Digestive System
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/150
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 7:43 PM on 5/2/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
151 Terms
1
New cards
what makes up the GI tract
oral cavity, most of pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines
2
New cards
what are the accessory digestive organs
teeth, tongue, salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
3
New cards
layers of GI tract
mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, serosa
4
New cards
purpose of muscularis mucosae in mucosa
causes folds which increase local movements increasing absorption w exposure to new nutrients
5
New cards
what GI tract sections have skeletal muscle aka voluntary control
mouth, pharynx, upper esophagus, anus
6
New cards
bolus
ball-like mixture of food and saliva that forms in the mouth during the process of chewing
7
New cards
where does chemical digestion start
mouth bc of saliva
8
New cards
where lipase is secreted from
under the tongue
9
New cards
chyme
gastric juices, saliva, food
10
New cards
pepsin function
begins digestion of proteins
11
New cards
intrinsic factor function
aids absorption of vitamin B12
12
New cards
gastric lipase function
aids in digestion of triglycerides
13
New cards
gastrin function
regulator of gastric acid/juice
14
New cards
what converts pepsinogen into pepsin
HCL hydrochloric acid
15
New cards
how lacteals get to right atrium
**liver slide talking about deoxygenated and oxygenated blood**
16
New cards
bilirubin definition
waste product, yellow in pigment produced from breakdown of heme group from the hemoglobin molecule found in RBCs
17
New cards
what type of tissue in mouth, esophagus, and anus
stratified squamous which is tough tissue
18
New cards
parts of the mucosa
epithelium, lamina propria, muscularis mucosae
19
New cards
epithelium mucosa composition
tough stratified squamous in mouth esophagus and anus and simple columnar everywhere else
20
New cards
epithelium mucosa function
secretes enzymes and absorbs nutrients, goblet cells secrete mucus onto cell surface, enteroendocrine cells secrete hormones controlling organ function
21
New cards
submucosa composition
loose connective tissue containing BV, glands, and lymphatic tissue
22
New cards
Meissner’s plexus responsibility
in submucosa, parasympathetic innervation, vasoconstriction, local movement by muscularis mucosa
23
New cards
muscularis composition
skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, auerbach’s plexus
24
New cards
why muscularis is important
third layer of GI tract, skeletal muscle allows voluntary swallowing and defecation, smooth muscle involuntary control mixing crushing and propelling food, and Auerbach’s plexus innervates circular and longitudinal smooth muscle layers
25
New cards
smooth muscle of muscularis function
inner circular fibers and outer longitudinal fibers, mix crush and propel food via peristalsis
26
New cards
serosa location
covers all organs and walls of cavities not open to outside of body
27
New cards
serosa function
secretes slippery fluid
28
New cards
serosa composition
CT covered w simple squamous epithelium
* an example of a serous membrane
* an example of a serous membrane
29
New cards
enteric nervous system (ENS)
brain of the gut controlling motility, secretions, chemoreceptors, and mechanoreceptors
30
New cards
Auerbach’s Plexus
longitudinal and circular smooth muscle layers of the muscularis controlling motility for both sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation
31
New cards
peritoneum parts
parietal peritoneum in abdominal cavity and visceral peritoneum acting like serosa to select organs
32
New cards
peritoneum significance
largest serous membrane of body containing large folds
33
New cards
greater omentum
peritoneum section draping over transverse colon and coils of the small intestine like a fatty apron
34
New cards
falciform ligament
attaches the liver to the anterior abdominal wall & diaphragm
35
New cards
lesser omentum anatomy
arises as an anterior fold of the serous of the stomach and duodenum connecting the stomach and duodenum to the liver
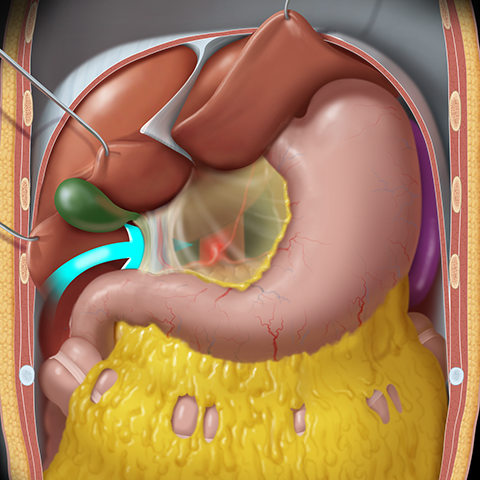
36
New cards
lesser omentum passageway
passageway for hepatic portal vein, common hepatic artery, and common bile duct
37
New cards
mesentery
binds the jejunum and ileum of the small intestines to the posterior wall
38
New cards
mesocolon
bind the transverse colon and sigmoid colon of the large intestine to the posterior abdominal wall
39
New cards
oral cavity function
initial phases of mechanical and chemical digestion begin and sensing food in it
40
New cards
roof of oral cavity
roof made of hard bones separating mouth from nasal cavity and soft palate projecting from hard palate that seperates mouth and pharynx
41
New cards
lateral boundaries of oral cavity
cheeks made of buccinator muscles & oral mucosa
teeth attached to jaws but not part of it
teeth attached to jaws but not part of it
42
New cards
oral cavity floor
tongue
43
New cards
anterior boundary of oral cavity
lips w vermillion border & incisor and canine teeth
44
New cards
tongue composition
skeletal muscle covered w mucous membrane
45
New cards
teeth anatomy location
embedded in the alveolar sockets of the maxilla and mandible
46
New cards
number of deciduous, baby teeth
20 deciduous erupting in first or second year
47
New cards
classes of teeth
incisors, canines, premolars, molars
48
New cards
molars
large teeth with four to five cusps adapted for crushing
49
New cards
premolars
most circular teeth with two cusps adapted for tearing (don’t exist for babies)
50
New cards
canines
pointed piercing teeth lateral to the incisors and have one root each
51
New cards
incisors
chisel shaped teeth for cutting in midline of jaw
52
New cards
lamina propria in mucosa composition
thin layer of loose CT containing BV and MALT lymphatic tissue
53
New cards
where are MALT lymphatic nodules
in mucosa of GI tract and in tonsils, appendix
54
New cards
muscularis mucosae in mucosa composition and function
thin layer of smooth muscle causing folds in mucosa that increase local movement increasing absorption of nutrients
55
New cards
salivary gland functions
soften and lubricate food, begin chemical digestion, taste, clean mouth to keep bacteria population regulated
56
New cards
types of salivary glands
intrinsic/minor and extrinsic/major
57
New cards
pharynx & esophagus digestion function
transport but NO digestion
58
New cards
where esophagus pierces the diaphragm
hiatus which can turn into a hiatal or diaphragmatic hernia
59
New cards
stomach location
large distensible muscular sac left upper abdomen immediately below the diaphragm
60
New cards
what forms chyme
stomach mixes saliva food and gastric juice
61
New cards
what attaches liver to anterior abdominal wall
falciform ligament
62
New cards
neural regulation digestive hormones
gastrin, secretin, CCK, somatostatin, histamine, serotonin, gastric inhibitory peptide
63
New cards
where is gastrin secreted from
G cells of the gastric glands in the stomach and intestinal glands in the duodenum
64
New cards
when is gastrin secreted
presence of peptides and amino acids as well as stomach distension
65
New cards
what does gastrin do
stimulates parietal cells in the gastric glands to secrete (HCL), stimulates motility of the stomach, relaxes the pyloric sphincter
66
New cards
what releases secretin
S cells of the intestinal glands in the duodenum
67
New cards
when is secretin released
when the pH in the small intestine is acidic it also prompts bile ducts to secrete more bile
68
New cards
what secretin does
stimulates pancreatic cells to secrete bicarbonate, the liver to produce bile & inhibits gastric motility and gastric juice secretion
69
New cards
what secretes Cholecystokinin (CCK)
CCK cells of intestinal glands in duodenum
70
New cards
when is CCK secreted
presence of lipids and polypeptides in small intestine
71
New cards
what CCK does
stimulates the pancreatic cells to secrete pancreatic juice, the release of bile from the gallbladder, and relaxes the hepatopancreatic ampulla sphincter
72
New cards
what secretes gastric inhibitory peptide
K cells in the intestinal glands of duodenum and jejunum
73
New cards
when is gastric inhibitory peptide secreted
presence of lipid and glucose in the small intestine
74
New cards
what does gastric inhibitory peptide do
release of insulin & inhibits gastric juice secretion and gastric motility
75
New cards
what secretes somatostatin
D cells of the stomach, intestine, and pancreas
76
New cards
what does somatostatin do
inhibits the secretion of gastrointestinal hormones, most importantly gastrin and histamine
77
New cards
what secretes histamine
enterochromaffin cells (histaminocytes) of stomach mucosa
78
New cards
what does histamine do
stimulates parietal cells to secrete hydrochloric acid
79
New cards
what secretes serotonin
enterochromaffin cells of the gastric mucosa
80
New cards
what does serotonin do
causes contraction of the stomach muscles
81
New cards
liver functions
excrete bilirubin, synthesize bile, excrete drugs, metabolize carbs/lipids/proteins, stores vitamins A/D/B12/Fe and glycogen
82
New cards
what liver produces
urea, bile, heparin, vit A, plasma proteins, antibodies
83
New cards
liver blood supply
oxygenated blood from hepatic artery and nutrient rich blood from stomach, spleen, and intestines carried via hepatic portal vein
84
New cards
liver blood supply order
hepatic artery, liver sinusoids, central vein, hepatic vein, inferior VC
85
New cards
liver’s carb metabolism
proteins into glucose, triglycerides into glucose, excess glucose into glycogen (to store), and glycogen into glucose as needed
86
New cards
liver’s lipid metabolism
synthesizes lipoproteins (HDL/LDL) and cholesterol, releases energy and stores fat, breaks down fatty acids
87
New cards
liver’s protein metabolism
convert one amino acid into another, converts ammonia into urea, synthesizes plasma proteins from clotting/immune system
88
New cards
deamination
liver removes NH2 (amine group) from amino acids so we can utilize the rest as energy
89
New cards
how much bile is secreted by the liver
1 quart per day
90
New cards
bile PH and color
PH 7.6-8.6 and yellow-green color
91
New cards
bile components
cholesterol, Na, K, bilirubin
92
New cards
liver’s heme
broken down into iron and bilirubin
93
New cards
how is bile released from the liver
released into the duodenum via the common bile duct
94
New cards
bile function
emulsify fats into micelle droplets by increasing surface area
95
New cards
how is bile reused
after fat emulsification, it can recycle back to gallbladder through ileum, via hepatic portal blood
96
New cards
what does bile synthesis stimulate
peristalsis
97
New cards
bilirubin and liver relationship
liver absorbs bilirubin from the blood and secretes it into the bile so it may be released into SI via biliary tree
98
New cards
bilirubin and LI relationship
bilirubin broken down in LI further by intestinal bacteria and excreted from the body in the feces.
99
New cards
drugs and kidneys
principle organs for drug excretion and their metabolites
100
New cards
liver and drug excretion
hepatocytes of the liver do play a small role in drug excretion by actively and passively excreting them into the bile