Systems I Exam 3 ALL
1/768
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
769 Terms
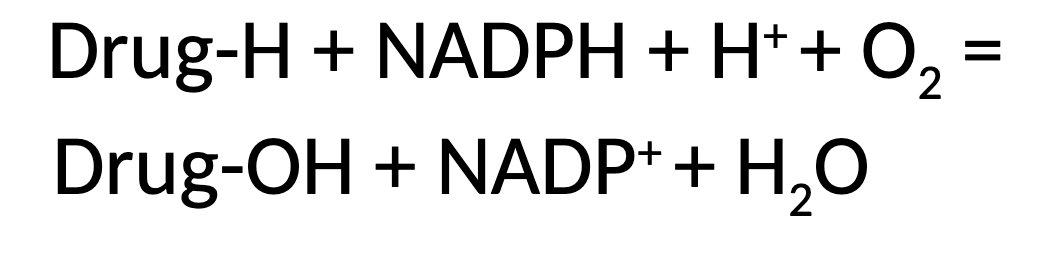
CYP450 enzymes
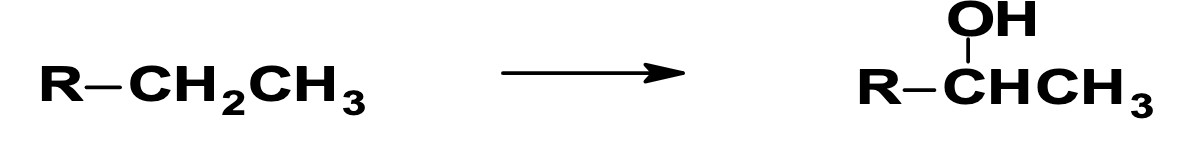
Aliphatic hydroxylation
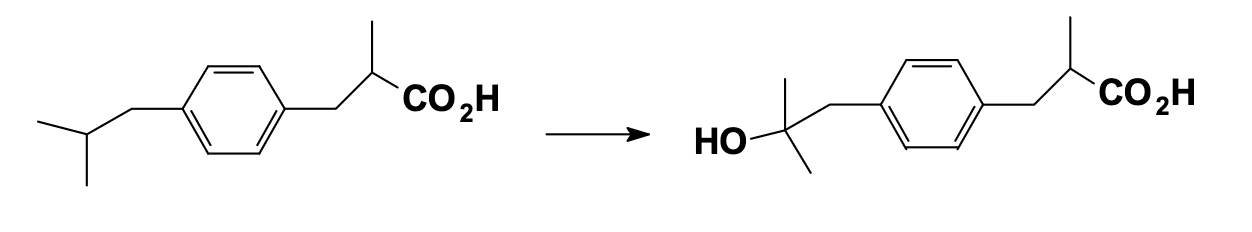
Aliphatic hydroxylation
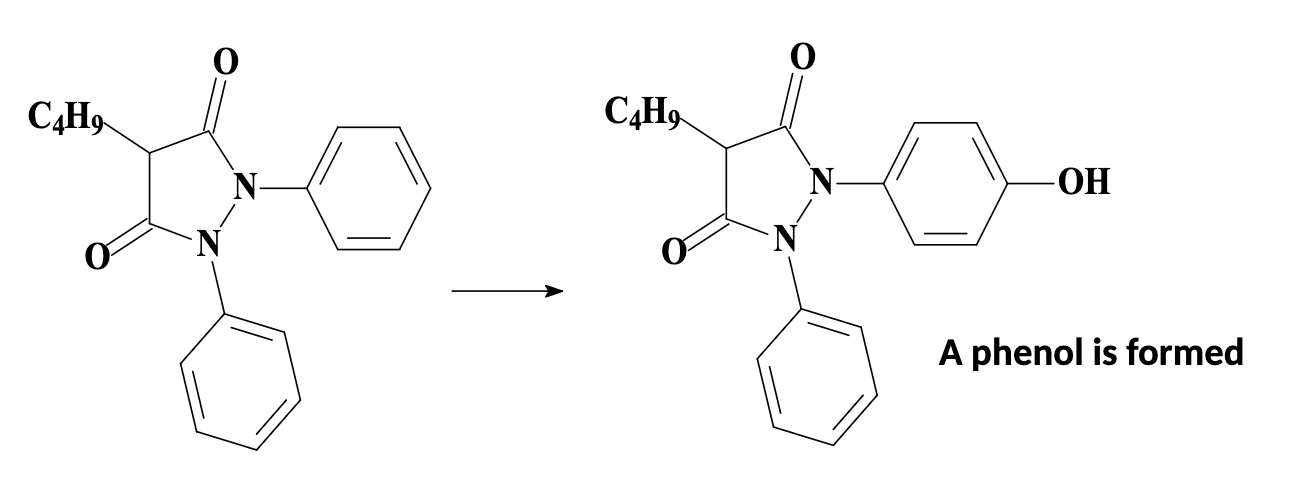
Aromatic hydroxylation
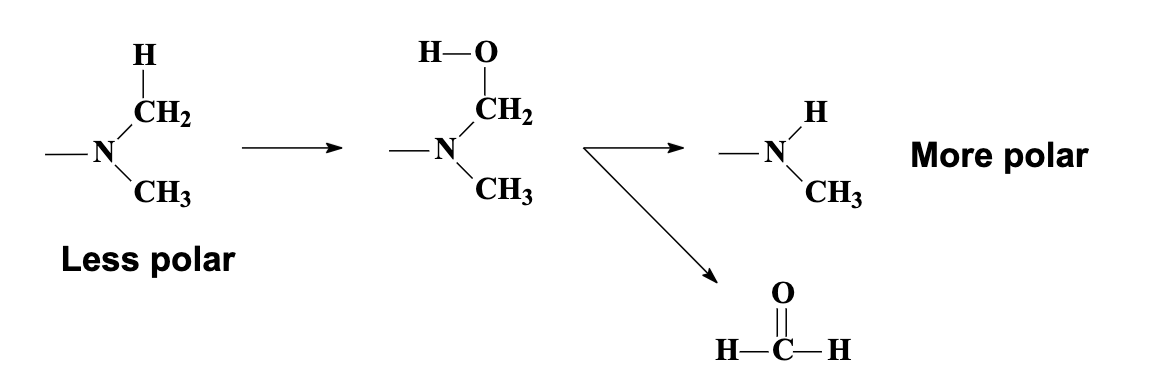
N-Dealkylation
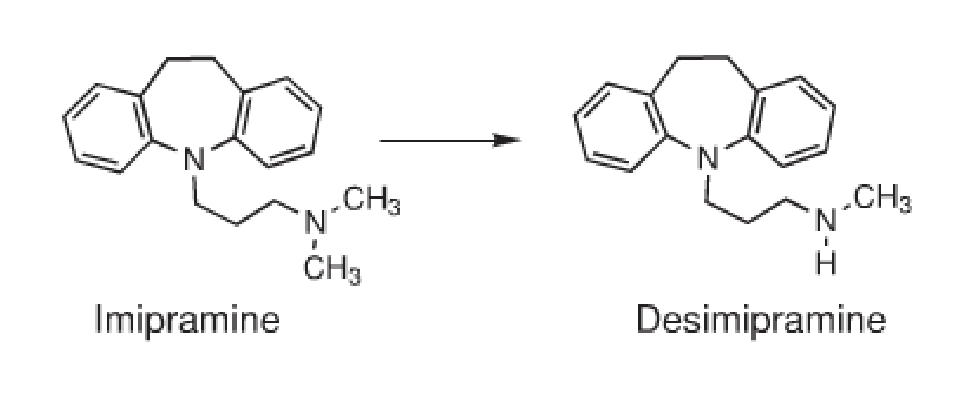
N-Dealkylation
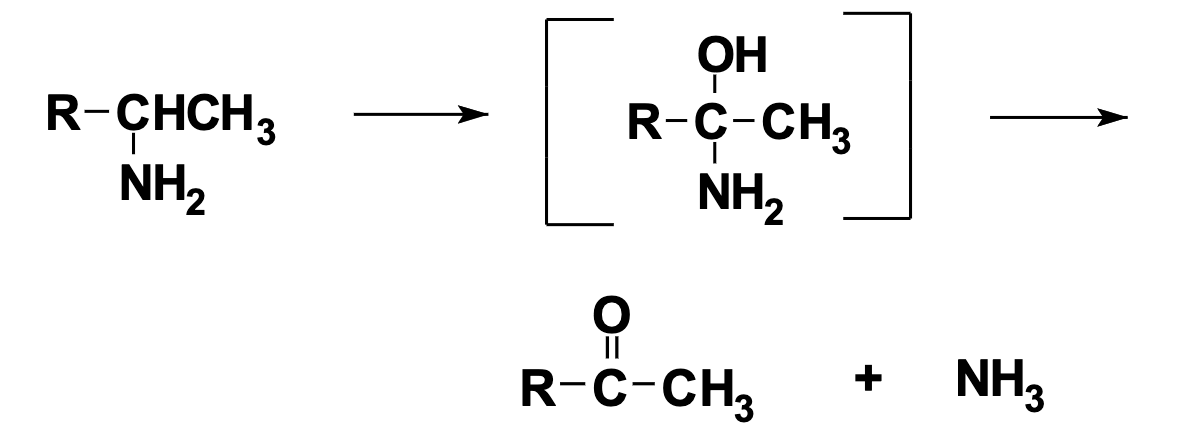
N-Deamination
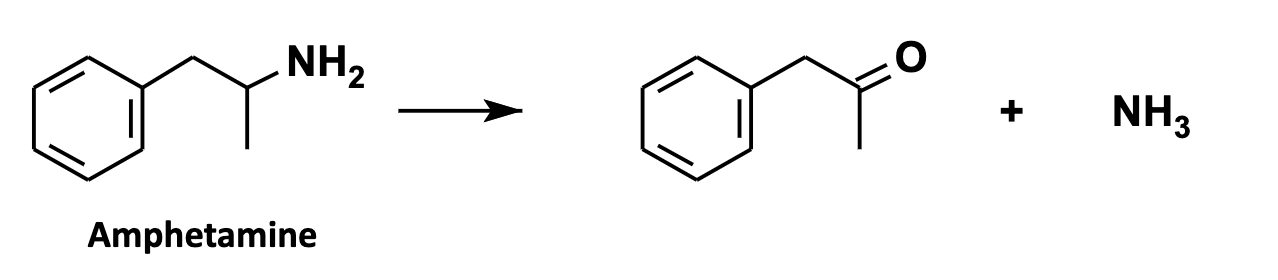
Deamination
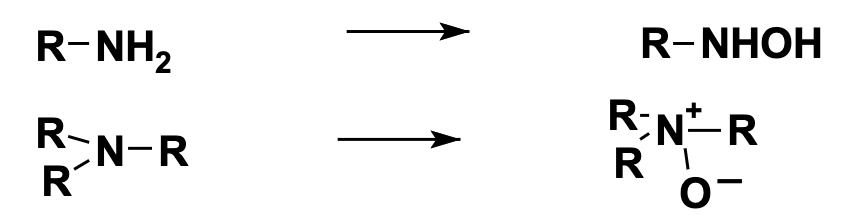
N-Oxidation
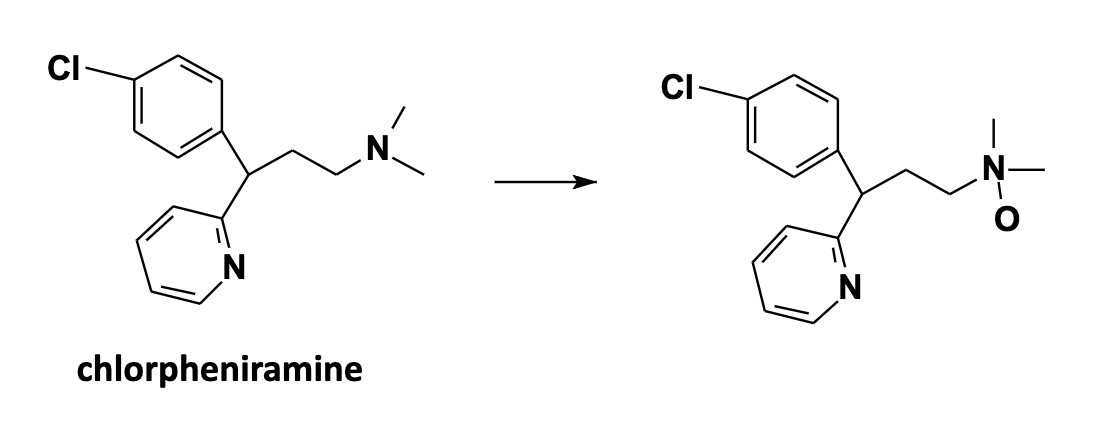
N-Oxidation
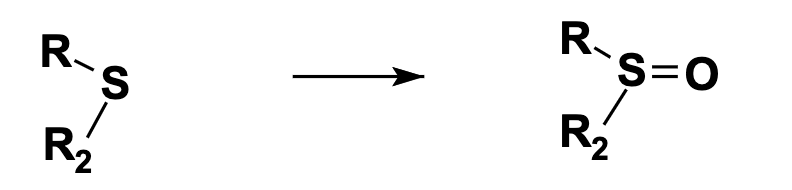
S-Oxidation
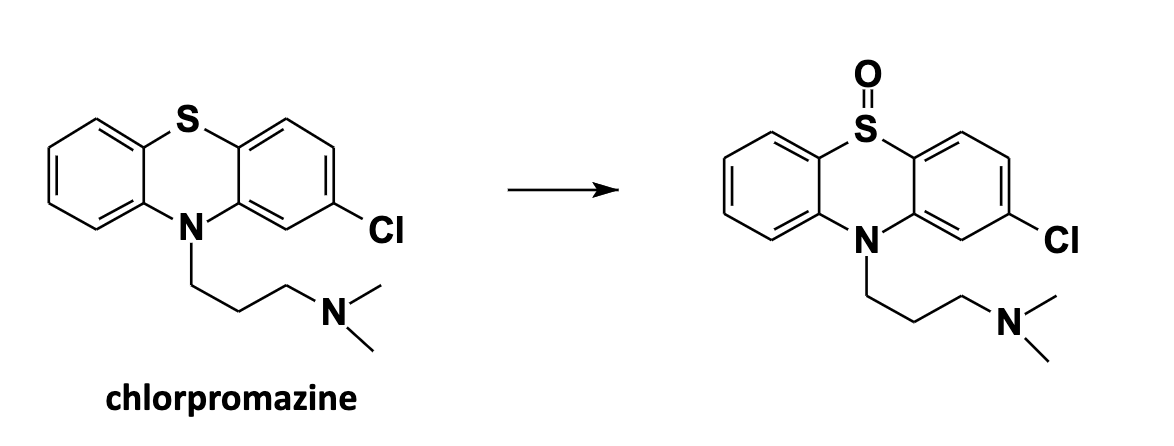
S-Oxidation
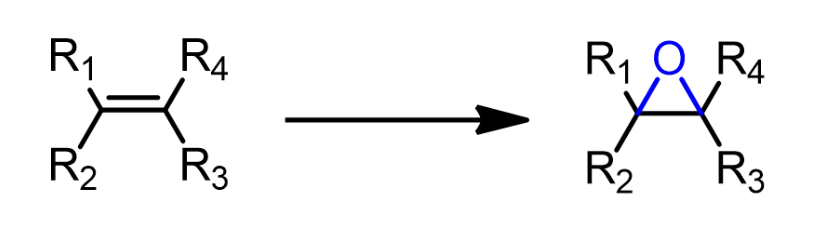
Epoxidation
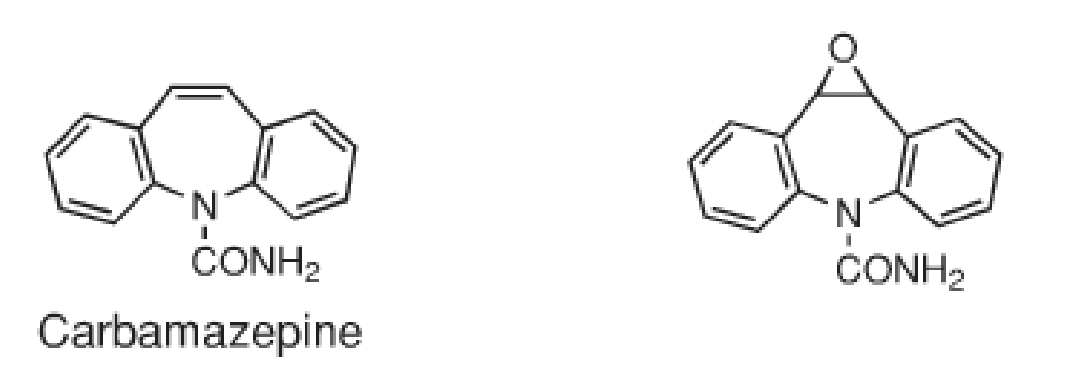
Epoxidation
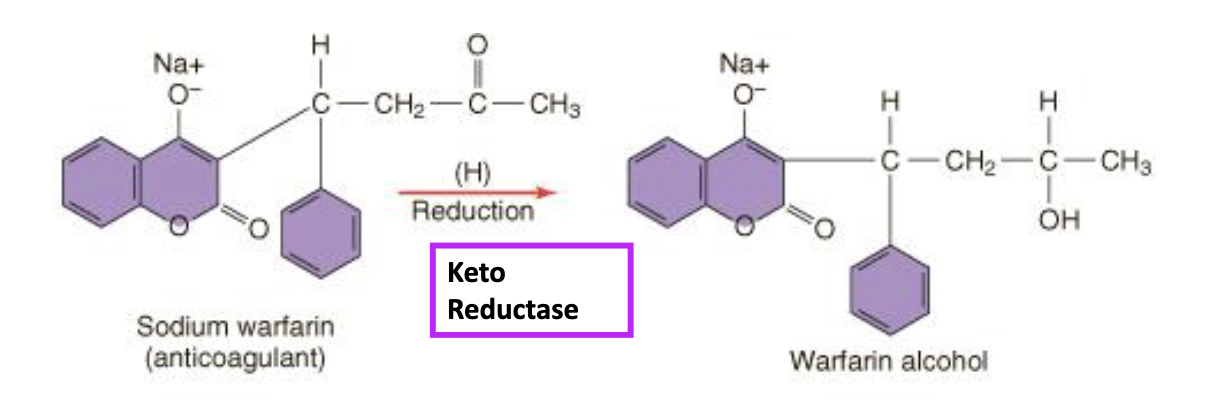
Reduction
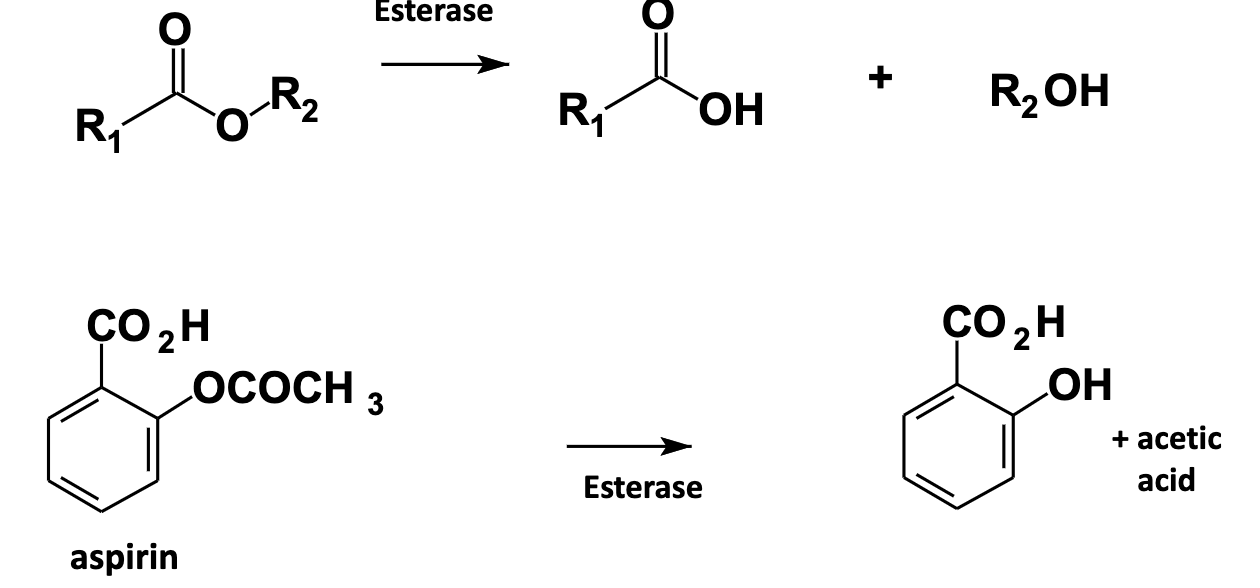
Hydrolysis
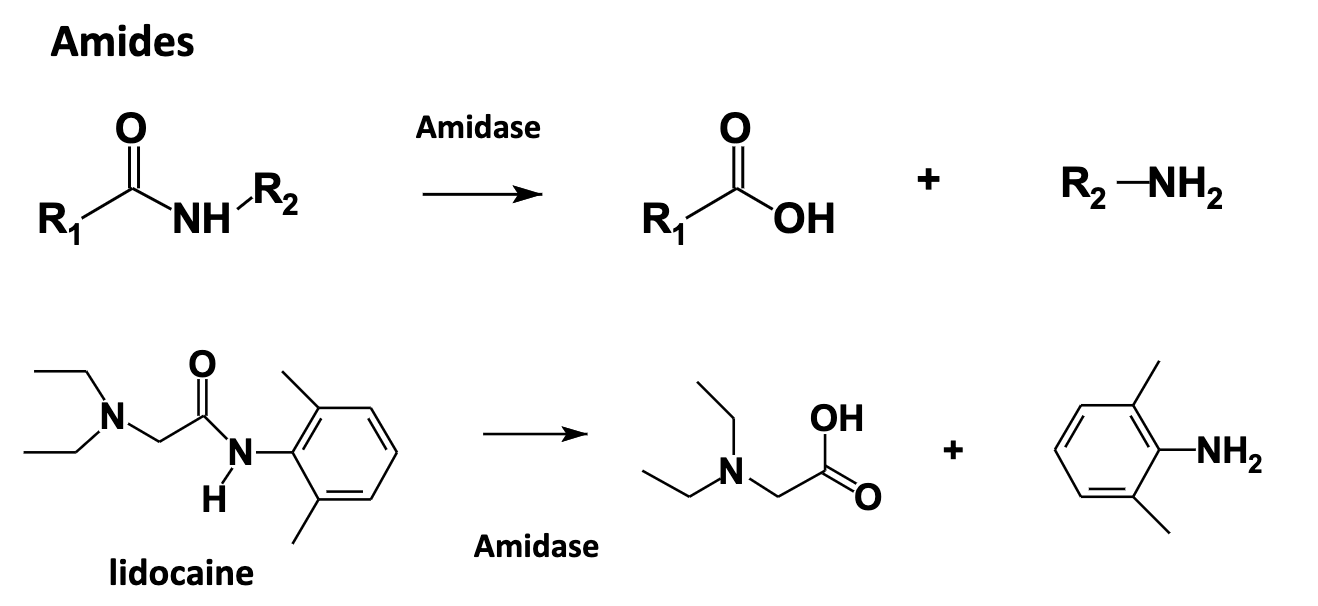
Hydrolysis
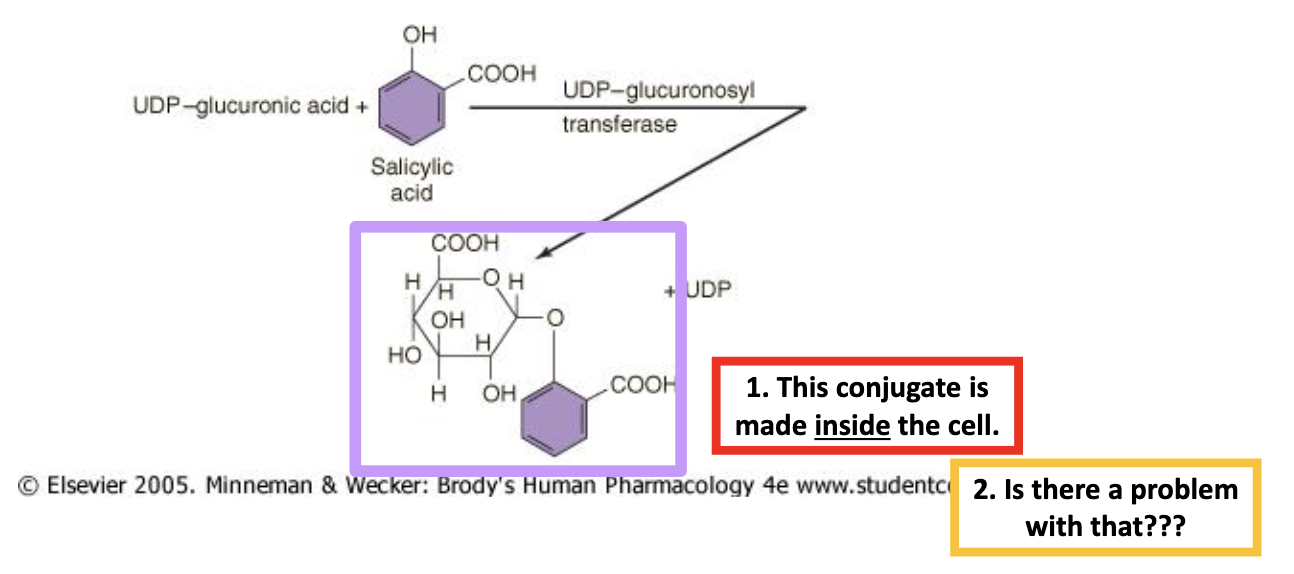
Glucuronidation
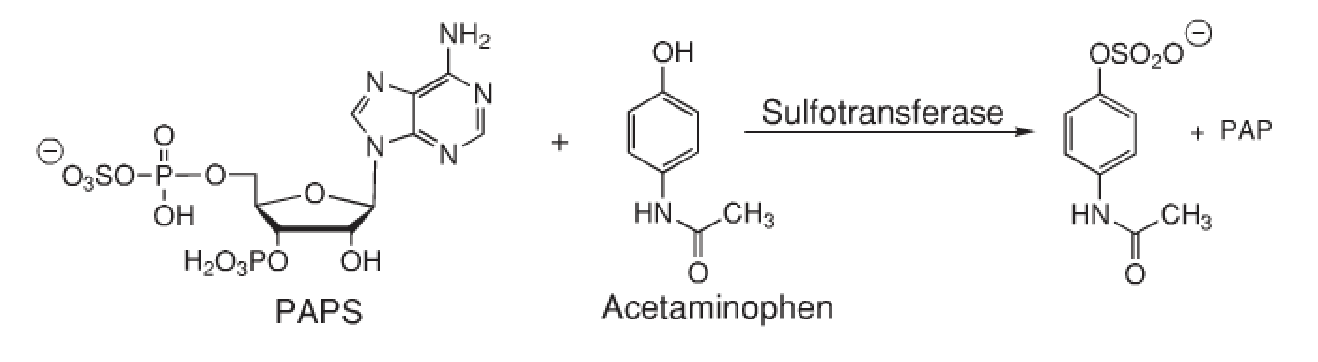
Sulfation
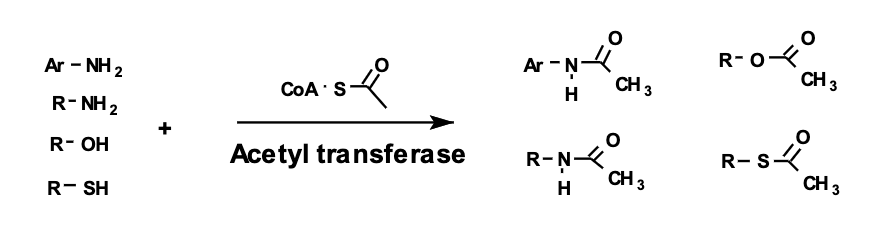
Acetylation
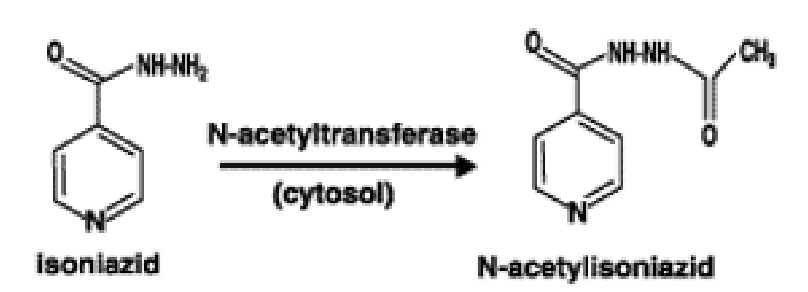
Acetylation
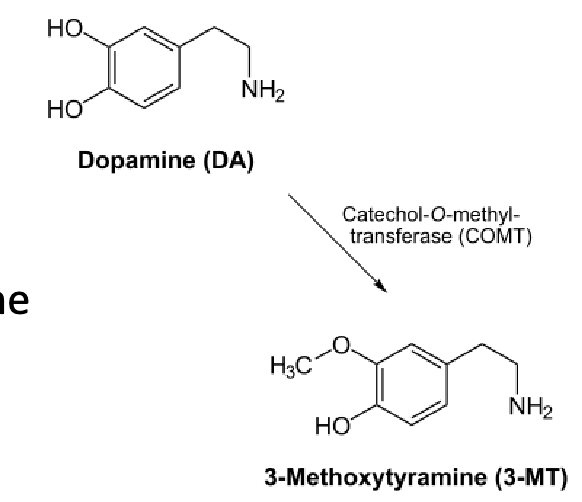
Methylation
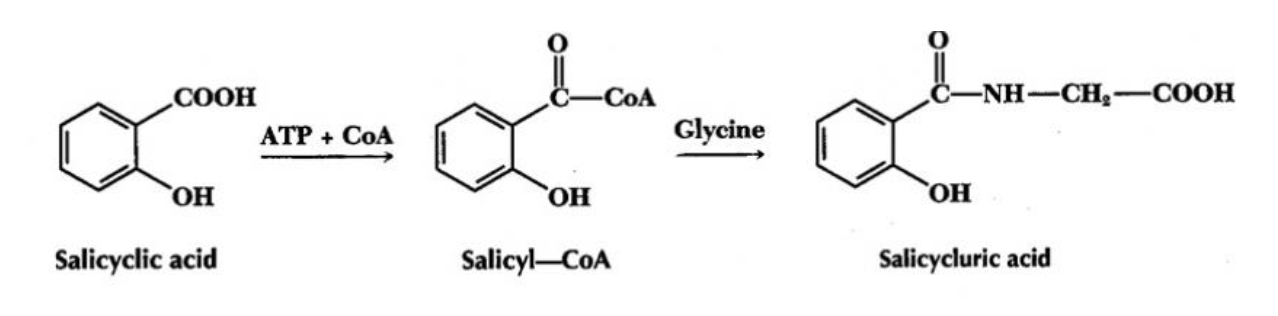
Amino acid conjugation
Two enzymes for amino acid conjugation
Acyl synthetase and transacetylase
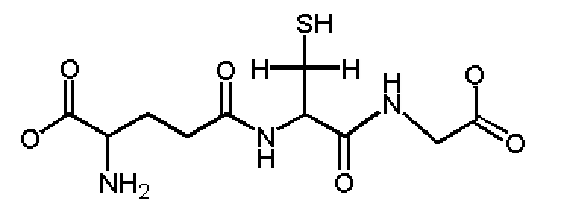
Glutathione
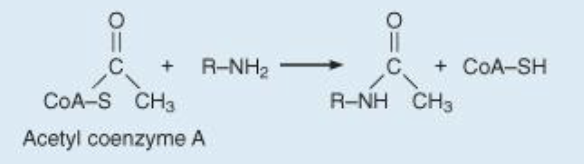
Acetylation
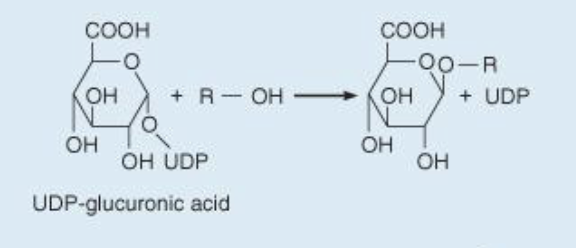
Glucuronidation
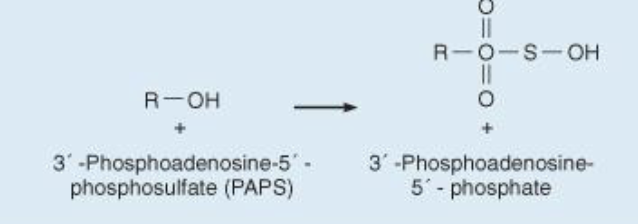
Sulfation
Glucuronidation
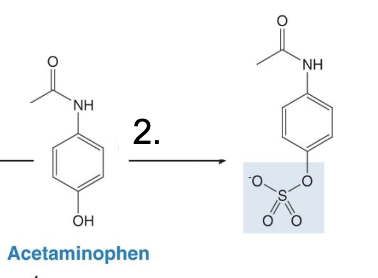
Sulfation
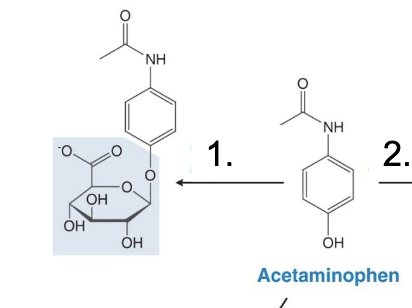
Converts acetaminophen to NAPQI
CYP2E1
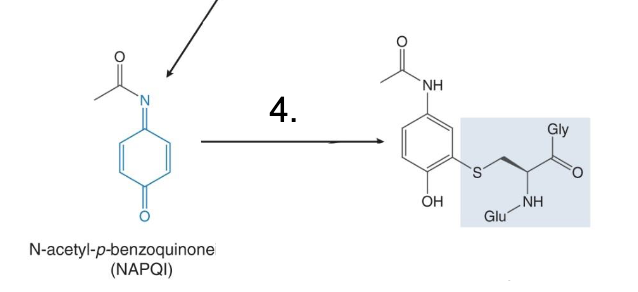
Glutathione conjugation
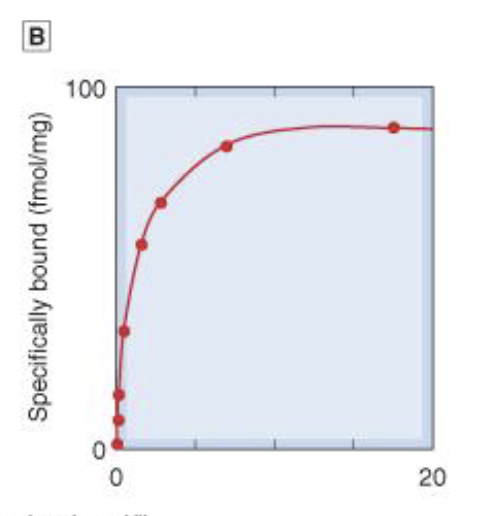
Specific binding
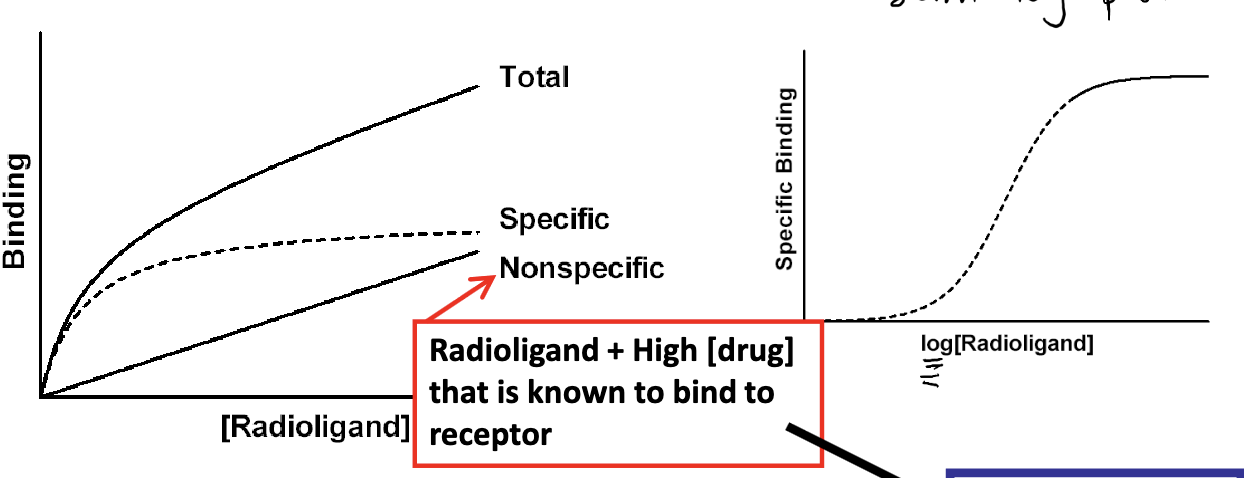
Saturation binding study
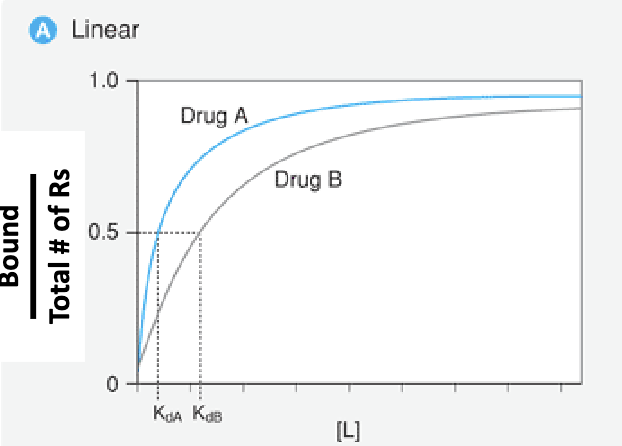
Which drug has a higher affinity?
Drug A
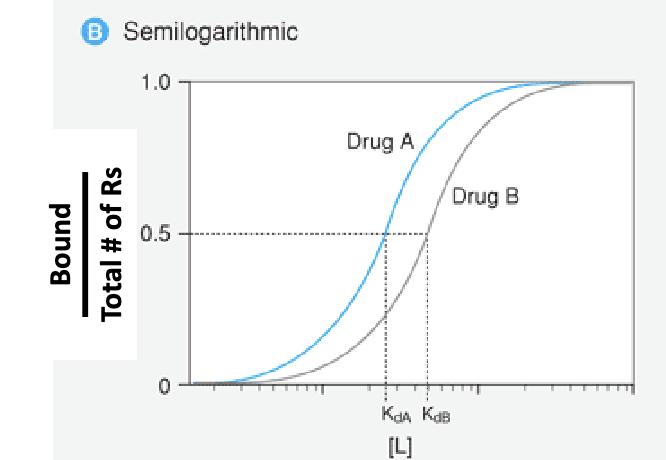
Which drug has a higher affinity?
Drug A
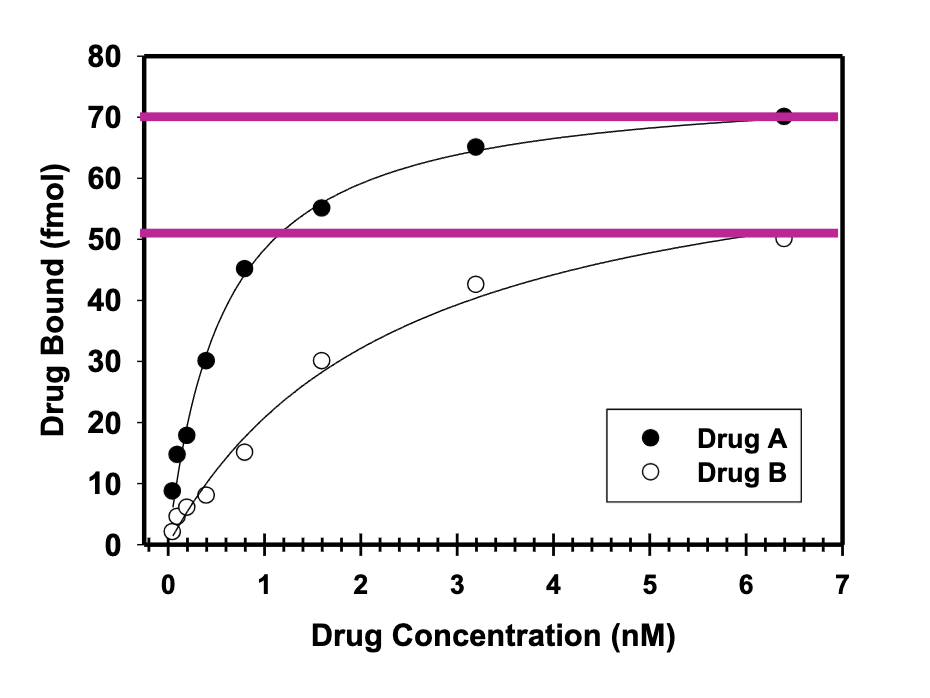
Which drug has a higher affinity
Drug A
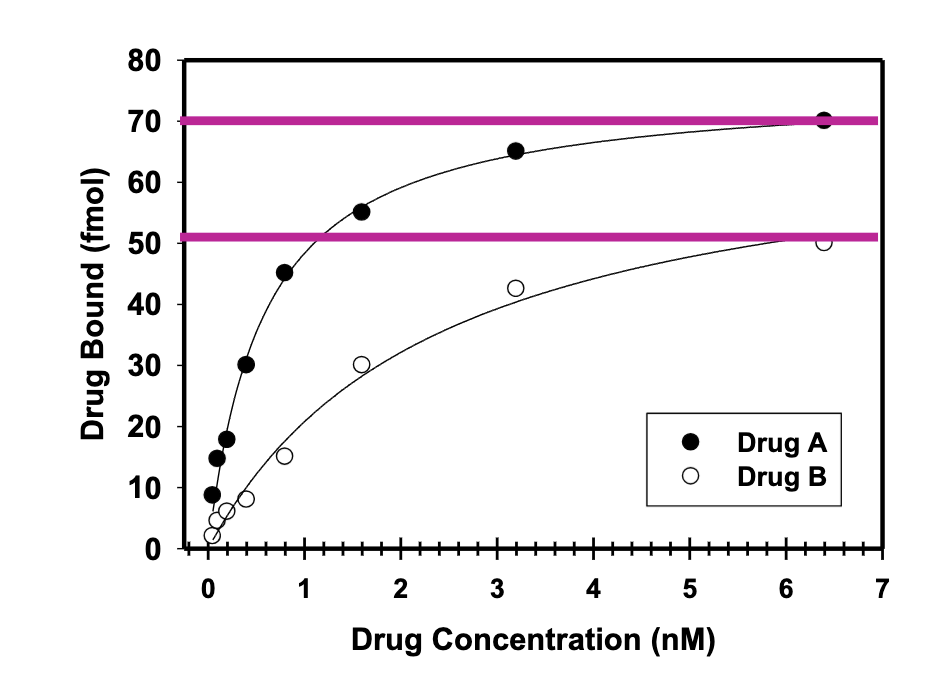
Which drug binds more receptors?
Drug A
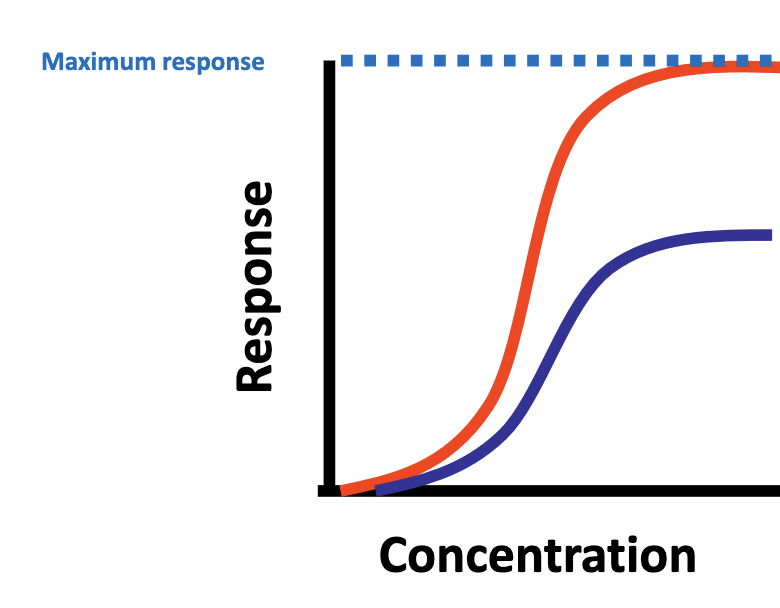
What does the blue line represent?
Partial agonist

Which drug has a higher affinity?
Drug A

Which drug binds more receptors?
Drug B

Which drug is more efficacious?
Drug B
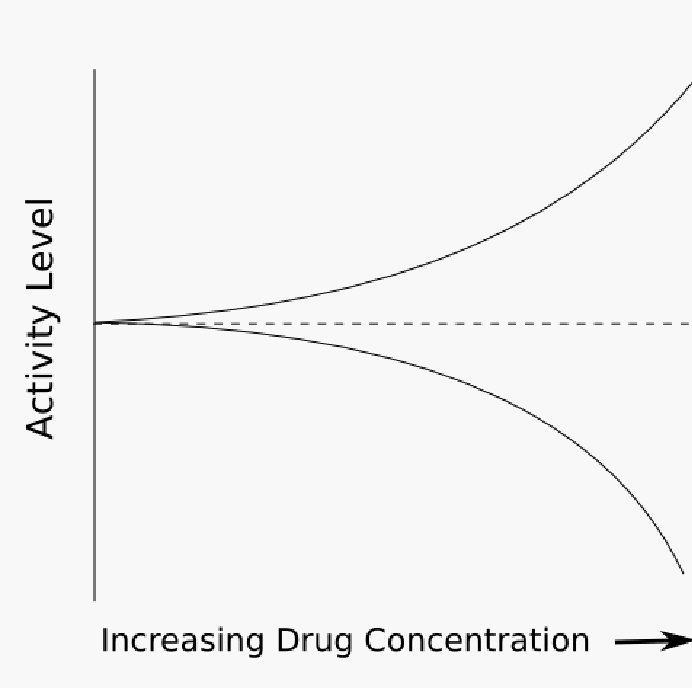
What does the top line represent?
Agonist
What does the middle line represent

Baseline activity

What does the bottom line represent?
Inverse agonist
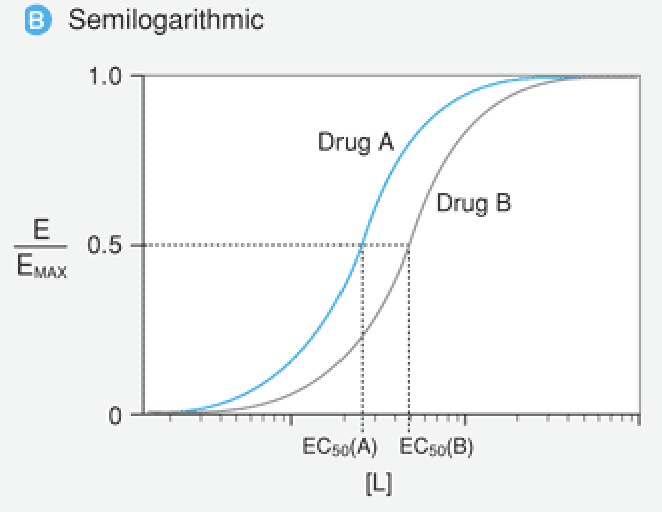
Which drug is more potent?
Drug A
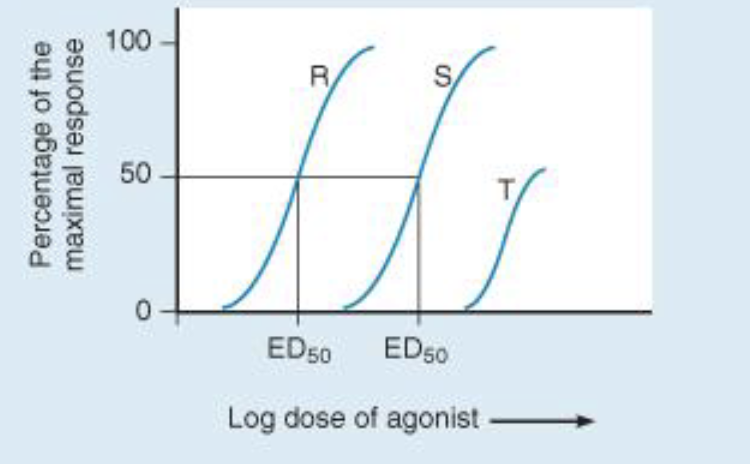
Which drug is the most potent?
Drug R
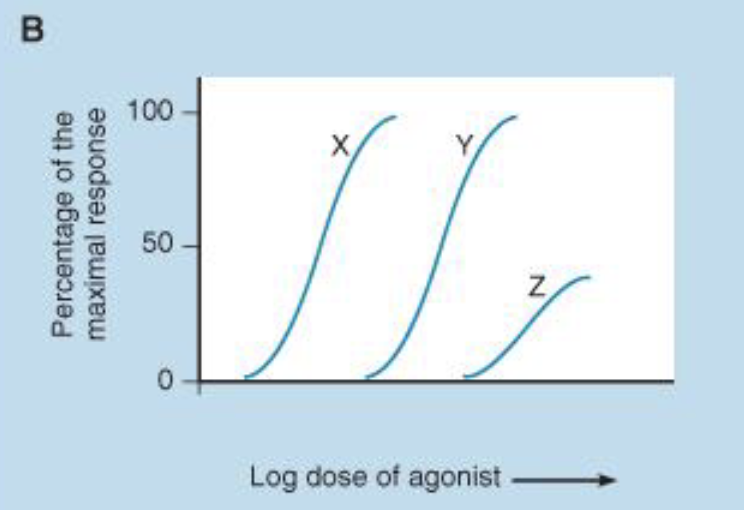
What is drug Z an example of?
Partial agonist
Most drugs produce their effects by interacting with ______ within cells or on cell surfaces
Targets
A drug ______ can be a molecule such as a protein, a lipid molecule, or DNA
Target
Common ________ for drugs include receptor proteins, ion channel proteins, enzymes, and transporters
Targets
Molecules on the cell surface or inside the cell that bind to hormones, neurotransmitters, or drugs to initiate a cellular response
Receptor proteins
Pores in the cell membrane that regulate the flow of ions, which can be opened or blocked by drugs
Ion channel proteins
Proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions, which drugs can inhibit or activate
Enzymes
Proteins that actively move substances across cell membranes
Transporters
It is important to note that some drugs do not have ____ specific target and may produce their effects through less targeted mechanisms
One
These drugs produce effects by changing the physical or chemical environment of a biological system rather than binding to a receptor or enzyme
Nonspecific
Antacids act nonspecifically by neutralizing the _____
Acid
______ drugs can result in changes in pH, osmolarity, and surface tension
Nonspecific
Many drugs target ______ to either activate or inhibit their function
Enzymes
The drug (inhibitor) binds to the same active site as the natural substrate
Competitive
The drug (inhibitor) binds to a different site (allosteric site), changing the enzyme’s shape and reducing its effectiveness
Non-competitive
________ are the target for drugs most of the time; binding usually changes its activity
Receptors
These can be extracellular or intracellular
Receptors
Drugs that exert osmotic effects are typically highly _________ and cannot easily cross cell membranes
Hydrophilic
Drugs that exert osmotic effects change the osmolarity of a solution, causing _____ to shift
Fluid
A hydrophilic alcohol used as a diuretic to rapidly reduce intracranial pressure or treat cerebral edema
Mannitol
Increase urine production
Diuretic
This remains in the blood, increasing its osmolarity, which draws excess fluid from the brain tissue into the blood and then the renal tubules, increasing the excretion of water in urine
Mannitol
Mannitol doesn’t directly interact with a __________
Receptor
This mechanism involves a drug changing the structure of proteins, typically by breaking chemical bonds
Protein denaturation
Used as an inhalational agent to treat respiratory conditions; acts as a disulfide breaking agent to reduce viscosity of mucus and make it easier to expel
NAC
This is used as an oral treatment for acetaminophen overdose because it serves as a precursor to glutathione, an important detoxifying cofactor
NAC
Antacids work by chemically ________ stomach acid, thereby increasing the pH of the stomach
Neutralizing
Examples are calcium carbonate and sodium bicarbonate
Antacids
This mechanism refers to compounds that are selectively toxic to foreign organisms or cells
Selective toxicity
Examples of selective toxicity
Germicides and disinfectants
These work by altering the surface tension between a liquid and a gas or another liquid
Surfactants
A natural lung surfactant replacement given to babies burn prematurely; composed of phospholipids, neutral lipids, and hydrophobic surfactant-associated proteins B and C
Intrasurf
Intrasurf reduces surface tension in the ______ of the lungs, preventing them from collapsing and allowing the premature baby to breathe easier
Alveoli
Surfactant, a mixture of lipids and proteins, lowers the _______ _______ between the wet lining of the alveoli and the air inside them
Surface tension
Surfactant lowers the _______ properties of water in the alveoli which helps them remain stable by preventing collapse and bursting
Cohesive
Without adequate surfactant, the strong ______ forces of water molecules lining the alveoli create a high surface tension
Cohesive
High surface tension can lead to alveoli ________
Collapse
High surface tension makes it extremely difficult to re-_______ the lungs with each breath
Inflate
Adequate _______ allows alveoli to stay properly open at various sizes throughout the breathing cycle
Surfactant
The definition of a receptor depends on the _______
Context
The component of a cell that interacts with a drug and initiates a chain of biochemical events leading to the drug’s therapeutic or toxic effects
Receptor
Receptors cause something to _____ inside the cell in addition to binding
Change
For a drug to bind to a receptor, there must be precise _________ involving chemical groups and the there-dimensional shape
Compatibility
The three-dimensional _____ of the drug must fit precisely into the receptor site, like a lock and key
Shape
A _________ shape will not bind effectively, while a complementary shape will
Mismatched
Various types of ______ chemical bonds form between the drug and receptor including ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds, and van der waals
Weak
Strongest type of bond; involves the sharing of electrons
Covalent
Involves the electrostatic attraction between a positively charged atom and a negatively charged atom (transfer of electrons)
Ionic
A weak interaction between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to an electronegative atom (like N or O) and another electronegative atom
Hydrogen bond
Weak interactions between non-polar groups, often involving aromatic rings
Hydrophobic
The weakest interactions, arising from temporary fluctuations in electron distribution
Van der Waals
Drug-receptor binding usually involves a combination of _______ ____ bonds, including ionic, hydrogen, hydrophobic, and Van der Waals
Multiple weak
We usually want __________ and reversible interactions for drug-receptor binding
Non-covalent