Disorders of Gallbladder and Extra-Hepatic Ducts
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Cholelithiasis =
gallstones
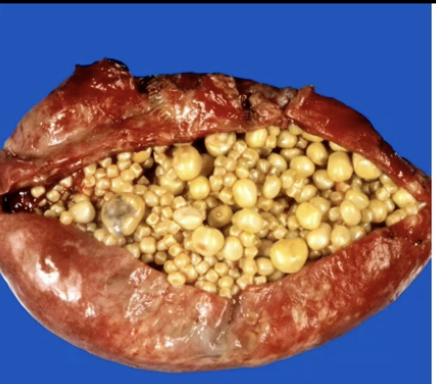
Cholesterol Cholelithiasis
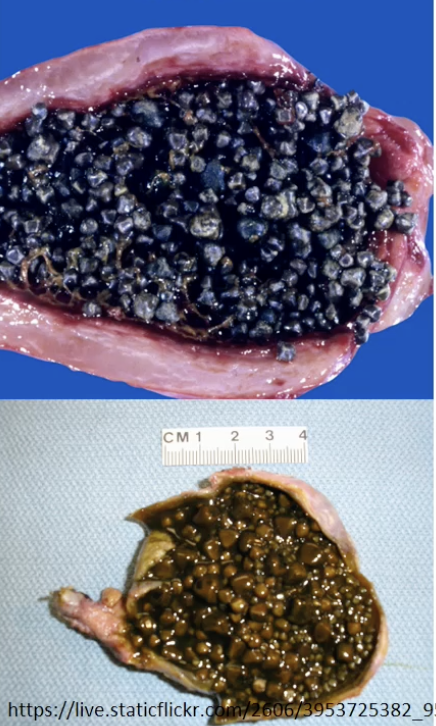
Biliruben-Calcium Cholelithiasis - Brown = infection, e coli, black = Hemolytic Disorders and Malaria
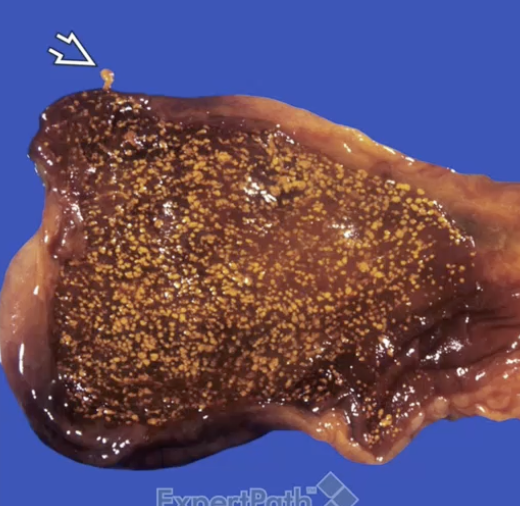
Cholesterolosis
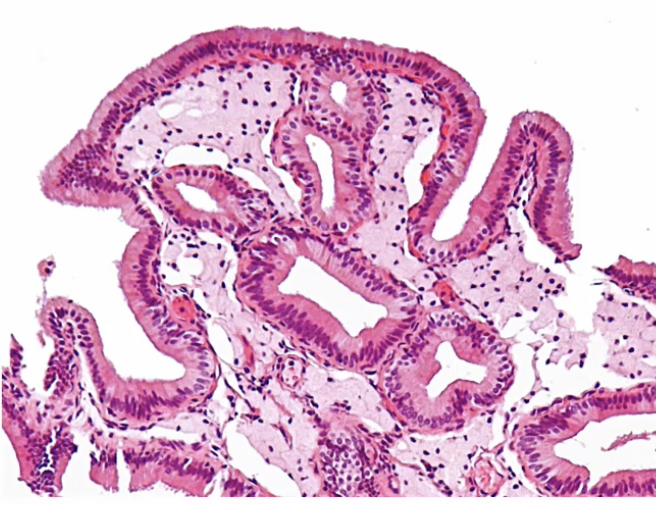
Cholesterolosis
Positive Murphys Sign
is a clinical test for gallbladder inflammation, where pain occurs upon palpation of the gallbladder during inhalation.
Acalculus Acute Cholecystitis
is a form of cholecystitis that occurs without the presence of gallstones, often related to malperfusion
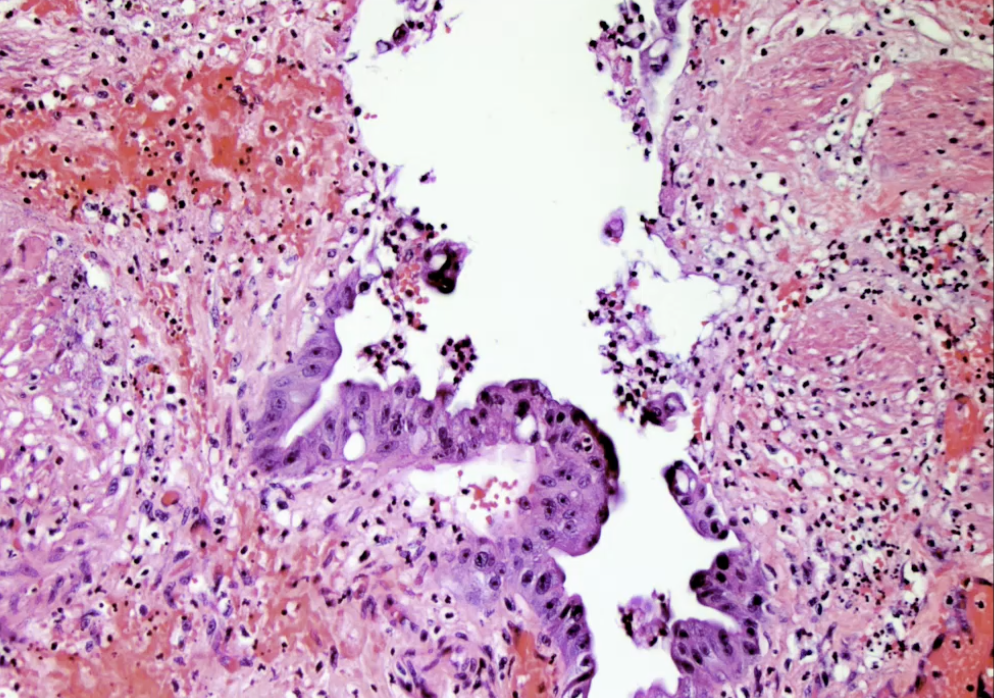
Acute Cholecystitis
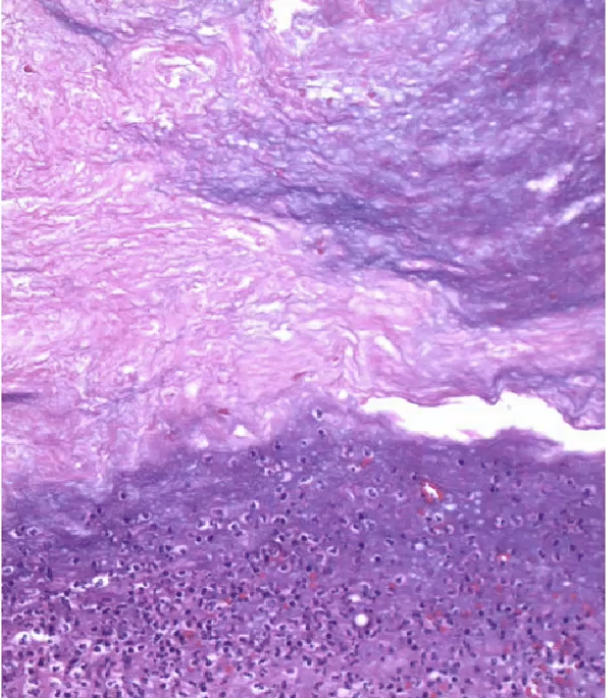
Gangrenous, necrotic cholecystitis
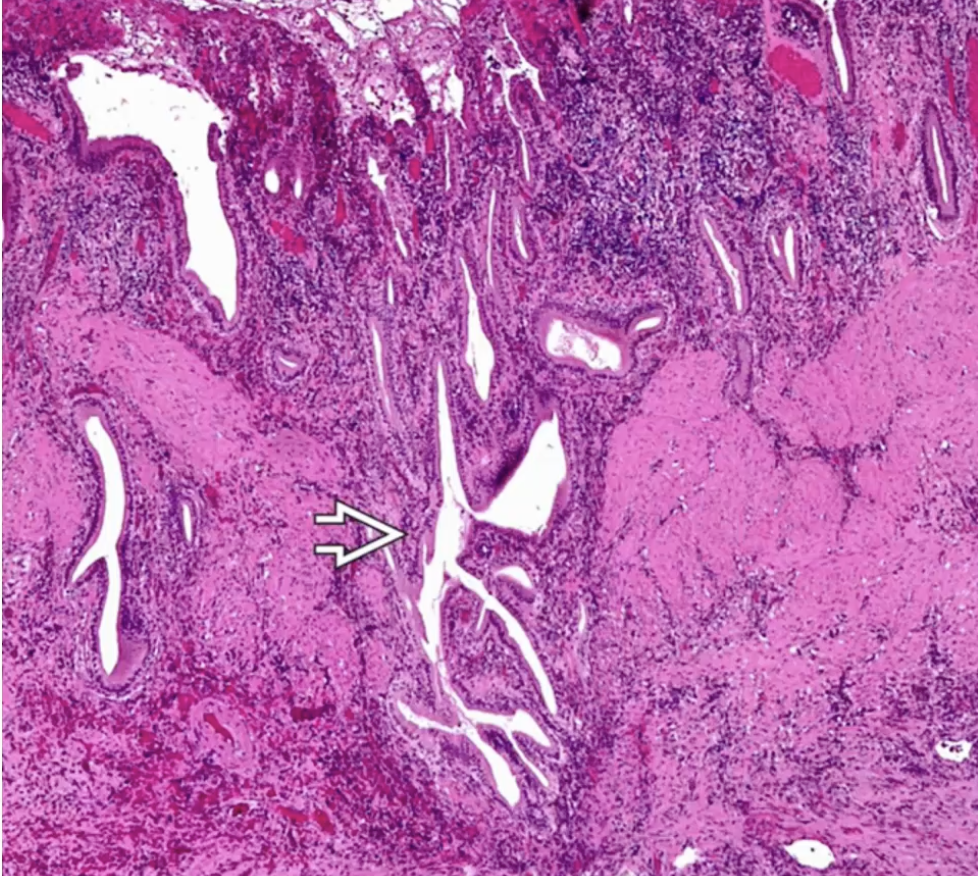
Chronic cholecystitis
Rokitansky-Aschoff Sinuses
small pouches that form in the gallbladder wall, often associated with chronic cholecystitis. They can contribute to inflammation and dysmotility of the gallbladder.
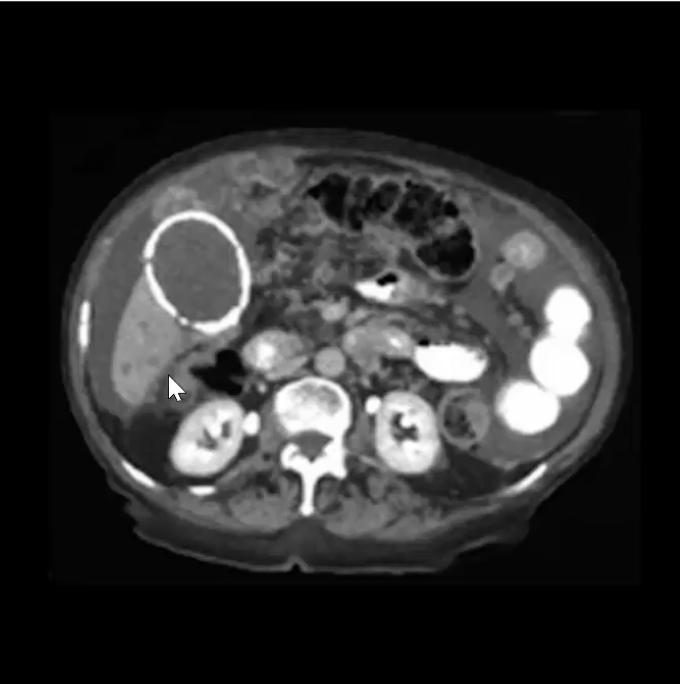
Porcelain Gallbladder - calcification of the gallbladder wall, seen in chronic cholecystitis
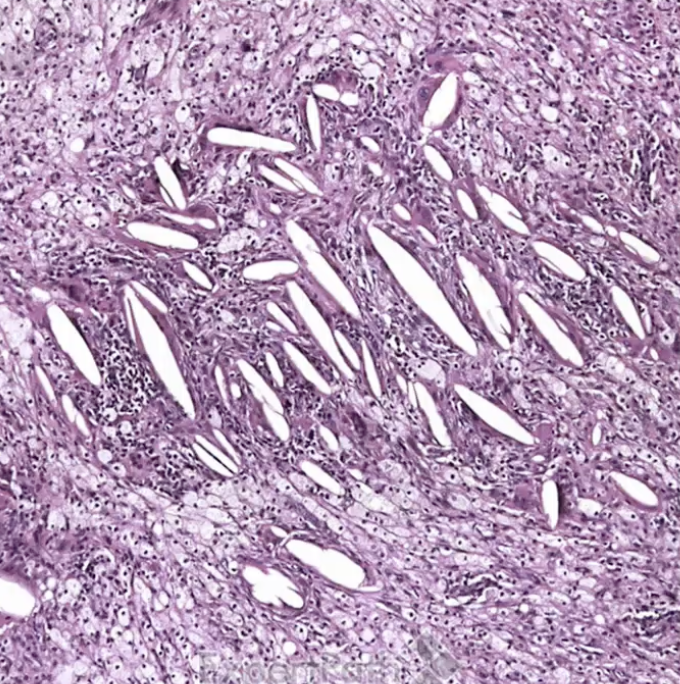
Xanthogranulomatous Cholecystitis
Choledocholithiasis
the presence of gallstones in the common bile duct, which can lead to obstruction and cause jaundice or pancreatitis.
Biliary Atresia
a congenital condition with absence or underdevelopment of the bile ducts —> bile accumulation, liver damage, and jaundice in infants.
For steatorrhea to occur, cholelithiasis has to occur at the
pancreatic duct
Type III Biliary Atresia =
Complete absence of a biliary tree
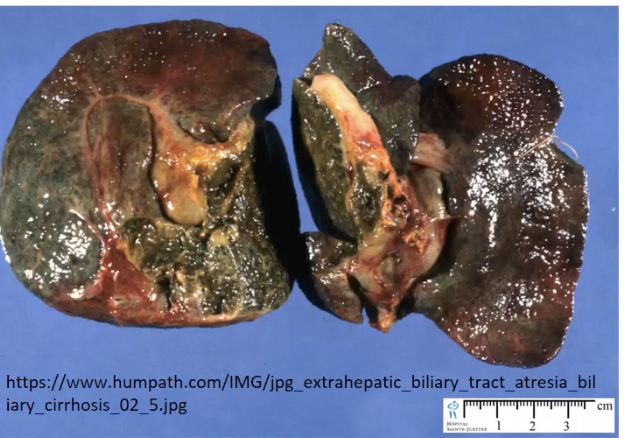
Green Liver = Biliary Atresia
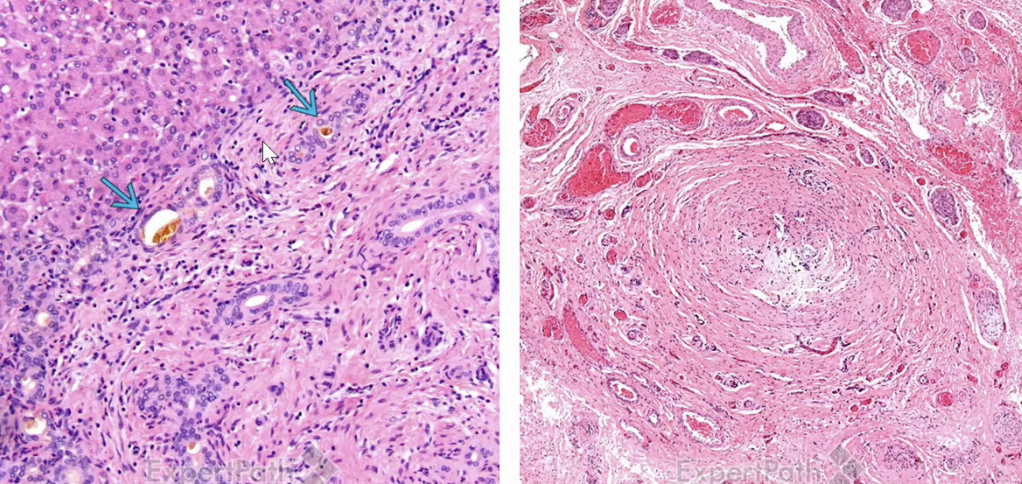
Biliary Atresia
Choledochal Cyst
a congenital dilatation of the bile duct that can lead to complications such as cholangitis and pancreatitis - even when removed predisposes to cancer
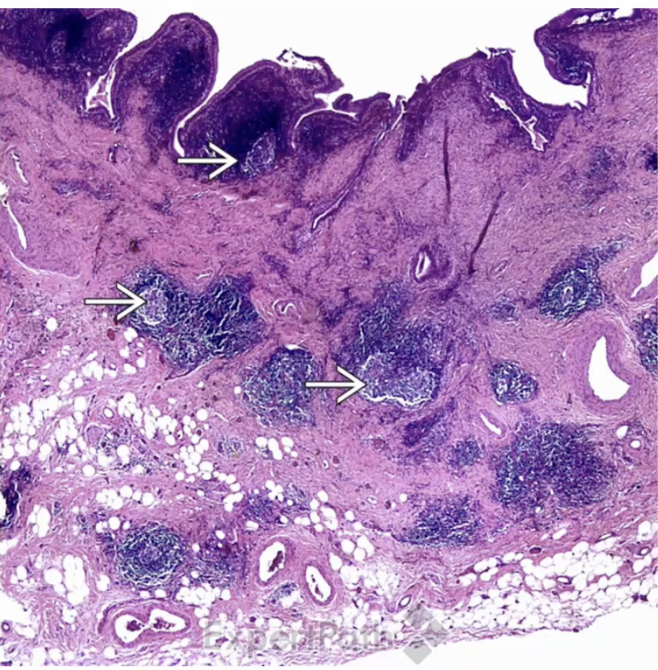
Follicular Cholecystitis
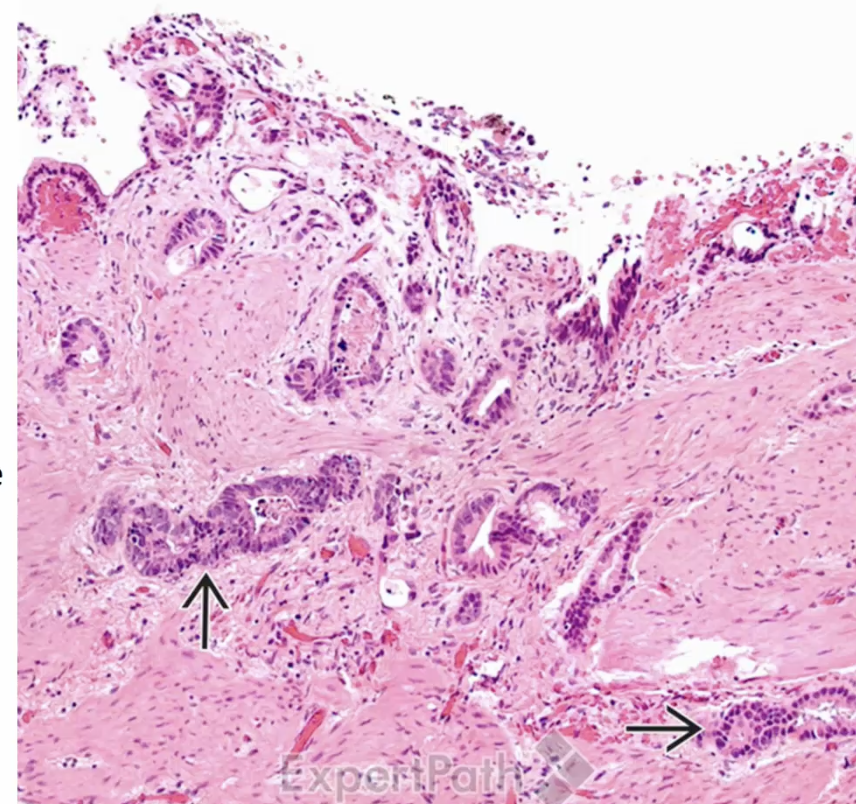
Adenocarcinoma of the Gallbladder
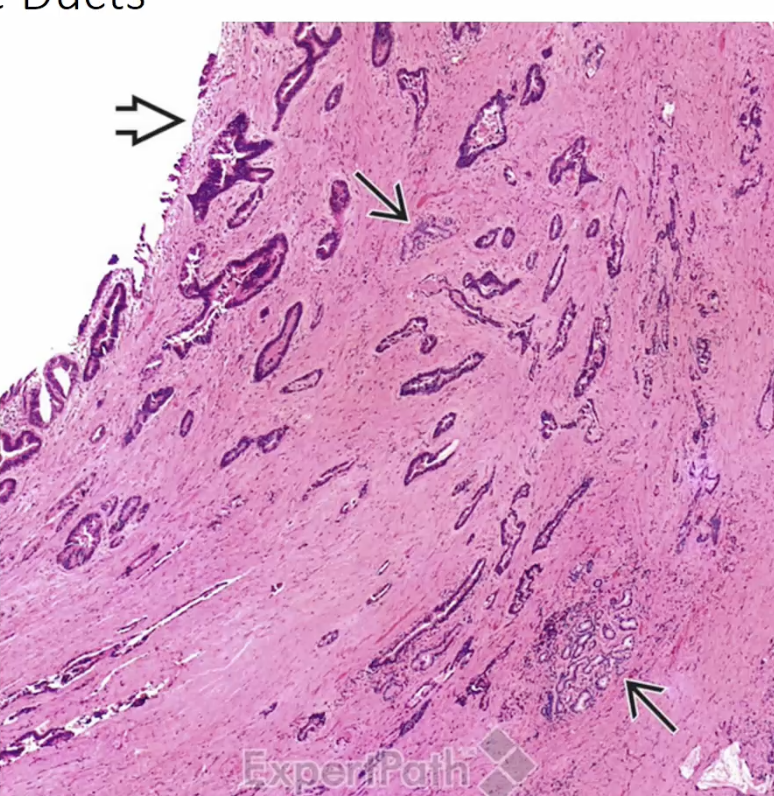
Extrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma
Klatskin Tumor
A type of extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma that occurs at the junction of the left and right hepatic ducts. It often leads to biliary obstruction and jaundice.