BIOE3100 Exam #2
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Where are peptide hormones synthesized and stored?
Made in advance; stored in secretory vesicles
Where are steroid hormones synthesized and stored?
Synthesized on demand from precursors
Where are amine hormones (catecholamines) synthesized and stored?
Made in advance; stored in secretory vesicles
Where are amine hormones (thyroid) synthesized and stored?
Made in advance; precursor stored in secretory vesicles
How are peptide hormones released from parent cells?
Exocytosis
How are steroid hormones released from parent cells?
Simple diffusion
How are amine hormones (catecholamines) released from parent cells?
Exocytosis
How are amine hormones (thyroid) released from parent cells
Transport protein
How are peptide hormones transported in blood?
Dissolved in plasma
How are steroid hormones transported in blood?
Bound to carrier proteins
How are amine hormones (catecholamines) transported in blood?
Dissolved in plasma
How are amine hormones (thyroid) transported in blood?
Bound to carrier proteins
Where is the peptide hormone receptor located?
Cell membrane
Where is the steroid hormone receptor located?
Cytoplasm or nucleus; some have membrane receptors
Where is the amine hormone (catecholamines) receptor located?
Cell membrane
Where is the amine hormone (thyroid) receptor located?
Nucleus
What are hormones?
Chemical messengers that are secreted by specialized epithelial cells into the blood for transport to a distant target, where it exerts its effect at very low concentrations.
Where are all hormones secreted into?
Blood
Synergism
Combined effect is greater than the sum of individual effects
Permissiveness
Need second hormone to get full effect
Antagonism
One substance opposes the action of another
What two components are the central nervous system composed of?
Brain & spinal cord
What two components are the peripheral nervous system composed of?
Somatic & autonomic (Sympathetic & Parasympathetic) nervous systems
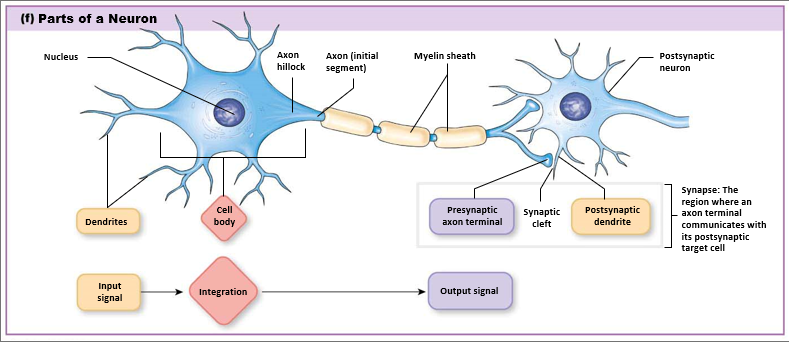
What are the parts of a neuron?
Myelin acts as a support and insulation for axon, made by Schwann cells and oligodendrocytes, made up of concentric layers of phospholipid
What type of signal is a graded potential?
Input signal; Depolarizing or hyperpolarizing
Where does a graded potential occur?
Dendrites and cell body
Where does an action potential occur?
Trigger zone through axon
What types of gated ion channels are involved in graded potentials?
Mechanically, chemically, or voltage-gated channels.
What types of gated ion channels are involved in action potentials?
Voltage-gated channels
What type of signal are action potentials?
Depolarizing; Regenerating conduction signal
What is the strength of graded potentials?
Depends on the initial stimulus; it can only be summed
What is the strength of action potentials?
All-or-none phenomenon; cannot be summed
What initiates the graded potential?
Entry of ions through gated channels
What initiates the action potential?
Above-threshold graded potential at the trigger zone opens ion channels
What are the 3 unique characteristics of graded potentials?
No minimum level is required to initiate
Two signals coming close together in time will sum
Initial stimulus strength is indicated by the frequency of a series of action potentials
What are the 2 unique characteristics of action potentials?
Threshold stimulus required to initiate
Refractory period: two signals too close together in time cannot sum
What are the 4 characteristics of reflexive (implicit) memory?
Recall is automatic and does not require conscious attention
Acquired slowly through repetition
Includes motor skills and rules and procedures
Procedural memories can be demonstrated
What are the 3 characteristics of declarative (explicit) memory?
Recall requires conscious attention
Depends on higher-level thinking skills such as inference, comparison, and evaluation
Memories can be reported verbally
What are the 4 types of sensory receptors?
Chemoreceptors
Mechanoreceptors
Photoreceptors
Thermoreceptors
What neurotransmitter/receptor is at the neuron-target synapse for the somatic neuron pathway?
Ach/nicotinic
What neurotransmitter/receptor is at the neuron-target synapse for the autonomic neuron pathway
ACh/muscarinic or NE/alpha- or Beta-adrenergic
What is the target tissue of the somatic motor pathway?
Skeletal muscle
What is the target tissue of the autonomic motor pathway?
Smooth and cardiac muscle; some endocrine glands; some adipose tissue
What are the somatic motor pathway effects on target tissue?
Excitatory only: muscle contracts
What are the autonomic motor pathway effects on target tissue?
Excitatory or inhibitory
How many neurons are in the efferent path of the somatic motor system?
1
How many neurons are in the efferent path of the autonomic motor system?
2
What is the function of the somatic motor pathway?
Posture and movement
What is the function of the autonomic motor pathway?
Visceral function, including movement in internal organs and secretion; control of metabolism
What is the fiber arrangement of skeletal muscles?
Sarcomeres
What is the fiber arrangement of smooth muscles?
No sarcomeres
What is the fiber arrangement of cardiac muscles?
Sarcomeres
Where is the skeletal muscle located?
Attached to bones; a few sphincters close off hollow organs
Where is the smooth muscle located?
Forms walls of hollow organs and tubes; some sphincters
Where is the cardiac muscle located?
Heart muscle
What does the skeletal muscle look like under a microscope?
Striated
What does the smooth muscle look like under a microscope?
Smooth
What does the cardiacmuscle look like under a microscope?
Striated
What is the initiation of contraction for skeletal muscles?
Requires ACh from motor neuron.
Somatic motor neuron
Fastest
Not graded contraction force
What is the initiation of contraction for smooth muscles?
Requires stretch, chemical signals. Can be autorhythmic
Autonomic neurons
Slowest
Graded contraction force
What is the initiation of contraction for cardiac muscles?
Autorhythmic
Autonomic neurons
Intermediate
Graded contraction force
What is the tissue morphology of skeletal muscles?
Multinucleate; large, cylindrical fibers
What is the tissue morphology of smooth muscles?
Uninucleate; small spindle-shaped fibers
What is the tissue morphology of cardiac muscles?
Uninucleate; shorter branching fibers
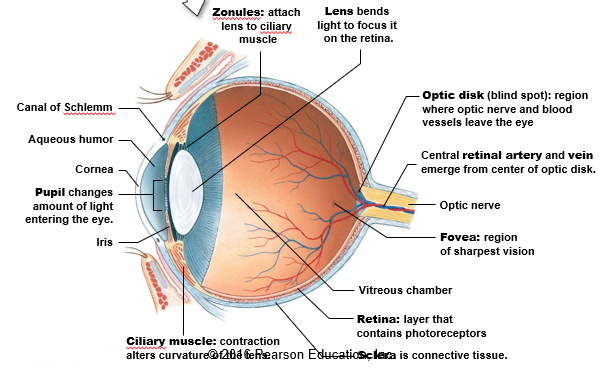
Label the (A) cornea, (B) optic nerve, (C) retina, (D) vitreous chamber, (E) lens, (F) aqueous humor, (G) sclera and (H) pupil.
In the somatic motor pathway, what is the neurocrine and receptor?
Neurocrine: Acetylcholine & Nicotinic receptor
In the parasympathetic pathway, what is the neurocrine and receptor?
Acetylcholine & Nicotinic receptor → Acetylcholine & Muscarinic receptor
In the sympathetic pathway, what is the neurocrine and receptor?
Acetylcholine & Nicotinic receptor → Norepinephrine & alpha receptor
In the adrenal sympathetic pathway, what is the neurocrine and receptor?
Epinephrine → Beta2 receptor
What is endocrinology?
The study of hormones
What are pheromones?
Specialized ectohormones that act on other organisms of the same species to elicit a physiological or behavior response
What are growth hormones?
A large group of substances that influence cell growth and division.
What are preprohormones?
Contain one or more copies of a peptide hormone, a signal sequence that directs the protein into the lumen of the rough ER, and other peptide sequences.
What is a prohormone?
As the inactive preprohormone mows through the endoplasmic reticulum, the signal sequence is removed, creating smaller, still-inactive molecule called a prohormone
What are the 3 types of hormones?
Peptide
Steroid
Amino-Acid Derived/Amine
Where are steroid hormones derived from?
Cholesterol
What is a trophic hormone?
Controls the release of other hormones
What is the posterior pituitary?
An extension of the brain that secretes neurohormones made in the hypothalamus
What is the anterior pituitary?
Master gland of the body. Neurohormones from the hypothalamus control the release of the anterior pituitary hormones.
What are afferent nerves?
Carry signals from the body to the brain
What are efferent nerves?
Carry signals from the brain to targets throughout the body
What is hypersecretion?
Excess hormone
What is hyposecretion?
Deficient hormone
What are neurohormones?
Specialized neurons release neurohormones into the blood.
What are the three integrating centers for endocrine control systems?
Hypothalamic stimulation
Anterior pituitary stimulation
Endocrine gland stimulation
What is down-regulation?
Decreased number of receptors
What is the sympathetic branch?
Fight or Flight & metabolic homeostasis
What is the parasympathetic branch?
Rest and Digest
Which sense triggers the strongest memories and emotions?
Olfactory
What are the 5 primary taste sensations?
Umami
Sweet
Salty
Sour
Bitter
The loudness or intensity of a sound is related to its
amplitude
The pitch of a sound wave is related to its
frequency
Which lasts longer: Emotions or moods?
Moods
Describe the spinal cord.
Gray matter - unmyelinated nerve cell bodies
White matter - myelinated axons
Meninges - 3 layered membranes
Dura - outer & thickest
Arachnoid - middle
Pia - inner
What is a convergent pathway?
Many presynaptic neurons provide input to influence a smaller number of postsynaptic neurons
What is a divergent pathway?
One presynaptic neuron branches to affect a larger number of postsynaptic neurons
What are the four properties of a sensory stimulus?
Modality
Location
Intensity
Duration
Where are peptide hormones derived from?
Linked amino acids
Where are amino acid derived/amine hormones derived from?
Tryptophan