AP Biology: DNA Structure &Function, Protein Synthesis & Regulation
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
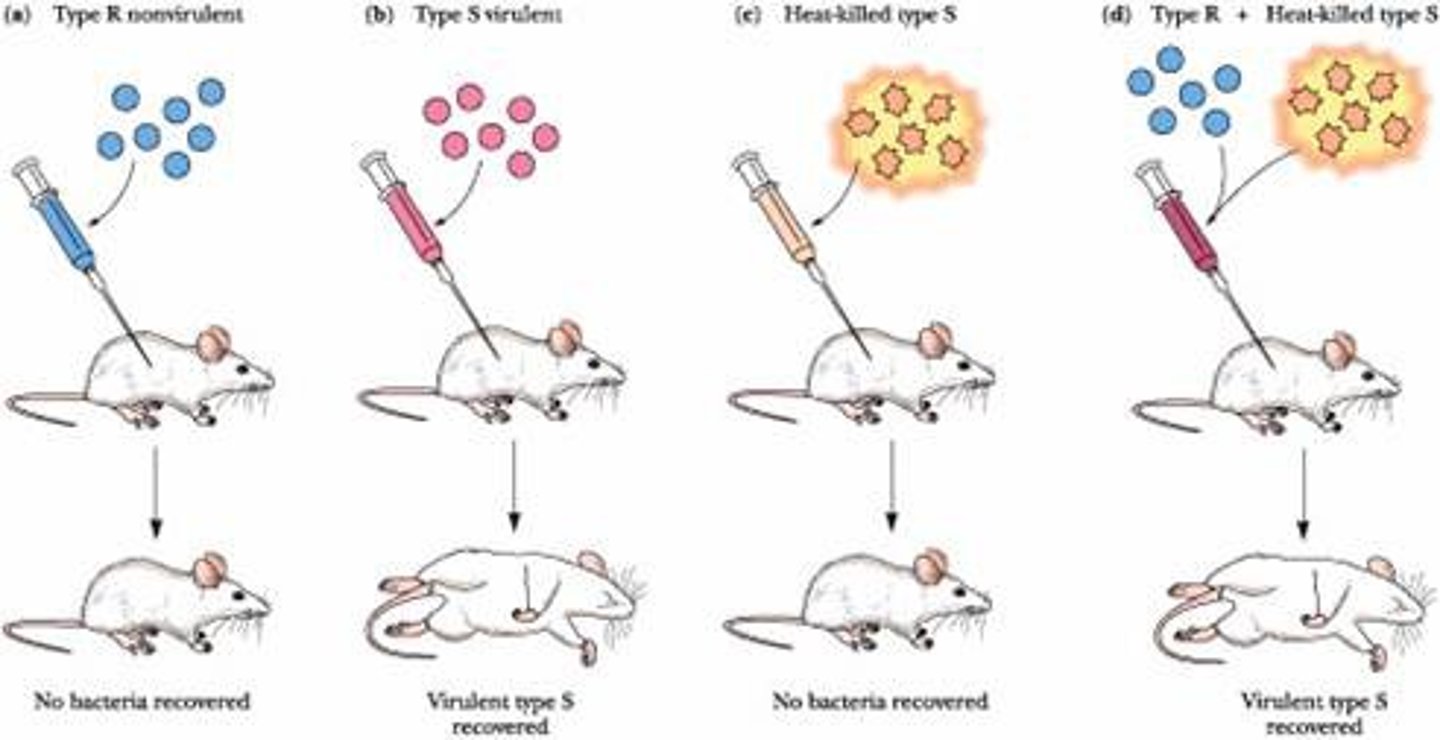
Frederick Griffith's Experiment
Discovered transformation during an experiment that involved injecting mice with smooth S cells, rough R cells, heat-killed S cells, and heat-killed S cells with living R cells.
Avery Experiment
demonstrated that DNA, not protein, was responsible for the transfer of genetic material. Verified the findings from Griffith's transformation experiment.
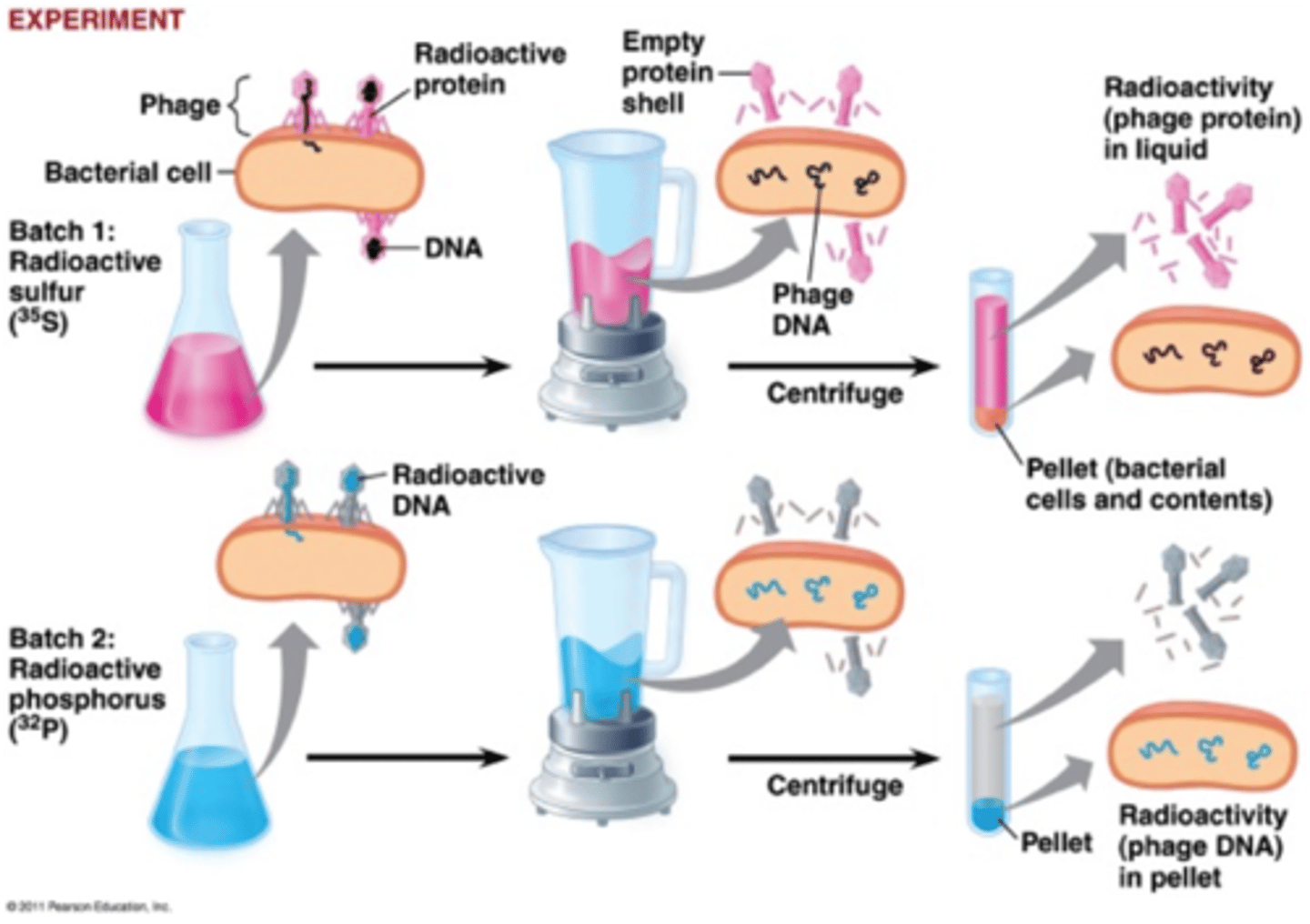
Hershey-Chase Experiment
showed using radioactive chemicals that DNA, not protein, was inserted into cells infected by viruses
If a DNA molecule is 31% A, then what percentage is C?
19%
base-pairing
principle that bonds in DNA can form only between adenine and thymine and between guanine and cytosine
hydrogen bond
found between purines and pyrimidines in DNA ( 3 or 2)
helicase
enzyme that breaks the hydrogen bonds between nitrogen bases in DNA
replication
Copying process by which a cell duplicates its DNA (occurs in the S phase of interphase)
semi-conservative
in each new DNA double helix, one strand is from the original molecule, and one strand is new

topoisomerase
An enzyme that untwists the double helix of DNA at the replication fork
DNA polymerase
An enzyme involved in DNA replication that reads DNA code and joins individual nucleotides to produce a DNA molecule. This enzyme 'spellchecks' its work
ligase
An enzyme that connects two fragments of DNA to make a single fragment
leading strand
The new continuous complementary DNA strand synthesized along the template strand in the mandatory 5' to 3' direction.
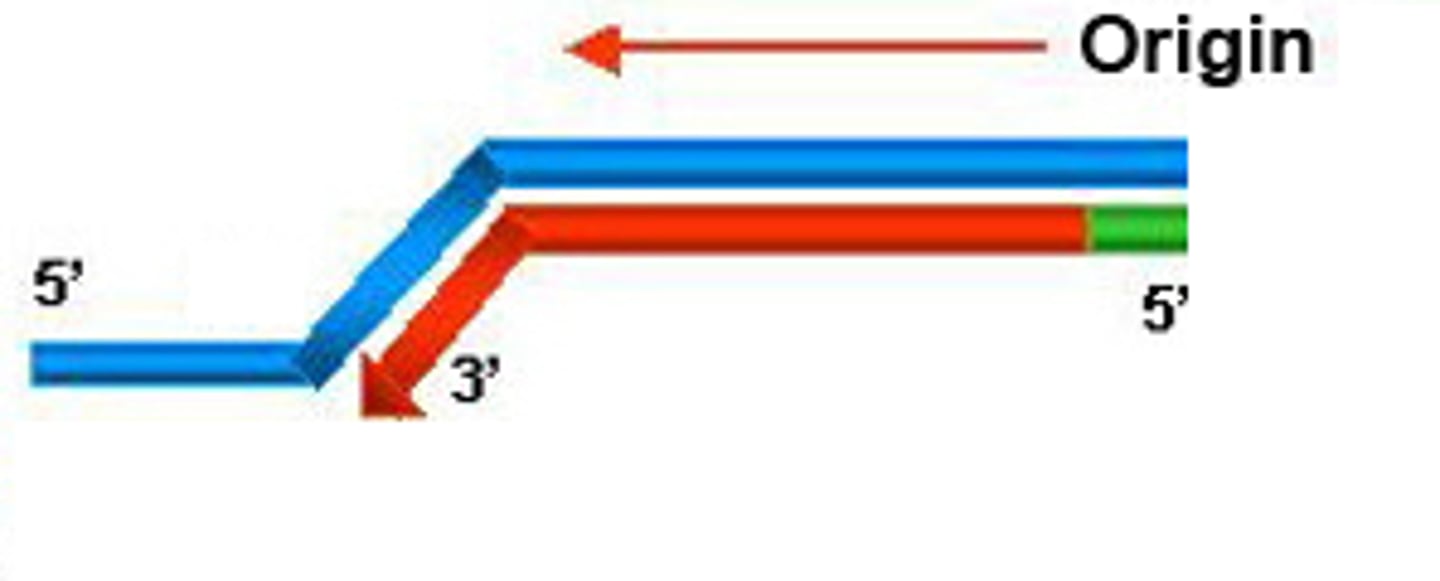
lagging strand
A discontinuously synthesized DNA strand that elongates by means of Okazaki fragments, each synthesized in a 5' to 3' direction away from the replication fork.
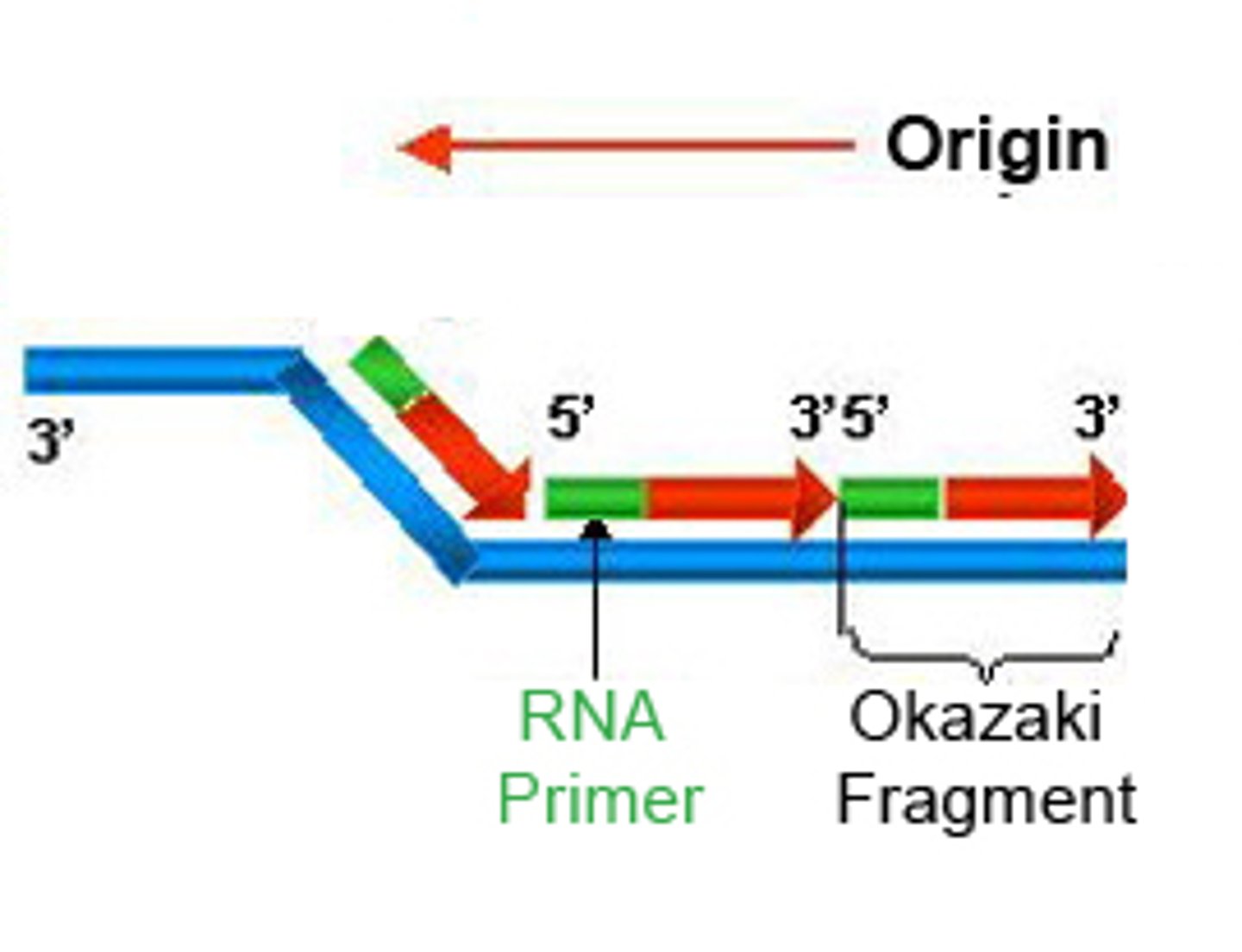
primer
short segment of RNA used to initiate synthesis of a new strand of DNA during replication
introns
Sequences of mRNA made from DNA that is not involved in coding for a protein, usually cut out.
exons
Sequences of mRNA made from coding segments of eukaryotic DNA, must be spliced together.
genetic code
collection of codons of mRNA, each of which directs the incorporation of a particular amino acid into a protein during protein synthesis
wobble effect
The last nitrogenous base can change but the amino acid it codes for stays the same
mutation
A change in a gene or chromosome.
deletion
A change to a chromosome in which a fragment of the chromosome is removed.
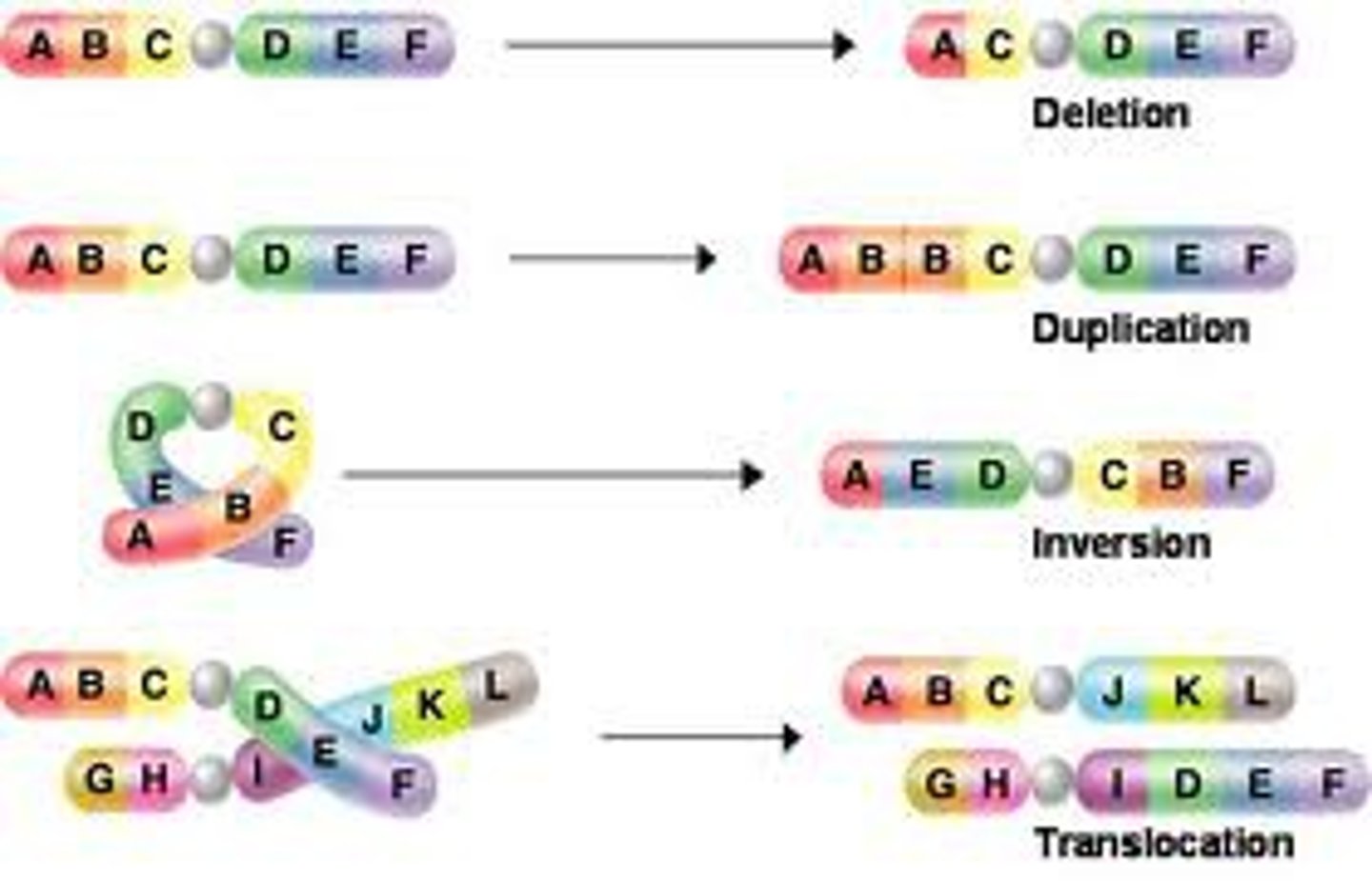
insertion
A change to a chromosome in which a fragment of the chromosome is duplicated
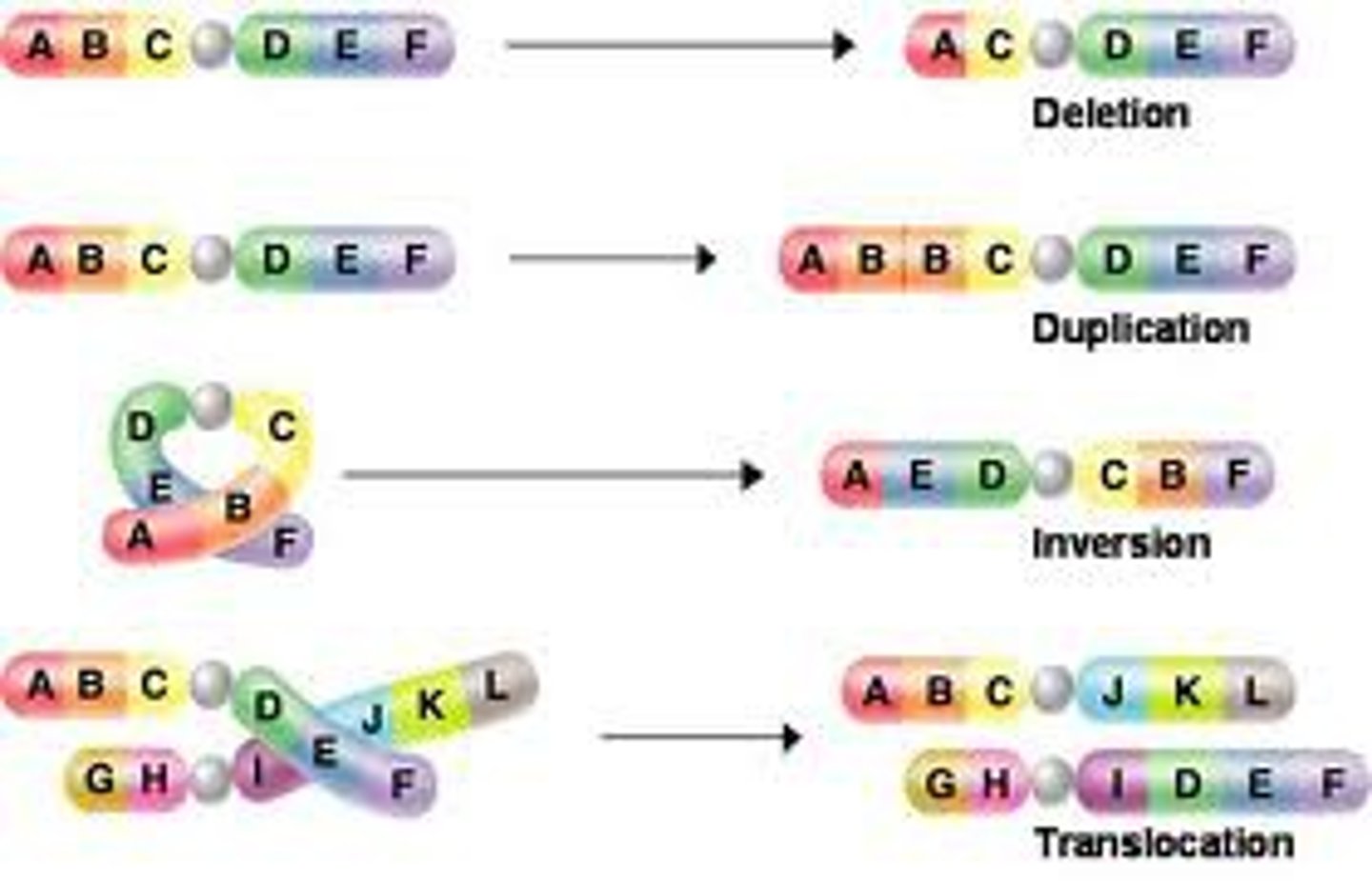
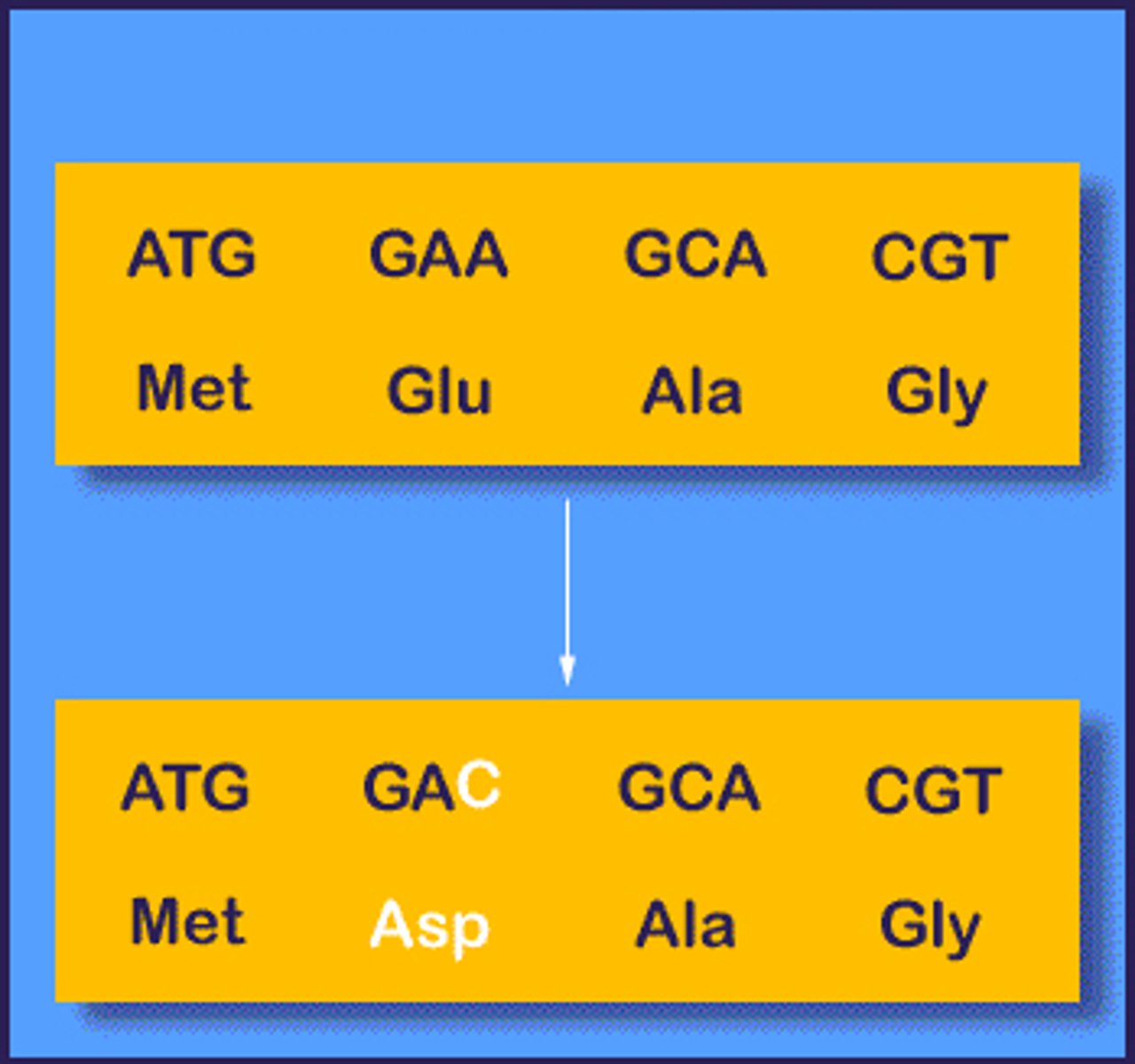
point mutation
Gene mutation involving changes in one or a few nucleotides
frameshift mutation
mutation that shifts the "reading" frame of the genetic message by inserting or deleting a nucleotide
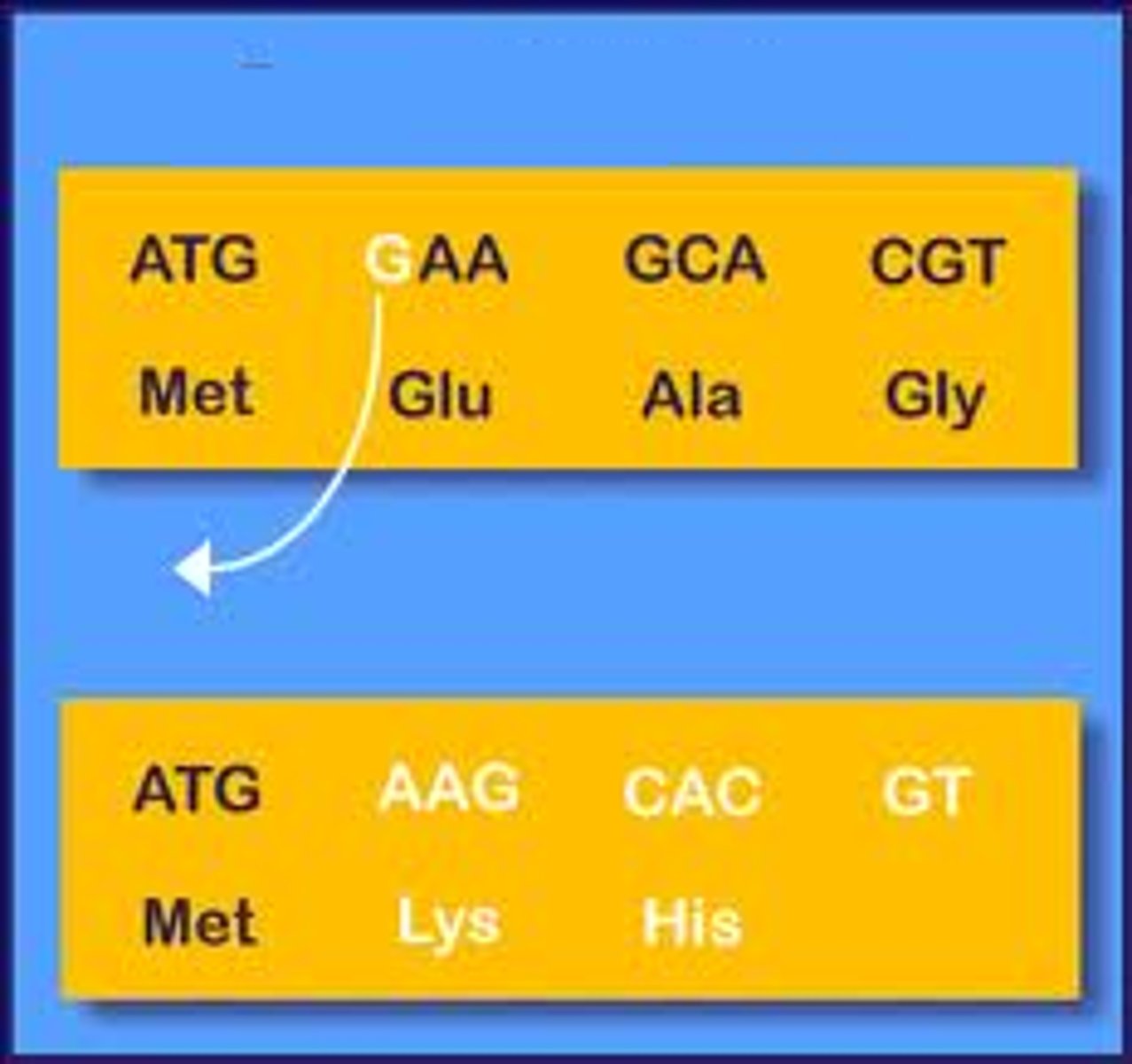
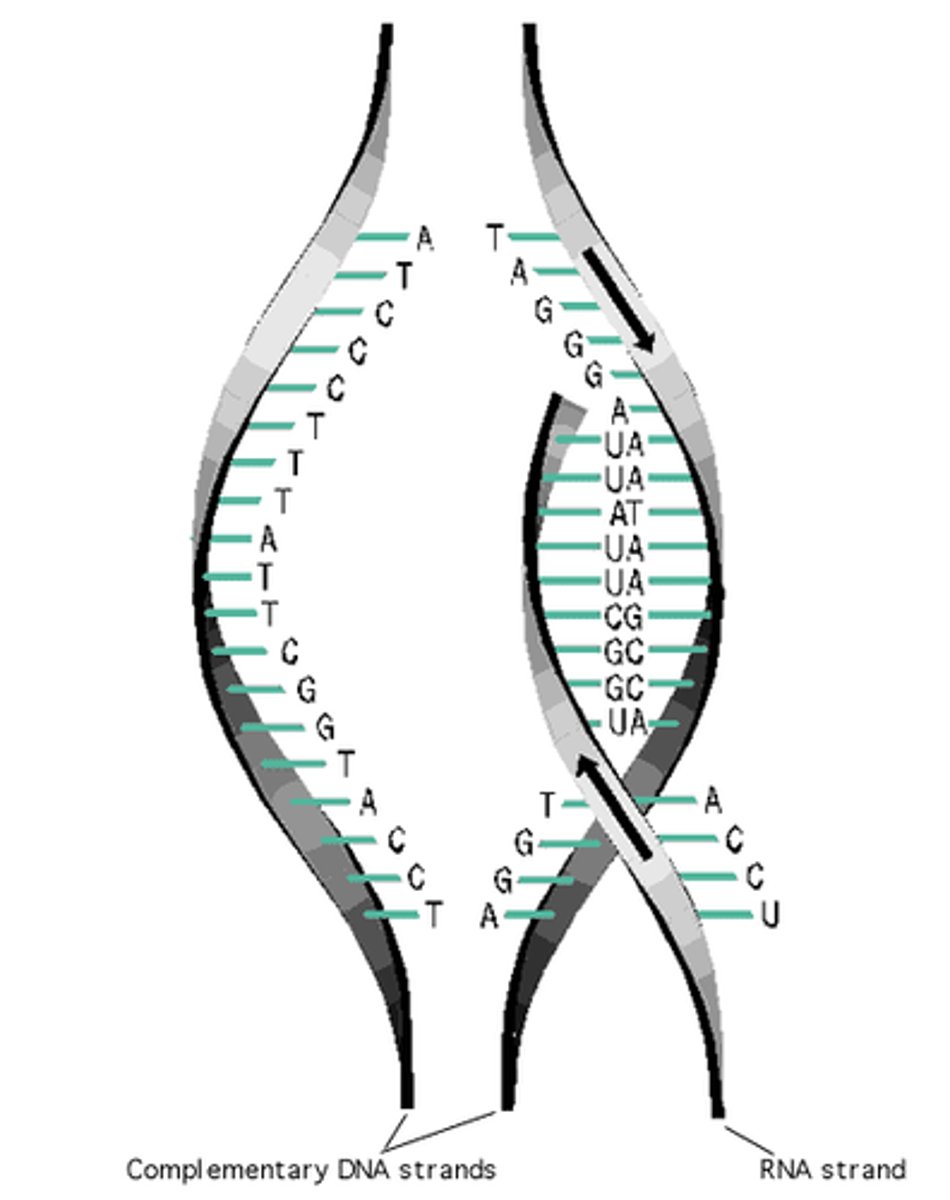
transcription
DNA to mRNA in nucleus
translation
mRNA to protein in cytoplasm
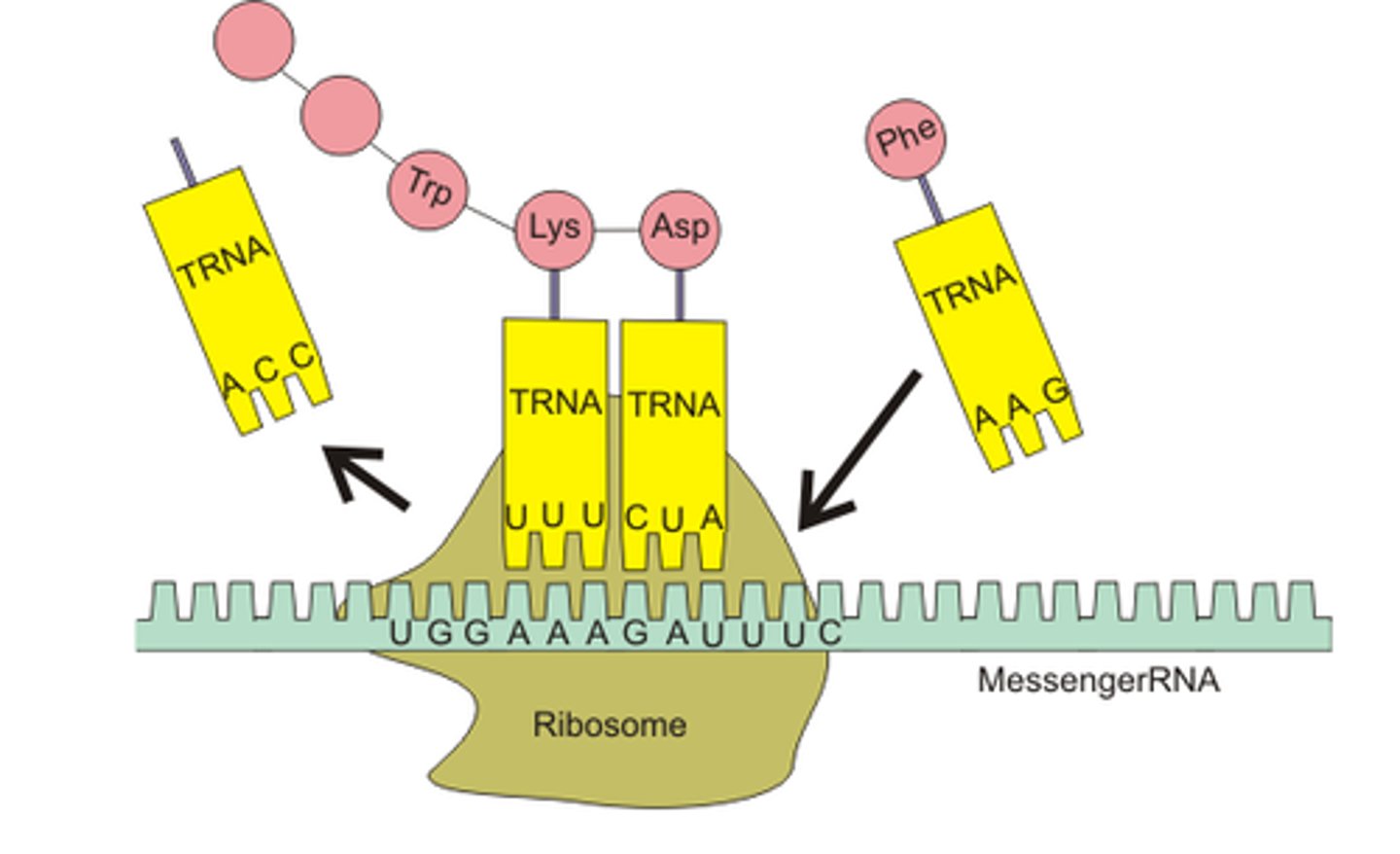
ribosome
organelles where proteins are synthesized (free or on RER)
mRNA
synthesized from DNA and used to determine the order amino acids will be added in to make a protein
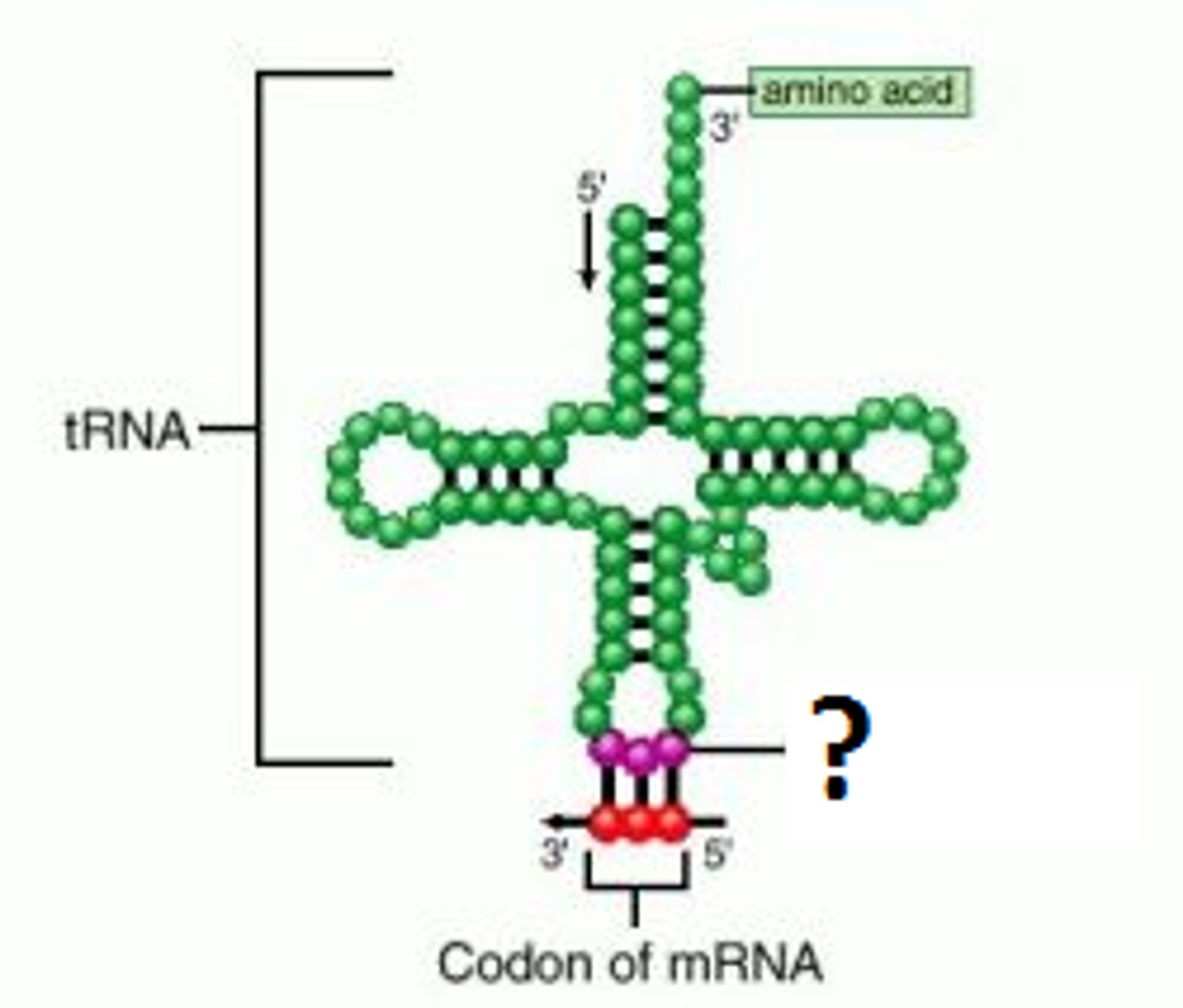
tRNA
brings amino acids to the ribosome in the order specified by mRNA
rRNA
binds together with proteins to form ribosomes
RNA polymerase
Enzyme that links together the growing chain of RNA nucleotides during transcription using DNA as a template
codon
Group of three nucleotide bases in mRNA that specify a particular amino acid to be incorporated into a protein
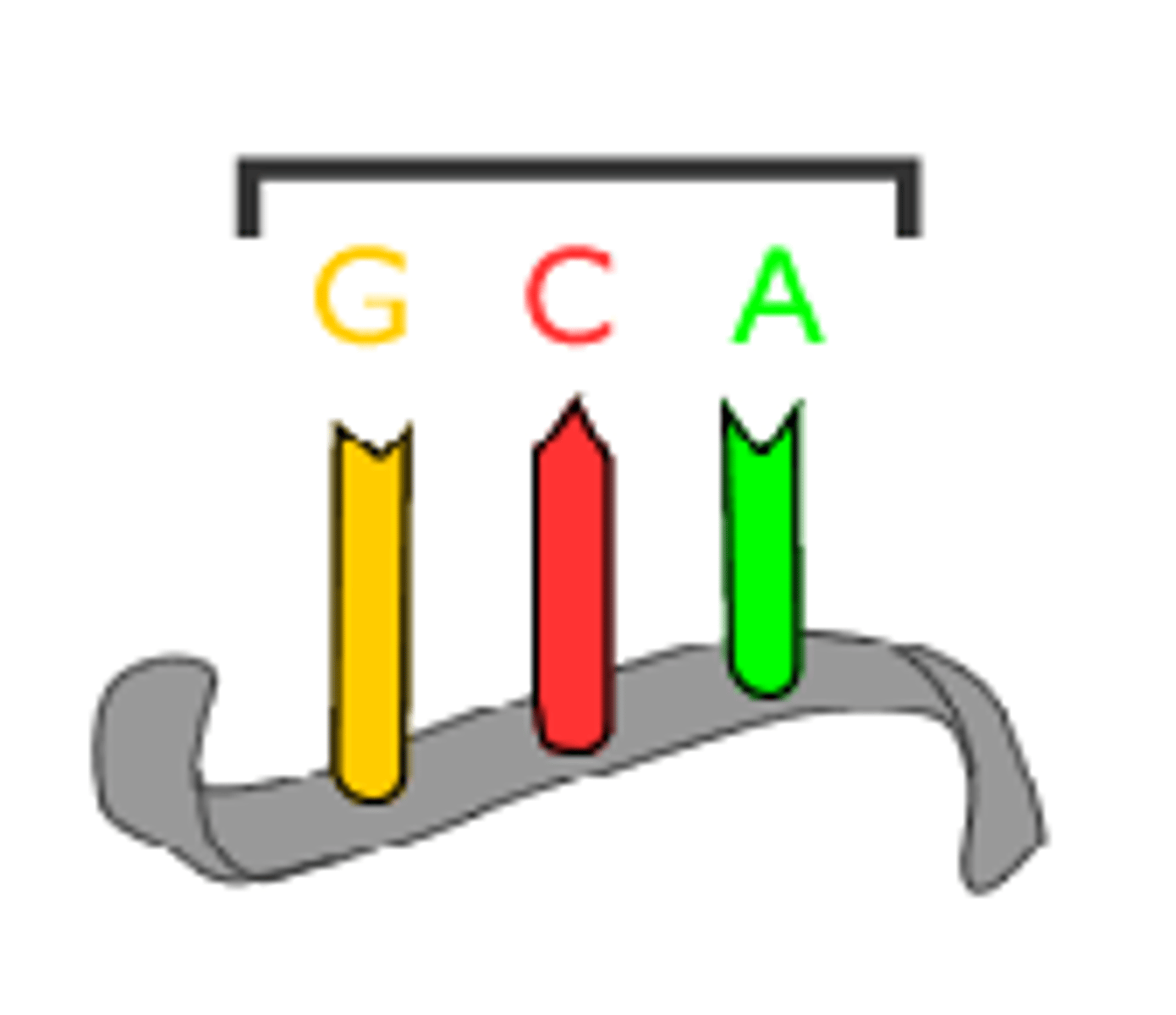
anticodon
Group of three bases on a tRNA molecule that are complementary to an mRNA codon. Each is associated with a particular amino acid.
A site
The site in the ribosome where new amino acids line up to be added to the growing protein
P site
The site in the ribosome where the process of building the polypeptide chain starts; the amino acid is added to the polypeptide chain here
E site
The site in the ribosome where tRNAs exit
promoter
DNA sequence at which RNA polymerase attaches during transcription.
Terminator
DNA sequence that signals the end of transcription during transcription.
RNA Processing
In eukaryotes only, in a premRNA transcript, introns are removed and exons are spliced together, a 5' cap is added, and a poly-A tail is added before the mRNA moves out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm.
What is the purpose of the 5' cap and poly-A tail on mRNA?
facilitates the export of mRNA from the nucleus to help protect the mRNA from degradation by enzymes and facilitate the attachment of the mRNA to the ribosomes.
How is it possible that we only have about 20,000 genes to make approximately 100,000 polypeptides?
One gene can make more than one polypeptide. An intron removed in the production of one protein can serve as an exon in the production of another.
Once polypeptides are formed, they are modified and can even be transported outside of the cell. How does this occur?
Protein modification can occur in the Rough ER and shipping outside of the cell occurs with the Golgi. A signal peptide, sequence of 20 amino acids on the end of a polypeptide chain, serves as a "zip code" directing proteins to their final destination..
Methylation of DNA
inactivates genes or altered gene activity (prevents binding of transcription factors and deacetylation of histones)
Acetylation of histones
opens chromatin, allowing transcription
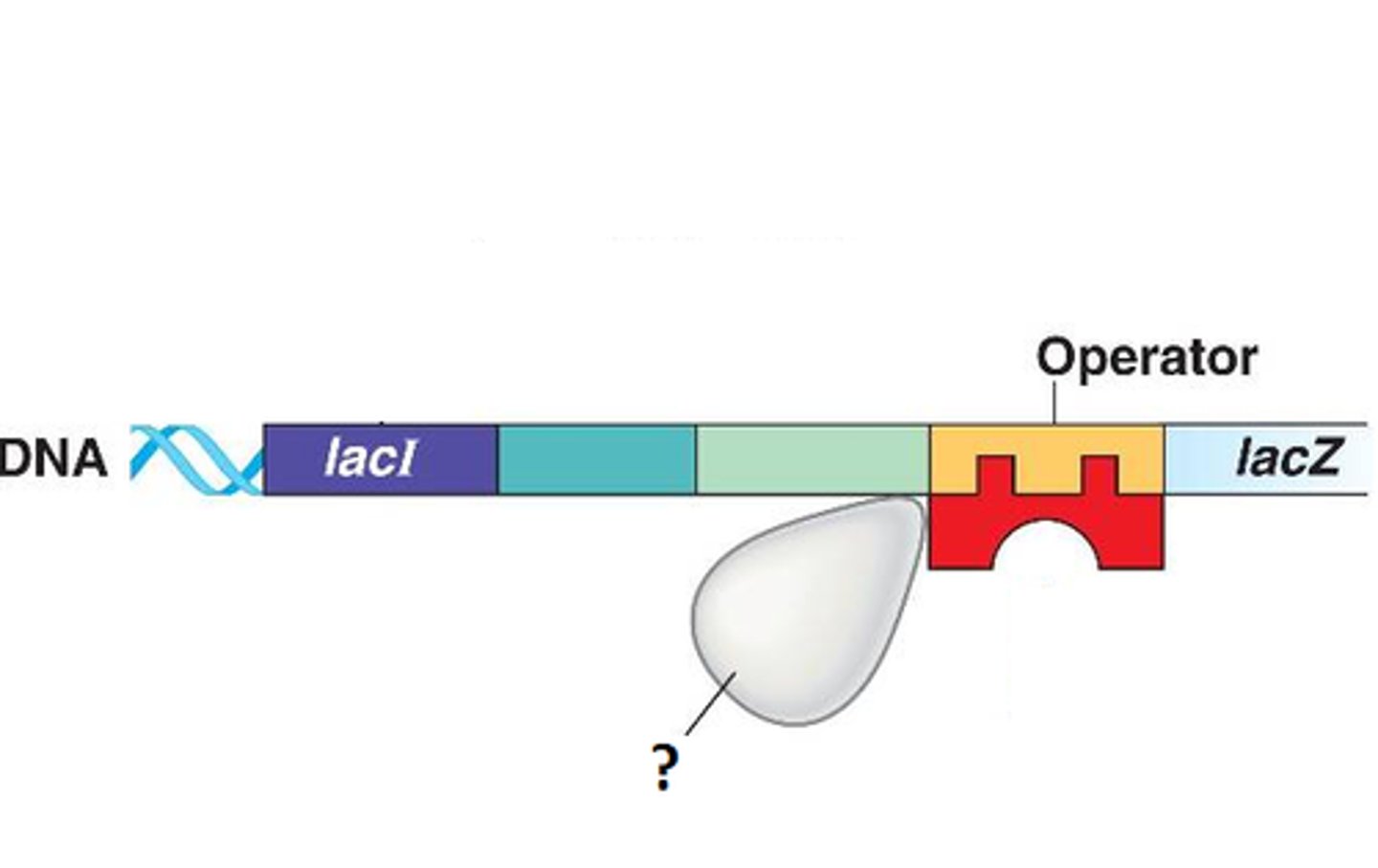
operon
A unit of genetic function common in bacteria; clusters of genes that help determine if bacterial genes are expressed.
repressible operon
transcription is usually on, but can be inhibited (repressed) when a specific small molecule binds to a regulatory protein (example tryptophan)
inducible operon
An operon under positive control. It is usually "off" but can be turned "on" in the presence of a specific molecule.
repressor protein
a regulatory protein that binds to an operator and blocks transcription of the genes of an operon
Epigenetics
the study of environmental influences on gene expression that occur without a DNA change
RNA interference (RNAi)
a mechanism for silencing the expression of specific genes; can block translation or trigger the degradation of the gene's messenger RNA; this happens naturally in some cells, and can be carried out in laboratory experiments as well