skills lab APGAR too
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Bubblesh
Breasts
uterus
bladder
bowels
lochia
episiotomy/perineum
swollen homans (homans sign)
head emotional status
Breasts
What you do: Inspect and palpate. Ask about pain with feeding. Check nipples and skin.
Expected: Breasts soft first 2 days, then filling/firm as milk comes in. Nipples intact, not cracked. Colostrum or milk may be present.
Abnormal: Engorgement, redness, warmth (mastitis), cracked/bleeding nipples, inverted nipples that make feeding hard.
Uterus
What you do: Palpate fundus with one hand supporting lower segment, the other pressing down just above umbilicus. Note height and firmness.
Expected: Firm, midline, at or slightly below umbilicus immediately after birth; descends ~1 cm per day. Should not be boggy.
Abnormal: “Boggy” (soft) fundus → uterine atony (risk for hemorrhage). Deviated to the side (often due to full bladder). Fundus higher than expected = retained tissue or poor contraction.
Bladder
What you do: Ask about voiding; palpate for distension if needed. Look for output if Foley in place.
Expected: Able to void spontaneously within hours after birth. Bladder should not be palpable after void.
Abnormal: Difficulty voiding (due to swelling/trauma), overdistension, residual urine, frequent small voids. A full bladder can displace uterus → increased bleeding.

bowels

Lochia
What you do: Inspect peripad and bed linen. Ask about flow, clots, odor. Estimate amount (scant, light, moderate, heavy). ask if she has changed her period pad
Expected:
Rubra (dark red, 1–3 days)
Serosa (pink/brown, 4–10 days)
Alba (yellow/white, up to 6 weeks)
Should be no foul odor. Small clots are normal.
Abnormal: Saturating >1 pad/hour, foul odor (infection), large clots, return to bright red bleeding after it had lightened.
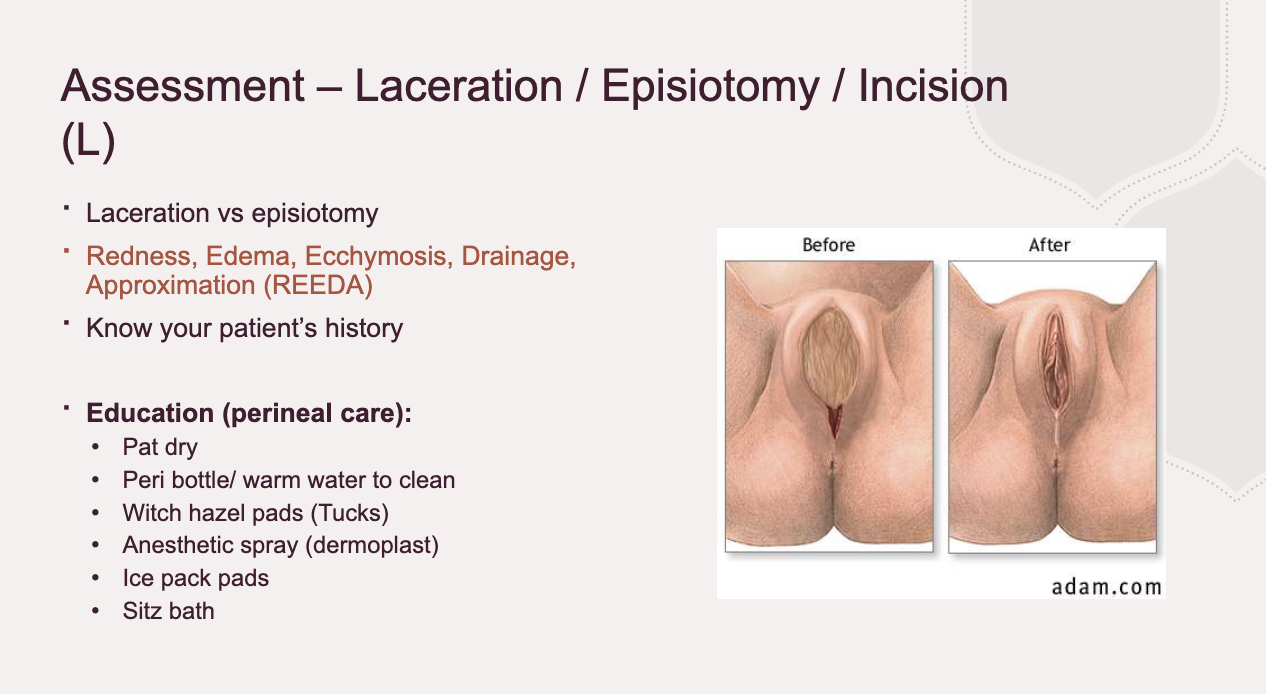
Episiotomy/ perineum (or incision if c-section)
What you do: Inspect perineum/incision using REEDA scale (Redness, Edema, Ecchymosis, Discharge, Approximation). Ask about pain.
Expected: Some swelling and tenderness normal. Incision well-approximated, no discharge. Hemorrhoids may be present but not severe.
Abnormal: Severe pain, hematoma (bulging, blue, very tender), infection (redness, pus, separation), uncontrolled bleeding.
swelling/extremitires (used to be homans sign)
What you do: Inspect and palpate legs for swelling, warmth, redness, tenderness. Check pedal pulses.
Expected: Mild edema common, especially in lower extremities. Pulses palpable, no pain or redness.
Abnormal: Unilateral swelling, warmth, redness, pain → possible DVT. Severe edema may suggest preeclampsia if BP elevated.

Heart.head (emotional status and bonding)
What you do: Observe interaction with baby, ask about feelings, screen for mood.
Expected: “Baby blues” (tearfulness, mood swings) are common but mild and resolve within 1–2 weeks. Positive bonding (eye contact, holding, responding to baby’s needs).
Abnormal: Flat affect, disinterest in baby, persistent sadness, signs of postpartum depression or psychosis (delusions, thoughts of harm). Needs urgent attention.
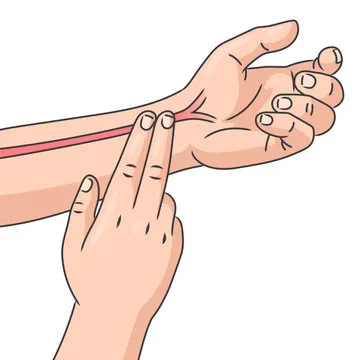
radial pulse
Radial, apical pulse
Pulse scale
1+=weak
2+=normal
3+=bounding
Is it regular or irregular
Radial
On radial side of arm. Count for 30 seconds. Thumb side
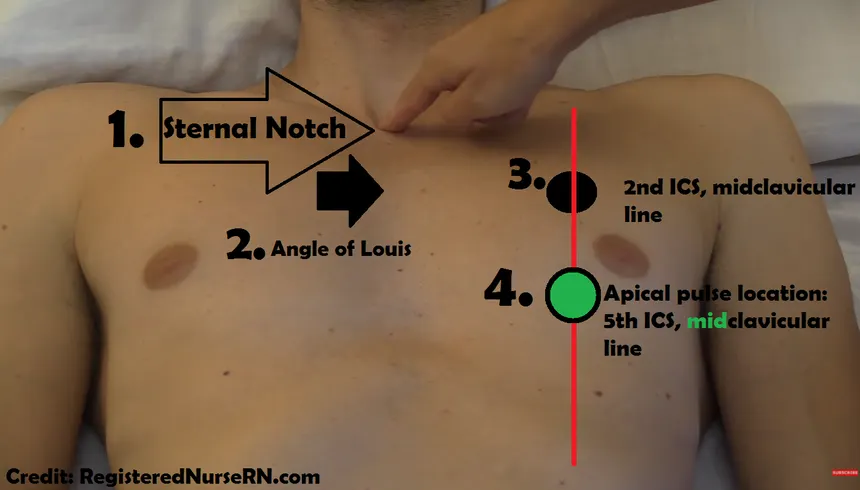
apical pulse
apical
It is the 5th intercostal space mid clavicularly
Find sternal notch (middle of neck)
Go donw till felt boney prominence
Go to second intercostal space midclavicularly
Go down from there until 5th place
if persons breasts are larg you hvae to get them to lift up
you need stethescope
catheter placement
this is a straight catheter meant to be removed after bladder is drained
They are a risk for infections
Perform hand hygiene imeeditaley before adn after insertion
Insert using sterile technique
Wash hands and don clean gloves
Explain procedure
Positioning
Women: Frog leg position
Men: supine legs extended
Use packet of wipes to cleanse periurethal area
Remove gloves and apply hand sanitixzer
Open csr wrap using aseptic technique
Then don sterile gloves
Place underpad beneath patient shiny side down
Position drape over patient (hole should be open to genitalia)
Then saturate three foam swabsticks in povidone iodine
Lubricate catheter
Use non dominant hand to grab genitalia (you should not move this hand and cannot touch anything sterile with it now)
Use swab only once
Women
Wipe downwards towards perineum with one swab stick
Repeat for left and right side then down the center
For male patients
Start at the urethra working outwards circularly
Insert catheter
Encourage to relax pelvic muscles like when urinating
Not not ask to push
take a slow deep breath in and out
Advance catheter on breath out
When catheter tip has entered bladder urine will be visible
Document according to hospital
remove on breath out
how do you know when baldder is empty
stream flows, slows, drips, then stops
if stopped sooner than expected gently advance catheter may be pressed against bladder wall
APGAR and scoring
appearance
pulse
grimace
activity
respiration
0–3 → Severe distress, immediate resuscitation needed
4–6 → Moderate difficulty, may need help
7–10 → Generally healthy, normal adaptation
appearance
Body pink, extremities may be slightly blue initially
0=blue/pale
1= body pink, extremities blue
2= completel
Pulse
Palpate brachial/femoral pulse or auscultate0=absent
1=<100 bpm
2= > or equal to 100 bpm
Grimace
reflec irratibiliyt (response to stimulants)
Stimulate via mild pinch or suction
0 = no response
1 = grimace/ facial movement
2 = cry or active withdrawal (normal)
Activity
muscle tone
Observe posture and movement
0=limp
1 = some flexion
2 = active motion
respirations
breathing effort
Respiration |
Observe chest rise or listen |
0 = absent
1 = slow/irregular
2 = good, crying