Classification and cladistics
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
HL topic Ib bio
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Why is classification needed?
Biologists group organisms to represent similarities and proposed relationships. Classification systems change with expanding knowledge about new and well-known organisms.

What are the two methods for modern Classification?
•Binomial Nomenclature – a two-part name (Genus, species) in Latin, e.g. Acer rubrum
•Hierarchical system of classification composed of 7 taxonomic categories, overarching domains and multiple subgroups.

What was the traditional way of classification?
Taxonomy is the classification using hierachical taxa (sgl. taxon) Goes from the broadest categories (domains) to the most specific (species).
Domain
kingdom
Phylum
class
order
family
genus
species

What are the difficulties of classifying organisms?
Carl Linnaeus created a system of classification based off of morphology which can cause some issues.
Traits based on morphology and the physical characteristics to distinguish one species from another are often arbitrary and subjective
A system based on hierarchy has strict ranking regulations. If one organism is moved out of a group it compromises all other ones in the same group.
The more organisms are discovered, the more often hierarchy doesn’t work. Hybridization in plants & development of subspecies complicate the system



What are the difficulties of using the Taxonomy system as a means of classification
uncertainties are the result of the evolution by gradual divergence of species over time. As species diverge from each other there will eventually be sufficient diversity for the genus to be divided into two or more separate genera. The exact point of when this happens cannot be determined.
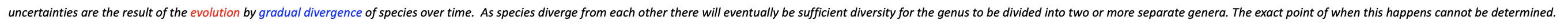
What is a phylogentic tree?
A diagram that shows the evolutionary relationships among various biological species based on their shared characteristics and ancestry. Identifying molecular differences in the proteins sequence and DNA
Define Phylogeny
The study of the evolutionary past of a species

What are the advantages of using phylogeny for classification?
•Features are not arbitrary or subjective
•Every organism that has evolved from a common ancestor is included in the same taxonomic group (called a clade) reflecting natural gene flow.
•Features or biomechanical responses of organisms within such a group can be predicted because they are shared with members of that clade.(maybe provide examples)
- Pridicting a new species of bat as we know the features of them. (mammels)
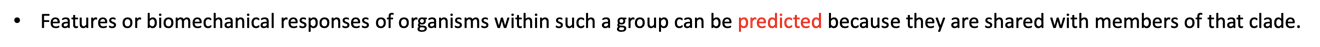


Define cladistics
Cladistics is a system of classification for grouping taxa based on the characteristics that have evolved most recently.
(the diagram illustrating this is called a phylogenetic tree or cladogram)
Define the term Primitive traits
Characteristics that have a similar structure and function. (e.g leaves with vascular tissue in order to transport water). and have evolved early in the history of the organism.
Define derived traits
Characteristics that have similar structure and function but have evolved more recently in the form of modification of previous traits.
Define a node in a cladogram
A point in a cladogram that represents the common ancestor of two or more taxa, indicating where a lineage diverges.
basically the dot
Whats a clade on the cladogram?
A group of organisms that includes an ancestor and all its descendants, representing a branch on a cladogram.
Whats a root on the cladogram?
The base of a cladogram that represents the most recent common ancestor of all the taxa in the diagram.
What are the terminal branches in a cladogram?
The tips of the diagram
whats the sister group in a cladogram
a group of the closest relatives
Whats a out-group on a cladogram?
A group that is less likely related to another.
What does branch length and node depth indicate on a cladogram?
Deeper nodes are older than shallower nodes to which they are connected, this indicates more distant relationships among the terminal taxa they connect. Along branches, hereditary genetic changes are accumulation.
When systematists talk about "branch lengths," they are typically referring to the number of these changes.


How can gradual accumulation of sequence differences be used as the basis for estimates of when clades diverged from a common ancestor.
mutation: differences in the base sequence of DNA and therefore in the amino acid sequencing of protein.
These changes accumulate over time gradually and if it happens roughly at a instant rate therefore scientists can track down using the number of differences to estimate the time since two species have diverged from a common ancestor
Whats the rule for the “molecular clock”
The larger the number of sequence differences between two species, the longer since they diverged from common ancestor.
How can base sequences be used to determine how closely related certain species are to one another?
fewer differences in base or amino acid sequences = closely related species/ diverged relatively recently
more differences in base sequences or amino acid sequencing = species that have diverged further along the line
Using cladistics to investigate whether the classification of groups corresponds to evolutionary relationships
Figworts species
A major reclassification has been carried out.
Less than half of the species have been retained in the family, which is now only the thirty-sixth largest among the angiosperms
How did the classification of all organisms fit into three domains using evidence from rRNA base sequencing
In the past all living organism were grouped into two overarching categories based on cell types – prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Base sequences of RNA have revealed that prokaryotes are much more diverse. As a consequence prokaryotes are now divided into Bacteria and Archea, resulting in a three domain system or Eukarya, Archea and Bacteria.
link: what else do you know about archea???