2-3. neuro sys path 2-3
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
leukodystrophy vs. demyelination
leukodystrophy: formation of abnormal myelin or lack of myelination during development
rare
genetic or infectious
demyelination: myelin forms normally, then is lost due to a disease process
more common
causes of demyelination
virus-induced
canine distemper virus
immune-mediated (type II or type IV hypersensitivity)
pathogenesis of lysosomal storage diseases
genetic defects in lysosomal enzymes that would usually break down specific substrates → material accumulates in lysosomes → lysosomes swell, causing cells to swell → loss of cellular function
neurons & oligodendrocytes are particularly sensitive (can affect other cell types too)
clinical signs usually appear early in life
breeds associated with globoid cell leukodystrophy
west highland white terriers
cairn terriers
what cells are involved in globoid cell leukodystrophy?
oligodendrocytes affected → demyelination
gitter cells help phagocytose degraded myelin
general routes of entry into the CNS
hematogenous
leukocyte trafficking
retrograde axonal transport
direct extension (ex. through ear canal, trauma)
causative agents of pyogenic infections
streptococcus spp.
staphylococcus spp.
e. coli
trueperella pyogenes
klebsiella spp.
corynebacterium spp.
histophilus somni lesions in the brain
infarction → thrombotic meningoencephalitis (TME)
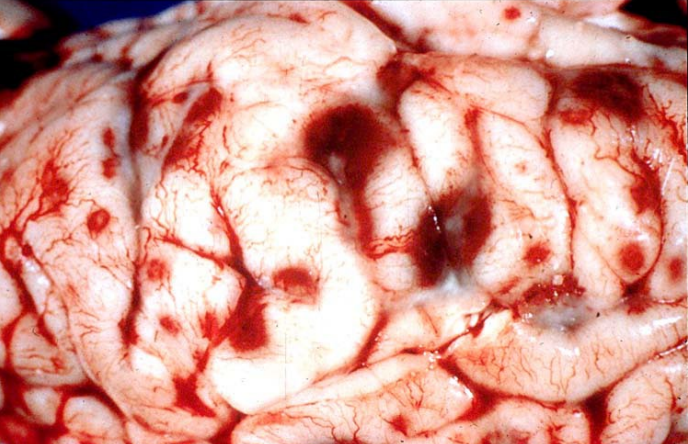
what is the typical distribution of listeriosis lesions in the brain? (how does it get to the brain?)
retrograde axonal transport via cranial nerves to enter the pons/medulla (often most severe in brainstem)
asymmetric inflammation → unilateral clinical signs
histological findings of listeriosis
gram stain: gram positive, short chains of bacilli
inflammation rich in neutrophils
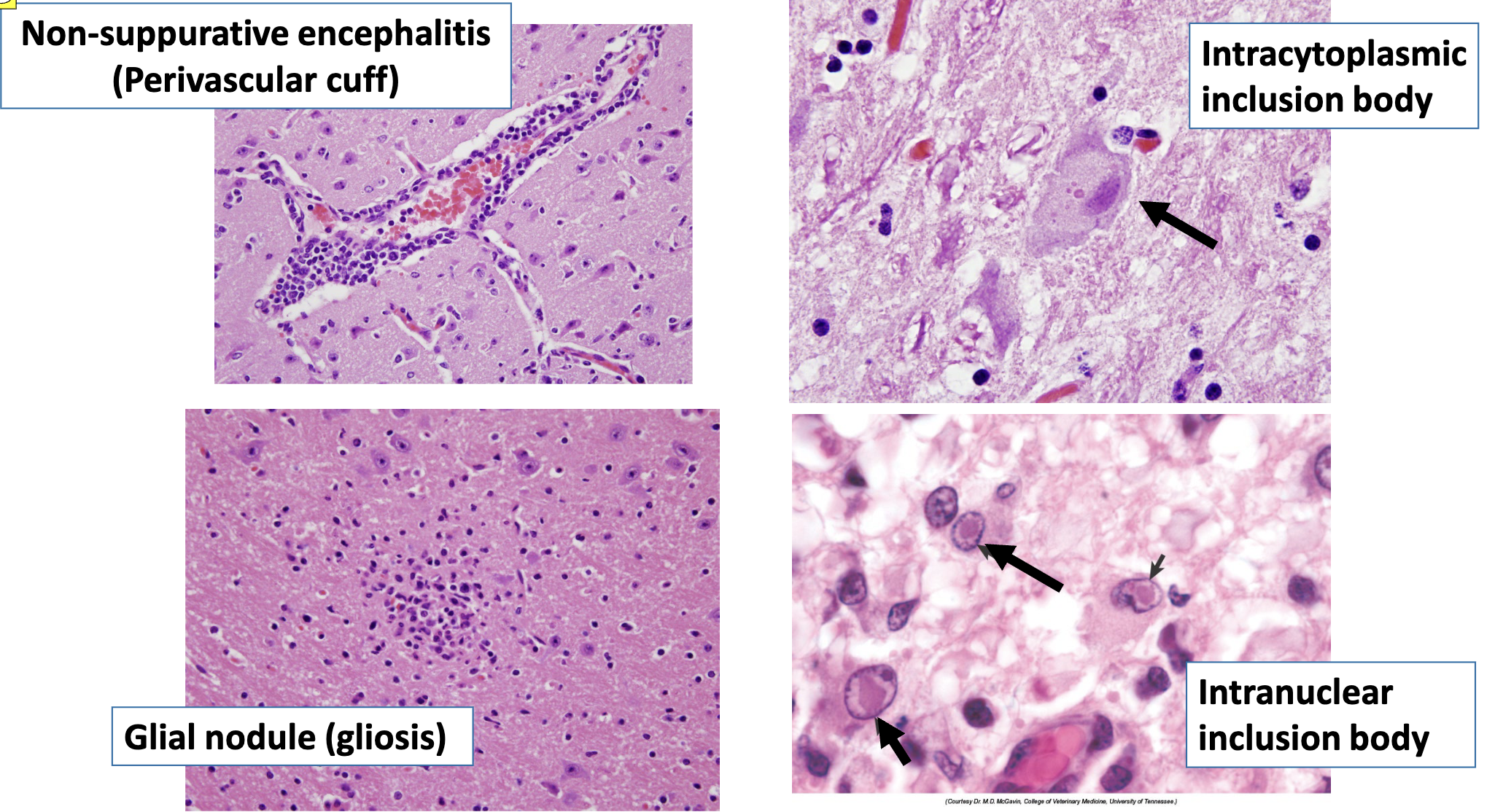
general histological findings of viral diseases
non-suppurative encephalitis (perivascular cuff)
glial nodule (gliosis)
intranuclear/intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies