Legal Issues and Risk Management in Entrepreneurship
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
Sole Proprietorship
A business owned by one person who has unlimited liability and unlimited rights to profits.
Advantages of a Sole Proprietorship
Ease of start, simplicity of registration, fewer government regulations, rapid decision making, greater rights to profits.
Disadvantages of a Sole Proprietorship
Difficult fund raising, significant time obligations and responsibility, unlimited personal liability, lack of emotional support, taxation of profits.
Partnership
A business with two or more owners that make decisions for the business together and share the profits, losses, assets, and liabilities.
Limited Partnership
A business partnership wherein there is a general partner with unlimited liability, and one or more limited partners with no official input in daily operations, and limited liability.
Corporation
A legal entity composed of stockholders under a common name, which has rights and responsibilities under the law.
General Partner
A partner in a partnership who manages the company and assumes legal liability.
Shareholders
Individuals or entities that own shares in a corporation and elect a board of directors.
Board of Directors
A group elected by shareholders to represent their interests in the management of the company.
Contract
A legally binding agreement between parties that outlines obligations and rights.
Contingency
A provision in a contract that specifies conditions under which certain actions will take place.
Boilerplate Language
Standardized text in contracts that is often used without modification.
Letter of Agreement
A document that outlines the terms of an agreement between parties and is used to confirm mutual understanding.
Breach of Contract
A violation of any of the agreed-upon terms and conditions of a contract.
Statute of Limitations
The maximum time period after an event within which legal proceedings may be initiated.
Small Claims Court
A court that handles minor civil disputes involving limited amounts of money.
Arbitration
A method of resolving disputes outside of court, where an arbitrator makes a binding decision.
Bankruptcy Filing
The legal process by which individuals or businesses declare inability to pay debts.
Intellectual Property
Creations of the mind, such as inventions, literary and artistic works, and symbols, names, and images used in commerce.
Service Mark
A type of trademark that identifies and distinguishes the source of a service rather than a product.
Trademark
A symbol, word, or words legally registered or established by use as representing a company or product.
Copyright
A legal right that grants the creator of original work exclusive rights to its use and distribution.
Electronic Rights
Rights related to the distribution and use of digital content.
Patents
Exclusive rights granted for an invention, allowing the patent holder to exclude others from making, using, or selling the invention.
Public Domain
Creative works that are not protected by intellectual property laws and are free for use by anyone.
Insurance Premium
The amount paid for an insurance policy.
Insurance Deductible
The amount that the insured must pay out of pocket before the insurance coverage kicks in.
Actuaries
Professionals who analyze financial risks using mathematics, statistics, and financial theory.
Data Protection
The process of safeguarding important information from corruption, compromise, or loss.
Permit
An official document giving someone authorization to do something.
License
A legal permission to do something that would otherwise be illegal.
Certificate
An official document attesting a certain fact, such as completion of a course or ownership of property.
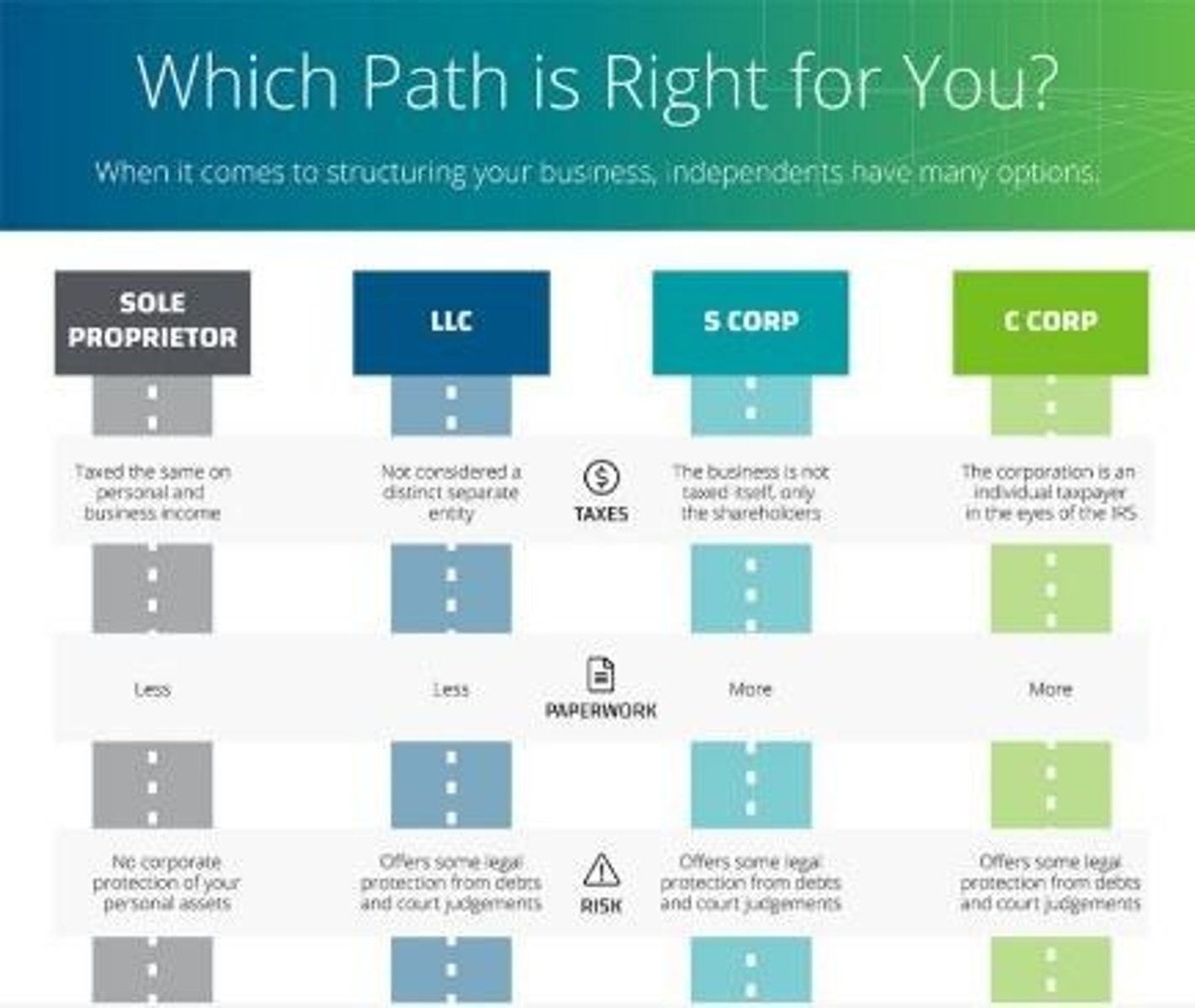
Advantages of a Corporation
The corporate legal structure offers key advantages: Ability to sell ownership shares, Ease of transfer, Limitation of personal liability, Continued existence.
Disadvantages of a Corporation
The corporate legal structure offers key disadvantages: Double taxation, Loss of founder control, Higher formation costs, Greater government regulation.
C corporation
Most large companies and many smaller ones are C corporations. They sell ownership as shares of stock.
Subchapter S corporation
This type of corporation has a limit of 100 stockholders.
Professional corporation (P C)
Medical practices, engineering firms, law firms, accounting firms, and certain other professions can form professional corporations.
Nonprofit corporation
A nonprofit corporation is not set up for the purposes of shareholder financial gain, but rather with a specific mission to improve society.
Public benefit corporation (B corporation)
This form of company explicitly includes a civic or environmental benefit in its charter, in addition to including profitability as a goal.
Limited liability company (L L C)
The L L C, which combines the best features of partnerships and corporations, can be an excellent choice for small businesses with a small number of owners.
Series limited liability company (S L L C)
The S L L C is a form of L L C that provides liability protection across 'multiple series' (akin to divisions or subsidiaries) while protecting each from the liability of the others.
Contract
An agreement between two or more parties that is enforceable by law.
A Successful Contract Should Achieve these Four Aims
Avoid misunderstanding, Ensure work, Ensure payment, Avoid liability.
Contingency
A condition that must be met for something else to occur.
Boilerplate language
A standard format for a specific type of legal agreement.
Letter of agreement
A document that puts an oral understanding in writing, in the form of a business letter.
Breach of contract
The failure of a signatory to perform as agreed.
Signatory
An individual who signs a contract.
Statute of limitations
The time period in which legal action may be taken.
Small claims court
A legal option for solving conflicts involving less than a certain sum of money.
Arbitration
A method of dispute resolution using an arbitrator to act as the decision maker rather than going to court.
Bankruptcy
The legal process in which an individual or business declares the inability or impaired ability to pay debts as they come due.
Intellectual Property
A critical practice for any entrepreneur is to protect his or her ideas, products, inventions, and designs.
service mark
a design that identifies and distinguishes the source of a service rather than a product.
Copyright
the form of legal protection offered under U.S. law to the authors of 'original works of authorship,' including literary, dramatic, musical, and artistic works.
Copyright creation
A work is 'created' when it is fixed in a copy or phono-record for the first time.
Copyright notice requirements
The symbol © (the letter c in a circle) and/or the word 'copyright,' or the abbreviation 'copr.' and the current year, and the name of the owner of the copyright.
electronic rights
the right to reproduce someone's work online.
patent
an exclusive right, granted by the government, to produce, use, and sell an invention or process.
public domain
property rights available to the public rather than held by an individual.
risk management
the process of protecting your physical property and managing potential losses.
insurance
a system of protection for payment provided by insurance companies to reimburse individuals and organizations when their property or wealth has been damaged, destroyed, or lost.
premium
the cost of insurance.
deductible
the amount of loss or damage a policyholder covers before the insurer pays on a claim.
Workers' compensation insurance
insurance that covers medical costs and disability benefits for employees injured at work.
Property insurance
insurance that covers damage to or loss of property.
Liability insurance
insurance that covers the cost of injuries to a customer or damage to property on a business's premises.
Disability insurance
insurance that provides income in the event a policyholder is unable to work due to a disability.
Product liability insurance
insurance that covers the risk of your product harming someone.
Business income insurance
also known as 'business interruption' insurance, it covers loss of income due to a disaster.
Commercial fleet insurance
insurance that covers vehicles used for business purposes.
Errors and omissions insurance
insurance designed to cover you in the event that you have overlooked something and a customer is harmed.
Key person life insurance
insurance that protects a business against the loss of a key employee.
actuaries
experts employed by insurance companies who calculate the odds of a particular event actually happening.
Disaster Recovery Plans
plans that address communications, base of operations, priority activities, and return to facilities.
permit
an official document that gives a party the right to hold a specific event.
license
an official document that grants the right to engage in an activity for a specified period of time.
certificate
an official document that verifies something.
Operations
A set of actions that produce goods and services.
Production-Distribution Chain
The process that involves converting inputs to outputs and varies based on the type of business.
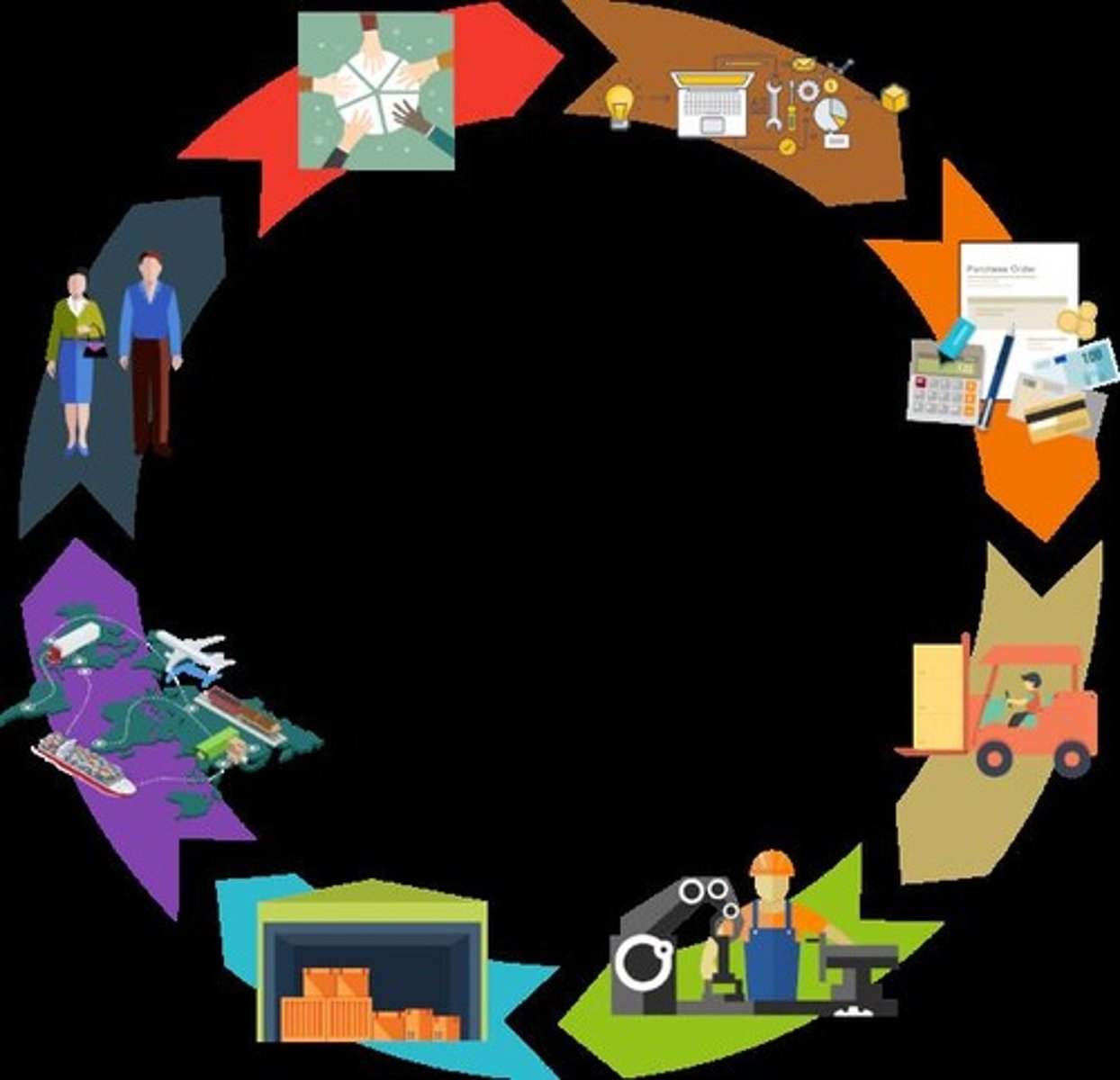
Supply Chain Management (SCM)
The management of sourcing, procuring, production, and logistics to go from raw materials to end customers across multiple intermediate steps.
Safety Stock
An inventory buffer to prevent stockouts, determined based on demand and lead time.
Reorder Point
The inventory level at which a new order should be placed to replenish stock before it runs out.
Economic Order Quantity (EOQ)
A formula used to determine the optimal order quantity that minimizes total inventory costs.
ERP
Enterprise Resource Planning; a system that helps businesses manage and integrate important parts of their operations.
Location Decision
The process of determining the best location for a business based on various factors.
Factor-Rating Method
A technique used in location decision-making that assigns weights to various factors affecting the decision.
Geographic Information Systems
Tools used to analyze and visualize spatial data for better decision-making.
Center-of-Gravity Method
A mathematical approach used to find the optimal location for a facility based on transportation costs.
Clustering Method
A strategy that involves locating businesses in proximity to one another to benefit from shared resources.
Quality
The degree to which a product or service meets customer expectations and requirements.
Quality Management System
A structured system of procedures and processes for ensuring quality in an organization.
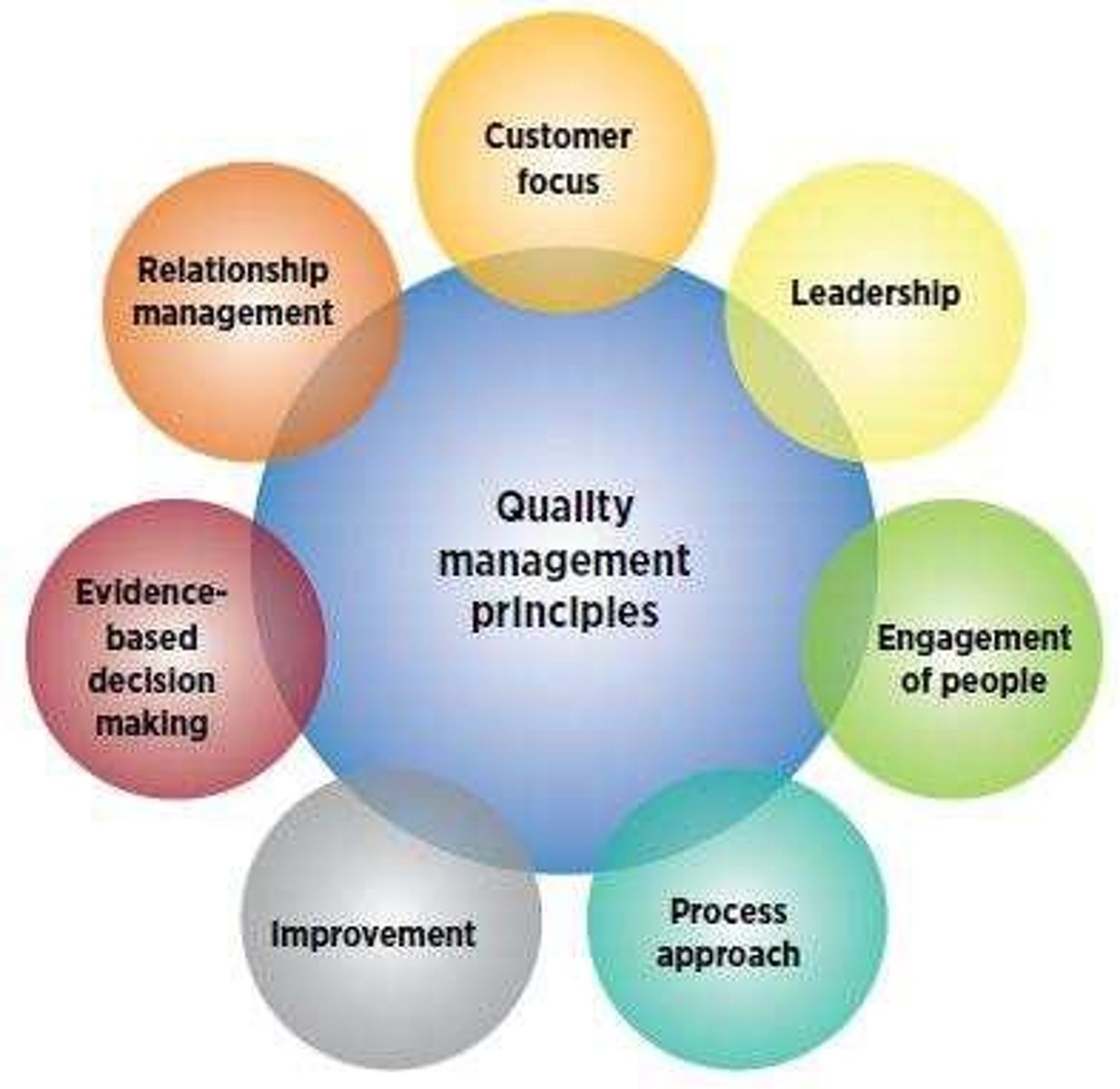
Total Quality Management (TQM)
A management approach focused on long-term success through customer satisfaction and continuous improvement.
Inventory Management
The process of ordering, storing, and using a company's inventory.
Demand Projections
Estimates of future customer demand used to inform inventory and production decisions.
Lead Times
The amount of time that passes from the initiation of a process until its completion.
Carrying Costs
The total cost of holding inventory, including storage, insurance, and depreciation.
Order and Setup Costs
Costs associated with placing orders and preparing to produce goods.
Sales Price
The amount charged to customers for a product or service.
visual control
inventory management method in which an individual assesses the stock level on hand by visual inspection and reorders when the supply appears low.