Visual System
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
started 5/8 (ended on slide 22)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
the optic cup develops from ___, while the lens develops from ___
diencephalon outgrowth, invaginated epithelium
the opening by which light enters the eye
pupil
the ___ can vary the size of the pupil and gives the eye its color
iris
the transparent external surface that is continuous with the sclera
cornea
the membrane that folds back from the inside of the eyelids and attaches to the sclera
conjunctiva
the ___ serve to move the eyeball
extraocular muscles
contains axons that carry visual information to the brain
optic nerve
what are the three tunics of the eye?
fibrous - cornea and sclera
vascular - iris, lens, ciliary body, choroid
neural - retina
how do the eyes adduct?
with the medial rectus muscle, innervated by CN III oculomotor
how do the eyes abduct?
by the lateral rectus muscle, innervated by CN VI abducens
what muscles are innervated by CNs III, IV, and VI?
CN III oculomotor → medial rectus, superior rectus, inferior rectus, inferior oblique
CN IV trochlear → superior oblique (intorsion)
CN VI abducens → lateral rectus (abduction)
radial fibers are innervated by ___ neurons to dilate the pupil
sympathetic
circular (sphincter) fibers are innervated by ___ neurons to constrict the pupil
parasympathetic
Which pupillary muscles are the edinger-westphal nucleus involved with?
circular (sphincter) fibers
the long ciliary nerve is associated with ___
the short ciliary nerve is associated with ___
long ciliary - radial fibers to dilate
short ciliary - sphincter fibers to constrict
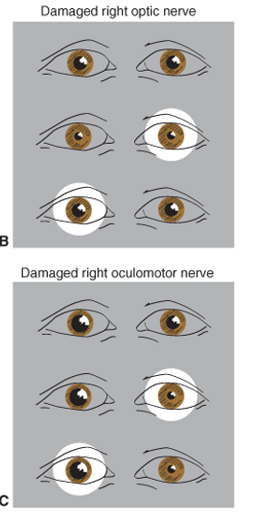
how can the difference between a damaged optic nerve and a damaged oculomotor nerve be seen with pupil reflexes?
with a damaged optic nerve: the eye constricts when light is shone in the other eye, but not when the light is shone in the affected eye.
with a damaged oculomotor nerve: the eye does not constrict
what are the three main layers of the retina?
from back of retina forward: photoreceptor layer, bipolar cell layer, ganglion cell layer
___ cells fire action potentials that are relayed to the brain via the optic nerves
ganglion
___ cells transmit signals from the photoreceptor cells to the ganglion cells
bipolar
what do horizontal and amacrine cells do?
horizontal cells modify responses of bipolar cells
amacrine cells modify responses of ganglion cells
all cell types in the retina except ___ generate only graded potentials
ganglion cells
what are the photopigments present in rods and cones
rods - rhodopsin
cones - iodopsin
there are many more (rods/cones) than (rods/cones)
more rods than cones
rods are present in the ___, while cones are present in the ___
rods - peripheral retina
cones - fovea
what is the macula?
a region of high visual acuity, containing the fovea at the center. shows on fundus as the area around the dark retina
what is the blind spot of the eye?
the optic disk
the three stages of vision processing take place in:
LGN of the thalamus
Visual cortex (V1) - striate
Secondary visual cortex - extrastriate
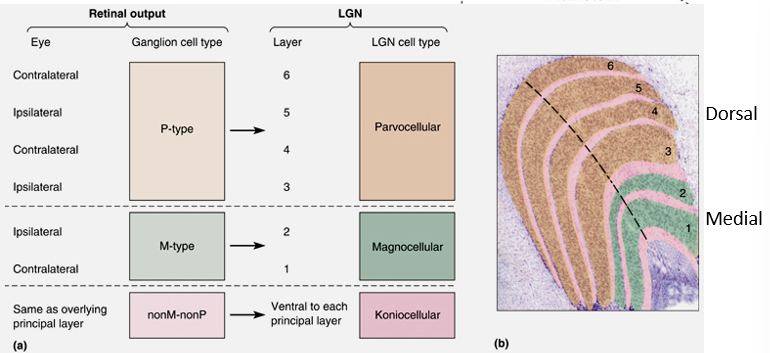
What are the 3 cell types of the LGN? describe each.
parvocellular - small cells, small receptive fields. make up the four dorsal layers
magnocellular - large cells, large receptive fields. make up the two ventral layers
koniocellular - layers with very small cells, in between the main layers
What LGN layers are associated with each LGN cell type?
1-2 (the two ventral layers): magnocellular
3-6 (the four dorsal layers): parvocellular
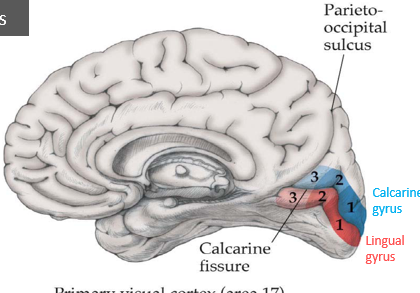
macular vision is most (anterior/posterior)
posterior
Inferior visual field goes to the ___ gyrus via the ___ radiation, while the superior visual field goes to the ___ gyrus via the ___ radiation.
inferior: calcarine by the parietal optic radiation
superior, lingual by the temporal optic radiation (Myer’s loop)
define each: unilateral field loss, bitemporal hemianopia, homonymous hemianopia
unilateral field loss - lesion to the optic nerve, no input from one eye
bitemporal field loss - lesion near the chiasm, nasal retina info (lateral visual field) does not cross, person only sees inner field
homonymous hemianopia - a visual field is lost, must be after chiasm.
superior quadrantanopia involves ___
inferior quadrantanopia involves ___
superior: temporal optic radiation (myer’s loop)
inferior: parietal optic radiation
___ perceives objects so it is needed to form all visual images
V1, primary visual cortex
___, ___, and the ___ lobe all perceive complex form
V2, V4, inferior temporal lobe
___ is specialized for motion perception
V5
___ fires before ___, meaning your brain asks if an object is moving before it asks what it is
V5 before V4
the ___ pathway is the “what” pathway
ventral
the ___ pathway is the “where” pathway
dorsal
Describe a normal fundus exam, and what abnormalities to look out for
normal fundus - can see vasculature, a defined light optic disk, a dark macula.
looking for cloudiness, blurriness, bulging of the optic disk, etc
if vision issue is monocular, the lesion must be ___ to the optic chiasm
anterior
if the visual issue is one field, the lesion must be ___ to the chiasm
posterior
If the visual issue affects a quadrant, the lesion must involve either ___ or ___
the temporal lobe or the parietal lobe
what is prosopagnosia? where is the lesion?
face blindness. the lesion is to the fusiform gyrus