holland ecology exam 2
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
when conditions are favorable for a population at low density, such as when a species colonizes a new environment, population growth is typically
exponential
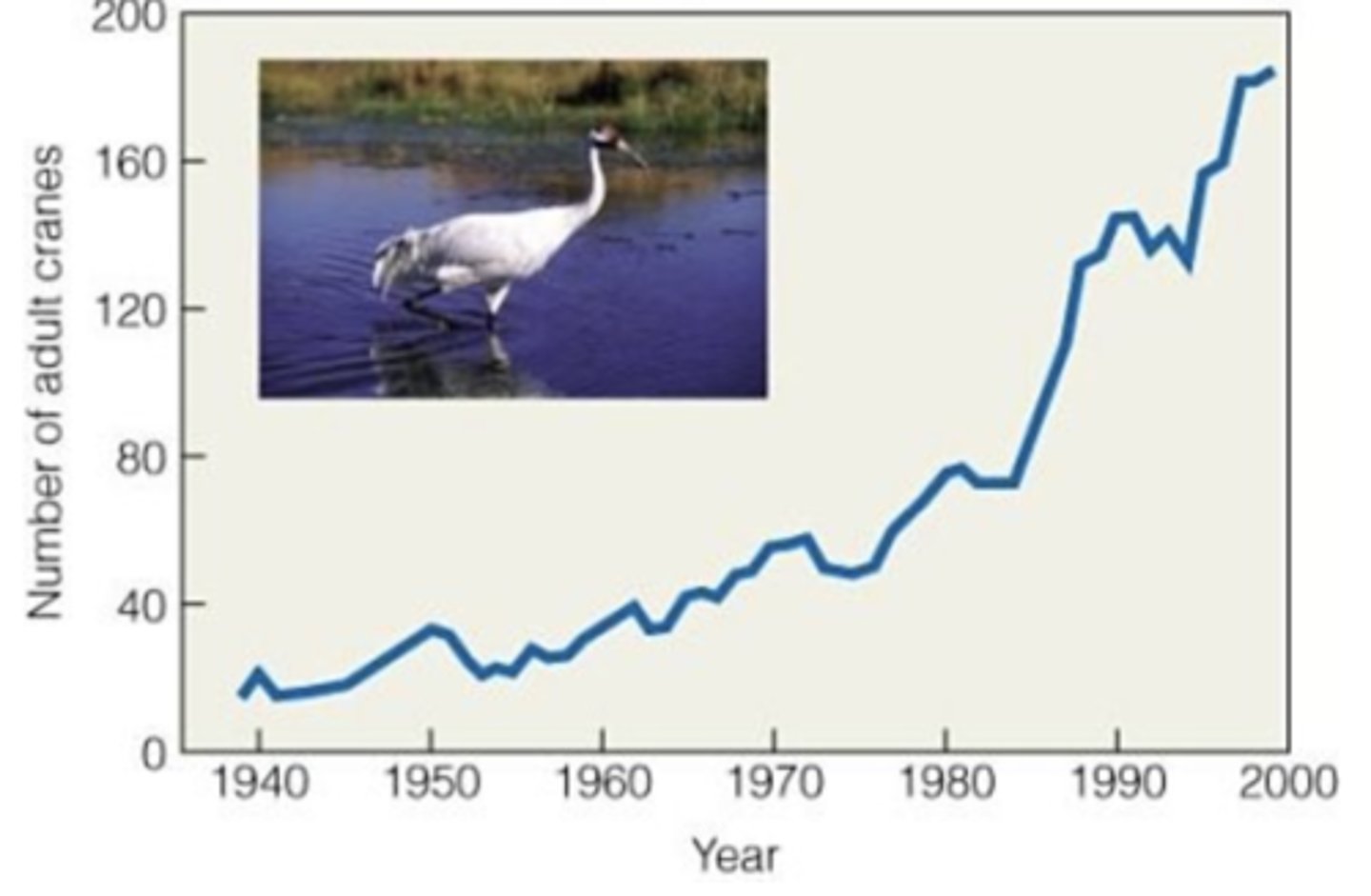
the pattern shown in figure 9.6 best resembles
exponential growth
Which model of population growth would you employ if reproduction occurs in discrete time periods rather than being continuous?
geometric
a systematic compilation of mortality and and survival data for a population is called a
life table
if survival rates do not vary with age as in many species of perennial plants, reptiles, adult birds, and rodents, survivorship curves are typically
type 2
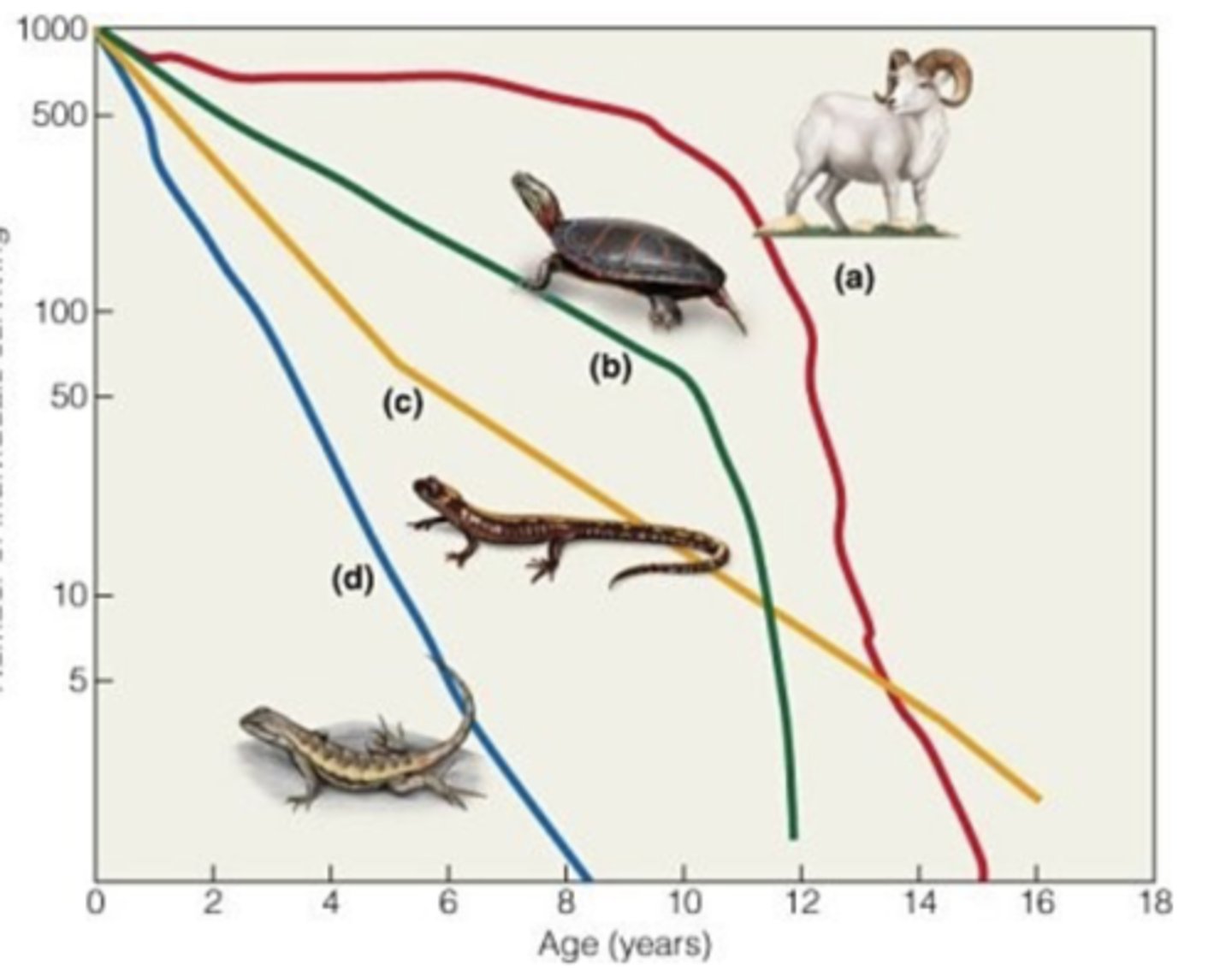
the Dall sheep (a) curve represents which type of survivorship curve?
type 1
the number of births per female of age x is referred to as the:
age-specific birthrate
the average number of female offspring born to a female over her lifetime is referred to as the
gross reproductive rate
why is the b0 = 0 at time period x0 for some species?
some species do not reproduce during the final time period
a population that is growing has a net reproductive rate (R0) that is
>1
a population reaches a stable-age distribution when the
proportion of individuals in each age group remains the same
the leading cause of current species extinction is
habitat destruction
which populations are at greatest risk for extinction?
very small ones
a trade-off for having many offspring would be
that they would likely be small in size
an advantage to sexual reproduction is
increased genetic variability
human reproductive systems are best described as
dioecious
at birth, California sheephead fish begin their life as females and then become males. this is referred to as
sequential hermaphroditism
the data in the figure above support which of the following trade-offs
the number of offspring is correlated with growth
in long-lived species, the primary advantage of delaying reproduction (late maturity) is
larger body size during the first reproduction event
animals with extremely high fecundity tend to have
lower survival rates
altricial young are relatively
helpless at birth but require relatively little time for incubation and gestation
an insect larva that is immediately ready to move away fromits hatching site and feed after birth is termed
precocial
pacific salmon migrate upstream and after breeding, soon die. they are termed
semelparous
true or false? weedy plants are considered to be k-strategists
false
the carrying capacity refers to the
maximum sustainable population size for the prevailing environment
in logistic growth, the point at which population growth ceases is referred to as the
carrying capacity
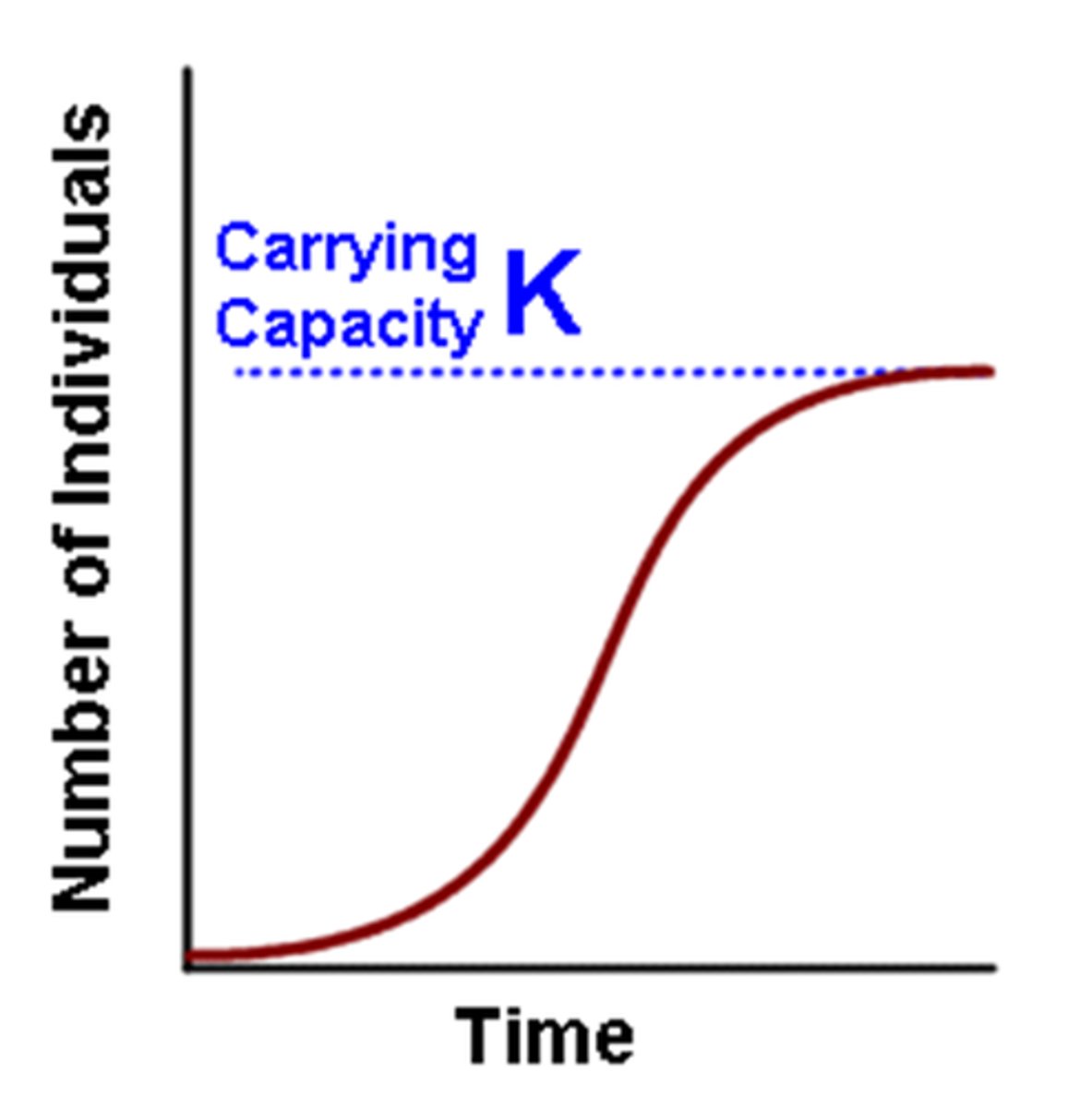
the figure above depicts which type of population growth
logistic
which of the following is density-independent factor?
extreme weather event
as the density of a population increases the
individual growth rate decreases
you see two squirrels fighting over a food resource. this most likely represents
contest competition
what might be an outcome of planting soybean plants at very high densities in a field?
reduced seed production per plant
As population density increases in harp seals (Phoca groenlandica), females
begin reproduction at a larger age
which statement about stress is incorrect?
- stress increases as population density increases
- stress can trigger the release of specific chemical signals or pheromones
- stress can stimulate growth and increase the rate of reproduction
- stress results in increased vulnerability to disease
stress can stimulate growth and increase the rate of reproduction
the induvial that disperse in response to high population density are
usually, the younger members of the population
among mammals the home range is usually larger for
carnivorous species than for herbivorous species of the same body size
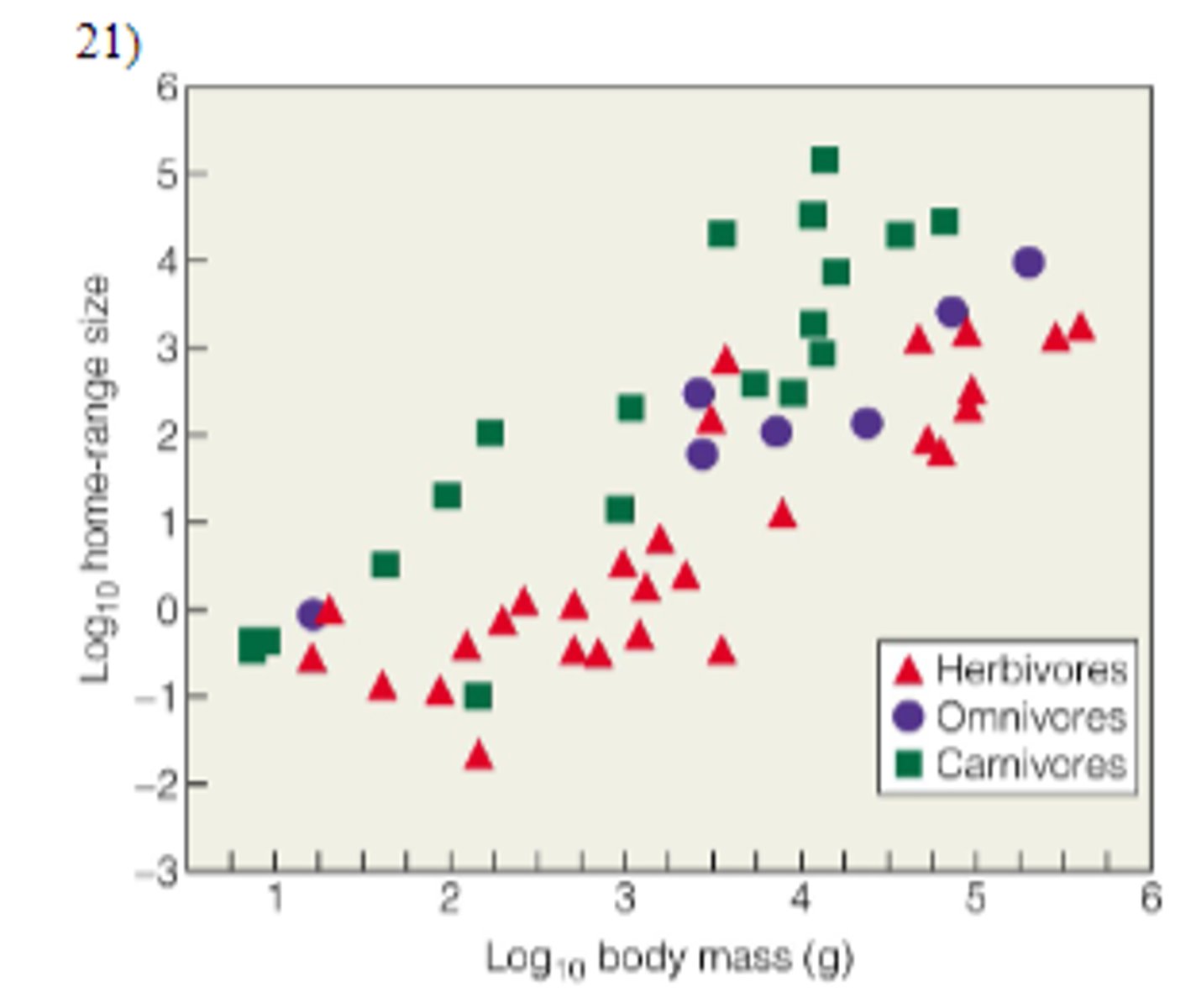
this figure illustrates that territory size is positively correlated with
body size
when individuals in a small population have difficulty finding a mate, this is referred to as
the allee effect
when the trunk or limb of a tree provides the substrate on which an epiphytic orchid grows, the arrangement benefits the orchid, which gets nutrients from the air and moisture from aerial roots while the tree is unaffected. the relationship is referred to as
commensalism
when the relationship between two interacting species is detrimental to the populations of both species the interaction is referred to as
competition
which of the following interactions would be considered predation?
+-
a remora feeds on the scraps that escape from a shark's mouth while feeding. it has no clear positive or negative impact on the shark. this is an example of
commensalism
what is the difference between a parasite and a parasitoid?
a parasitoid typically kills its host
which of the following has the strongest impacts on species 1 population size? N2 =
750
the length of a butterfly tongue perfectly matches the nectar tube of a flower it pollinates. this is an example of
coevolution
what might happen over time if two bird species competed for the same seed resource and one preferred larger seed while the other species preferred smaller ones
break sizes might shift over time
On a dare, a student challenges another student to lick a California newt (Taricha torosa). From which population of newts should the student grab an individual to reduce his or her risk of a toxic dose?
from a population with no garter snakes
the neurotoxin that taricha spp. possess to ward off predators is
tetridotoxin
mycorrhizal fungi have a mutually beneficial relationship with plants in environments with soils that are
low in nutrients
the red line in the figure above (the furthest to the right) represents
highly resistant garter snake population
A species of cattail inhabits both deep and shallow water in the absence of a competitor but only shallow water in the presence of it. This is an example of
a realized niche
the process where one species gives rise to several others that exploit different features of the environment and occupy different niches is known as
adaptive radiation
what does the following formula represent? dN1/dt = r1N1(1-(N1+N2)/K1)
population growth of species 1 in presence of species 2 limited by a shared carrying capacity
chemicals released by plants to inhibit germination and establishment of other species is known as
allelopathy
in the following formula, what does B (beta) represent in dN2/dt = r2N2(1-(N2+BN1)/K2)
competition coefficient
according to the figure above, when these 2 species are grown together, what will the outcome be?
P. aurelia wins
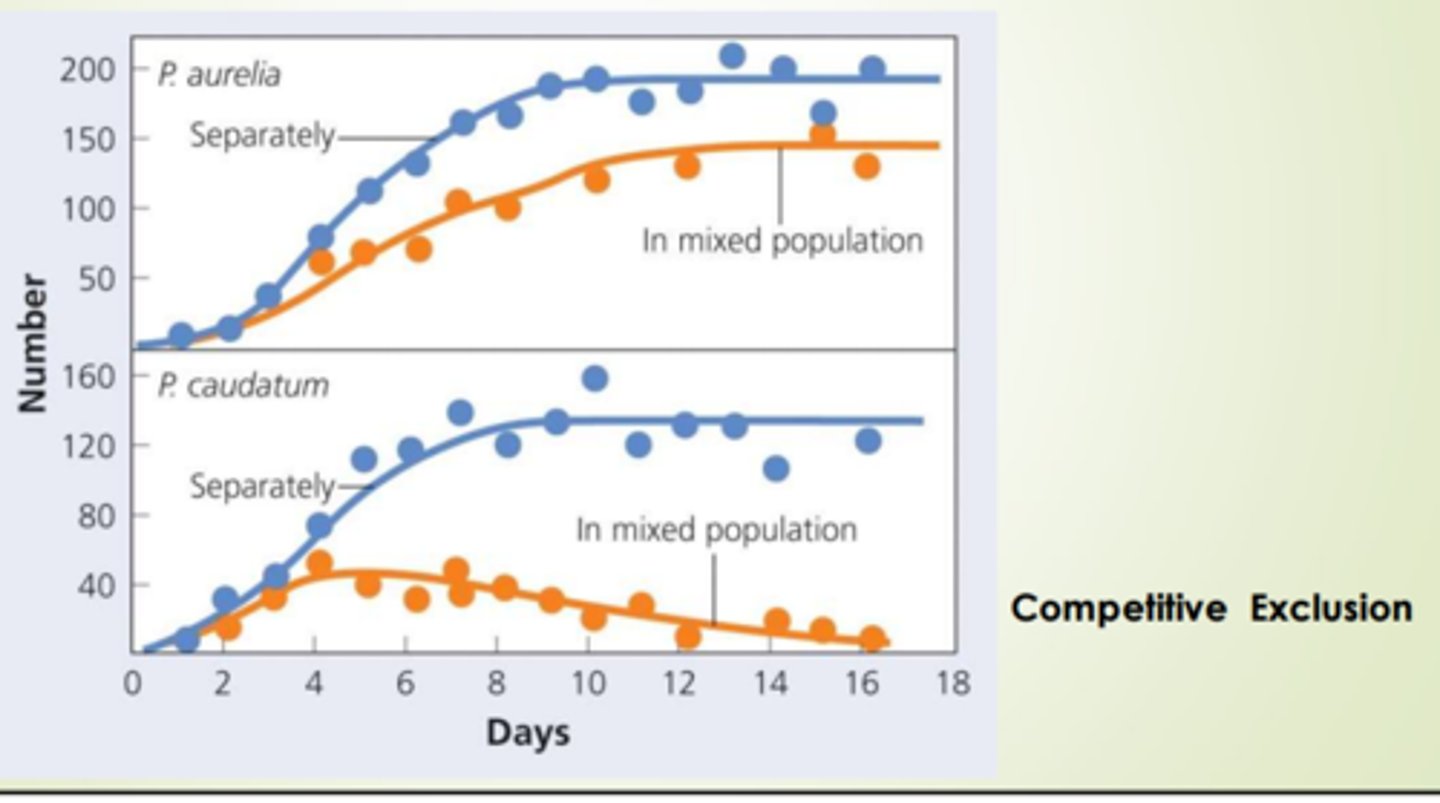
competitive exclusion principle assumes that the
environmental conditions remain constant
How can one grass species be dominant one year, while another is dominant a few years later and then the first becomes dominant again?
changes in precipitation across years
Typically species compete for
multiple resources simultaneously.
The different chipmunk species correspond to the different tree species along an elevational gradient. This is likely because
several resource factors for both groups change with elevation
The K in the term K-strategist refers to
carrying capacity
The net outcome of predator-prey interactions in the basic Lotka-Volterra models is that
predator and prey populations oscillate with each predictably increasing and decreasing in response to the other
in a simple experiment involving only predator and prey with no refuge,
predators will typically drive their prey to extinction
Huffaker's experiment involving 2 species of mites and oranges show that
with sufficient complexity, predator and prey populations will oscilate
in the lotka-volterra model of predator- prey interactions, population growth is regulated through
reproduction for the predator and mortality for the prey
when predators come together in areas of high prey density, it is referred to as
an aggregative response
the figure above shows that
lynx populations numerically respond to hare populations
Coevolution between predator and prey suggests
as predators become smarter at catching prey, prey will become smarter at escaping predation.
If you are stranded on a desert island, which prey should you avoid consuming?
brightly colored brey
which of the following is an example of cryptic coloration?
a motled brown bird that nests on the ground
which of the following has caused massive declines in US commercial fish populations?
huge factory trawlers and high tech detection methods such as use of planes and drones