HUBS192 - lectures 4-13 - CARDIOVASCULAR
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
Describe the blood vascular system?
a closed supply and drainage system - a continuous loop
Describe the lymphatic (vascular) system
an open entry drainage system - one way system
What are the 3 general principles of organisation of the cardiovascular system? Describe them
supply side
arteries are the only supply path
major arteries are situated to avoid damage
important structures often receive supply from 2 sources
arteries change their name at each major branch
exchange network
capillaries of varying degrees of permeability - continuous (tight), fenestrated (leaky), sinusoidal (very leaky)
Drainage
deep veins
superficial veins
lymphatics
Where is the apex located on a human body and what is the apex also known as?
Located at midclavicular line and between 5 and 6 ribs
AKA point of maximal impulse
What does the right atrium receive? What type of blood does it carry?
superior vena cava
inferior vena cava
coronary sinus
(deoxygenated blood)
what does the left atrium receive? What type of blood does it carry?
four pulmonary veins (oxygenated blood)
What are the 4 layers of the heart wall? What do each of them mean?
endocardium - within
myocardium - muscle
epicardium - upon
pericardium - around
what is myocardium AKA?
the pumping chamber
How thick is the left and right ventricle of myocardium?
left = 1.5cm
right = 0.5cm
where does the heart sit?
pericardial space
What are the 3 layers of pericardium? From the outermost layer to the innermost layer
Parietal pericardium
pericardial fluid
visceral pericardium
Name all the layers that make up the heart wall
fibrous pericardium
parietal layer of serous pericardium
pericardial cavity
epicardium - the visceral serous pericardium, lose irregular FCT, blood vessels
myocardium
endocardium
What are the left and right atrioventricular (AV) valves called and what is their function?
Left - bicuspid (mitral) valve
Right - tricuspid valve
Prevent blood returning to atria during ventricular contraction
What are the left and right semilunar valves called and what are their functions?
Left - Aoritc valve, 3 cusps
Right - pulmonary valve, 3 cusps
Prevent blood returning to ventricles during filling (diastole)
When are the semilunar valves open and closed?
open = as blood flows out of heart
closed = as blood starts to backflow
What is the function of cardiac muscle?
beating of the heart
Describe the structure of Cardiac muscle cell
striated
branched, short
one or 2 nuclei
oval shaped nucleus
connected with neighbouring cells by ICD
What are electrical conduction pathways made of?
non contractile cardiac muscle
What are the 3 layers that make up blood vessels? What are each of these layers made of?
tunica intima - endothelium, sub-endothelium, internal elastic lamina
tunica media - smooth muscle, connective tissues = elastin and collagen
tunica adventitia (external) - loose FCT, vasa vasorum, lymphatics and autonomic nerves
What is the function of an arteriole?
determine blood pressure
What is the function of capillaries?
site of exchnage between blood and tissues
What do veins have to ensure arteries can only go in one direction?
valves
What are the functions of veins?
large volume transport system
one way flow
capacitance vessels
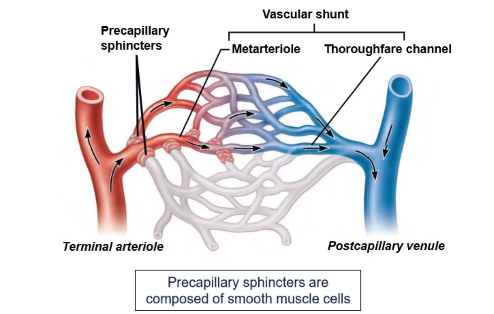
What are precapillary sphincters composed of?
smooth muscle cells
How big is a continuous capillary? what structures is it made of?
8-10um diameter
basement membrane, endothelial layer, intercellular cleft
How big is a fenestrated capillary? what structures is it made of?
8-10um diameter
fenestrations
How big is a sinusoidal capillary? what structures is it made of?
30-40um diameter
intercellualr gap, incomplete basement mebrane
What are the functions of the lymph vascular system?
drains excess tissue fluid and plasma proteins from tissues and returns it to the blood
filters foreign material from lymph
screens lymph for foreign antigens and responds by relasing antibodies
absorbs fat and transports to blood
What are lacteals?
a group of lympatic vessels that drain fat into a collecting vessel called cisterna chyli
What do lymph vessels not have?
red blood cells
What type of blood flow moves to the heart and away from the heart?
away - arterial
towards - venous
Does the atria or ventricles contract first?
Atria
Describe the cellular mechanism of cardiac contraction
Ca levels go up and more Ca is released from the SR
myosin binds to actin to form cross bridges
myosin pulls on actin to shorten the sacromere and generate force
How can you increase force of cardiac contraction?
every cardiomyocyte is activated during contraction
increase cytosolic Ca levels
increase number of cross bridges formed
Describe the cellular mechanism of cardiac relaxation
decrease in Ca2+ levels = Ca is pumped back into SR
cross bridges release when ATP binds to mysoin
reduction in force means the heart can relax
What is diastole?
relaxation, falling pressure
What is systole?
contraction and rising pressue
What is pulse pressure?
difference between the highest and lowest points
Does the heart spend more time in systole or diastole?
diastole
is systemic or pulmonary pressure higher?
systemic
What is the main difference between electrical and contractile cells of the heart?
electrical = low actin and myosin
contractile = high actin and myosin
where does depolarisation start?
in the sinoatrial node
What are gap junctions?
pores with low resistance to ionic current
allow current flow between adjacent cells
What is a ECG? and what does it do?
electrocardiogram - line between two surface electrodes that detect a difference between electrodes
records depolarisation and repolarisation of cardiac cells
What does P wave control?
atrial depolarisation
what does QRS complex control?
ventricular depolarisation
What does T wave control?
ventricular repolarisation
Blood pressure is very low where?
in the veins
What is the equation for flow?
pressure difference/ resistance
What is the equation for mean arterial pressure?
Cardiac output x total peripheral resistance
During the “blood flows in” stage what is happening?
fills arteries
increases arterial blood volume
raises arterial pressure
During the “blood flows out” stage what is happening?
drains arteries
decreases arterial blood volume
lowers arterial pressure
How is cardiac output calculated?
stroke volume x heart rate (SV x HR)
What are baroreceptors? where are they located?
blood pressure sensors
carotid sinus and aortic arch
What is the difference between sympathetic and parasympathetic signalling? Where does the pathway cross through for both?
sympathetic = increases heart rate and force of contraction and increases stroke volume (vagus nerve)
parasympathetic = decreases heart rate (sympathetic trunk ganglion)
Why is there a parallel design of systemic ciruclation?
reduces resistance and decide how much blood flow.
During exercise where does blood flow increase?
muscle
heart
skin
During exercise where does blood flow decrease? where does blood flow stay constant?
GI tract
kidneys
brain
in individual circulations in muscle and kidneys describe the flow rate and resistance rate
muscle - increased flow = decreased resistance
kidneys - decreased flow = increased resistance
What is the resistance equation to blood flow and vessel radius?
R= 1/r4 = 1/(0.5d)4
What has a huge effect on flow?
radius of the vessel lumen
Where is blood mainly found?
in the systemic veins
What is the total blood volume in a 70kg human?
5Litres
thin walls =
more compliance
what is compliance? what is the equation for compliance?
the extent to which a vessel allows deformation in response to an applied force
difference Volume/ Difference Pressure
Which one is bigger… arterial volume or venous volume?
venous volume
What structures counteract with pooling? and what do they do?
venous valves - prevent backflow of blood
skeletal muscle - stiffens veins making them less compliant and therefore less prone to pooling.
What is starlings law fo the heart?
The more stretched muscle fibres are before a contraction, the stronger the contraction will be
Increased venous retun =
increased stroke volume
What are the 3 functions of blood? describe them in detail
transport - o2, co2, nutrients, waste, heat, hormones, immune cells
immune response - white blood cells, immunoglobulins
coagulation - platelets, coagulation factors in plasma
What 3 things is plasma made of?
plasma proteins
other solutes
water
What 3 things are formed elements made of? describe each of them
platelets - stop bleeding
white blood cells - immune response and defence mechanism
red blood cells - transport oxygen
What is haematopoiesis? where is it initiated?
formation of blood cells. In red bone marrow which contains stem cells
What is the structure of red blood cells?
biconcave disc shape - large surface area and movement through capillaries
What are the 4 characterisitcs of RBCs?
contain large amount of haemoglobin
one third weight of RBC
Uses iron as part of the haem structures to bind oxygen
4 haem units, so each haemoglobin can bind four oxygen molecules
What is packed cell volume (PCV)?
the fraction of blood occupied by the red cells
What does low haemoglobin levels = _____ and how does this happen?
anaemia
blood carried less O2 - reduces amoutn delivered to tissues
What is RBC production stimulated by?
Erythropoietin (EPO)
How does the process of erythropoiesis work?
low levels of oxygen in blood
kidneys sense that the oxygen levels in blood are low
kidneys release EPO
EPO circulates to bone marrow
stimulates the production of more RBCs - which carry more O2