C13 - The Earth’s Atmosphere
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
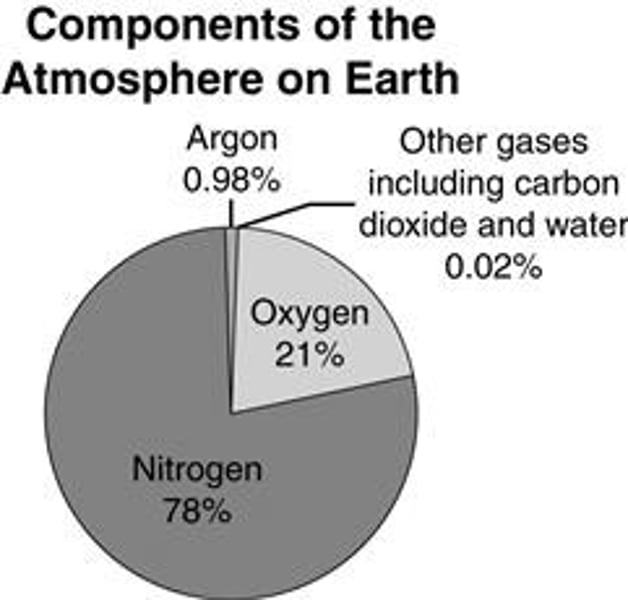
Earth's Atmosphere Now
- 78% nitrogen
- 21% oxygen
- 0.04% carbon dioxide
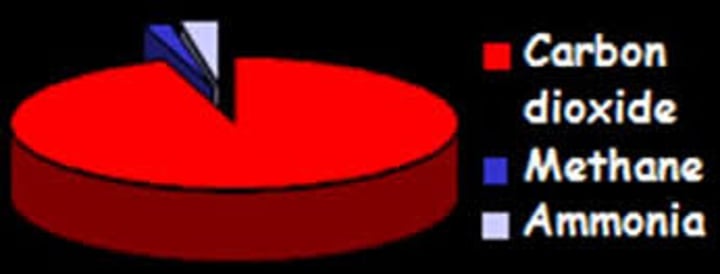
Earth's Atmosphere 4.6 to 2.7 Billion Years Ago
- mainly carbon dioxide
- very little oxygen
- some nitrogen and water vapour from volcanoes
- some other gases
How was the Earth Changed
- volcanoes released gases: mainly CO2 with water vapour & nitrogen
- the earth cooled down, condensing water vapour into an ocean
- some of the CO2 dissolved in the water, reacting with metals to from carbonate rock
- bacteria formed: life started
- bacteria started photosynthesis
- as photosynthesis decreased CO2, oxygen increased
- the oxygen formed the ozone layer
- plankton evolved: photosynthesis
- the plankton died and will form fossil fuels in the future
- pangea/ the supercontinent
- animals formed

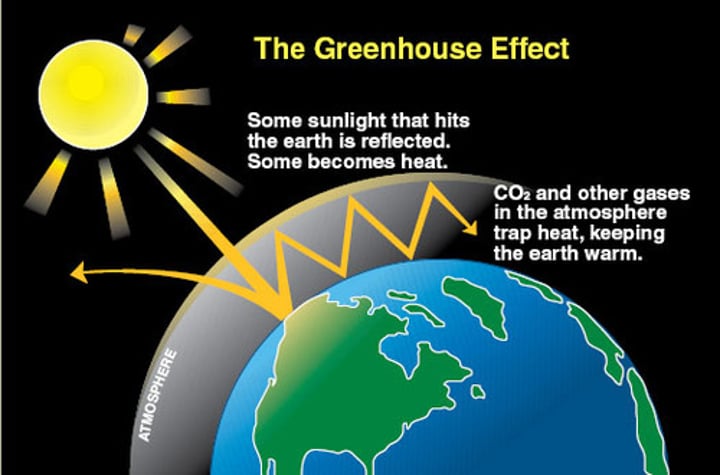
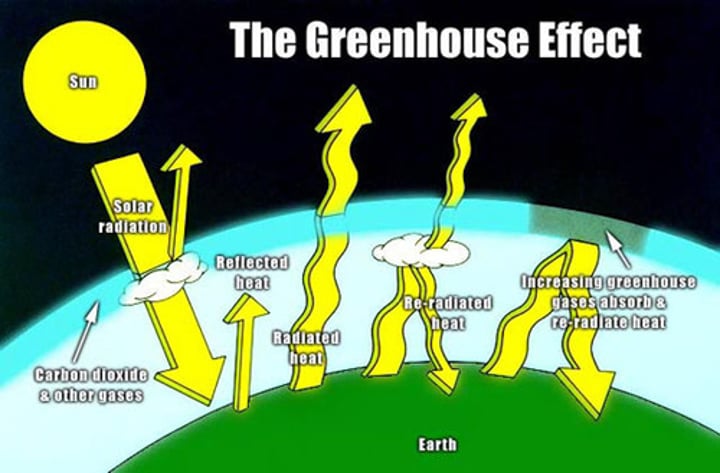
Why are Greenhouse Gases Important
- maintain temperatures on earth high enough to support life
- regulate temperature during the night
Human Activities that Increase CO2
- burning of fossil fuels
- deforestation: reduces the amount of photosynthesis which can occur, so less carbon dioxide is absorbed.
- increasing populations: to fuel the growing demand

Human Activities that Increase Methane
- rearing animals like cows: agriculture
- swamps
- rice fields
- waste disposal

Carbon Footprint
- the total carbon dioxide emissions produced
- by an individual, group, or location

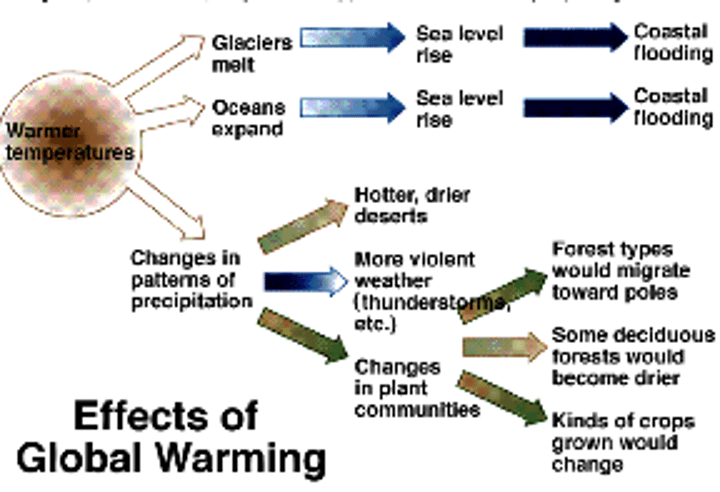
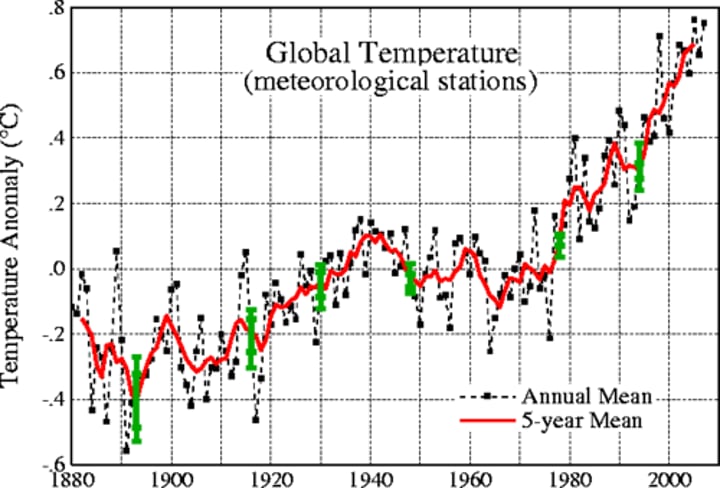
The Effects of Global Warming
- rising sea level (thermal expansion)
- extreme weather
- drought
- famine
- reduced biodiversity & habitats: extinctions
Global Warming Mitigation
- the Paris agreement
- the London congestion charge
- carpool lanes
- less demand for meat
- taxing fossil fuels
- planting plants

Global Warming
a gradual increase in average global temperature
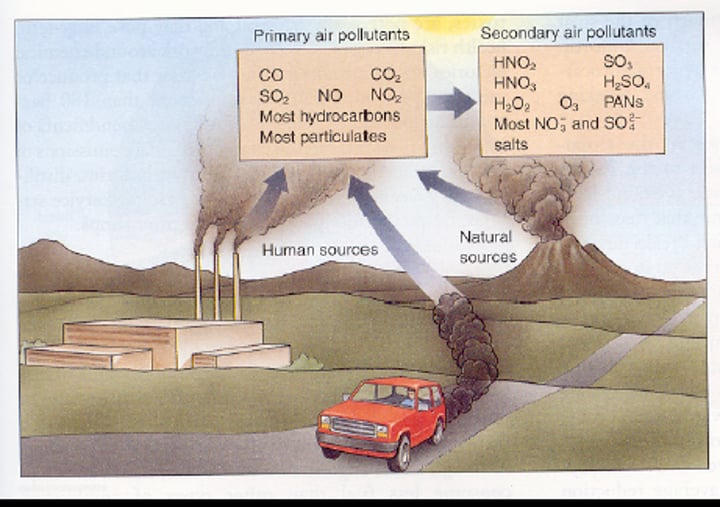
Pollutant Gases
- carbon dioxide
- carbon monoxide
- sulphur dioxide
- particulates
- oxides of nitrogen
How does Global Warming Work
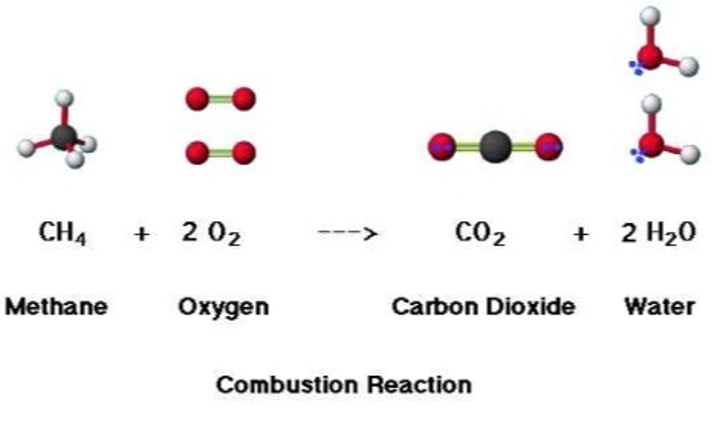
Complete Combustion
- combustion that occurs when there is plenty of oxygen
- produces carbon dioxide and water vapour
Incomplete Combustion
- a fuel burns in insufficient oxygen
- producing carbon monoxide as a toxic product.
Pollutant Gases - Carbon Dioxide
- carbon in a hydrocarbon fuel reacts with plentiful oxygen
- causes global warming
- by trapping infrared radiation in our atmosphere that would usually be reflected into space

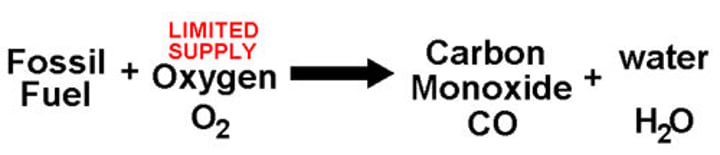
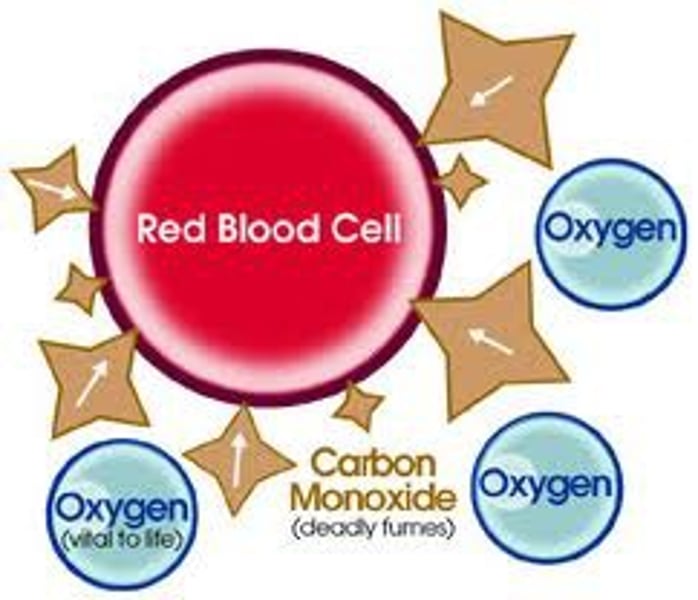
Pollutant Gases - Carbon Monoxide
- when hydrocarbons combust where there is a lack of oxygen
- binds to the hemoglobin in your red blood cells so they cannot carry oxygen around your body: oxygen starvation
- is toxic
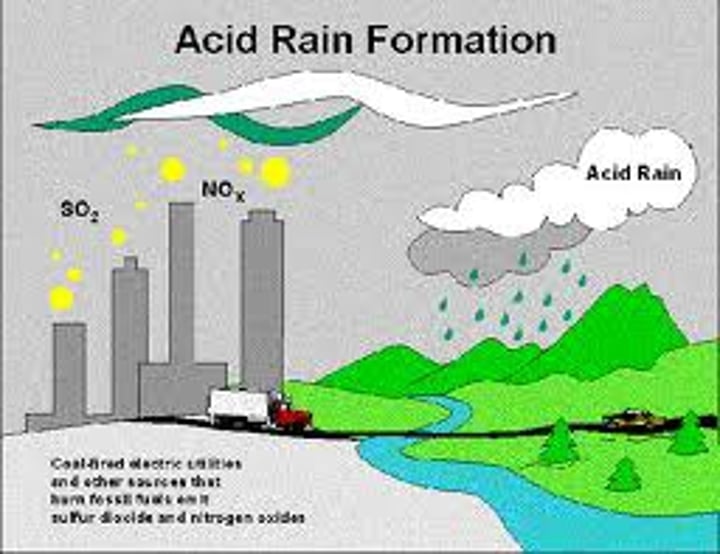
Pollutant Gases - Sulphur Dioxide
- sulphur impurties in the fuel react with oxygen
- can damage the lungs and lead to asthma attacks
- dissolve in rain as it falls to make sulphuric acid (acid rain) which damages
buildings and plants
Pollutant Gases - Particulates
- when hydrocarbons combust where there is a lack of oxygen
- soot particules can cause lung damage
- can reflect light from the sun back into space leading to global dimming

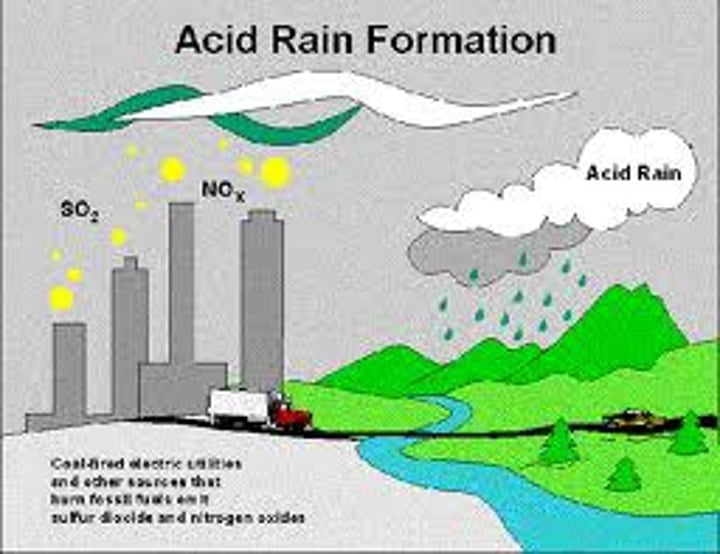
Pollutant Gases - Nitrous Oxides
- nitrogen in the air reacts with oxygen in the high temperatures and pressures of an internal combustion engine
- can damage the lungs and lead to asthma attacks
- dissolve in rain as it falls to make nitric acid: acid rain which damages buildings and plants
Reducing Atmospheric Pollution
- filtering of waste gases to remove sulphur dioxides, oxides of nitrogen, soot etc
- keeping car engines maintained to prevent nitrogen reacting with oxygen to make oxides of nitrogen
- keeping boilers etc maintained to prevent incomplete combustion
- carbon capture
- using fuels with little or no sulphur in
- using less hydrocarbon fuels: renewable
