patho things i dont know
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
iatrogenic
ex. infection from a foley cath
incidence
rate at which new cases occur over a set time
prevalence
total number of disease cases at a certain time new and old
hypertension imposes extra workload on the left ventricle, causing this. symptoms are SOB, chest pain, syncope, irregular heartbeat
CH
this condition is a result of hyperplasia and it alters glucose levels so they often test for it with glucose tolerance
acromegaly
chemical
vascular response involves what mediators
tissue injury vascular response
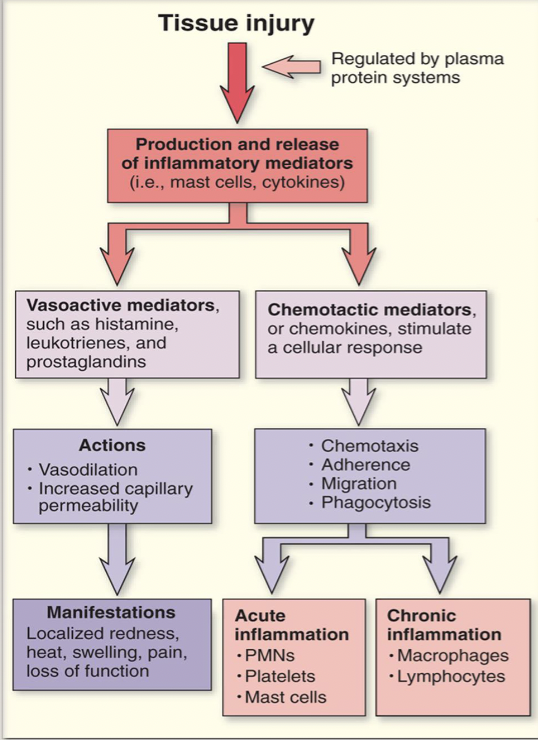
cell derived
what kind of mediators are WBC, platelets, endothelial or damaged tissue cells
plasma derived
what kind of mediators are complement system, kinin system, and clotting system
acute inflammation vs chronic (cells involved)
acute= PMNs, platelets, mast cells, neutrophils.
Chronic= macrophages, lymphocytes, monocytes, fibroblasts
ask which are phagocytes
sinusitis
cant get mucous out bc of inflammation of sinuses
primary cause is viral infections
acute is 4-8 weeks, chronic is treated with steroids as well as antibiotics
tissue healing and repair
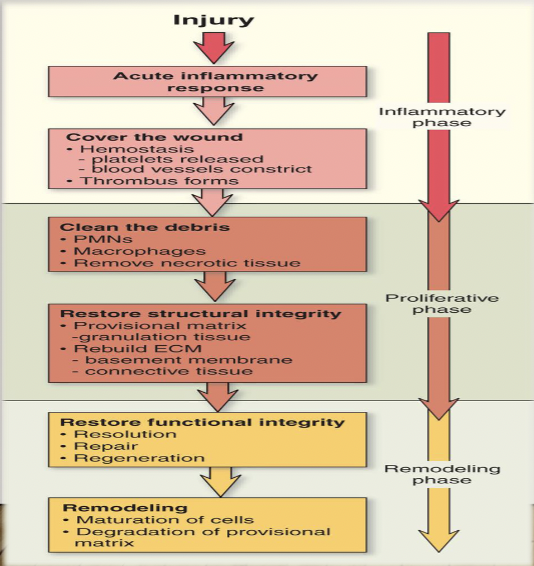
vitamins needed for every phase of wound repair
a and c
primary intention and secondary intention healing
primary is cleaner and smaller and stuff, secondary is opened and slow and heals from bottom up
RA (3 labs, CMs, patho)
-elevated ESR and CRP, presence of RF
-basically arthritis but tired, symmetrical, exacerbations, nodes, pannus
-autoimmune attack on joints
acute gastritis causes
long term NSAID use,
H. Pylori
extreme stress
alcohol, caffeine, smoking
(use PPIs and antacids)
chronic gastritis can cause what
impaired absorption of B12, impaired production of gastric acid, anemia
crohns unique sign and patho, common location,
skip lesions, chronic inflammation (granulomatous- thick) in the small intestine
obstructions can result
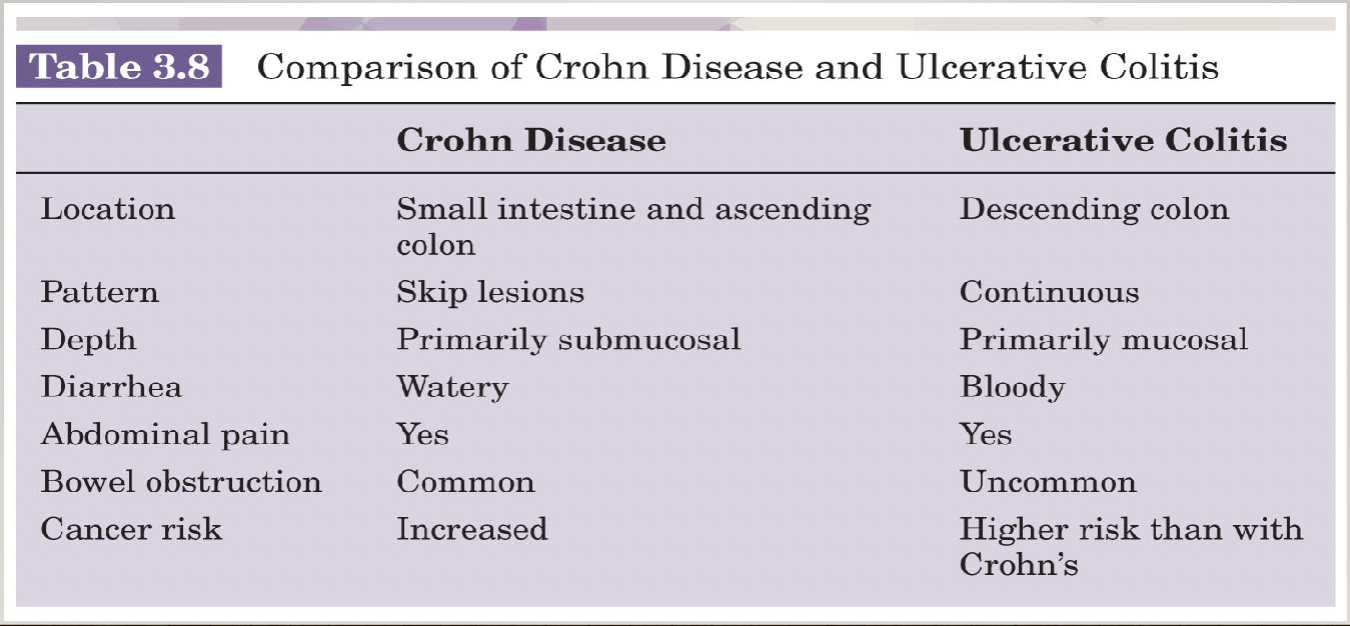
ulcerative colitis patho and location
chronic inflammation mostly superficial in colon, can cause more bleeding issues and anemia
what is the 3rd line of defense against infection
immune system
most common opportunistic infection and its deets
oral thrush
maceration and fungal infection
function of antimicrobial, antibacterial, antifungal drugs
antimicrobial: destroy and alter cell structure of pathogens
antibacterial: inhibits synthesis of cell wall
antifungal: binds to cell membrane to increase permeability
viral hepatitis specific signs, treatment
-jaundice, dark urine, clay stool
-antivirals, low fat diet
walled off area of bacteria (granuloma) in TB is called
ghon focus
pyelonephritis patho, most common cause, manifestation triad
infection/inflammation of renal parenchyma causes scarring
-urinary obstruction like kidney stones, E. Coli
-fever, cva pain, N/V
what type of meningitis is less severe and often resolves without treatment, specific CMs
viral
photophobia, nuchal rigidity, kernigs and brudzinskis (with neck) signs
along with systemic, what organ will be affected by malaria
liver
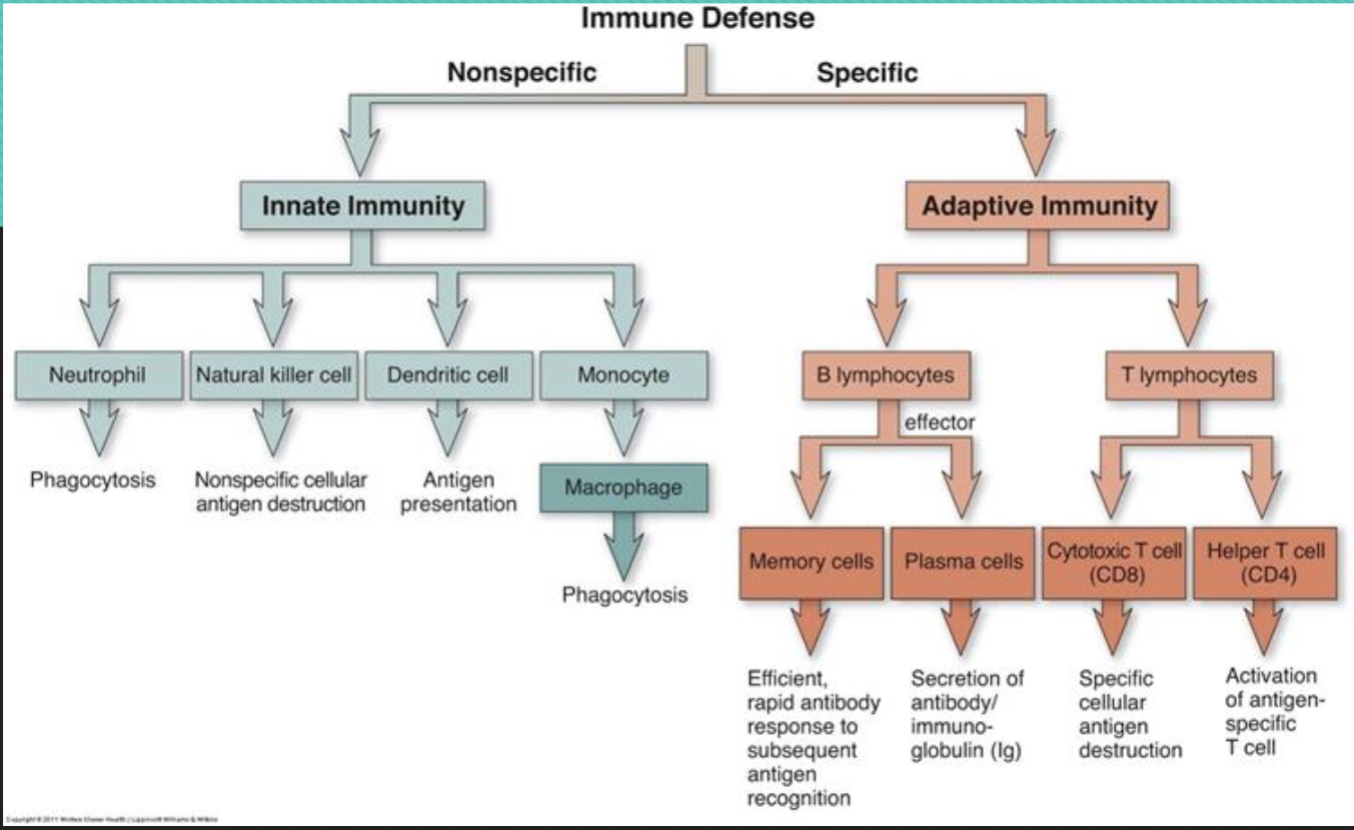
difference between t lymphocytes and b lymphocytes, NKC
T: from thymus, 3 types (cytotoxic, helper, suppressor)
B: from bone marrow, become plasma cells and antibody producers
NKC: natural killer cells, primary defense, innate
difference between IgG and IgE
IgG: most common, active against a lot of toxins, viruses and stuff and activates complement
IgG: stuck to mast cells, stimulates histamine for allergic reactions
central vs. peripheral organs
C: bone marrow, thymus
P: spleen, lymph nodes and lymph tissue
innate vs adaptive immunity
types of hypersensitivity reactions 1, 2 and 3
1: mast cells and IgE release through blood (anaphylaxis)
2: specific organs (rh isoimmunization)
3: whole body (lupus)
aids patho and stages
uses rna transcription to change genetic makeup of cells, loss of immunity due to loss of CD4 T lymphocytes
causes you to get more rare diseases.
kaposi sarcoma (cancer that comes from herpes virus)
0- positive infection
1- over 500 cells
2- 200 to 499 cells
3- under 200 cells
anaphylaxis CMs
bronchospasm, itching, angioedema, BP drop
SLE symptoms
-butterfly rash, joint pain/swelling, fatigue, swelling around heart and lungs, proteinuria, ulcers, arthritis
explain rh isoimmunization
normally blood between mom and baby dont mix, but when someone has an amnio, miscarriage, ectopic, or abortion the blood can mix, and if they are different rh types, the mom will make antibodies against the babys blood. If this occurs, blood mixing in the NEXT pregnancy will cause a type 2 hypersensitivity reaction and attack the baby, resulting in hemolytic disease.
then the baby can have hearing loss, learning problems, cerebral palsy, elevated bilirubin
treat with rh immunoglobulin
fluid compartments
intracellular and extracellular (interstitial vs intravascular)
hypervolemia
increase in extracellular volume from:
-increased sodium, aldosterone
-decreased intravascular fluid, albumin
can result in:
-symptoms, Decrease in hematocrit, serum osmolality, serum sodium, BUN, BNP
hypovolemia
-from VPPS losses, hyperventilation, hemorrhage, third spacing
-Decreased skin turgor, ortho and postural bp, urine output, perfusion
-increase in hematocrit, BUN, spec grav, osmolality, sodium, ADH, SERUM POTASSIUM AND SODIUM
Hyponatremic dehydration: sodium, type of fluid loss, fluid shift
Low sodium, hypertonic loss, fluid shifts into the cells (causing low bp)
isonatremic dehydration: sodium, type of fluid loss, fluid shift
(most common) normal sodium, isotonic fluid loss, no fluid shifts
hypernatremic dehydration: sodium, type of fluid loss, fluid shift
high sodium, hypotonic fluid loss, fluid goes from in the cell to outside the cell because its so salty out there, causing cellular dehydration
hypotonic iv fluids cause
water to move from extra to intracellular space
hypertonic iv fluids cause
water to move from intra to extracellular space
types of cirrhosis (scarred liver)
alcoholic, biliary, post-necrotic
albumin- made by liver, makes sure fluids doesnt leak from vessels and tissue
-decreased production of clotting factors, coagulation disorders
-palmar erythema, spider angioma, peripheral edema, ascites, flapping tremors, toxic ammonia levels, varices
hypokalemia

normal pH, bicarb, PaCO2
7.35-7.45
22-26
35-45
anion gap=
sodium — (chloride and bicarb),, big gap= acidosis
ways of regulating pH
lungs: control elimination of CO2
Kidneys: excrete H+, reabsorbs and generates new bicarb
(chemical) bicarb buffer system: most important—> weak acids or bases exchange for strong ones to neutralize
(chemical) KH exchange: excess H+ is exchange for K+ across the membrane
(chemical) Protein buffer: largest—> intracellular proteins, albumin, and plasma globulins combine with or liberate H+ (amphoteric)
repiratory: chemoreceptors detect changes in PaCO2 and pH—> increased ventilation decreases PaCO2 and H+ to prevent acidosis
how to determine the acid base imbalance
respiratory involves weird CO2 level (up= acidosis)
metabolic involves weird bicarb level (up= alkalosis)
acid-base imbalance causes
metabolic acidosis: overdoses, liver failure, hyperkalemia, hyperchloremia, diarrhea, kidney injury
metabolic alkalosis: vomiting, diuretics, hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, hypochloremia, hypomagnesemia, antacid abuse, inadequate renal perfusion
respiratory acidosis: hypoventilation, over-sedation, brain stem dysfunction, OSA, acute resp distress, COPD, pneumothorax
respiratory alkalosis: hyperventilation, anxiety/pain, respiratory distress, stroke/head injury
types of chemoreceptors for ventilation
peripheral: in the aorta and carotid, detect oxygen levels, respond to low levels by increasing ventilation
central: in the brain, levels of PaCO2
V/Q mismatch
either the lungs are ventilated but not perfused or the lung is perfused but not ventilated
(ex. PE and atelectasis)
hypoxemia and hypoxia
decreased oxygen leading to decrease in partial pressure of oxygen, leads to hypoxia
hypoxia first sign is restlessness/anxiety
cancer patho
neoplasms: irreversible deviant cell clusters that have autonomy and anaplasia
cancer: highly invasive and destructive neoplasms
—caused by alteration in genes that control cell repro, growth, differentiation and death (acquired mutations are most common but also can be genetic)
mutator genes: repair DNA, protect genome
protooncogenes: normal genes
oncogenes: mutated protooncogenes that cause cells to divide and multiply like crazy
tumor suppressor genes: regulates cell division and death rate
initiation promotion progression theory
initiation: causes mutation in cell
promotion: oncogenes activated, dependent on exposure to promoter
progression: independent growth, no longer need the promoter
leukemia acute vs chronic and patho VERSUS lymphoma
rapid production of abnormal WBCs, philadelphia chromosome for CML
versus
lymph tissue tumors, abnormal B and T cells (hodgkin— neck lymph nodes, night sweats, REED-STERNBERG CELLS or non-hodgkin— systemic)
synovial membrane has ______ blood supply, tendons and ligaments do NOT
rich
fat embolism
can be from a fracture, first symptoms include subtle change in behavior, then non-blanching petechial rash
types of bone cancers
osteosarcoma, ewing sarcoma, chondrosarcoma
osteoarthritis
-progressive loss of articular cartilage
-synovitis
-bone spurs
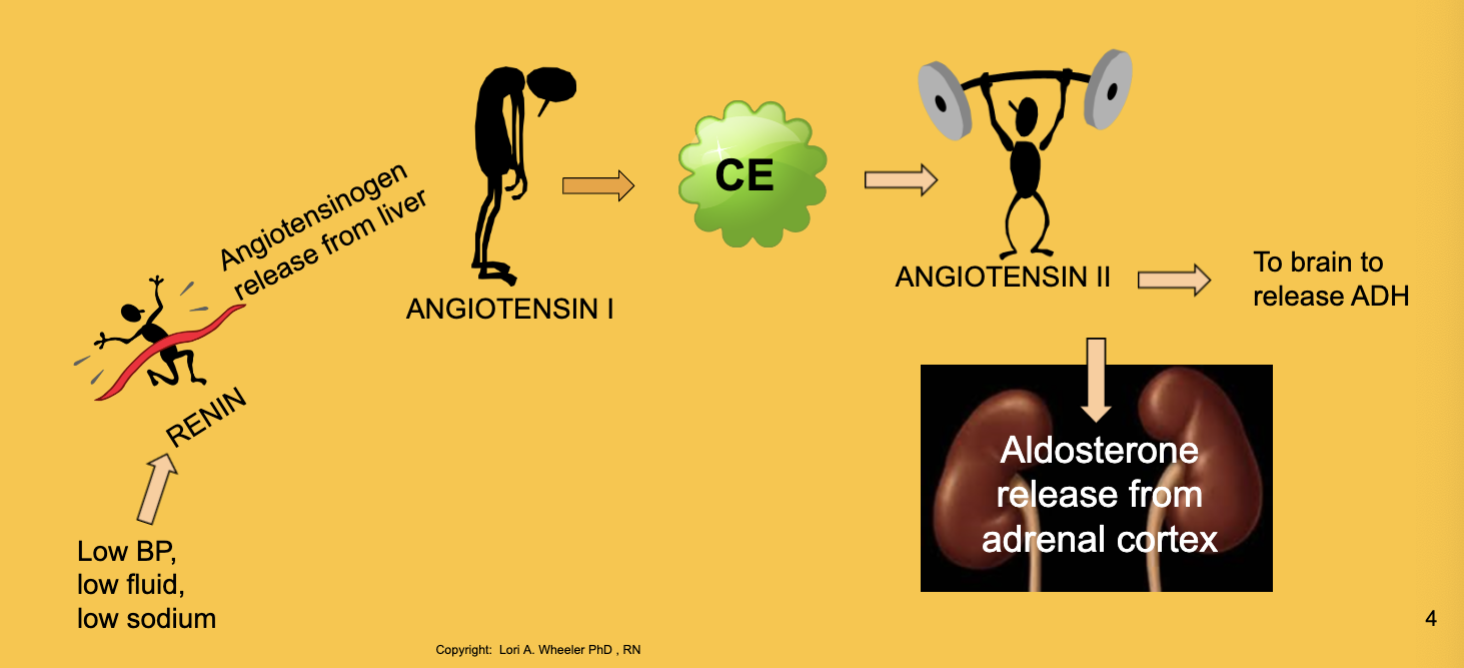
kidney functions and RAAS
filters blood, F/E balance, produces vitamin D and erythropoietin and renin (for bp)
GFR: how fast the glomerulus is filtering blood
polycystic kidney disease
genetic autosomal dominant, replacement of kidney tissue with cysts, earliest CM is HYPERTENSION, high risk of fluid volume overload
what is in white and gray matter
white= axons and dendrites, myelin
gray= cell bodies outside in the brain
PNS components
somatic (cranial nerves, spinal nerves, peripheral nerves)
autonomic (sympathetic and parasympathetic)
pyramidal vs extrapryamidal
extra= basal ganglia, background and suportive movement like coordination and balance
pyramid= delicate movement
parkinsons
tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia
progressive destruction of nigrostriatal pathway, reduction in dopamine
MS
demyelinating autoimmune disease of CNS
plaques in brain, spinal cord, optic nerve
VISUAL FIELDS is first sign
steroids for exacerbations
cerebral palsy
lack of oxygen event during fetus-ery damaging upper motor neurons, not progressive
spastic, dyskinetic, ataxic, and all the plegias
seizure precautions
increased ICP
increased BP, lower HR, papilledema
negative vs positive feedback loop
hormones in stress response
corticotropin releasing hormone, acth, cortisol, catecholamines
GAS
alarm stage triggers HPA axis, sympathetic ns and body defenses
resistance begins w actions of adrenal hormones, mobilization
exhaustion only happens when stress doesnt go away after adaptation
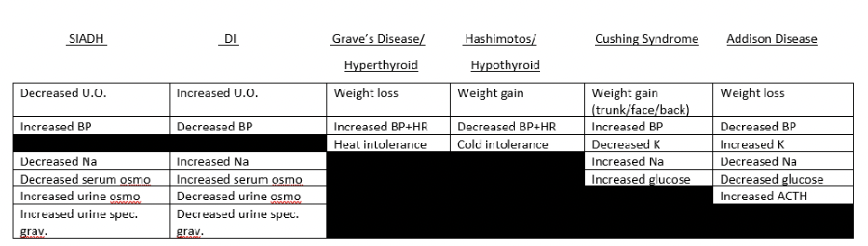
too little hormone
DI: too little ADH, diuresis increasis, water intoxication and dehydration
-treat w hydration and desmopressin
Hypothyroidism: complication is myxedema coma
Addisons: autoimmune destruction of adrenal cortex, acth increases to help, causing farmer tan adn like skinny weak sick dehydrated ppl. hyponatremia, hyperkalemia
-fluid replacement and steroids, increase sodium
too much hormone
SIADH: too much ADH commonly from tumor, water accumulates in cells and sodium is diluted in extracellular space, causing hypotonic hyponatremia, NOT PEE ENOUGH
-treat w iso/hyper IV, diuretics
Hyperthyroidism: graves disease is autoimmune, binds to tsh receptors. goiter, crazy thin and oily and eyes poppin
—treat by just taking that bitch out w surgery or iodine
Cushing: excess glucocorticoids from adrenal cortex from long term steroid use or tumors. fat trunk, back and head with glucose intolerance. test cortisol levels in urine
-remove the bad shi
hormonal disease effects chart
NORMAL age related changes
longer healing, less padding and temp control, more inactive sweat glands, dry skin
decrease in muscle and increase in fat, causing decrease in total body water and F/E effects
immune senescence, enhanced autoimmune stuff, reduced allergy response, decreased Tcell function and Bcells dont make antibodies as fast, cancer not detected as quickly
decrease in brain mass, neurons, synapses, and myelin. bigger ventricles and altered neurotransmitter production, slower reaction times, decreased blood flow to brain
presbyopia and presbycusis
loss of bone, more brittle bones, joint cushion worn down, synovial fluid gets thicker, sarcopenia, mild kyphosis
less springy lungs, alveolar enlargement
decreased resting HR, heart valves thicken and harden, increased workload on left ventricle
declining ingestion/absorption and movement in gi tract, liver function declines, reduced renal blood flow
less elastic baldder and urinary retention, stress incontinence, prostate issues
even though more common in older adults, still ABNORMAL changes
cataracts, glaucoma, MD, parkinsons, hyperkyphosis, constipation, full incontinence
older adult assessment tools
MOCA, SPICES, morse fall risk, TUG, SCALES (malnutrition)
progeria
autosomal dominant, hyaluronic acid in blood
alzheimers
amyloid plaques, tau tangles, neuronal loss
1: minimal cognitive impairment
2: mild, evident only to self
3: mild, evident among family, friends
4: moderate, evident by examiner
5: moderately severe, requires assistance for day to day activities
6: severe, significant personality changes, assistance with ADLs, episodes of incontinence, delusions and wandering
7: very severe: loss of ability to respond to environment
malnutritions
marasmus: starvation, skinny
Kwashiorkor: protein deprivation with adequate CHO intake, big round belly
protein contains nitrogen, need to maintain nitrogen balance for protein synthesis and production of things like hormones, neurotransmitters, cell mediators, antioxidants
macro vs micronutrients
macro: protein (10% to 35%), carbs (45% to 65%), lipids (20% to 35%)
micro: vitamins (fat soluble ADEK, water soluble BC) and minerals
water
nitrogen balance
homeostasis is zero nitrogen balance
positive is when the intake exceeds the output and can happen in growth periods, tissue repair, hypothyroidism, pregnancy, and bodybuilding
negative is when output exceeds intake and can happen with prolonged immobility, malnutrition or absorption, burns, trauma, and surgery
carbs
monosaccharides (glucose and fructose), di-/oligosaccharides (sucrose and lactose) and polysaccharides (starches and fiber)
for energery, reducing cholesterol, fiber aids gastric motility
Vitamins
organic substances the body needs but isnt able to manufacture
aids in metabolism of macros, helps develop genetic materials and hormones and collagen and NS tissue
Vit K produced in the intestines, newborns get a Vit K shot because they arent getting it from solid food and it helps to clot blood and form bone
Vit D absorbs and metabolizes calcium and phosphorus
Vit C does iron absorption, metabolizes amino acids, synthesizes steroid hormones
Vit B metabolizes carbs, folate forms blood cells in the bone marrow
minerals
inorganic substances critical to cellular processes
sodium, potassium, calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, sulfur (macros)
iron, zinc, flouride, copper (micros)
they constitute bone, hemoglobin, enzymes, hormones and chemical mediators, they mediate impulses and maintain fluid and acid/base balance
appetite hormones from hypothalamus
when full, increased BG triggers the release of insulin, and increased lipids trigger adipose tissue to release leptin
when tummy is empty, we release ghrelin
obesity
hypertrophic: bigger adipose cells
hypercellular: more adispose cells (often starts in childhood)
adipocytes synthesize triglycerides (three fatty acids)
measure mid-arm circumference
iron deficient anemia
Cx: chronic hemorrhage, iron malabsorption, high iron demands, inadequate iron intake, milk and celiac (??)
insufficient iron stores to meet needs for RBC development
low RBC, hematocrit, and hemoglobin, stool guaiac positive (black and tarry), PICA
microcytic (smaller RBCs) and hypochromic (less vibrant red)
celiac
T-Cell mediated hypersensitivity reaction
gluten is found in wheat, rye, oats, barley
strong hereditary component
lab value for nitrogen use in the body
BUN- the nitrogen in your blood that comes from urea
proteins broken down in intestines produce ammonia
liver changes ammonia to urea
kidneys filter out urea from the blood
insulin increases when what increases?
glucose and potassium
altered perfusion: V/Q mismatch, impaired circulation, inadequate cardiac output, exccessive perfusion demands
V/Q mismatch: ratio is 0.8:0.9, resp disease and PE
impaired circulation: hemorrhage, obstruction or disruption in flow like atheroma or DVT, inadequate blood comp. or volume
inadequate cardiac output: inadequate blood comp or volume, impaired ventricular function (CHF or defect), structural defect (ASD and VSD), excess peripheral vascular resistance (aterial diseases), conduction defects (arrhythmias)
exccessive perfusion demands: prolonged exertion, metabolic disease (thyroidisms), increased work load
a rise in troponin means
u had a heart attack
a rise in what protein indicates inflammation
c-reactive
homocysteine
an amino acid from breakdown of animal protein that some of the B vitamins like folate break down. if theres a lot it can cause a heart attack or stroke
clotting stuff dont really need to know i think)
platelets
prothrombin time
partial thromboplastin time
international normalized ratio
central vs tissue perfusion
central: pacemakers, electrical cardioversion, ablation therapy, intraaortic balloon, cardiac valve surgery, cardiac transplant
tissue or local: bypass, graft, stent or angioplasty, endarterectomy (blade takes away buildup)
starlings law
if thangs were more stretched at the start there would be more output like balloon (contractility)
preload: more stretch, better flow (volume)
afterload: more resistance, less flow (constriction and dilation)
atherosclerosis process
monocytes adhere to the vessel wall and change configuration to macrophage i think?
then they eat up the LDL and become foam cells
group of foam cells is a fatty streak
calcification of the plaques is fibroatheroma
next step is MI or stroke
doesnt happen overnight