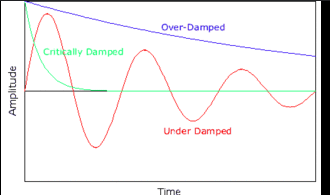
3- Damped oscillations
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is damping in oscillatory systems?
The process by which the amplitude of oscillations decreases over time due to energy dissipation
What are the three types of damping?
Underdamped: Oscillations gradually decrease in amplitude.
Critically Damped: The system returns to equilibrium without oscillating (completes no cycles).
Overdamped: The system returns to equilibrium slowly, without oscillating (completes no cycles).
What is the damping force equation for linearly damped motion?
b = the damping constant
v= the velocity.
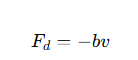
How does the damping force affect the energy of the system?
The damping force does negative work
This causes the mechanical energy of the system to decrease over time.
How does damping affect the amplitude of oscillations?
The amplitude decreases exponentially with time
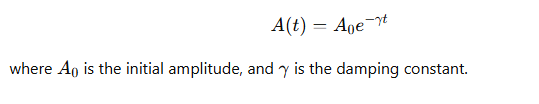
What is the time constant (τ) in damped harmonic motion?
The time it takes for the amplitude to decrease by a factor of e−1, or approximately 37% of its initial value.
What is the equation of motion for a damped harmonic oscillator?
m = mass
b= the damping constant
k= the spring constant.
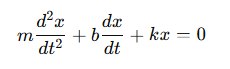
How is the displacement of a damped harmonic oscillator expressed?
ωd (ω’) = the damped angular frequency
δ= the phase constant.
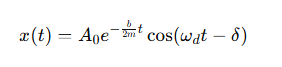
What is the formula for the damped angular frequency ω′?
ω0=√k/m is the undamped natural frequency.
γ=b/2m is the damping constant
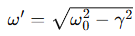
What happens to the angular frequency when damping increases?
As the damping constant increases, the angular frequency decreases
At the critical damping value, the angular frequency becomes zero.
What is the condition for the system to become overdamped?
When the damping constant b is greater than or equal to the critical damping value
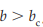
What is the equation for the damping constant at critical damping?
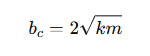
What is the equation for the time constant in a damped system?
m is the mass of the object,
b is the damping constant.
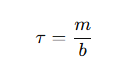
How does the energy of an underdamped oscillator change with time?
it decreases exponentially with time.
E0 is the initial energy,
γ=b/2m is the damping constant
t is time.
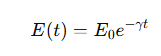
What is the formula for the Q-factor?
ω0 is the natural angular frequency of the system
τ=m/b is the time constant of the oscillator
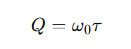
What is the physical interpretation of the Quality Factor (Q) for weak damping?
For weak damping, the Quality Factor Q is inversely proportional to the fractional energy loss per cycle.
The larger the value of Q, the smaller the energy loss per cycle, and the longer the oscillations persist.
What is the relationship between Q factor and resonance?
The Q factor determines the sharpness of resonance.
A high Q gives a narrow, sharp resonance, while a low Q gives a broad, flat resonance.
How is the fractional energy loss per cycle related to the energy of a damped oscillator?
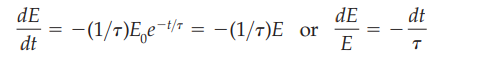
How is the factor Q related to the fractional energy loss per cycle for weak damping?
ΔE= energy lost per cycle
E= Energy stored
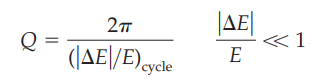
What is the formula for the exact angular frequency of an underdamped oscillator in terms of Q?
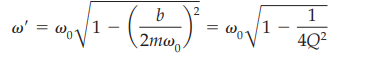
What is the formula for the power dissipated by the damping force?
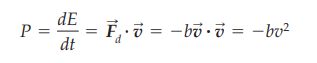
How does damping affect the period of oscillations?
