Pedi Exam 1 Memorization
1/49
Earn XP
Description and Tags
tables and charts
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
ch. 4 - behaviors that indicate blurred vision in a child
squinting, rubbing eyes, clumsiness
ch. 4 - signs of hearing loss in a child
loud speech, inattentiveness, needing repetition
ch. 4 - symptom suggesting increased ICP
vomiting associated with eating
ch. 4 - pediatric concern associated with enuresis
bedwetting (daytime or nocturnal)
ch. 4 - adolescent screening for boys
testicular self-exam
ch. 4 - adolescent gynecologic history
menarche, LMP, menstrual regularity, STI history
ch. 4 - respiratory signs of chronic issues
chronic cough, wheezing, snoring
ch. 4 - integumentary findings suggesting bleeding disorders
petechiae and bruising
ch. 4 - musculoskeletal screening in adolescents
scoliosis
ch. 4 - endocrine signs to monitor
rapid/slow growth, puberty signs
ch. 4 - what is the difference between cyanosis in light vs dark skin?
light = blue lips/nails; dark = gray lips/tongue
ch. 4 - what is the difference between pallor in light vs dark skin?
light = pale face; dark = gray/yellow-brown
ch. 4 - what is the difference between erythema in light vs dark skin?
light = red skin; dark = feel warmth/swelling
ch. 4 - what is the difference between ecchymosis in light vs dark skin?
light = purple, yellow bruise; dark = mouth/eye only
ch. 4 - what is the difference between petechiae in light vs dark skin?
light = purple pinpoints; dark = mouth/eye only
ch. 4 - what is the difference between jaundice in light vs dark skin?
light = yellow skin/eyes/nails; dark = eyes and palate best
ch. 6 - how does chickenpox look and when is it contagious?
vesicles start on trunk/face then spread out; contagious until all crusted
ch. 6 - what is the key sign of diphtheria?
gray patches in throat; can block airway
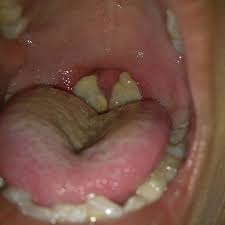
ch. 6 - what is the rash in Fifth’s disease (erythema infectiosum)?
bright red “slapped cheek”
ch. 6 - what happens in roseola (exanthem subitum)?
high fever first; rash shows up after fever goes away
ch. 6 - what is the classic sign of mumps?
swelling of one parotid gland (cheek/jaw)
ch. 6 - what are the early signs of measles and what can it lead to?
fever, cough, runny nose, Koplik spots, red eyes; pneumonia or brain swelling (encephalitis)
ch. 6 - what is the cough like in pertussis?
severe “whooping” cough; can cause vomiting or turning blue
ch. 6 - what is the main danger of polio?
muscle weakness or paralysis
ch. 6 - why is rubella dangerous in pregnancy?
can cause serious birth defects (congenital rubella)
ch. 6 - what are classic signs of scarlet fever?
strawberry tongue; rough, red rash
ch. 9 - what supportive care helps preterm babies thrive?
Kangaroo care (skin-to-skin), cluster care, quiet/low-stim environment, tucking for comfort
ch. 9 - what defines apnea of prematurity (AOP)?
pause in breathing for 20 seconds
ch. 9 - what is the step-by-step response for AOP?
stimulate, suction airway, bag oxygen (compressions only if HR <60)
ch. 9 - what medication is used for AOP and what is its side effect?
caffeine; toxicity = jittery, irritable, tachycardia
ch. 9 - what are the signs and first steps in necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC)?
distended belly, green vomit; NPO, oxygen, TPN, labs, antibiotics (often needs surgery)
ch. 9 - what are 3 signs of neonatal hypoglycemia and how is it treated?
jittery, poor feeding, hypotonia; feeding or IV dextrose
ch. 9 - what are common signs of neonatal withdrawal (NAS)?
inconsolable cry, rigid/flexed tone, seizures, sneezing
ch. 7 - newborn age
0-4 wks
ch. 7 - infant age
0-12 mo
ch. 7 - toddler age
12-36 mo
ch. 7 - pre-school age
3-5 yrs
ch. 7 - school age
6-12 yrs
ch. 7 - adolescent age
12+ yrs
ch. 7 - what are the 3 major circulation changes in a newborn?
foramen ovale closes due to increased LA pressure; ductus arteriosus closes ~4 days; ductus venosus closes with cord clamp
ch. 7 - how do newborns stay warm and how do they lose heat?
brown fat generates heat; lose heat by conduction, radiation, convection, and evaporation
ch. 5 - what does FLACC stand for?
Face, Legs, Activity, Cry, Consolability; ages 0-19
ch. 5 - what is the CRIES scale used for?
newborns (32-40 wks), after surgery; looks at Cry, Oxygen, Vitals, Face, Sleep
ch. 5 - what does PIPP-R measure?
premature babies (25-40 wks); checks HR, oxygen, and facial signs
ch. 5 - what is NPASS for?
babies 23-40 wks; scores crying, face, tone, behavior, and vitals
ch. 5 - why do we use morphine in kids?
strong pain relief, no ceiling dose, main IV opioid for big pain
ch. 5 - what are common opioid side effects?
sleepy, nausea, constipation, itching, slowed breathing
ch. 5 - what do you watch for with sedation?
breathing and heart—if too sleepy, stop medicine and give Narcan®
ch. 8 - what are the main newborn birth injuries?
bruises, scalp swelling, head bleeds (caput, cephalhematoma, subgaleal), and clavicle fracture
ch. 8 - what are 3 common newborn health problems?
jaundice (phototherapy), low blood sugar (feed/IV glucose), and bleeding from low vit K (give vit K shot)