Maternity Exam 1
1/163
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
164 Terms
Apgar scores are done when?
at 1 and 5 minutes of life
Apgar scoring allows the nurse to rapidly assess ____ ____ and intervene with appropriate nursing actions.
extrauterine adaptation
Apgar score of 0-3 indicates
severe distress
Apgar score of 4-6 indicates
moderate difficulty
Apgar score of 7-10 indicates
minimal or no difficulty with adjusting to extrauterine life
Apgar score measures
heart rate
respiratory rate
muscle tone
reflex irritability
color
Apgar score: heart rate
0- absent
1- slow, <100 bpm
2- >100 bpm
Apgar score: respiratory rate
0- absent
1- slow, weak cry
2- good cry
Apgar score: muscle tone
0- flaccid
1- some flexion of extremities
2- well- flexed
Apgar Score: reflex irritability
0- none
1- grimace
2- cry
Apgar score: color
0- blue/ pale
1- pink body, cyanotic hands and feet (acrocyanosis)
2- completely pink
Ballard score is a newborn maturity rating score used to assess ____ and ____ maturity.
neuromuscular and physical maturtiy
Ballard score neuromuscular measures
posture
square window (wrist)
arm recoil
popliteal angle
scrap sign
heel to ear
Ballard score physical maturity measures
skin
lanugo
plantar surface
breast
eye/ ear
genitals (male)
genitals (female)
Ballard score maturity rating
-10: 20 weeks
-5: 22 weeks
0: 24 weeks
5: 26 weeks
10: 28 weeks
15: 30 weeks
20: 32 weeks
25: 34 weeks
30: 36 weeks
35: 38 weeks
40: 40 weeks
45: 42 weeks
50: 44 weeks
Leopold maneuvers determine
number of fetuses
presenting part, fetal lie, and fetal attitude
degree of descent of the presenting part into the pelvis
location of fetus’s back to assess for fetal heart tones
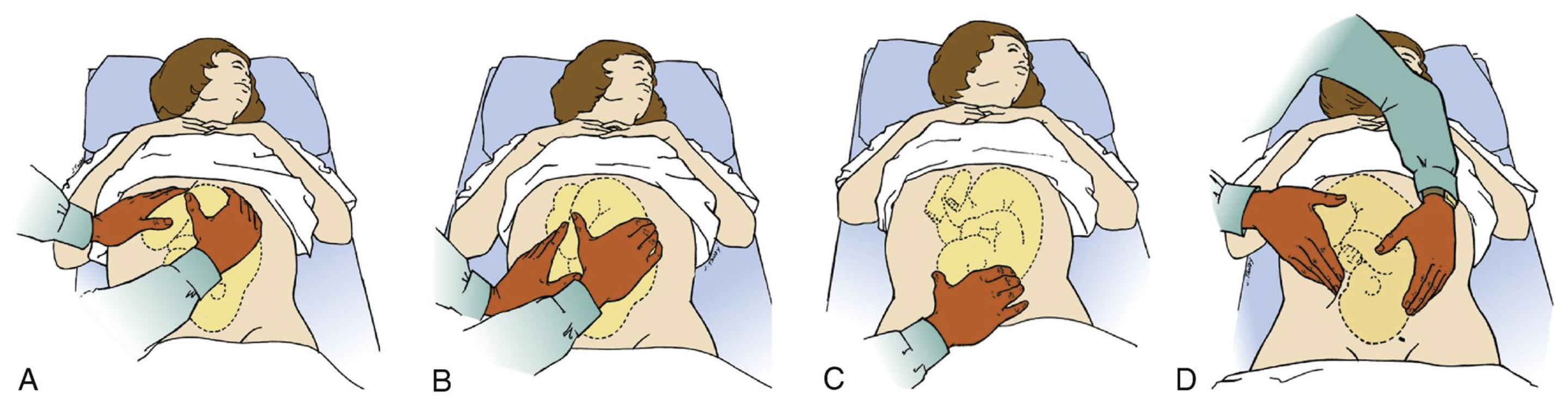
Vertex presentation: fetal heart tones should be assessed below the client’s ____ in either the right or left ___ quadrant of the abdomen.
umbilicus, lower
Breech presentation: fetal heart tones should be assessed ____ the client’s umbilicus in either the right or left ____ quadrant of the abdomen.
above, upper
Newborn vital signs are assessed in this order
RR
HR
BP
temperature
Normal newborn RR
30-60 breaths/min with short periods of apnea occurring most frequently during the rapid eye moment sleep cycle (<15 sec)
Normal newborn HR
110-160 bpm
Apical pulse is assessed for 1 min, preferably done when sleeping
Normal newborn BP
60-80 systolic
40-50 diastolic
Normal newborn temperature
97.7- 98.6 F
36.5-37.5 C
Lochia (PP uterine discharge) contents
amniotic fluid, WBCs, RBCs, blood, mucous, uterine tissue
Lochia rubra
1-3 days PP
dark red color, bloody consistency, fleshy odor, can contains small clots
transient flow increases during breastfeeding and upon rising
Lochia serosa
4-10 days PP
pinkish brown color, serosanguineous consistency
can contain small clots and leukocytes
Lochia alba
10 days- 8 weeks PP
yellowish white creamy color, fleshy odor
can consist of mucus and leukocytes
Scant bleeding
0-1in
Small bleeding
1-3in bleeding
Moderate bleeding
4-6in bleeding
Heavy bleeding
fully saturated pad in 1 hour
Homan’s sign: assesses for DVT in lower calf
check pedal pulse
have pt lift calf, flex and point feet
painful=positive
observe, dont touch
Oxytocin (Pitocin: synthetic form)
classification: uterine stimulant
promotes uterine contractions; labor induction
milk ejection/ let down
stimulation can lead to hypertonic uterine contractions
Oxytocin is released by
posterior pituitary
Prolactin
milk production
Prolactin is released by
anterior pituitary
Risk factors for shoulder dystocia
previous shoulder dystocia
cephalopelvic disproportion
fetal macrosomia
maternal diabetes mellitus
maternal obesity, short stature
uterine abnormalities
prolonged first stage of labor
maternal age > 40 years
pelvic soft tissue obstructions/ pelvic contracture
prolonged second stage
augmentation/ induction of birth
operative vaginal birth
Complications of shoulder dystocia
brachial plexus injury of neonate
neonatal fractures; humerus and/or clavicle
hypoxia & stillbirth
maternal trauma; ex. PPH and 3rd degree tears
Recognition of shoulder dystocia
slow & difficult delivery of fetal face and chin
when fetal head is born, it remains tightly applied to vulva
chin retraction “turtle sign”
anterior shoulder fails to deliver with ‘routine’ traction (diagnostic traction)
Shoulder dystocia management
McRoberts’ maneuver- thighs to chest, bottom lifted
suprapubic pressure- use palm/ fist, directly applying pressure over fetal anterior shoulder to dislodge it
Gaskin maneuver- hands and knees position. May be difficult to accomplish if mom has significant loss of motor function caused by regional anesthesia
Prolapse of the umbilical cord occurs when
the umbilical cord is displaced, preceding the presenting part of the fetus, or protruding through the cervix.
Results in cord compression and compromised fetal circulation.
Prolapsed umbilical cord is diagnosed by
seeing/ palpating the prolapsed cord, accompanied by the presence of abnormal FHR tracings
First stage of labor
lasts from onset of regular uterine contractions to full effacement and dilation of cervix (longer than second and third stage combined)
First stage; latent phase
onset of labor; contractions
irregular, mild to moderate
frequency: 5-30 min
duration: 30- 45 secs
dilation: 0-3cm
First stage; active phase
contractions
more regular, moderate to strong
frequency: 3-5 min
duration: 40-70 sec
dilation: 4-7cm
First stage; transition phase
contractions
strong to very strong
frequency: 2-3min
duration: 45-90sec
Second stage of labor
full dilation
progresses to intense contractions every 1-2min
Third stage of labor
delivery of the neonate
Fourth stage of labor
delivery of placenta, then maternal stabilization of vital signs
MR SOPPA- NRP
Mask adjustment (consider 2- hand technique)
Reposition (head neutral/ slightly extended
once seal is achieved, evaluate chest movement, air entry, then HR
Suction mouth (depth nose tip to earlobe)
Open mouth
once seal is achieved, evaluate chest movement, air entry, then HR
Pressure increase to 25/ 5cm H2O
once seal is achieved, evaluate chest movement, air entry, then HR
Pressure increase to 30/ 5cm H2O
once seal is achieved, evaluate chest movement, air entry, then HR
Airway alternative (ETT or LMA)
once seal is achieved, evaluate chest movement, air entry, then HR
NRP; the most important indicator of successful PPV is
a rising HR
NRP; maximum recommended pressures
30/5 in preterm baby
40/5 in full term baby
NRP; assess the need for decreasing pressures when HR is above
100 bpm
Provide __ seconds of effective ventilation before progressing through the NRP algorithm. Ensure there is ____ before starting compressions; if not, consider increasing PIP if appropriate.
30 seconds, chest rise
*PIP= peak inspiratory pressure
Immature lungs in the newborn may need
surfactant (keeps alveoli open)
Amniotic fluid volume
700-1000mL
Amniotic fluid properties
watery, clear, slightly yellow tinge
nonodorous
alkaline; pH 6.5-7.5
Five Ps of labor
passenger (fetus & placenta)
passageway (birth canal)
powers (contractions)
position (of the woman)
physiological response
Expected blood loss; vaginal delivery
300-500mL (10% of blood volume)
Expected blood loss; c- section
500-1000mL (15%-30% of blood volume)
Possible orthostatic hypotension within the first __ hours PP can occur immediately after standing up.
48 hours
Maternal BP after birth is usually ___ but can have
unchanged
an insignificant slight transient increase
Significant decrease of maternal BP after birth could indicate
bleeding
Significant increase of maternal BP after birth could indicate
PP hypertension
What vital signs increase for the first hour PP, then gradually decreases to a pre pregnant baseline by _-_ weeks.
____ in the PP period should be evaluated.
pulse, stroke volume, cardiac output
6-8 weeks
tachycardia
Due to elevations in stroke volume during the first _ days PP, maternal HR can be as low as
2 days PP
40 bpm
Elevation of maternal temperature to __F (38C) resulting from ____ after labor during the first 24 hours can occur, but should return to normal after 24 hours PP.
Elevation after 24 hours or that persists after 2 days could indicate ____.
100F, dehydration
infection
PP hemorrhage is blood loss over
1000mL
Risk factors for PP hemorrhage (PPH)
#1 cause: uterine atony
history of uterine atony
grand multiparity/ high parity
fetal macrosomia
manual removal of placenta, retained placental fragments
trauma to perineum (lacerations), hematoma
polyhydramnios; buildup of increased amniotic fluid
multiple gestation (twins, triplets, etc)
complications during pregnancy (placenta previa; placenta attaches below uterus, placental abruption/ abruptio placentae)
precipitous/ rapid labor
administration of magnesium sulfate therapy during labor
ruptured uterus, inversion/ subinvolution of uterus
coagulopathies (DIC)
Uterine atony results from
the inability of the uterine muscle to contract adequately after birth
Grand multiparity
≥5 births (live or stillborn) at ≥20 weeks of gestation
4 Ts of PPH
tone; uterine atony
tissue; placenta
trauma; lacerations, use of forceps, etc
thrombus; bleeding disorders, client on blood thinners
Physical assessment findings of PPH
uterine atony
blood clots larger than a quarter
perineal pad saturation in 15min or less
constant oozing, trickling, or frank flow of bright red blood from vagina
tachycardia & hypotension
pallor of skin & mucous membranes; cool, and clammy with loss of turgor
oliguria (low urine output)
Lab tests for PPH
Hgb & Hct
coagulation profile (PT)
blood type and crossmatch
Nursing care for PPH
fundal massage
monitor vital signs
assess for source of bleeding
assess fundus for height, firmness, position. If boggy, massage to increase muscle contraction
assess lochia for color, quantity, clots
assess for clinical findings of bleeding from lacerations, episiotomy site, or hematomas
assess bladder for distention; insert indwelling catheter to assess kidney function and obtain accurate measure of urinary output
maintain/ initiate IV fluids to replace fluid volume loss with IV isotonic solutions; LR or 0.9% sodium chloride; colloid volume expanders, such as albumin; and blood products (packed RBCs and fresh frozen plasma)
provide oxygen 2-3L/min per nasal cannula and monitor O2 sat
elevate client’s legs to 20-30 degree angle to increase circulation to essential organs
breastfeeding can stimulate uterine contractions
Medications for PPH
uterine stimulants
oxytocin; promotes uterine contractions
methylergonovine; controls PPH
misoprostol; controls PPH
carboprost tromethamine; controls PPH
Docusate sodium may be administered after birth to
prevent constipation
The position and location of the uterus after birth should be documented according to the number fingerbreadths.
If above umbilicus, document as
If below umbilicus, document as
above umbilicus +1, U+1, 1/U
below umbilicus -1, U-1, U/1
Location of fundus after delivery
Dday: at U
Dday 1: U-1
Dday 2: U-2, etc
(Dday= delivery day)
The fundus is located
at the top of the uterus
Gravidity
# of pregnancies
Nulligravida
a client who has never been pregnant
Primagravida
a client in their first pregnancy
Multigravida
a client who has had two or more pregnancies
Parity
# of births in which the fetus(es) reach 20 weeks of gestation
not affected whether the fetus is born stillborn or alive
Nullipara
no pregnancy beyond stage of viability
Primapara
has completed one pregnancy to stage of viability
Multipara
has completed two or more pregnancies to stage of viability
Viability
the point in time when an infant has the capacity to survive outside of the uterus
~20 to 25 weeks gestation
GTPAL
Gravidity; # of pregnancies
Term births; 37 weeks or more
Preterm births; viability- 37 weeks
Abortions/ miscarriages (prior to viability)
Living children
GTPAL
Gravidity; # times pregnant
GTPAL
Terms- # live/ still births at or passed 37 weeks (full term)
GTPAL
Preterm- # pregnancies delivered at less than 36 6/7 weeks
GTPAL
Abortion/ miscarriage less than/ before 20 weeks
GTPAL
Living- # living children
What is the GTPAL for a 27 y/o who is 16 weeks pregnant and has
2 y/o twins delivered at 39 weeks
5 y/o delivered at 40 weeks
no miscarriages or abortions
G3 T2 P0 A0 L3
What is the GTPAL for a 30 y/o woman who is 25 weeks pregnant with twins and has
5 living children
4/5 born at 39 weeks
1 born at 27 weeks
1 miscarriage at 10 weeks
G7 T4 P1 A1 L5
Naegele’s rule is used to calculate
the expected due date based on the birthing person’s last menstrual period.
Only used if the person is sure of their LMP.
How is Naegele’s rule calculated?
subtract 3 months from the date of their LMP and add 7 days. Usually the year remains the same unless the date calculated takes us into the next calendar year.
What is the expected due date of a woman whose LMP was May 21, 2023 using Naegele’s rule?
February 28, 2024