Ch. 3 - Short-term memory
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
Digit span
Maximum number of sequentially presented digits that can reliably be recalled in the correct order. Reflect short-term memory.
Working memory span
Term applied to a range of complex memory span tasks in which simultaneous storage and processing is required. Reflect working memory
Short-term memory (STM)
Refer to performance on a particular type of task, one involving the simple retention of small amounts of information, tested either immediately or after a short delay.
Working memory
A system that not only temporarily stores information but also manipulates it so as to allow people to perform such complex activities as reasoning, learning, and comprehension.
Memory span measures require two things:
Remembering what the items are
Remembering the order in which they were presented
Things that affect memory span
In the case of the digits, we already know the items very well, so the test becomes principally one of memory for order.
If an order of letters in the sequence allowed you to break it up into pronounceable word-like subgroups or chunks.
C T A I I L T C S F R O vs. F R A C T O L I S T I C
Chunking
The process of combining a number of items into a single chunk typically on the basis of long-term memory. Proof that LTM can influence STM. Grouping can also be induced by the rhythm with which a sequence of items is presented.
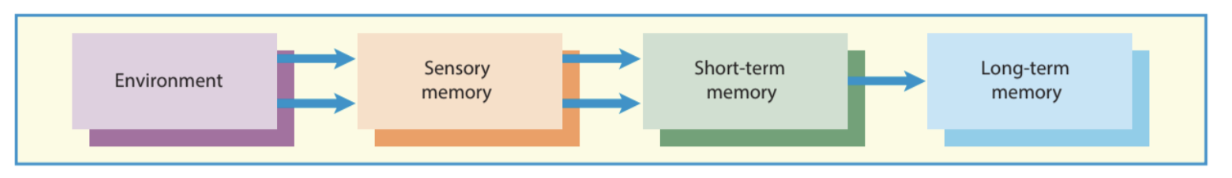
The modal model
Flow of information from the environment
Into a series of parallel sensory memory systems, the iconic and echoic systems
From here it enters a short-term memory store which also serves as a “working memory” capable of both storing and manipulating material
Which is then fed into a more durable long-term store.
Phonological loop
Term applied by Baddeley and Hitch to the component of their model responsible for the temporary storage of speechlike information.
Phonological similarity effect
A tendency for immediate serial recall of verbal material to be reduced, when the items are similar in sound.
Articulatory suppression
A technique for disrupting verbal rehearsal by requiring participants to continuously repeat a spoken item. The subvocal rehearsal system can be blocked if you are required to repeatedly say something unrelated.
Word length effect
A tendency for verbal memory span to decrease when longer words are used.
Irrelevant sound effect
A tendency for verbal STM to be disrupted by concurrent fluctuating sounds, including both speech and music.
Changing State hypothesis
This assumes that retention of serial order can be disrupted by irrelevant auditory stimuli provided that these fluctuate over time
The problem of serial order
The purely verbally specified phonological loop model had two major shortcomings.
No adequate explanation of how serial order is stored.
Given that the classic digit-span task principally involves retaining serial order, this is clearly a major limitation.
Second, the model had no clear specification of the crucial processes involved in retrieval from the phonological store.
Free recall
A method whereby participants are presented with a sequence of items which they are subsequently required to recall in any order they wish.
Recency effect
A tendency for the last few items in a list to be well recalled during free recall.
Primacy effect
A tendency for the first few items in a sequence to be better recalled than most of the following items during free recall.
LTM variables studied include:
Presentation rate: slower is better
Word frequency: familiar words are easier
Imageability of the words: words that are visualizable are better
Age of the participant: young adults remember more than children or the elderly
Physiological state: drugs such as marijuana and alcohol impair performance.
Long-term recency
A tendency for the last few items to be well recalled under conditions of long-term memory.
Two aspects of visual working memory
Spatial memory (where?)
Memory for objects (what?)
Active rehearsal in visual STM
Visual STM appears to benefit from an active attempt to maintain an item in the focus of attention.
What is stored in visual STM?
The visual system processes the world through a range of separate sensory channels, with shape, color, and movement for example all being detected by different neural systems. The fact that we experience an object such as a red square means that the separate features of color and shape that are present in the stimulus, must then have been recombined, allowing the separate channels encoding shape and color to be experienced as a single object, a colored square
Binding
The capacity to reunite the features of an object. The attentional disruption did not differ across conditions, suggesting that the process of binding shape and color is automatic.
The act of binding appears to be relatively automatic, although remembering is clearly not, as overall performance in all conditions suffers from the additional task.
Visuo-spatial STM
We have made a distinction between spatial STM, remembering where, and object memory, remembering what. In practice, these two systems work together but tasks have been developed that particularly emphasize one or other of these two forms of visuo-spatial memory. Visual STM is not of course limited to remembering patterns, but also involves shapes and colors.
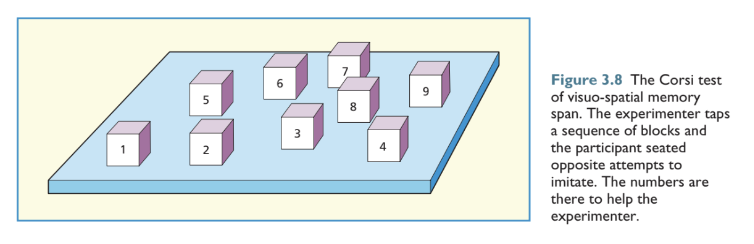
The Corsi test (Corsi block tapping)
Visuo-spatial counterpart to digit span involving an array of blocks that the tester taps in a sequence and the patient attempts to copy.
What limits the capacity of visual STM?
Attentional blindness
Fixed slots versus flexible resources
Deficits in visuo-spatial short-term memory
Impaired performance on either visual or spatial STM
Colors or shapes
Impaired visual memory coupled with a grossly impaired capacity to draw
Visuo-spatial STM
Retention of visual and/or spatial information over brief periods of time.