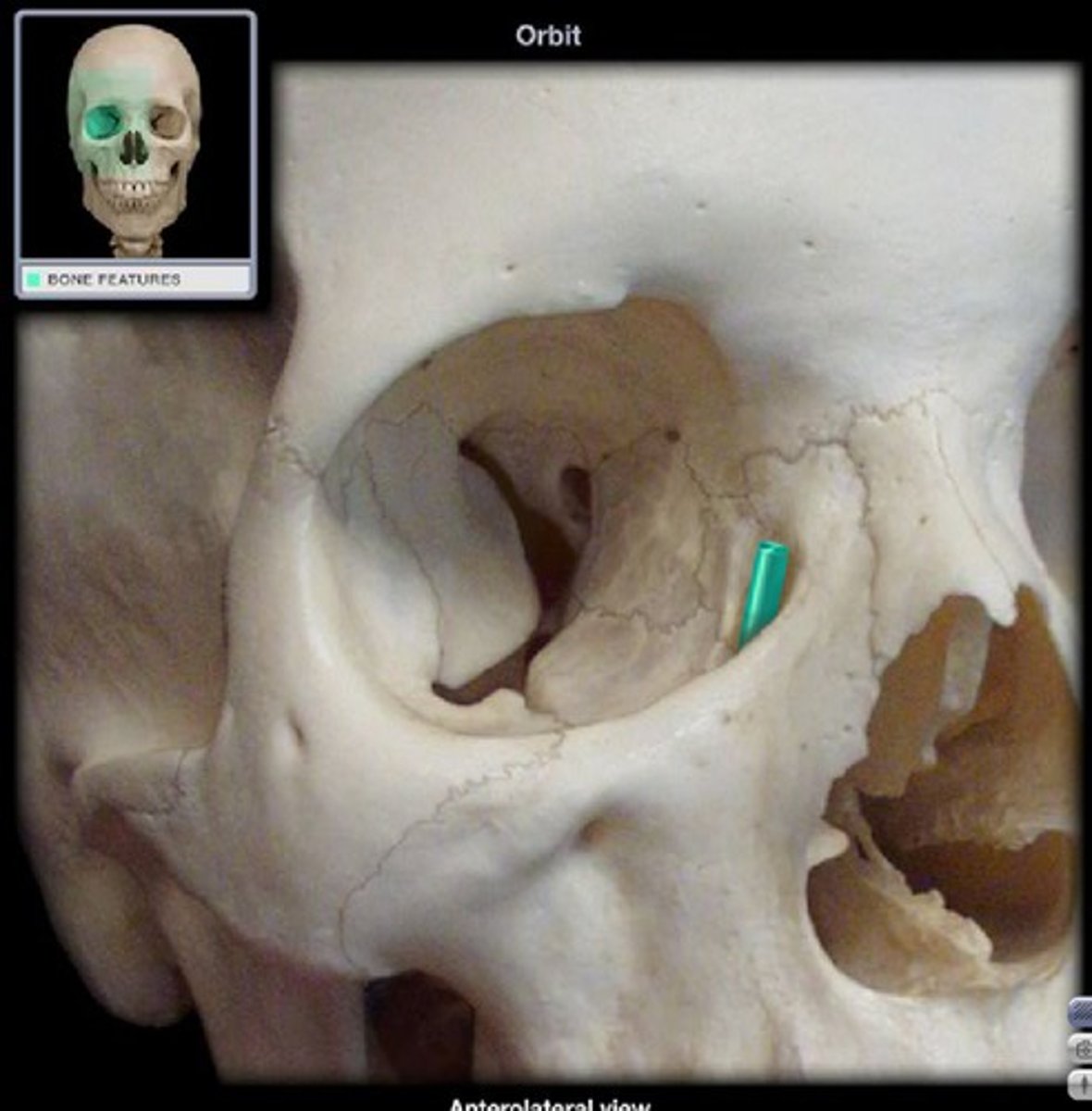
lacrimal fossa
Houses the lacrimal sac, which helps to drain tears from the nasal cavity.
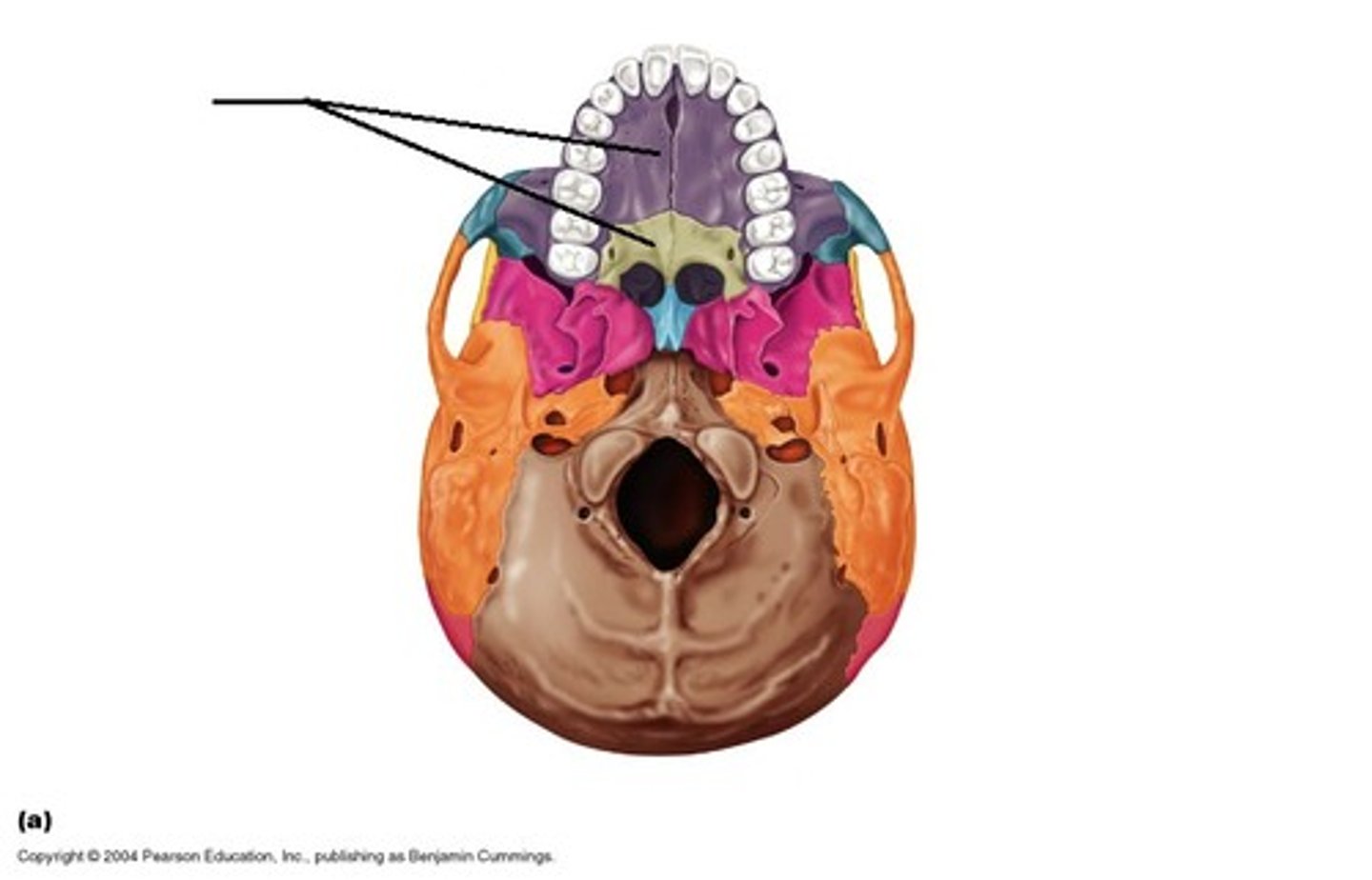
hard palate
the bony front part of the palate.
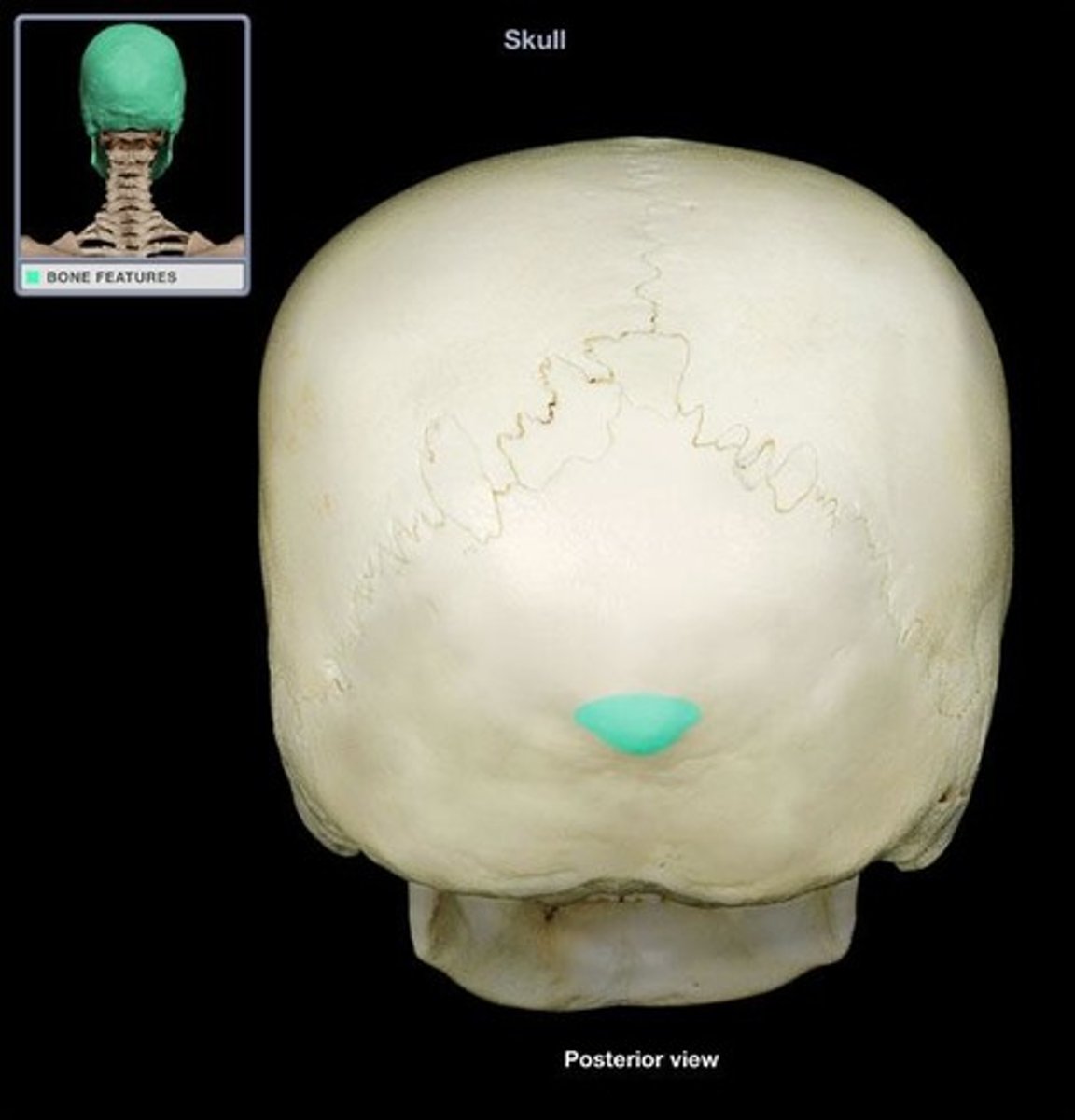
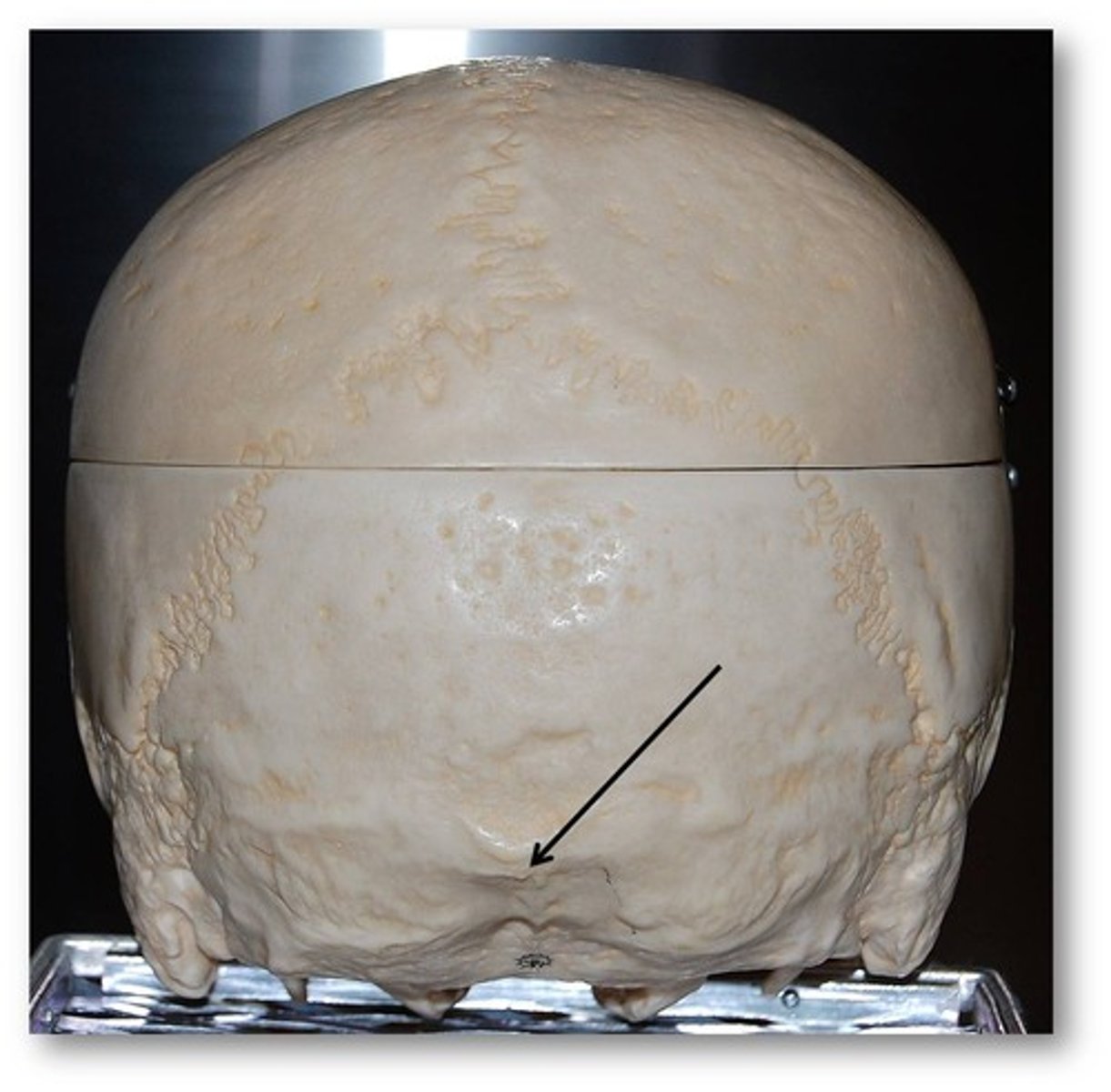
external occipital protuberance
Midline prominence posterior to the foramen magnum.
external occipital crest
part of the external surface of the squamous part of the occipital bone

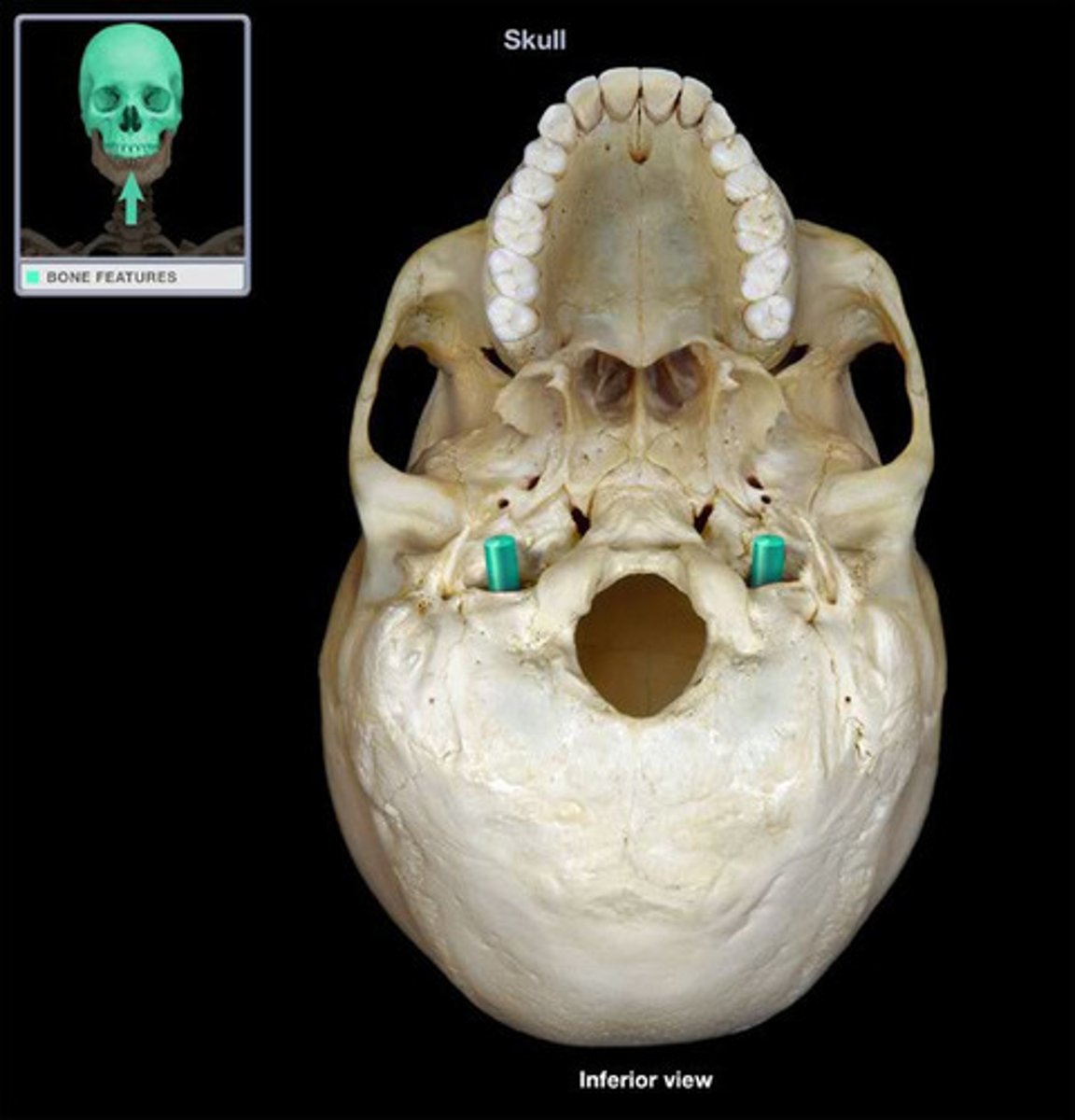
Foramen magnum
Large opening in the base of the bone, which allows the spinal cord to join with the brain stem.
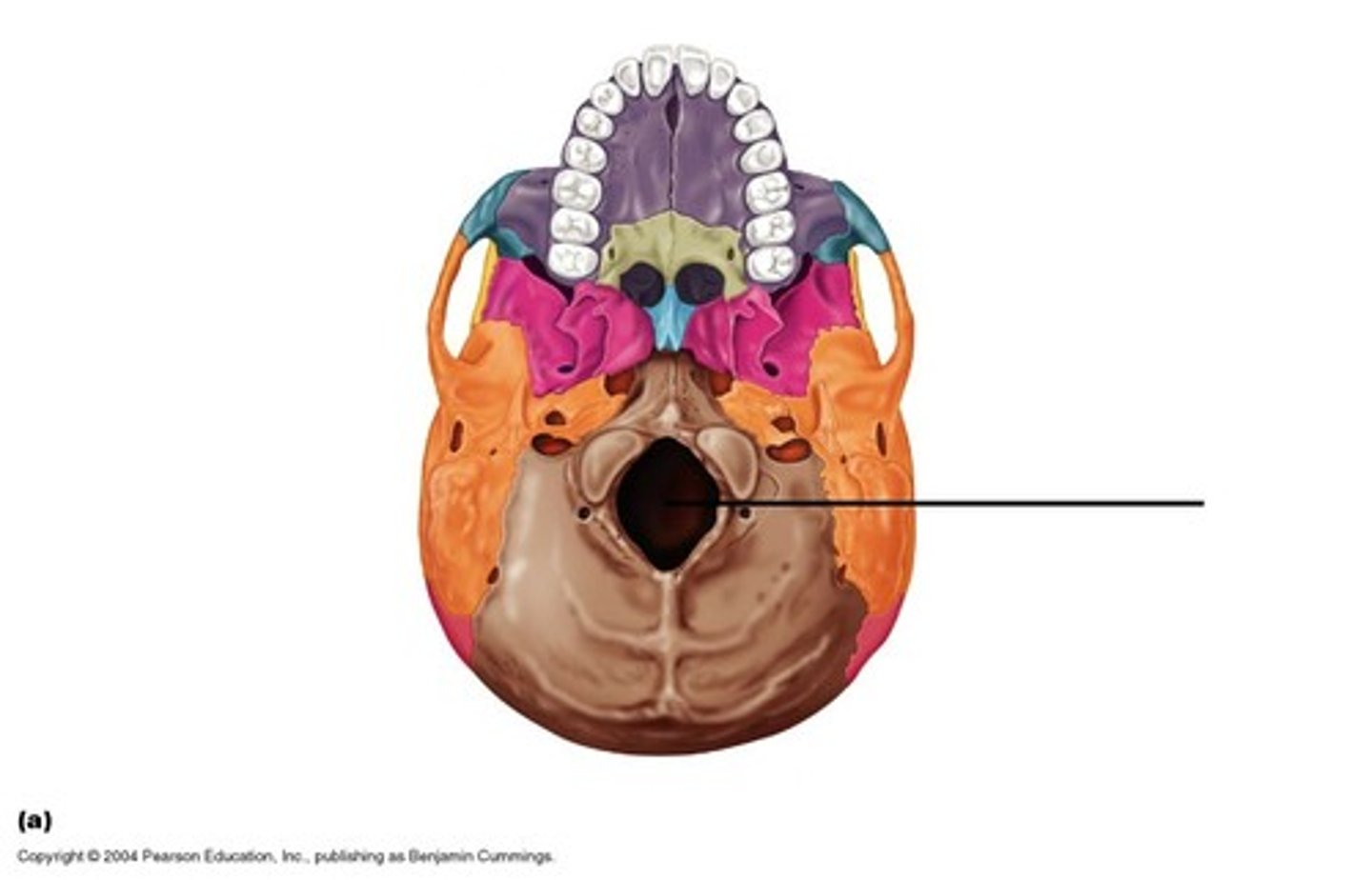
occipital condyle
each of two rounded knobs on the occipital bone that form a joint with the first cervical vertebra
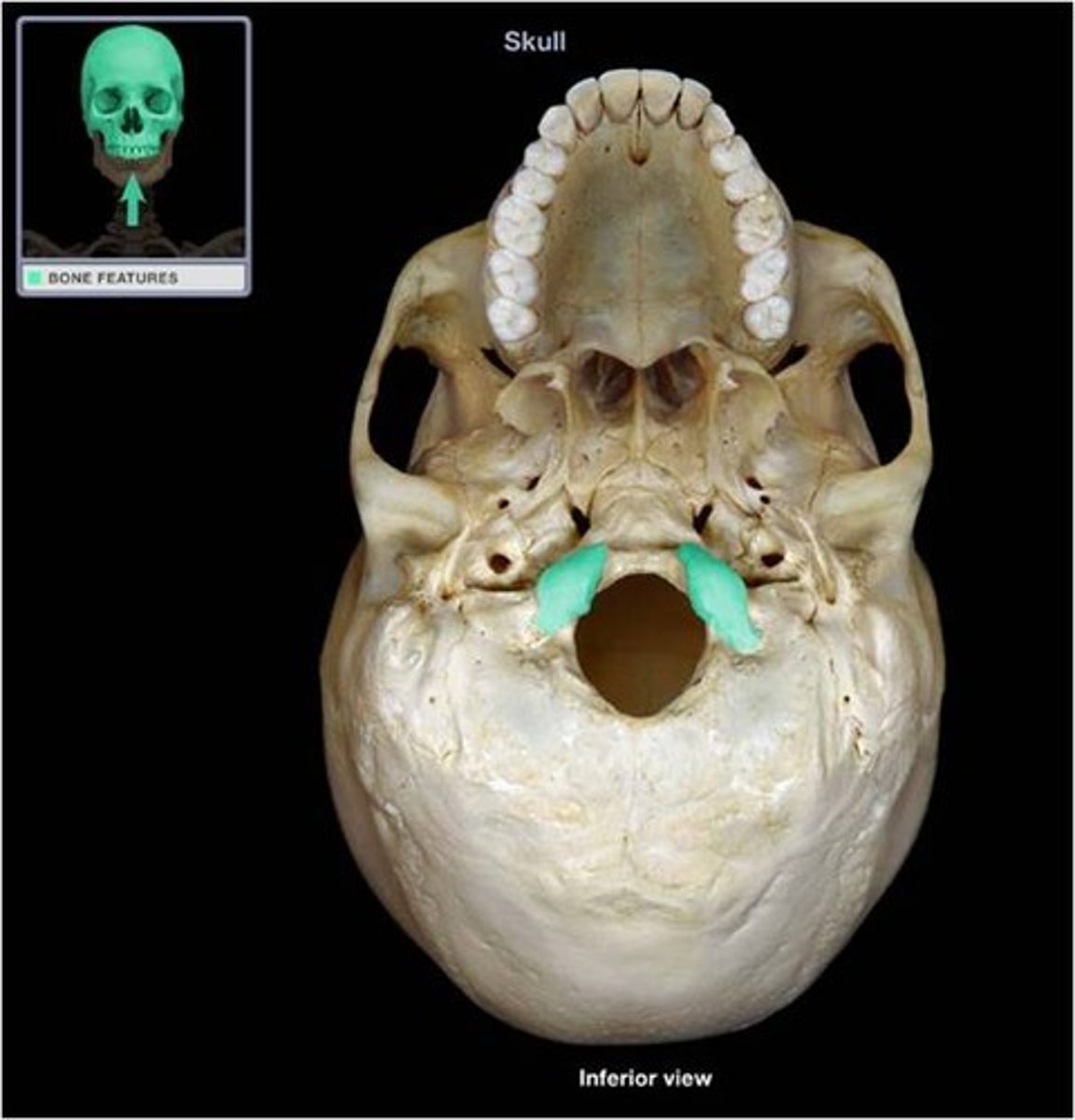
jugular foramen
Located where the petrous part of the temporal bone joins the occipital bone. Forms an opening which the internal jugular vein and cranial nerves IX, X, and XI! pass.