SPLEEN PATHOLOGIES 😮🥳🤨
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
Hematopoiesis
Granulocytopoiesis
Reactive hyperplasia to acute and chronic infection (Low sonodensity)
Noncaseous Granulomatous inflammation
Myeloproliferative syndromes (normal)
Chronic myelogenous Leukemia
Acute myelogenous leukemia
Lymphopoiesis (low sonodensity or focal sonolucent)
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Lymphoma
Hodgkin disease.
Erythropoiesis (normal)
sickle cell disease
Hereditary spherocytosis
Hemolytic, anemia
Chronic anemia
other
Multiple Myeloma (low sonodensity) myleoproliferative syndrome
Reticuloendothelial hyperactivity (normal)
still disease
Wilson disease
Felty Syndrome
Reticulum cell Sarcoma
Congestion (normal or low sonodensity)
Hepatocellular disease
Non specific
Neoplasm-metastasis (Focal sonodense)
Cyst (focal sonolucent)
Abscess (Focal sonolucent)
Malignant neoplasm (Focal sonolucent)
Hodgkin disease
Lymphoma
Benign neoplasm (focal sonolucent)
Hematoma (perisenic)
Splenomegaly
As the largest unit of the Reticuloendothelial System, the spleen is involved in all systemic inflammation and generalized hematopoietic Disorders in much metabolic disturbance Whenever the spleen is involved in systemic disease, splenic enlargement, or splenomegaly, usually develops.
Causes of splenomegaly:
Collagen-vascular disease
Congestion
Extramedullary hematopoiesis
Hemolytic anemia
Infection
Neoplasm
Storage disease
Trauma
Clinical signs of splenomegaly may include LUQ Pain (Secondary to stretching of the splenic capsule or Ligaments) Or fullness
Enlargement of the spleen may encroach upon surrounding Organs, such as the left kidney, pancreas, stomach and intestines.
Congestion of the spleen
Two types known as acute and chronic
In acute congestion, Active hyperemia accompanies the reaction in The moderately Enlarged spleen
In chronic venous congestion, diffuse enlargement of the spleen occurs.
The Venus congestion maybe of systemic Origin, caused by intrahepatic obstruction to portal, venous, drainage, or obstructive venous disorders in the portal or splenic veins.
Systemic venous congestion is found in cardiac decompensation involving the right side of the heart.
It is particularly severe in tricuspid or pulmonary valvular disease and chronic cor pulmonale.
Most common causes of striking congestive splenomegaly are the various forms of cirrhosis of the liver Also caused by obstruction to the extra hepatic portal or splenic vein.
Wandering spleen
(here out from video, yes there will be repeats perhaps)
Abnormal migration during developmental stages of embryology
Positioned outside of normal LUQ location
Clinically; Asymptomatic, tenderness torsion is possible
Sonographic: Abdominal/pelvic mass, Decreased color, Doppler velocity in complete torsion.
Splenic agenesis
AKA asplenia
Complete embryologic absence of spleen
Occurs with additional major congenital abnormalities
Rare, benign
Clinically: Increased risk of infectious disease
Sonographic: No splenic tissue visualized in LUQ or abdominal/pelvic region
Accessory spleen
AKA splenule
Collection of normal splenic tissue separate from the spleen
Common congenital, anomaly, 30% of population
Clinically; Asymptomatic, palpable lump depending on size/location
Sonographic: Homogeneous, isoechoic to Spleen near hilum or superior border
Atrophy
AKA autosplenectomy
Decrease in splenic tissue volume
Technically benign disorder, but associated with “ Wasting” Diseases
Clinically: Asymptomatic, symptoms associated with causative disease
Sonographic: Small spleen, non-visualized due to lack of tissue
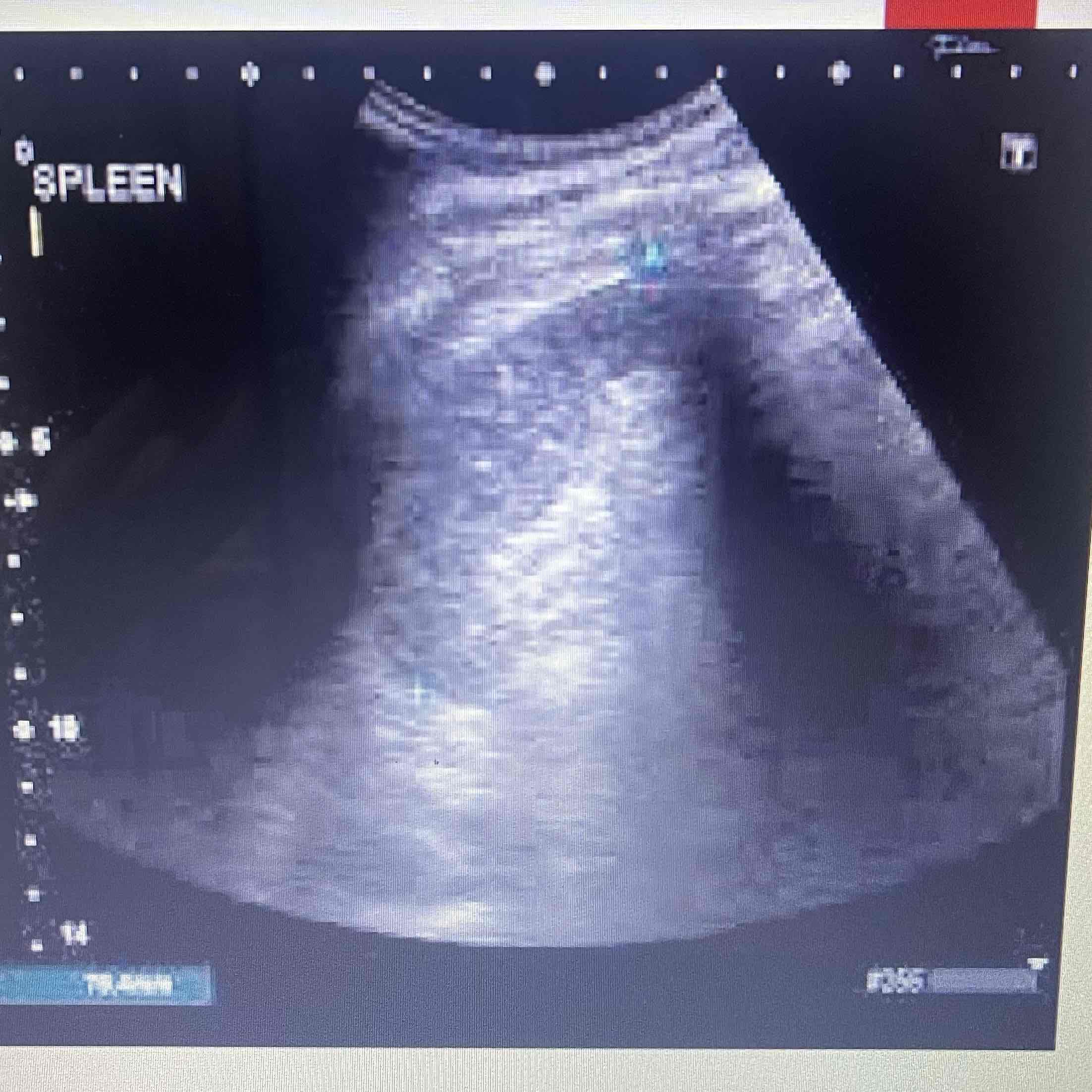
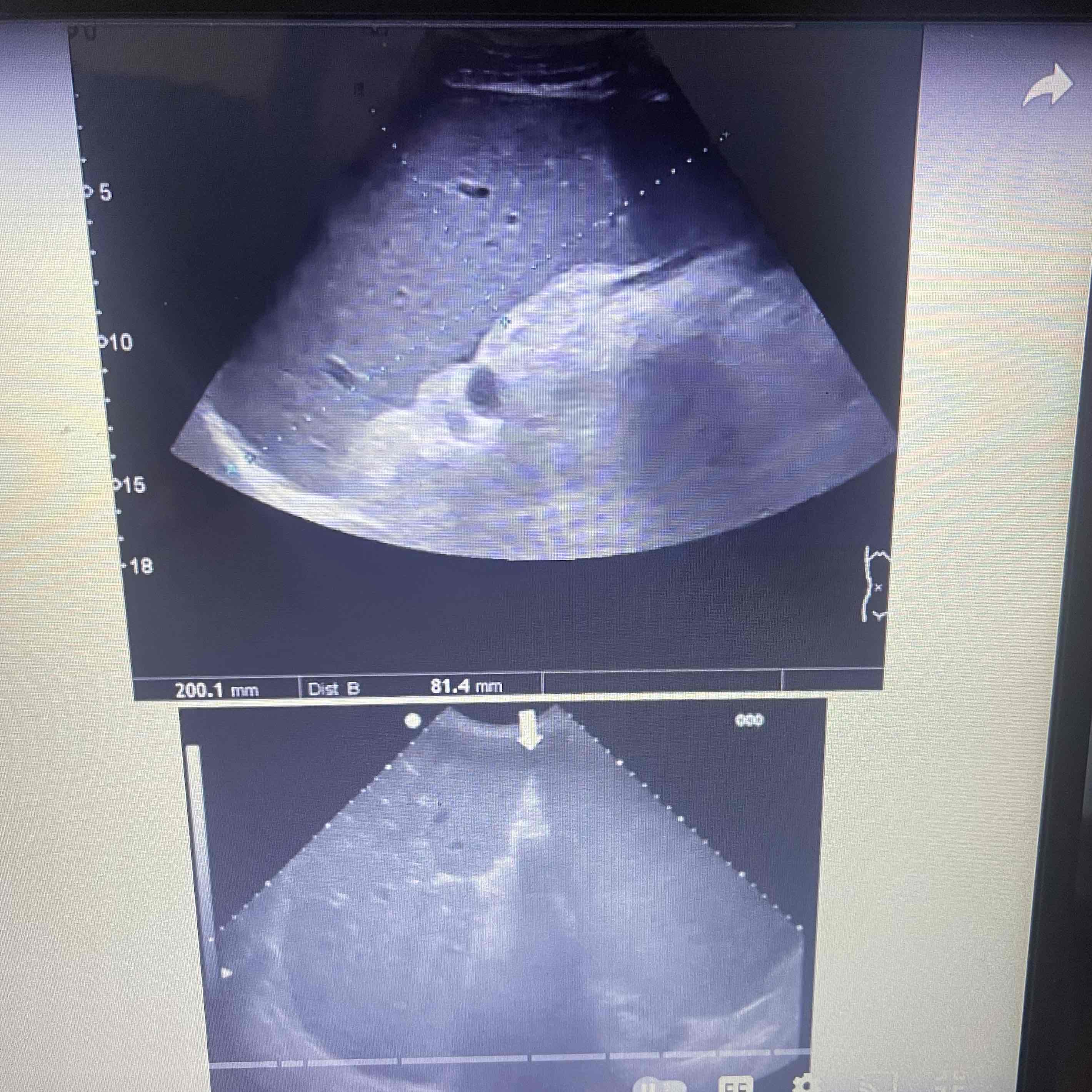
Splenomegaly
Splenic enlargement
Caused by systemic disease
Clinically: Infectious pts, Metabolic disturbances, hematopoietic disorders
Sonographic: changes in size texture and vascularity, Increased volume
Amyloidosis
Excessive production of amyloid Proteins in organs
Spleen is the most commonly effected organ
Clinically: Systemic diseases, fatigue/weakness, joint pain, weight loss, skin changes
Sonographic: Enlarged, size depends on the amount of buildup
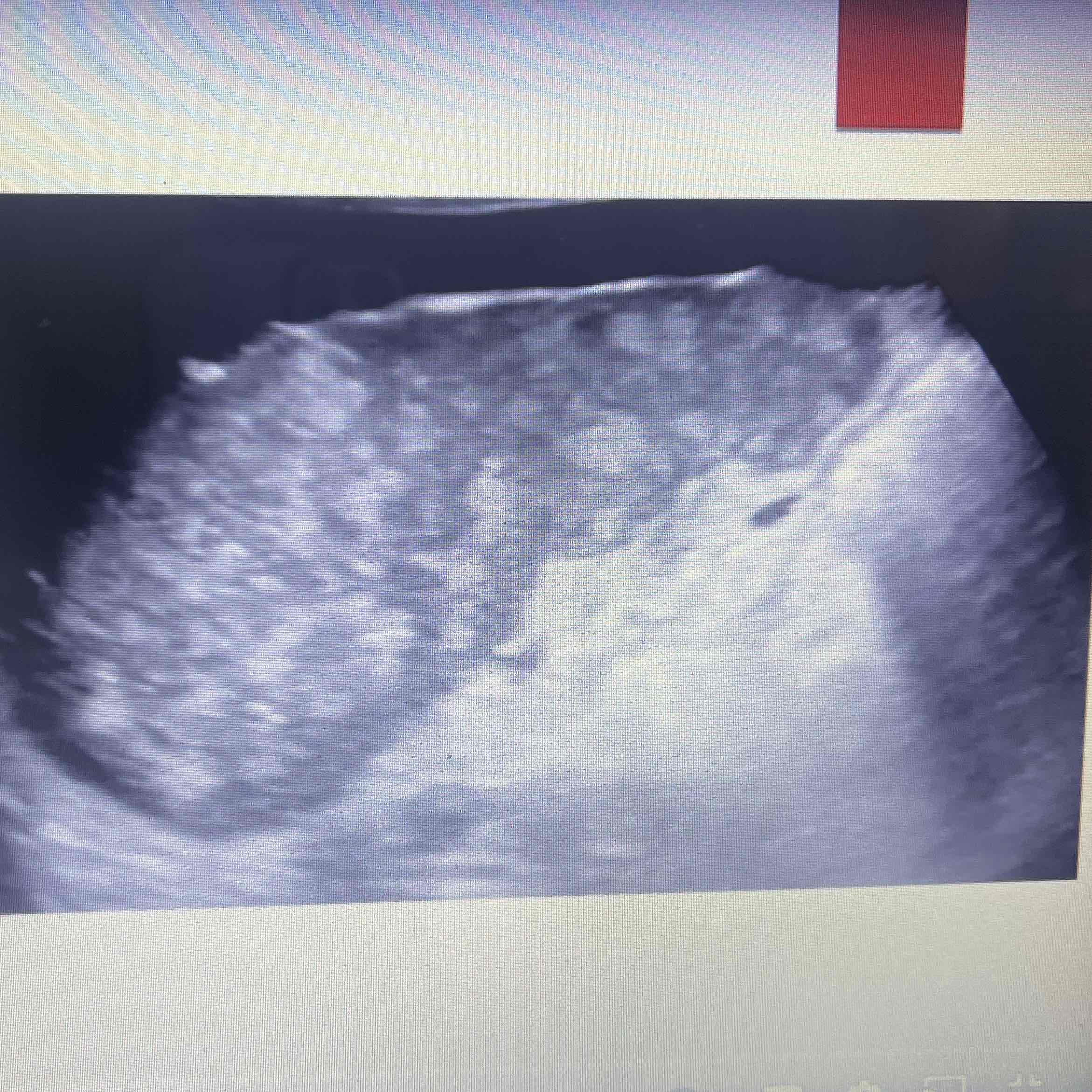
Gaucher’s disease
Rare metabolic disorder
Abnormal accumulation of specific lipid cells in specific organs → Mainly spleen and liver
Clinically: All ages, 50% younger than eight years old, 17% younger than one years old
Sonographic: Splenomegaly, heterogeneous, spleen, multiple hyperechoic nodules
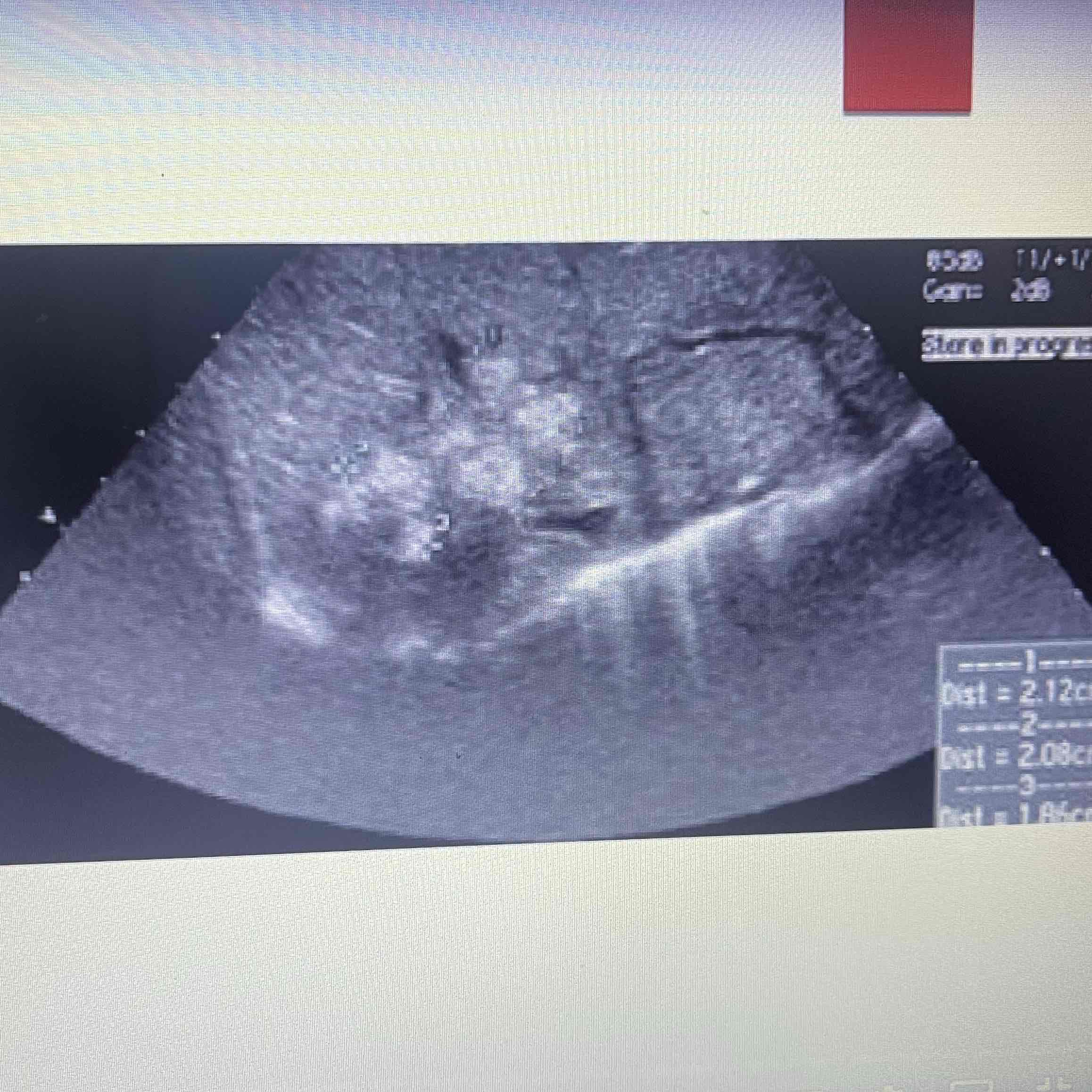
Neimann-pick disease
Metabolic disorder
Unable to metabolize lipid cells → Sales malfunction, and lead o apoptosis
Clinically: Female infants, rapidly progresses, fatal
Sonographic: Hepatomegaly, lymphadenopathy, Digestive complications
Sickle cell anemia
Irregularly shaped RBC; Difficult to travel
Inadequate healthy RBC
Slow flow and lack of oxygen to organs
Clinically: Inherited, geographic locations; 8% of African-Americans, Fatigue/weakness, infections, joint pain, dizziness
Sonographic: Variable due to severity, early: Enlarged, late: Infarction, fibrosis, atrophy
Hemolytic anemia
Inadequate healthy RBC
Decrease lifespan of erythrocytes
Rate of destruction is higher than bone marrow can compensate for
Autoimmune hemolytic anemia
Anemic caused by auto immune response or disease
Primary: Without disease
Secondary: With disease
Clinically: Occurs with underlying disease, Lymphoma/leukemia, infectious mono
Sonographic: Splenomegaly
Polycythemia Vera
Excess of RBC
Unknown cause that involves all bone marrow elements
Clinically: Weakness/fatigue, vertigo, tinnitus, irritability, erythema, painful extremities, contusion
Sonographic: Splenomegaly, infarction, thrombosis
Thalassemia
Inadequate amount of hemoglobin
Leads to anemia
Destruction of healthy RBC
Clinically: Inherited
Sonographic: Splenomegaly
Mononucleosis
Viral infection that severely affects the Spleen
Kissing disease
Associated with EBV
Clinically: Teens and adolescence, tenderness and swelling in LUQ, Swollen, lymph nodes, fever, sore throat
Sonographic: Splenomegaly
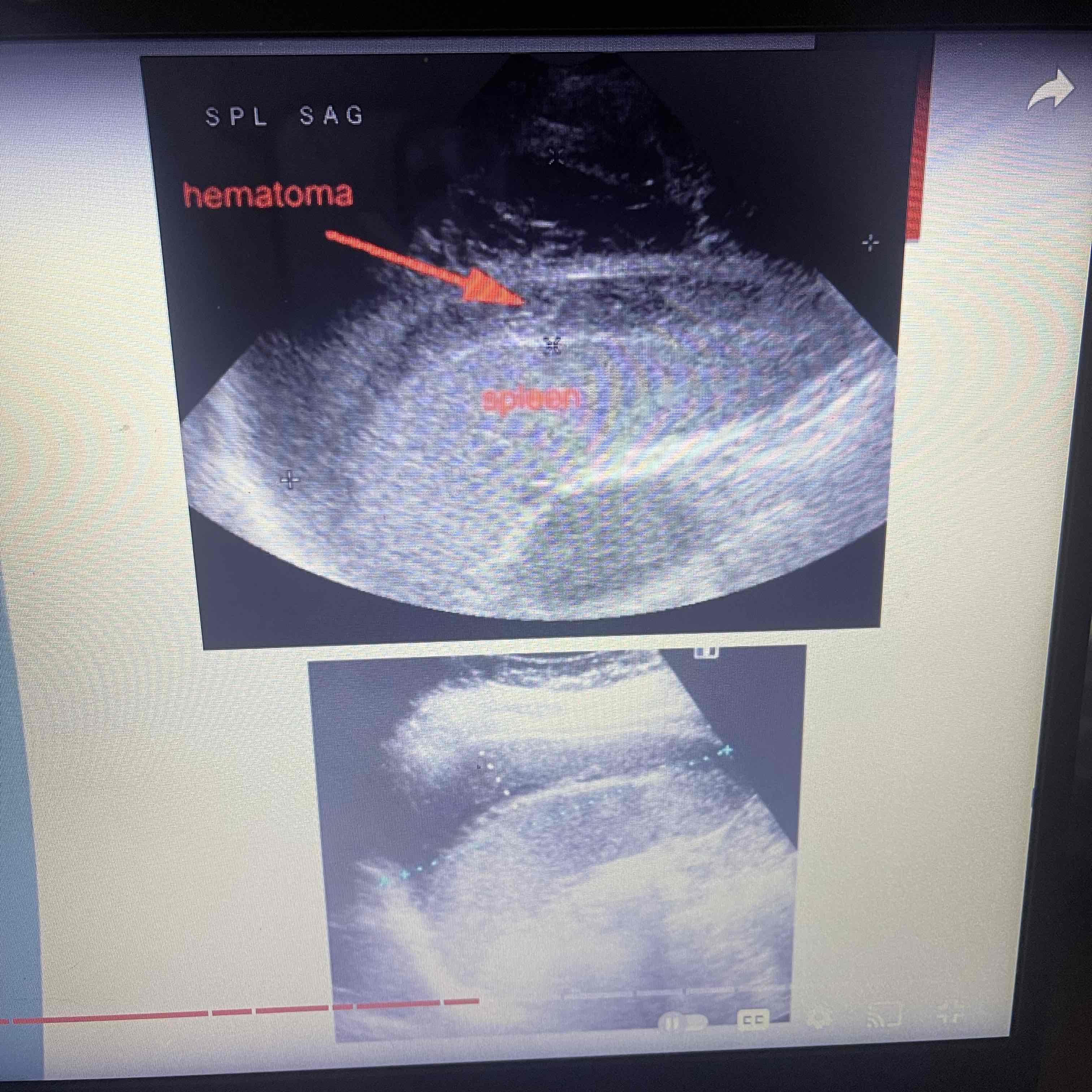
Trauma
Blood abdominal force; MC injury
FAST exam : Focused assessment with sonography for drama. Check 4 quads, Morrisons pouch, subdiaphragm, liver and splenic capsules, bladder and rectal regions
Clinically: Decreased hematocrit, Shock
Sonographic: eval for eternal hemorrhage, eval for FF
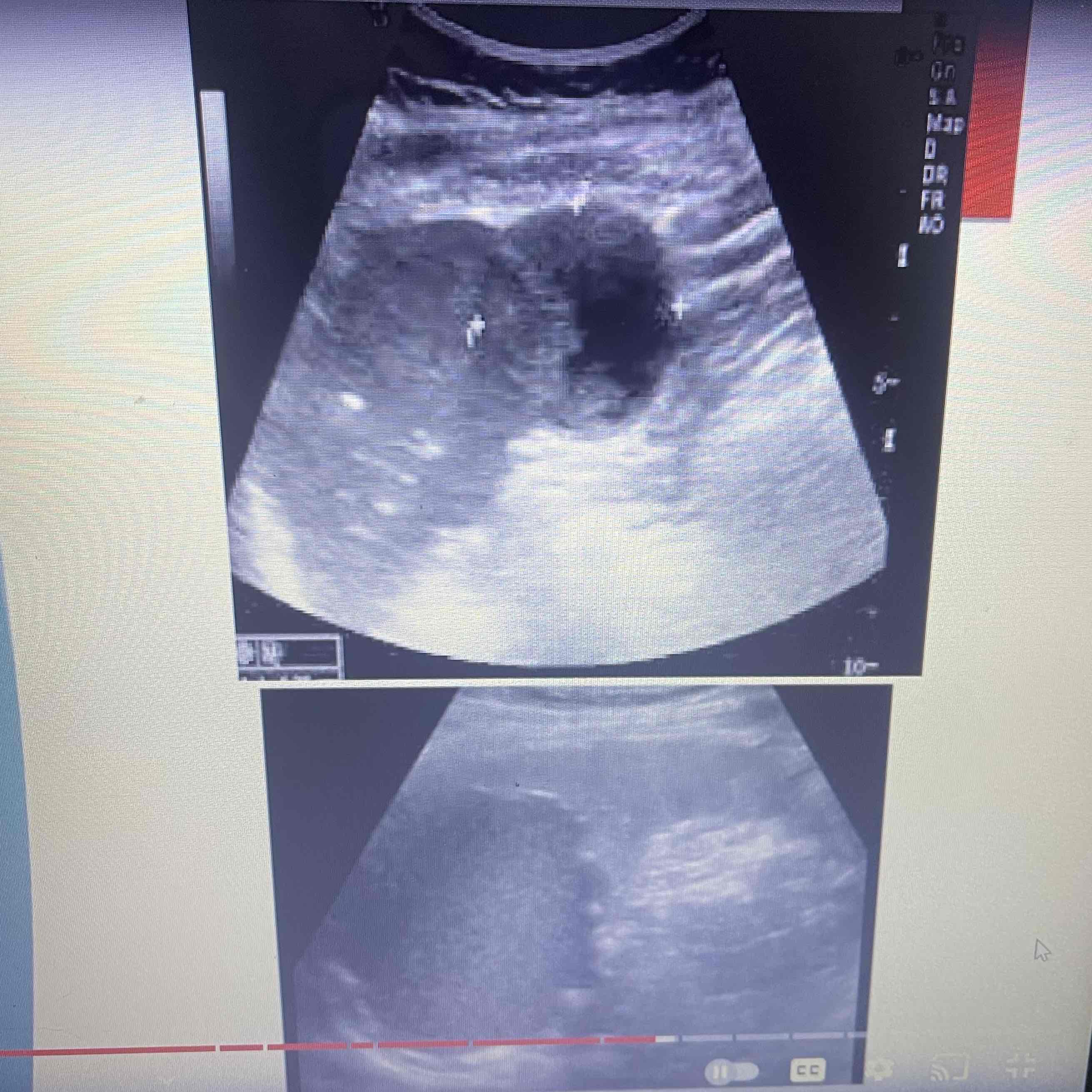
Abscess
Collection of pus
Infection from abdominal organ
Inflammation from direct adjacent organ
Clinically: Increased risk for pts, Drug use, endocarditis, decreased immunity, trauma
Sonographic: Focal collection of purulent material w/i splenic parenchyma, Target or Bullseye appearance, splenomegaly
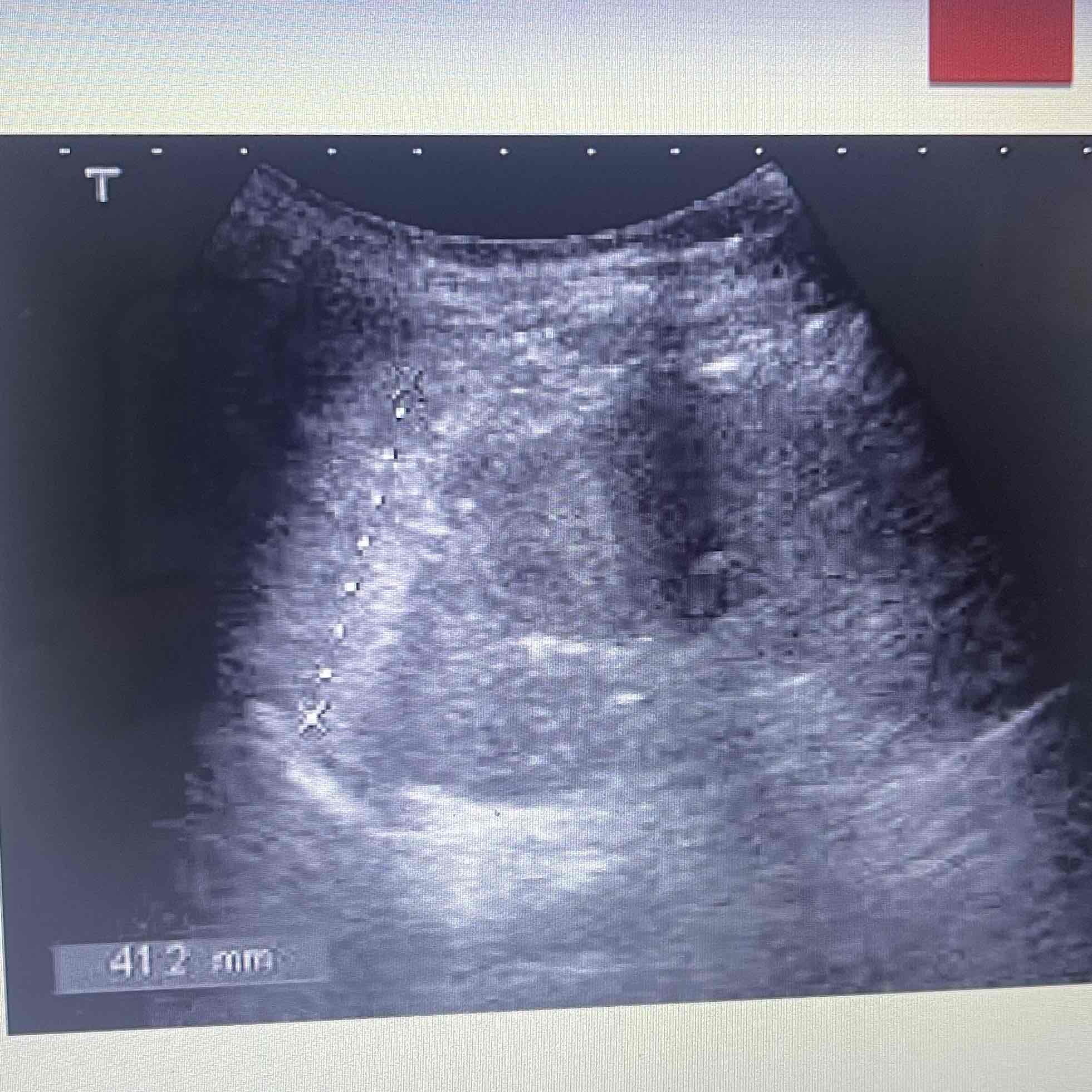
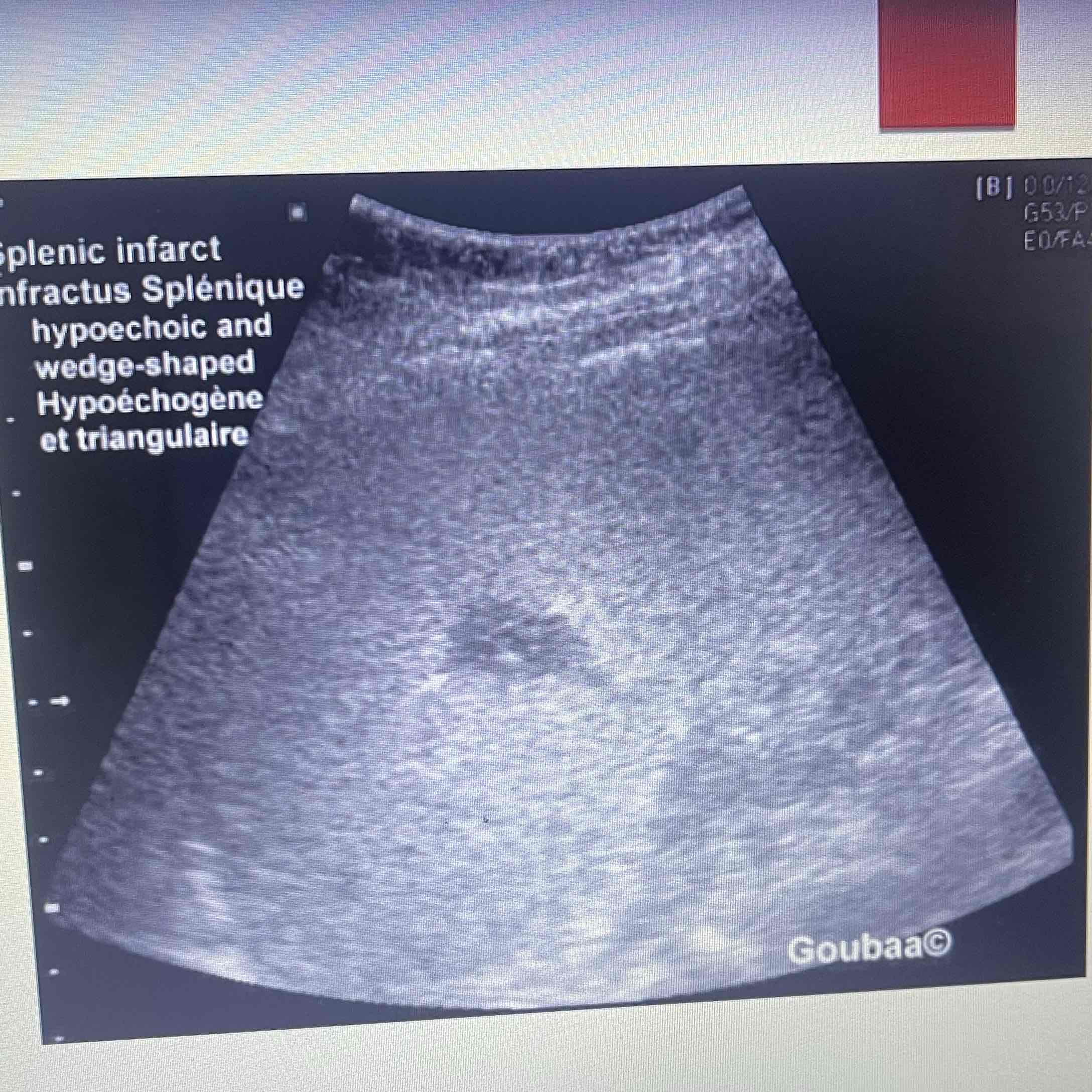
Infarction
Death of focal splenic tissue: May affect a segment or entire organ
MC cause of focal splenic lesions
Caused by occlusion of splenic arteries/Branches: Result of embolus from heart
Clinically: Pancreatitis, leukemia, lymph disorders, SCA
Sonographic: NO Splenomegaly, acute: Hypoechoic wedge, Chronic: echogenic Wedge
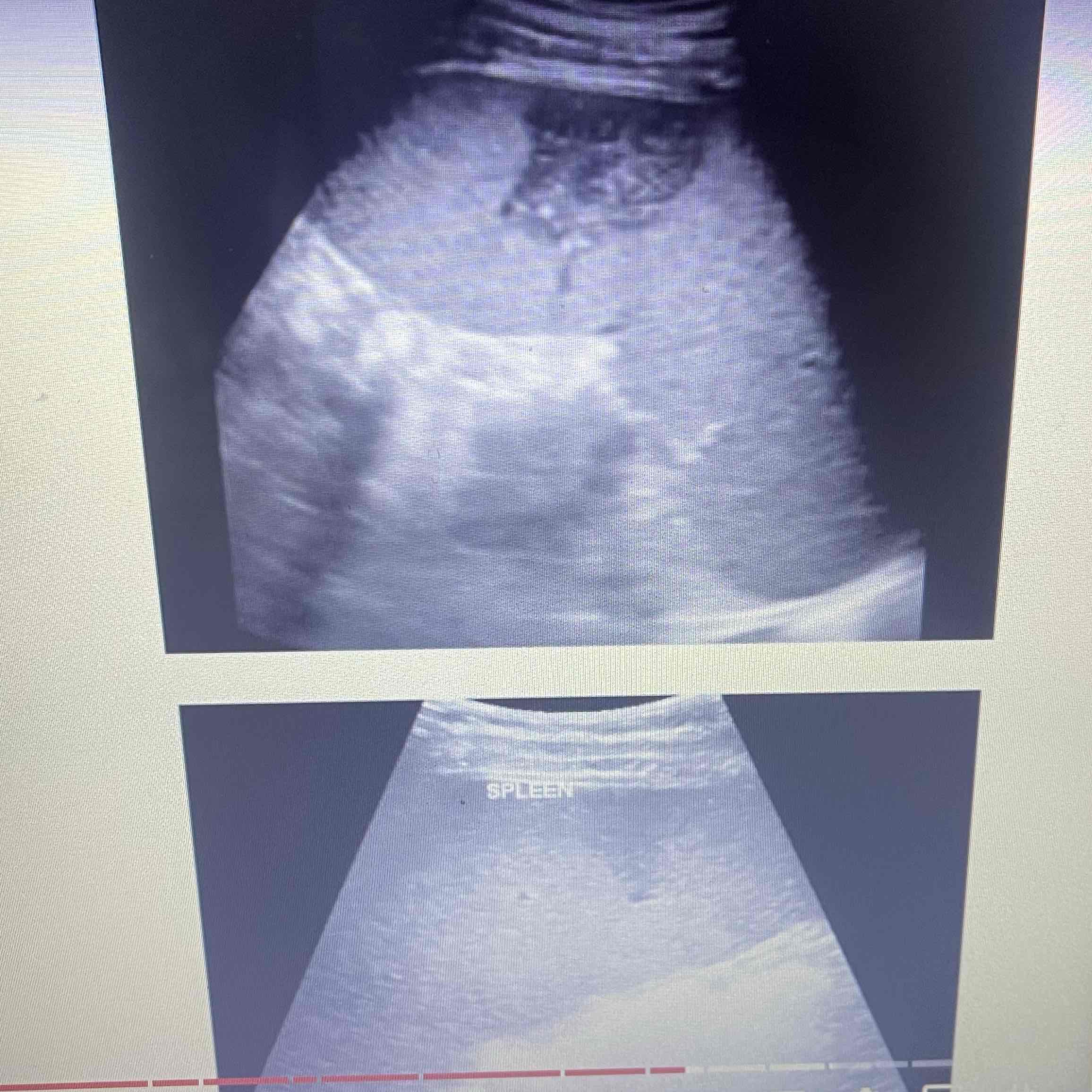
Hemangioma
Proliferation of vascular channels: cluster of blood vessels
MC, benign splenic tumor
Clinically: Asymptomatic
Sonographic: Isolated, Heterogeneous echogenic mass with multiple hypoechoic areas, Heterogeneity Caused by areas of cystic changes or hemorrhage
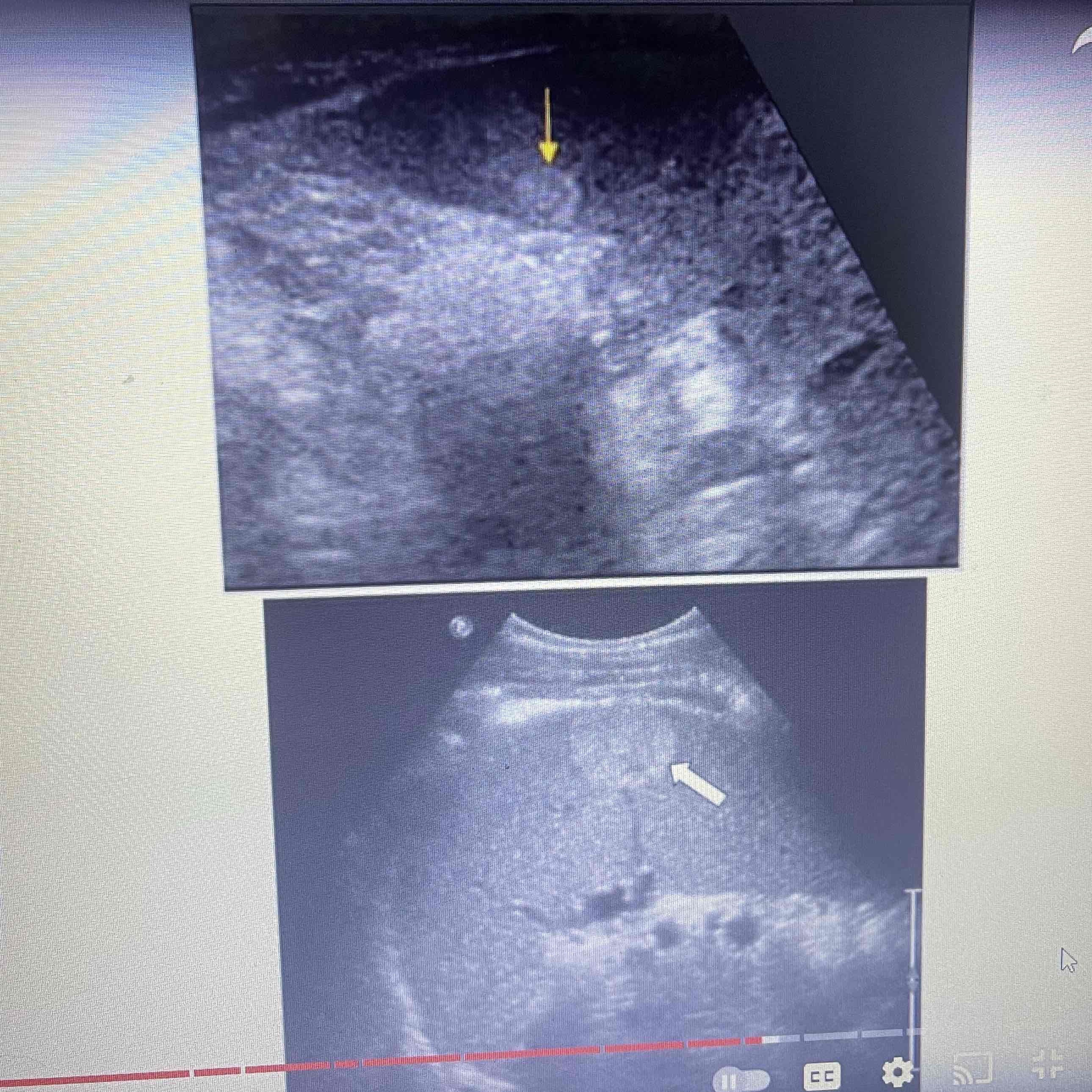
Hemangiosarcoma
Rare, malignant neoplasm rising from vascular endothelium of spleen
Clinically: Weakness/fatigue, loss of appetite/weight loss, tumor rupture, hemorrhage
Sonographic: Cystic and solid components, hyperechoic
Hamartoma
Abnormal mixture of cells and tissues: Mainly lymphoid tissues
Rare, Benign
Clinically: Asymptomatic
Sonographic: Cystic and solid components, isoechoic / hyperechoic
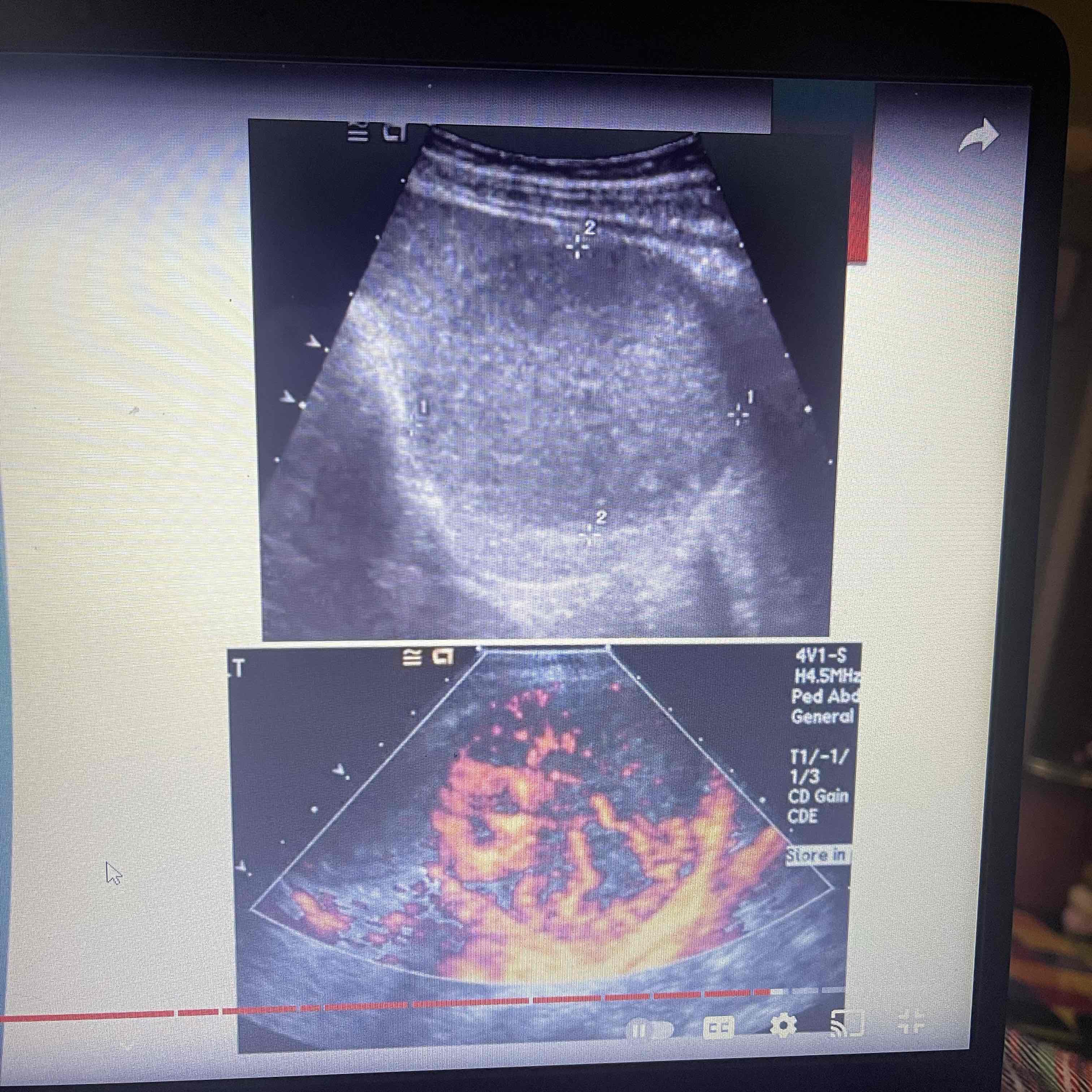
Lymphangioma
Malformation of Lymphatics
Consists of cystic spaces that vary in size
May involve other organs
Rare, benign
Clinically: Spleen- Asymptomatic, possible tenderness. Variable symptoms due to additional organs
Sonographic: Multiple cysts, solitary or grounded
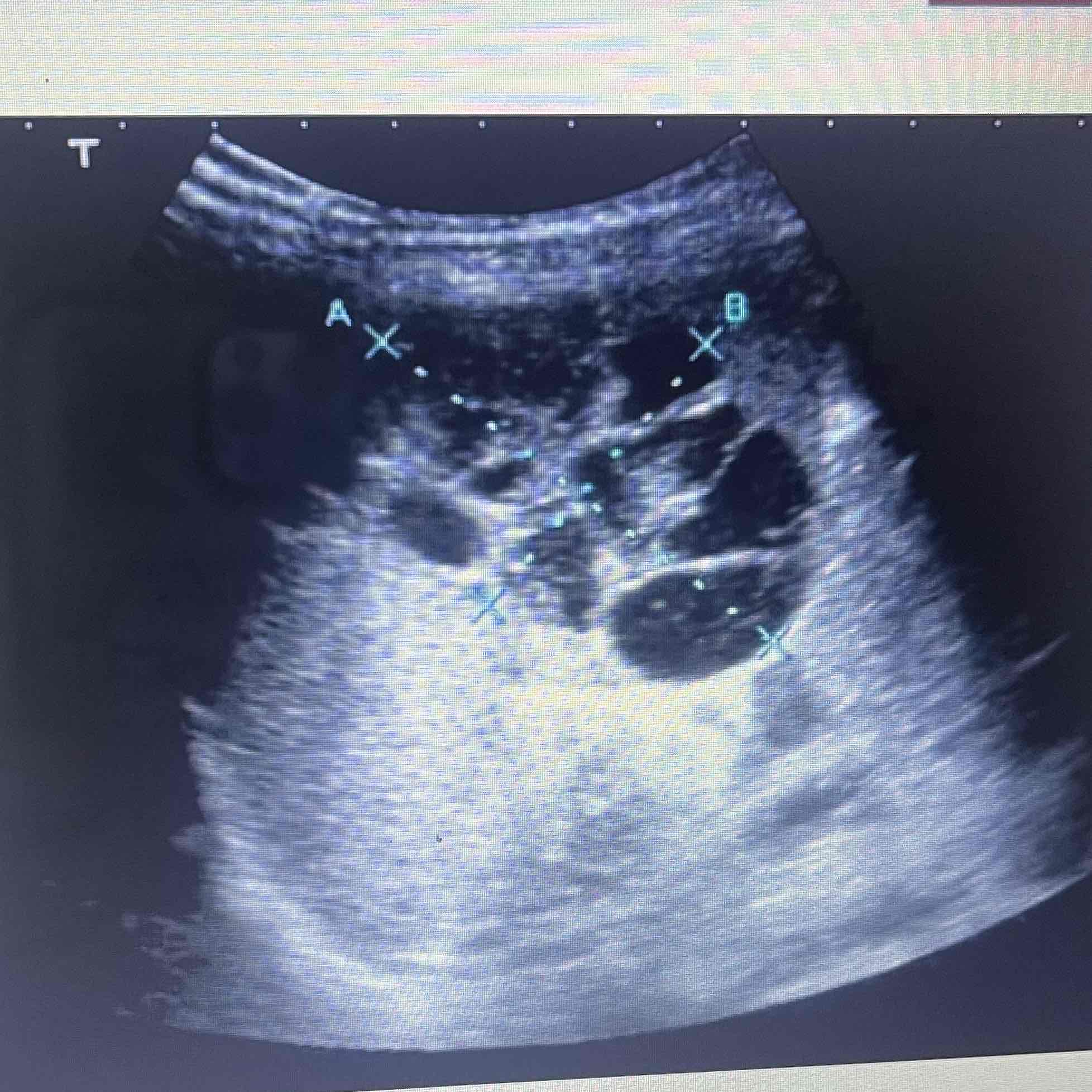
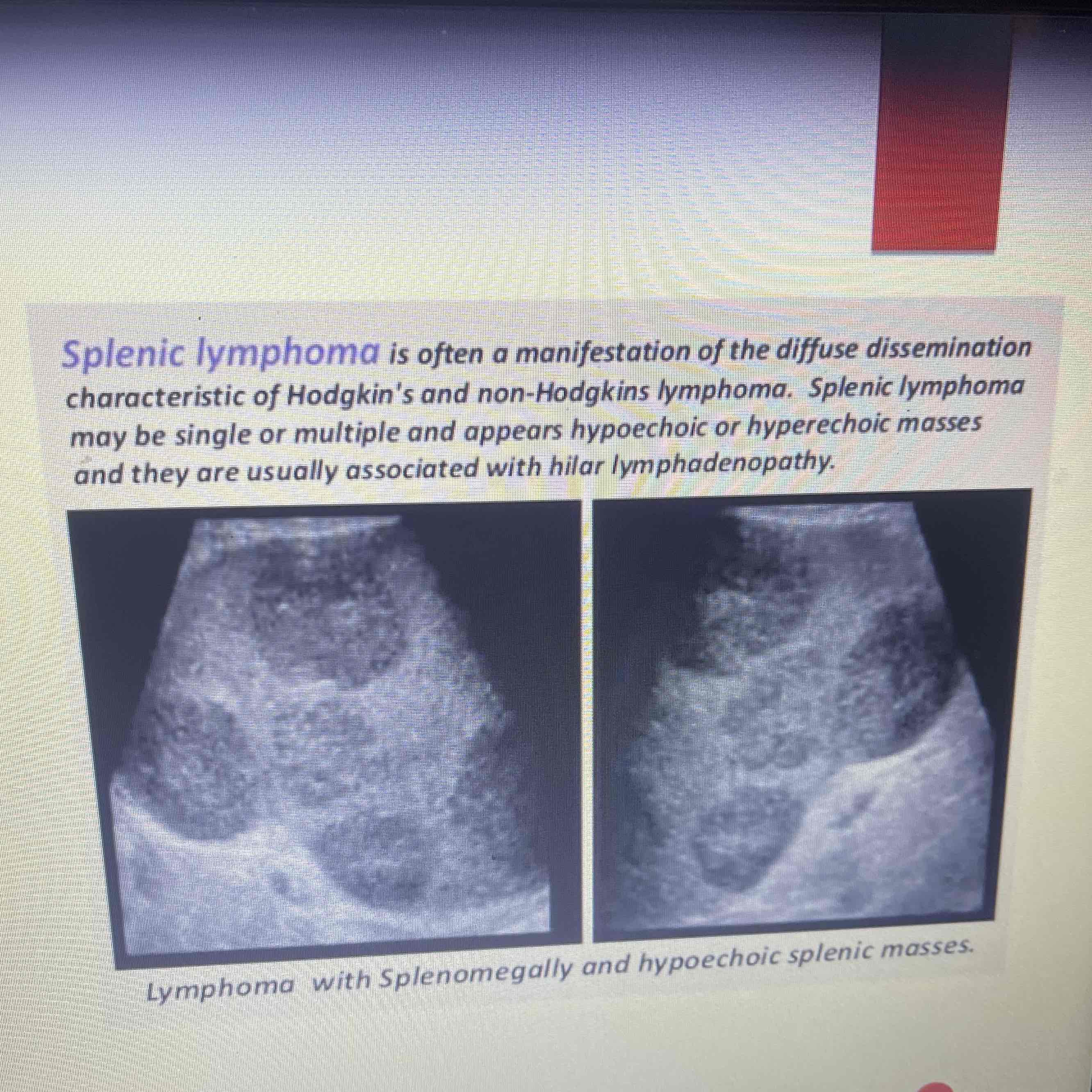
Lymphoma
Spleen is most commonly involved organ
MC malignant tumor is Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin’s
Clinically: history of ca
Sonographic: Difficult to visualize on ultrasound, bulky disease, focal or diffuse lesions, splenomegaly may occur, AIDS Lymphoma: Uniform decreased echogenicity or focal hyperechoic lesions
Metastatic disease
Hematogenous spread from primary site
Spleen is 10th MC site of mets
Clinically: history of ca
Sonographic: Multiple or solitary, nodularity, diffuse lesions, target or halo lesions