ensuring Quality health products for pt
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
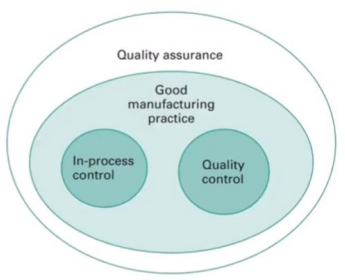
Inter-relationship b/w QA, QC, GMP
A company that manufactures pharmaceuticals should have a Quality Assurance department which oversees all aspects of quality issues through documentation of the processes in the form of standard operation procedures. Is sufficiently staffed with competent personnel and be independent of the other departments in the company.
Whereas the Quality Control department ensures that the in-process and the products are closely monitored and analysed through sampling, testing and checking for compliance to specifications.
Therefore, a manufacturing company must adhere to Good Manufacturing Practice through QA compliance and QC testing.
Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) consists of a set of regulations that must be adhered to in all manufacturing processes. Compliance with GMP is achieved through QA oversight and QC testing to ensure product quality and safety.
Who overlooks the quality and safety of medicines?
The International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements For Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) is the organization that brings together the regulatory authorities and pharmaceutical industry to discuss scientific and technical aspects of drug registration.
ICH provides four categories of guidelines
Quality
Efficacy
Safety
Multidisciplinary — aspects that do not fit into the above categories
Essential elements of GMP for manufacturing of quality products
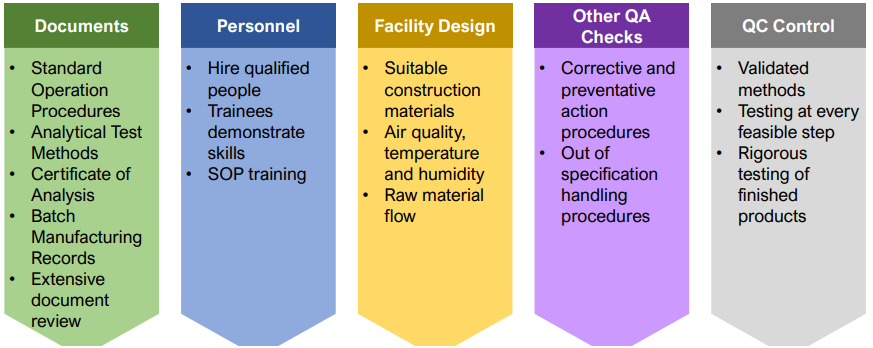
How to ensure quality of pharmaceuticals
Identity
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
Infrared (IR) Spectroscopy
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
Ultraviolet (UV) Spectroscopy
Mass Spectrometry (MS)
Quantity
Ultraviolet-Visible (UV-Vis) Spectroscopy
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
Purity
Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)
Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS)
sources of impurities

Limit tests - comparison method
Limit tests are quantitative or semiquantitative tests designed to identify and control small quantities of impurity which may be present in the drug substance.
Comparison Methods – A standard containing a definite amount of impurity is set up at the same time and same conditions as the test experiment.
The extent of reaction in the experiment is determined by comparison of the test solution and the standard solution.
The official limits for chlorides, sulphates, iron, and heavy metals are based on this principles
e.g. if sample is less turbid than standard, has lesser impurities
Limit Tests – Quantitative Determinations

Identification tests in USP - Acetaminophen USP
Infrared Absorption
Ultraviolet Absorption
Solution: 5 ug/mL
Medium: 0.1N hydrochloric acid in methanol (1:100)
It responds to the Thin Layer Chromatographic Identification Test, a test solution in methanol containing about 1mg/mL and a solvent system consisting of a mixture of methylene chloride and methanol being used
Use all 3 to determine identity
Identification tests in USP - Infrared Absorption Test
Compare the IR spectrum of the test sample and the USP reference standard to seek evidence for identity.
IR absorption relates to stretching and bending of bonds in different functional groups to the structure of the analyte.
Fingerprint region (600 -1400 cm-1) of the IR spectrum useful for identification, as it contains unique absorption patterns specific to each compound.
Identification tests in USP - UV Absorption Test
UV absorption measured of a test solution and a standard solution, using a 1cm cell, over 200-400nm.
Compare the UV spectra of the test and standard solution
Determine the absorptivities and or absorbance ratios as indicated in the monograph
The requirements are met if the UV absorption spectra of the test and standard solutions exhibit maxima and minima at the same wavelength and the absorptivities and/or absorbance ratios are within specified limits.
Identification tests in USP - Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)
Develop a TLC using silica gel chromatographic plate impregnated with a suitable fluorescing substance.
Apply 10uL of test solution and 10uL of Standard solution prepared from USP reference standard for drug substance to be identified.
Use TLC developing solvent system consisting a mixture of chloroform, methanol, water (180:15:1), unless otherwise stated in the monograph.
The Rf value of the principal spot obtained from the test solution corresponds to that obtained from the Standard solution – indicates a positive identity to the Standard reference
Titrimetric Analysis for Pharmaceuticals
Principles
The amount of a standard reagent of precisely known concentration is used to react chemically with an analyte such that the amount of the standard reagent used can be used to estimate the purity of the analyte.
Applications
Used in pharmacopeial assays to determine the purity of active pharmaceutical ingredient (API), content of API in a dosage form, purity of raw materials for medicinal product preparation
Advantages
Capable of high degree of precision and accuracy
Methods are generally robust
Analyses can be automated and cheap to perform
Limitations
Method may not be selective
Time-consuming
Require large amount s of sample and reagents
Types of Titrimetric Analysis in Pharmacopeia
1. Direct acid/base titration in aqueous phase
2. Indirect titration in aqueous phase
3. Argentometric titration
4. Complexometric titration
5. Redox Titration
6. Non-aqueous Titration
7. Potentiometric Titration
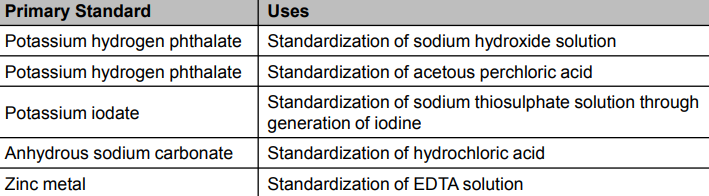
Titrimetric Analysis for Pharmaceuticals - Primary Standards
Primary standards are stable chemical compounds that are available in high purity and that can be used to standardize the standard solutions used in titrations.
Titrant such as sodium hydroxide standard solution may be standardized against potassium hydrogen phthalate, which is available in high purity.
Use to determine the correction factor (f)
Titrimetric Analysis for Pharmaceuticals - The Correction Factor
The correction factor (f) is usually used in volumetric analysis to simplify calculations.
The factor is calculated as a ratio of (Actual concentration)/(Desired (or nominal)concentration).
It tells us how much a given solution differs from the nominal (true) concentration.
If f < 1, the prepared solution is of lower concentration that what was desired.
If f > 1, the prepared solution is of higher concentration that what was desired.
If f = 1, the prepared solution is prepared precisely to the desired concentration.
For example, if f of a 0.5 N H2SO4 solution = 0.96, its actual concentration is 0.5 N × 0.96 = 0.48 N. (f x vol)
Titrimetric Analysis for Pharmaceuticals - Indirect Titration (Back Titration)
Back titrations involve addition (from a pipette) an excess of a standard volumetric solution (VS) to a weighed amount of the analyte, and followed by the determination of the excess unreacted VS.
In general, this indirect (back) titration is used for:
Volatile substance (e.g. ammonia, volatile oil)
Insoluble substances (e.g. CaCO3)
Substances for which a quantitative reaction proceeds rapidly only in excess of a reagent (e.g. lactic acid)
Substances which require heating with a volumetric reagent during the determination in which a decomposition or loss of the reactants or products would occur in the process (e.g. aspirin)
Titrimetric Analysis for Pharmaceuticals - Back Titration with Blank Titration
It is necessary to perform a blank determination in assay which involve heating a liquid containing excess of standard alkali, cooling and back titrate the excess.
The heating and cooling may cause apparent changes in the strength of the excess reagent.
Therefore, the blank titration will standardize conditions in both the blank and the sample determination.
The USP assay for aspirin adopts this approach in the determination of aspirin
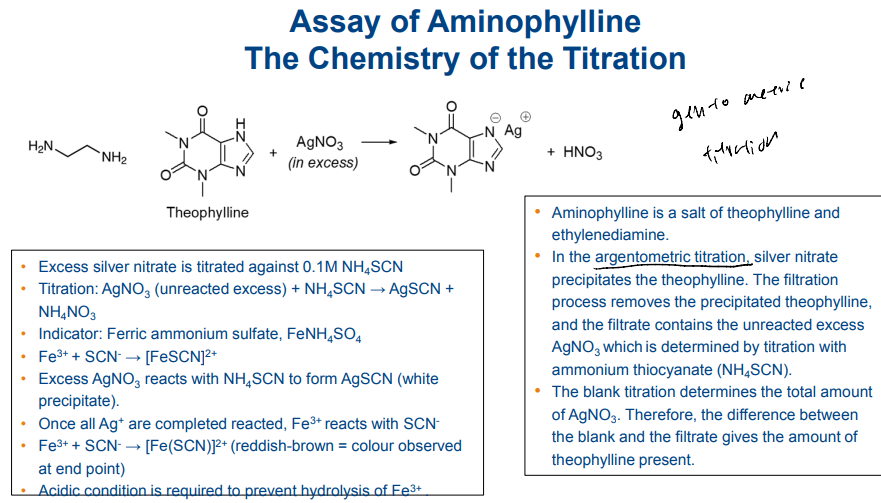
Titrimetric Analysis for Pharmaceuticals - Argentometric Titration (Direct)
Quantitative precipitation can be used for volumetric determinations, provided the point at which precipitation is complete can be determined. In argentometric titration, this principle is applied.
For example, a sodium chloride solution can be determined by titration with silver nitrate in which silver chloride precipitates as silver nitrate VS is added to a solution of sodium chloride.
At the end point, the excess silver nitrate reacts with potassium chromate used as the indicator where a red colouration indicates the end point
Argentometric Titration (Direct) - assay of aminophylline
Application of HPLC Analysis to the Quantitative Analysis of Drugs in Formulations

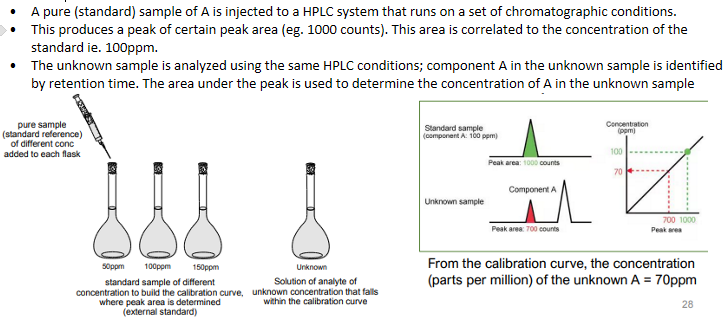
HPLC - Calibration with an External Standard
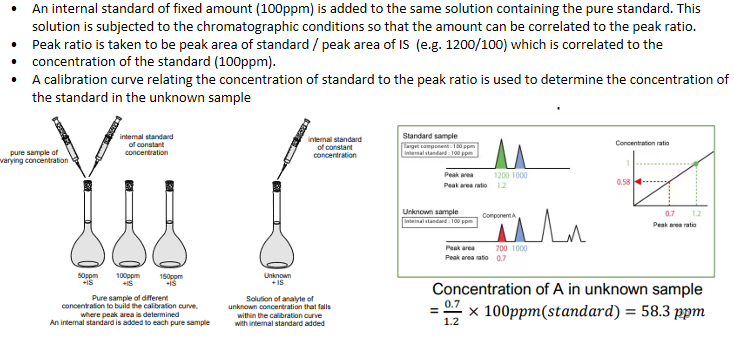
HPLC - Calibration with Internal Standard
HPLC - Application of Internal Standard in Biological Fluid Analysis

Who overlooks the quality for medicines?
The International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements For Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) is the organization that standardizes the requirements for medicines regulation throughout the world.
ICH standardizes the validation of analytical procedures and indicates that validation is required for
Identification tests
Quantitative tests for impurities
Limits tests for the control of impurities
Quantitative tests of the active pharmaceutical ingredients, drug products and selected components(s) in the drug product
Regulation of health products (medicines)
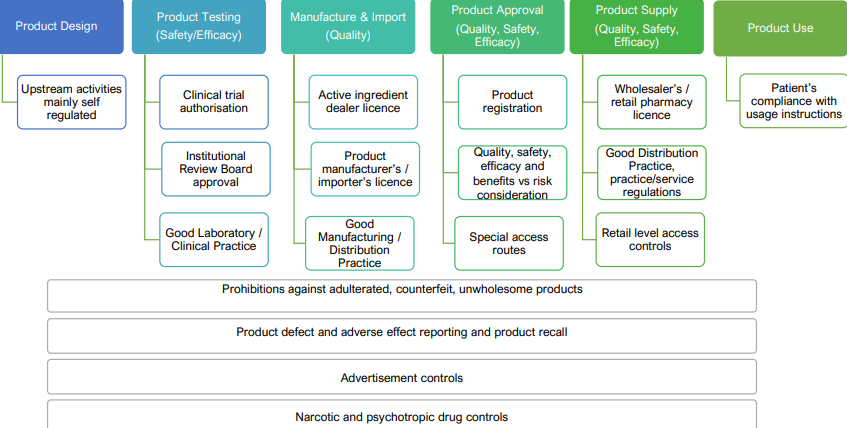
The Health Products Act regulates the requirements for registration of the medicines, conducting clinical trials, the manufacturing process, importation, wholesale sales, retail sales and the advertising of medicinal products throughout their life cycle.
Ensure quality of products are not compromised
Regulation of health products - Overview of health products regulation
Regulation of health products - Registered Pharmacists as Responsible Persons

Regulation of health products - duties of the responsible person
