AP Biology Review Guide
Matter
Anything that has mass and takes up space
Matter is made up of?
Elements
1/201
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
202 Terms
Matter
Anything that has mass and takes up space
Matter is made up of?
Elements
Elements differ by...?
number of protons, neutrons, and electrons
Atomic mass equals
protons + neutrons
Elements are made of...?
atoms
S,Px, Py, Pz orbitals hold how many electrons?
2 electrons
How many val e- makes an element stable
8 val e-
How are covalent bonds formed?
Bonds created by sharing electrons with other atoms.
How are ionic bonds formed?
by the transfer of electrons
Oxidation
loss of electrons
Reduced
gains electrons
Is energy stored or released when e- are elevated to higher levels?
energy is stored
Is energy stored or released when e- are dropped to lower levels?
energy is released
The movement of e- between energy levels is used in...?
Cellular reactions (Photosynthesis and respiration)
Compound
A substance made up of atoms of two or more different elements joined by chemical bonds
What 4 elements make up 96% of living matter?
oxygen, carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen
Essential element
A chemical element required for an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce.
Trace element
an element that is essential for life but required in extremely minute amounts
Helium-3 has how many protons?
2 protons
Helium-3 has how many electrons?
2 electrons
Helium-3 has how many neutrons?
1 neutron
Neutron
A subatomic particle that has no charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
Proton
A subatomic particle that has a positive charge and that is found in the nucleus of an atom
Electron
A subatomic particle that has a negative charge
Atomic number
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. Specific to each element
Atomic mass
Number of protons and neutrons
Isotope
An atom with the same number of protons and a different number of neutrons from other atoms of the same element.
Electron shells
An energy level representing the distance of an electron from the nucleus of an atom.
Energy
The ability to do work or cause change
Radioactive isotope
An isotope whose nucleus decays spontaneously, giving off particles and energy.
What is directly involved in chemical reactions between atoms
Electrons
Which shell is the highest energy level- 1st or 3rd
3rd energy level
Which shell is the lowest energy level- 1st or 3rd
1st energy level
What is potential energy?
The energy that matter posses because of its location/structure
Which has more potential energy- water or glucose
Glucose due to more bonds being present
Valence electrons
Electrons on the outermost energy level of an atom
How many val e- does Na have
1 val e-
Molecule
two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds
Is water a molecule or a compound?
both
Is carbon dioxide a molecule or a compound?
compound
Is methane a molecule or a compound?
compound
Is oxygen a molecule or a compound?
molecule
Why does oxygen bond to 2 hydrogen atoms
They satisfy the val e- of an oxygen atom
What type of bond is seen in O2
Double, non-polar, covalent bond
What is electronegativity?
a measure of the tendency of an atom to attract a bonding pair of electrons
Nonpolar covalent bond
a covalent bond in which the electrons are shared equally by the two atoms
Polar covalent bond
A covalent bond in which electrons are not shared equally. The shared electron is pulled closer to the more electronegative atom, making it more negative and the other atom more positive
Anion
A negatively charged ion
Cation
A positively charged ion
Van der Waals interactions
Weak attractions between molecules or parts of molecules that result from transient local partial charges.
What is the strongest bond?
ionic bond
What is the weakest bond?
van der Waals interactions
Which is stronger- covalent or hydrogen bonds
covalent bonds
Why is molecular shape important?
it determines how biological molecules recognize and respond to one another with specificity
dynamic equilibrium
a state of balance between continuing processes
What bonds are present in water
Polar covalent bonds
Are covalent bonds usually non-polar or polar
Non-polar
What happens to water molecules when they are heated
They separate from each other
What is high specific heat
The ability to absorb and give off heat without changing temperature
What is high heat of vaporization
The ability to absorb heat upon evaporation - it is used as a cooling mechanism (sweating)
Define cohesion
Attraction between molecules of the same substance
Define adhesion
An attraction between molecules of different substances
What is it called when water dissolves something
Dissolution
What does water do to prevent ions from re-associating
water surrounds the ions
Hydrophobic
Water fearing
Hydrophilic
water loving
What is the polarity of the interior and exterior of a protein
Interior- Non-polar
Exterior- Polar
Define calorie
the amount of energy/heat needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water 1 degree Celsius
Does water have a high or low specific heat?
high specific heat
Why does water have a high specific heat?
hydrogen bonds
Evaporization
Liquid to gas
What is heat of vaporization?
the heat a liquid must absorb for 1 g to be converted to gas
Why does ice float on water?
Ice is less dense than water
why is 4 degrees celsius a critical temperature with water?
Water behaves like other liquids, expands when warmed, contracts when cooled
Solvent
A liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances
Solution
A homogeneous mixture of two or more substances
Solute
A substance that is dissolved in a solution.
aqueous solution
a solution in which water is the solvent
Define molarity
the number of moles of solute per liter of solution
What 2 ions form when water dissociates?
hydronium (H+) and hydroxide (OH-)
What is a hydronium ion?
H3O+ or H+
What is the concentration of H+ and OH- in pure water at 25 degrees celsius
10^-7 M
What is pH
a measure of the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution
What is an acid
An acid is a source of hydrogen ions, H⁺
What is a base
a substance that reduces the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution by releasing OH- ions
How many times more acidic is a pH of 3 compared to a pH of 5
10^2=100
How many times more basic is a pH of 12 compared to a pH of 8
10^4=10,000
What is a buffer
a substance that minimizes changes in pH
How do buffers moderate pH change?
By accepting hydrogen ions from the solution when they are in excess and donating them to the solution when they have been depleted.
What type of bond is the water molecule?
polar covalent bond
What part of a water molecule is negative?
oxygen atom
Bonds between carbon and hydrogen are...
nonpolar due to carbon having less electronegativity
Bonds between nitrogen and hydrogen are...
polar due to nitrogen having more electronegativity
Ionic bonds are formed when...
electrons are completely transferred from one atom to another
What is dehydration synthesis?
The process that allows cells to remove a hydrogen from one molecule and a hydroxyl group from another (forming water) and bond the remaining subunits together
What is hydrolysis?
Hydrolysis is the separation of two macromolecules by adding water.
examples of dehydration synthesis
2 amino acids -> protein and H2O
3 monosaccharides-> polysaccharide and 2 H2O
3 fatty acids and glycerol -> lipid and 3 H2O
examples of hydrolysis
adding water to break...
- polysaccharide into a monosaccharide
- proteins into amino acids
- triglycerides into fatty acid chains
Types of carbohydrates
monosaccharides, disaccharides, polysaccharides
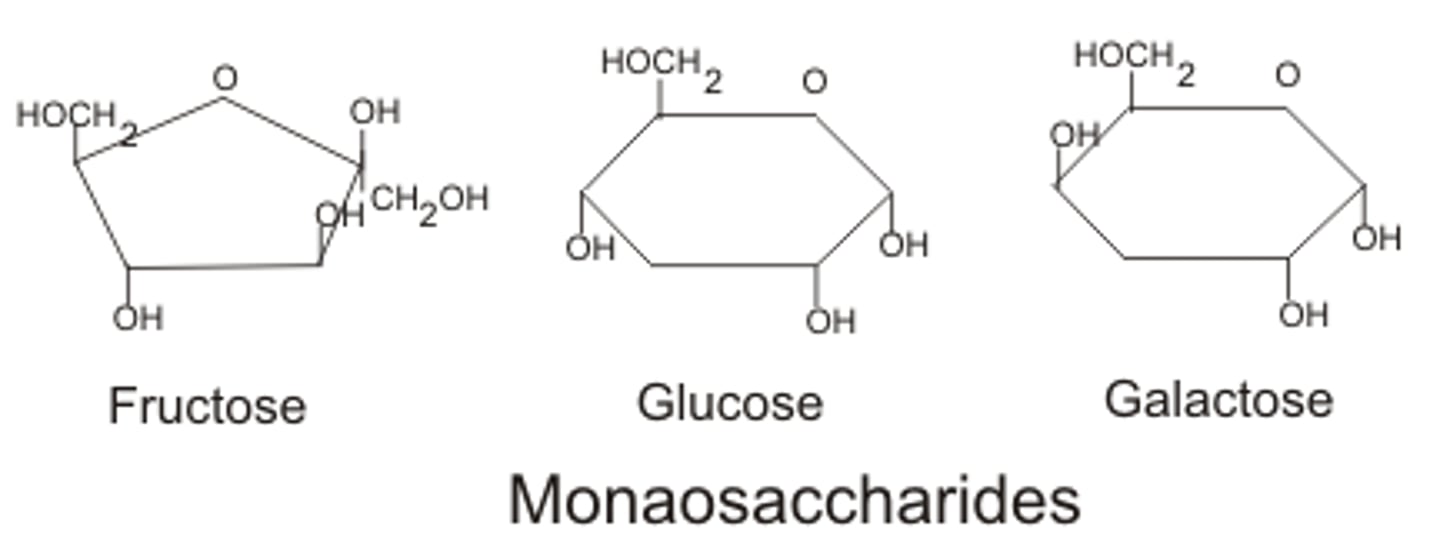
Examples of monosaccharides
glucose, fructose, galactose