Energy Resources
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Energy cannot…
Be created or destroyed it can only be converted from one form to another
Watts are the measure of..
The amount of energy per unit time
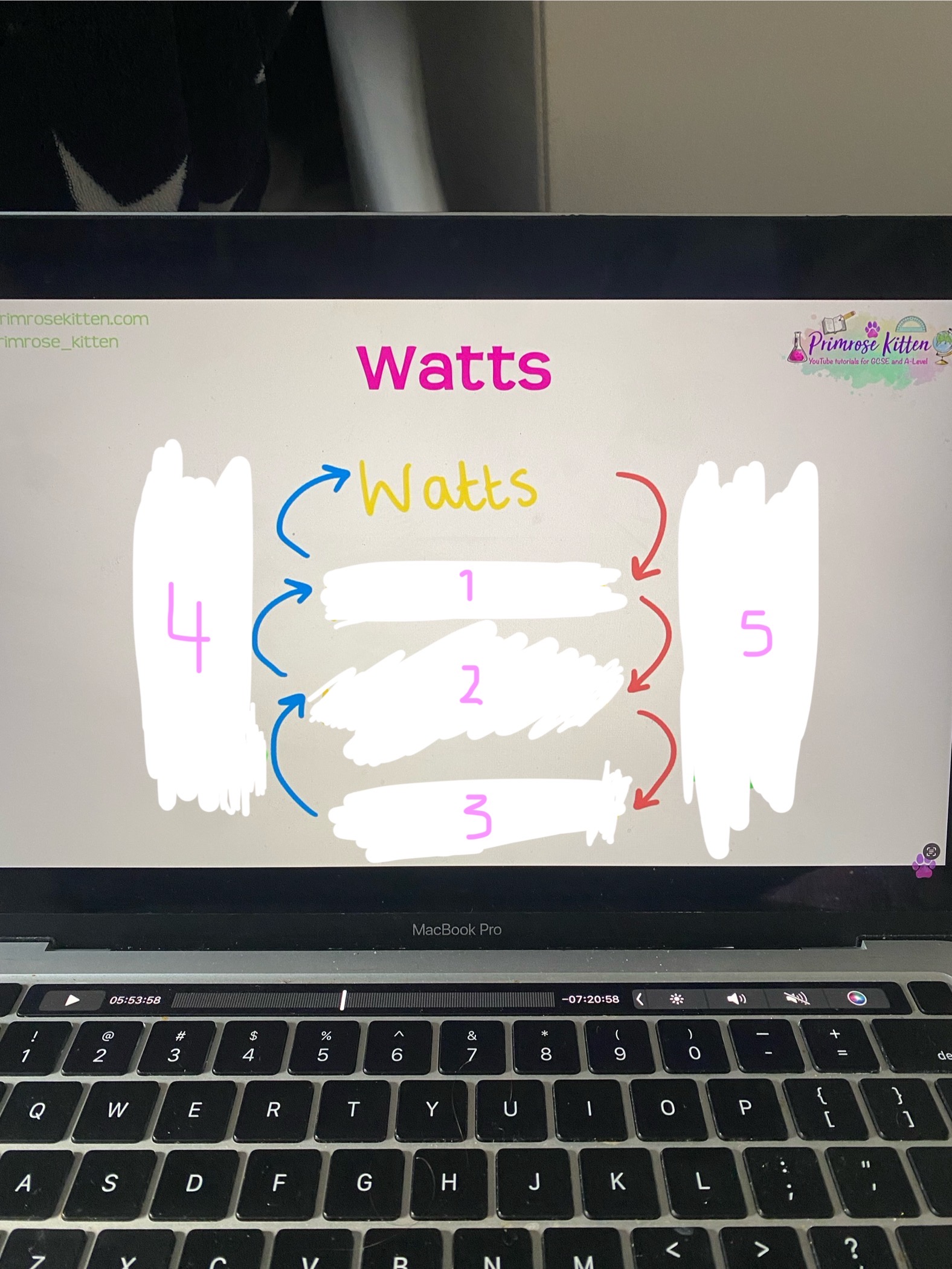
Watts conversions
1- kilowatts
2- megawatts
3- gigawatts
4- x1000
5- /1000

Joules conversions
1- kilojoules
2-mega joules
3- gigajoules
4- x1000
5- /1000
Conversions between joules and watts
Watts= joules/seconds
Joules= watts x seconds
Seconds = joules /watts
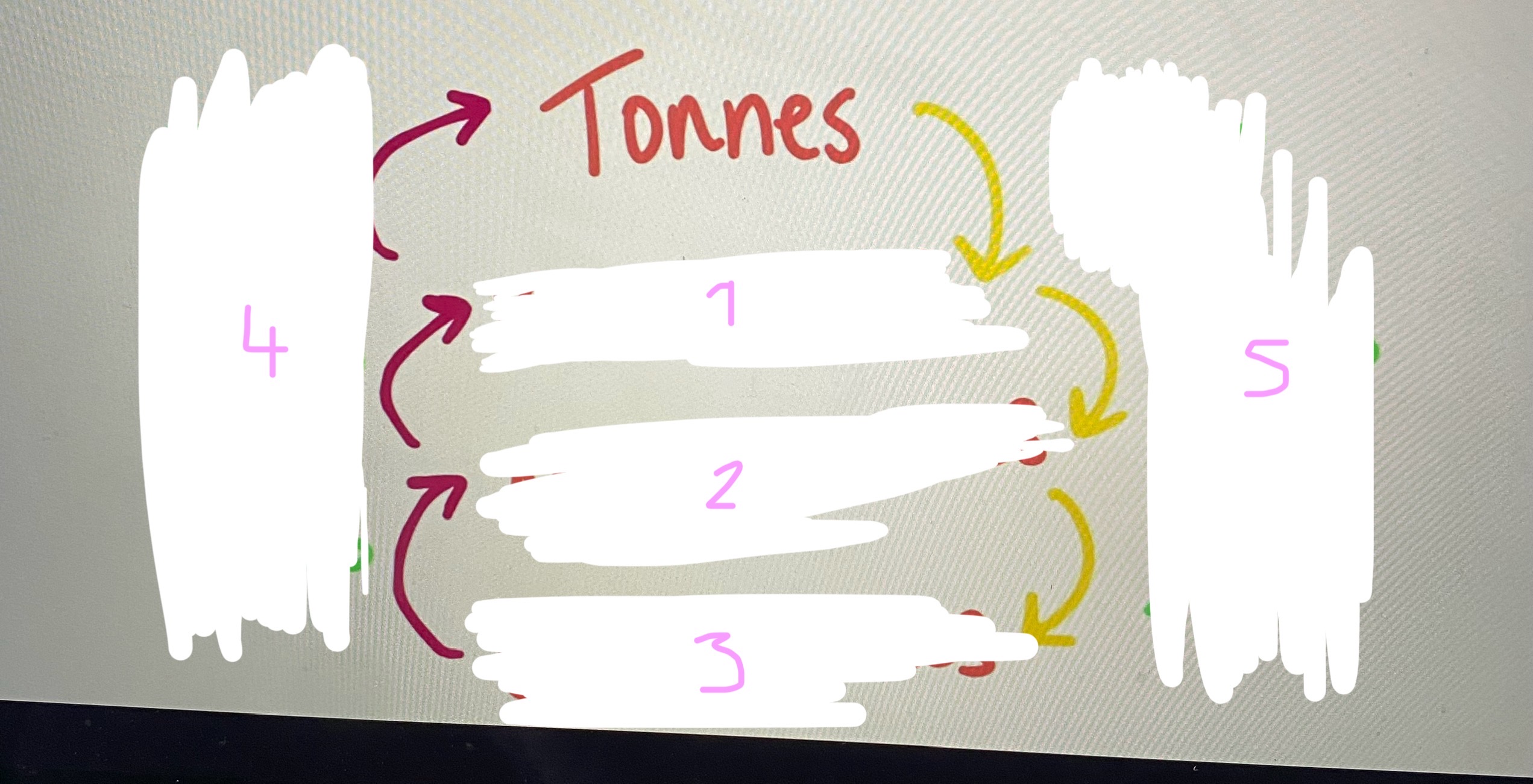
Tonnes conversions
1-kilo tonnes
2- megatonnes
3- gigatonnes
4- x1000
5- /1000
Energy uses in agriculture
Making fertilisers/pesticides and applying them to fields
Fossil fuels used to run large machinery eg tractors
Pumping of water in irrigation
Electricity used for lighting and heating in barns
Energy uses in fishing
Fossil fuels used to power boat engines
Making fishing equipment such as nets
Freezing/keeping stock cold while on board the ship
Energy uses in transport
Fossil fuels used in vehicle engines such as trains, cars, buses, aeroplanes
Manufacturing vehicles and infrastructure associated eg roads/train tracks
Lighting and traffic signals
Electric cars -generate electricity and make batteries
Energy uses in mining
Blast overburden and create the mine site
Extracting the mineral using heavy machinery eg fossil fuels in engines
Smelting to separate minerals
Primary fuel
A natural source of energy which can be used without conversion eg coal
Secondary fuel
A fuel made from a primary fuel eg petrol made from crude oil, as well as electricity, energy is usually lost because of conversion
Per capita
Per person/ population
Equation= total energy used/population
Factors that effect a countries per capita energy consumption
Affluence
Relative cost of energy
Type of industry
Social and environmental awareness of a country
Climate
Affluence
How wealthy a country is on average,
often the more wealth a country has the more energy they use in households through appliances such as dishwashers, washing machines etc
Although some wealthy countries have a greater environmental awareness and invest more money into reducing energy use eg greener public transport
Relative cost of energy
Impacts how much a country uses on average, if energy prices are extremely high, then it’s possible less energy will be used and vice versa
In some countries fossil fuels may be much cheaper than renewables so higher proportion of people will use them like coal oil and gas
Type of industry
Will affect how much energy is used on average, a countries main industry can be put into catagories:
Primary industry- extraction/harvesting of raw materials
Secondary Industry- manufacturing of products
Tertiary industry- providing services
Quaternary industry- high technology industries such as research
Type of industry (primary and secondary)
Primary- require a lot of energy for extraction and harvesting of raw materials like mining, fishing, water abstraction and farming
Secondary- Will require energy for manufacturing processes themselves such as heat or electricity
For this reason they both tend to have a higher energy usage than tertiary and quaternary industries
Social and environmental awareness
If a countries population have been educated about the negative impacts of Climate change then they may make a more conscious effort to reduce energy usage by using energy saving appliances for example or utilise public transport
Climate
impacts how much energy population uses for example in hot climates air conditioning units are installed in most buildings which use a lot of energy
In colder climates large amounts of energy are used to heat buildings
Mid latitude areas most likely use the least energy as they won’t require constant heating/cooling because of moderate temperatures
Why could the energy usage of a country change?
Global climate change- causes warmer temps leading to more AC and water required in farming for irrigation
Industrialisation- if a country becomes a secondary industry than their energy usage may increase however if they move from secondary to tertiary energy usage may decrease
Population growth- more people = more energy use
New technology development- new car designs such as hydrogen may reduce reliance on fossil fuels in the future
Changes to Domestic gross product (DGP)- if the country’s economy is doing well then affluence will increase
Changes in environmental awareness- people may become more environmentally aware overtime leading to a conscious effort to reduce energy usage or vice versa
Case study for economically stable/less stable country for energy usage
Countries such as Brazil china and India have industrialised a their use of energy has increased rapidly especially mining and manufacturing industries while this activity has declined in the UK so industrial energy use has reduced
Properties of energy resources non renewable vs renewable
Renewable energy resource- natural resource that reforms fairly quickly so current use does not impact upon future supply eg solar, wind, tidal, geothermal etc
Non renewable energy resource- a resource that doesnt reform at all or reforms so slowly that our current usage rate depletes future usage eg fossil fuels/uranium
Properties of energy resources depletable vs non depletable
Depletable- a resource that’s supply can be depleted if used at a rate higher than the maximum sustainable yield eg we may run out completely eg fossil fuels/wood
Non depletable- a resource that’s supply cannot be depleted and we shouldn’t be able to run out completely eg solar power
Maximum sustainable yield- maximum harvest/use without depleting future supplies
Properties of energy resources abundance
The amount of energy resource that exists including the amount we could use and the amount we arent able to use, with some resources we can’t harvest all available energy for example:
solar energy may be reflected by clouds
, wind energy can only be harnessed at the height of wind turbines,
Some fossil fuels are too deep underground or under Antarctica where they can’t be extracted
Wave power- hard to harness energy from waves that arent close to the coastline
Intermittence is…
A measure of how often the energy resource is available, an energy resource with a low intermittence will always be available for example fossil fuels, as long as we keep extracting them they will always be available and the availability doesn’t change on the day/because of weather
Energy resources with high intermittence such as solar and wind power will not be available all day every day eg solar power can only be harnessed during the day
Predictability is…
A measure of how easy it is to predict when an energy resource will be available
High predictability would include tidal power as we can now accurately predict when high tide and low tide will be each day and therefore when we’ll be able to harness the energy
Solar power has low predictability as weather predictions are constantly changing and factors like cloud cover are almost impossible to predict correctly
Locational contraints of an energy resource
An example of high locational constraints this is geothermal power as it can only be harnessed in a location where there are very hot rocks close to the earths surface which is limited
Wave power also has high locational contracts because it can only be harnessed in coastal regions
A resource with lower locational contraints can be used in a wider range of areas such as use of fossil fuels in vehicle engines
Energy density of energy of energy resources is…
The amount of energy in a given mass of an energy resource
High energy density vs low
Resources with high energy density like coal and oil have a large amount of energy per unit mass whereas resources with a low energy density like solar power have a small amount of energy per unit mass
Having higher energy density increases the usefulness of the resource as less is needed to provide the same amount of energy as a low energy resource which can make it easier to transport
Example of high - nuclear power
Example of low - solar/wind power
Energy density of energy resources (conversions)
Some energy resources need to be converted to other energy forms to increase their usefulness whereas some don’t. This can increase the usefulness of the energy resource as it can convert it to a form used in appliances for example
When harnessing wind power for example we convert heat energy into electrical energy, yet conversions arent 100% efficient so energy will be lost which may reduce usefulness and increase waste
Properties of energy resources (transportation)
In order to reach consumers energy resources will have to be transported in one form or another so being easy to transport will increase their usefulness
The ease at which it’s transported depends on lots of properties such as state of matter (solid liquid gas) and energy density (higher density products require a lower volume to carry)
Environmental factors and impacts to consider with each energy resource
Environmental impacts caused from production/extraction of energy resource before use, while being used and at the end of its life such as how it will be disposed of
Technological development available for the energy resource
Some energy resources like fossil fuels have had lots of money invested to increase supplies and usability so technological development is high
For some renewables such as wave and tidal power there hasn’t been much investment so technological development is fairly low which reduces the usability of the resources
Government assistance
Some governments provide grants and funding for implementing renewable energy resources to encourage its use usually to help the country reach a sustainability goal
Being sustainable means…
We are meeting needs of the current human population without depleting resources for the future population so it would only be sustainable if the amount of energy we are supplying can be maintained indefinitely without any environmental economic or social impacts
Reasons why energy supply is not sustainable
A large proportion of how we supply energy to the general population relies on energy conversions which involve energy loss
eg when harnessing energy from coal we combust it to release heat which is then used to turn a turbine which turns a generator to convert it to electrical energy, this involves multiple energy conversions in this process leading to a huge loss of energy
usage processes arent 100% efficient such as internal combustion of petrol or diesel in a vehicle engine results in large amounts of energy loss as heat or friction or exhaust gases l, as a result only a small proportion of the energy available is used to power the vehicle
Another reason is that we rely on depletable resources much more than non depletable because we use fossil fuels to power most vehicles and for a lot of industrial processes such as electricity generation
How to become more sustainable within the energy industry
We need to invest in technology for renewable, non depletable energy resources to make them more accessible and efficient as fossil fuels will run out
Alternatives to renewables
Nuclear power is being trialled but is expensive technology to run and can have negative environmental impacts with the radioactive waste it produces
What is a fossil fuel?
A fuel made from decomposed remains of dead organisms eg coal oil or gas
Coal overview
Made from terrestrial lands plants that lived millions of years ago, when dead they partially decomposed in anoxic (no oxygen) conditions within peat to be converted into DOM, over time the peat become buried increasing temperature and pressure to form coal deposits
Properties of coal as an energy resource
Non renewable
Easy to store because it’s a solid
High energy density
Energy form is chemical as it’s stored within the chemical bonds
Depletable
High abundance (theoretical but some deposits will never be extracted because they’re too deep)
Low intermittency and predictable supply
Locational contraints: high due to extraction sites but can be used for lots of purposes
How it’s used: combusted to release heat energy eg for electricity generation or smelting in the mining industry
Conversions: conversion required to release heat but not before combustion

1- reserves will run out one day soon
2- may require more habitat damage to reach remaining deposits
3- increases usefulness as it can be stored in times of surplus and used in shortage without losing energy
4- energy not wasted/list to the environment so may reduce need to continue mining more if demand drops
5-need a small volume to release large amounts of energy
6- need to mine small volumes to release large volumes of energy, may reduce environmental impacts of mining eg noise dust
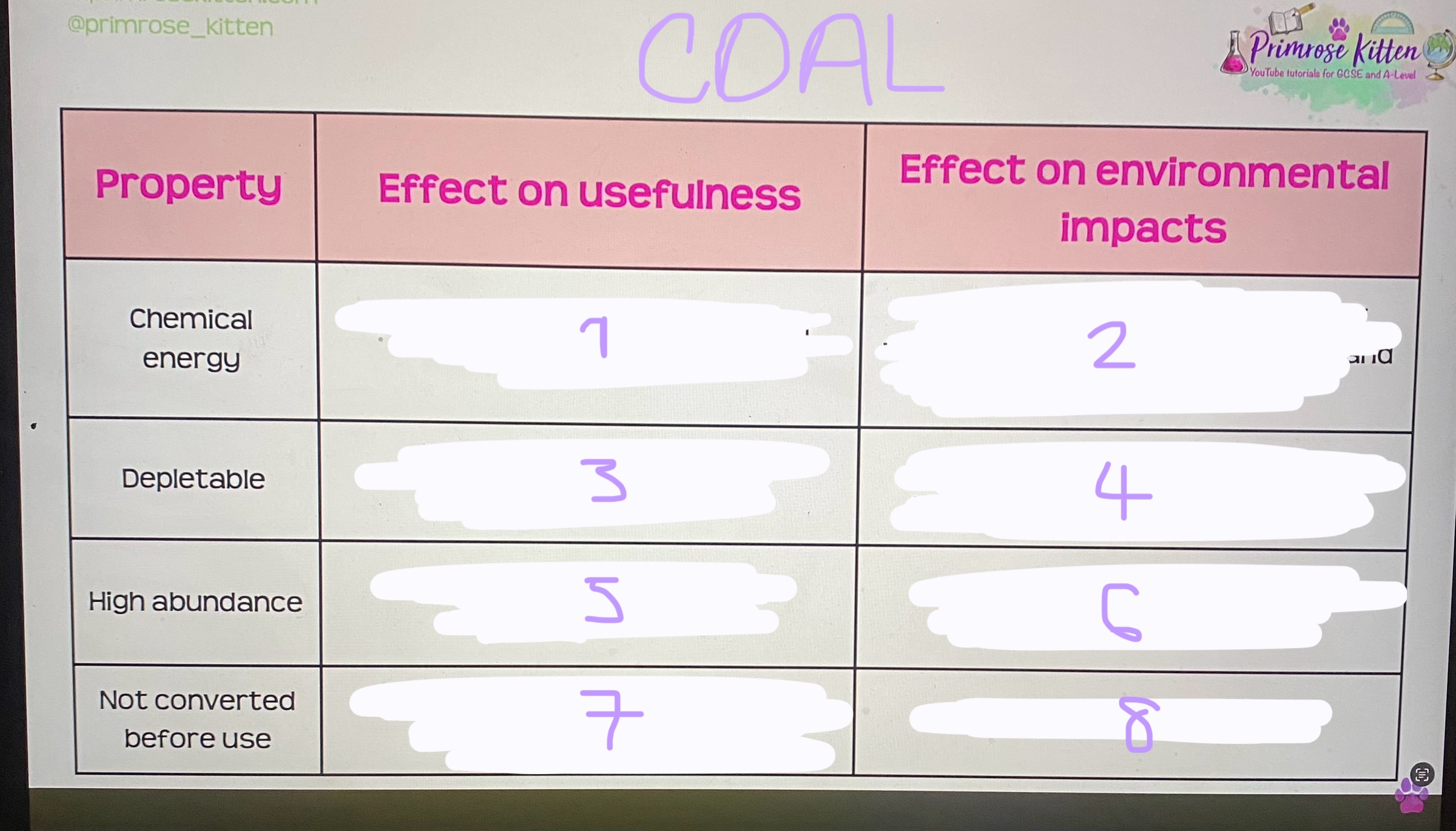
1- can be stored and release lots of energy
2- has to be combusted to release it which releases GHG snd smoke
3- we will run out one day soon need to find alternative
4- places like Antarctica may end up being mined as supply gets lower
5- increase usefulness as more available
6- loss of habitat and destruction in open cast mining
7- increases usefulness as no energy lost in conversion process
8- less energy wasted
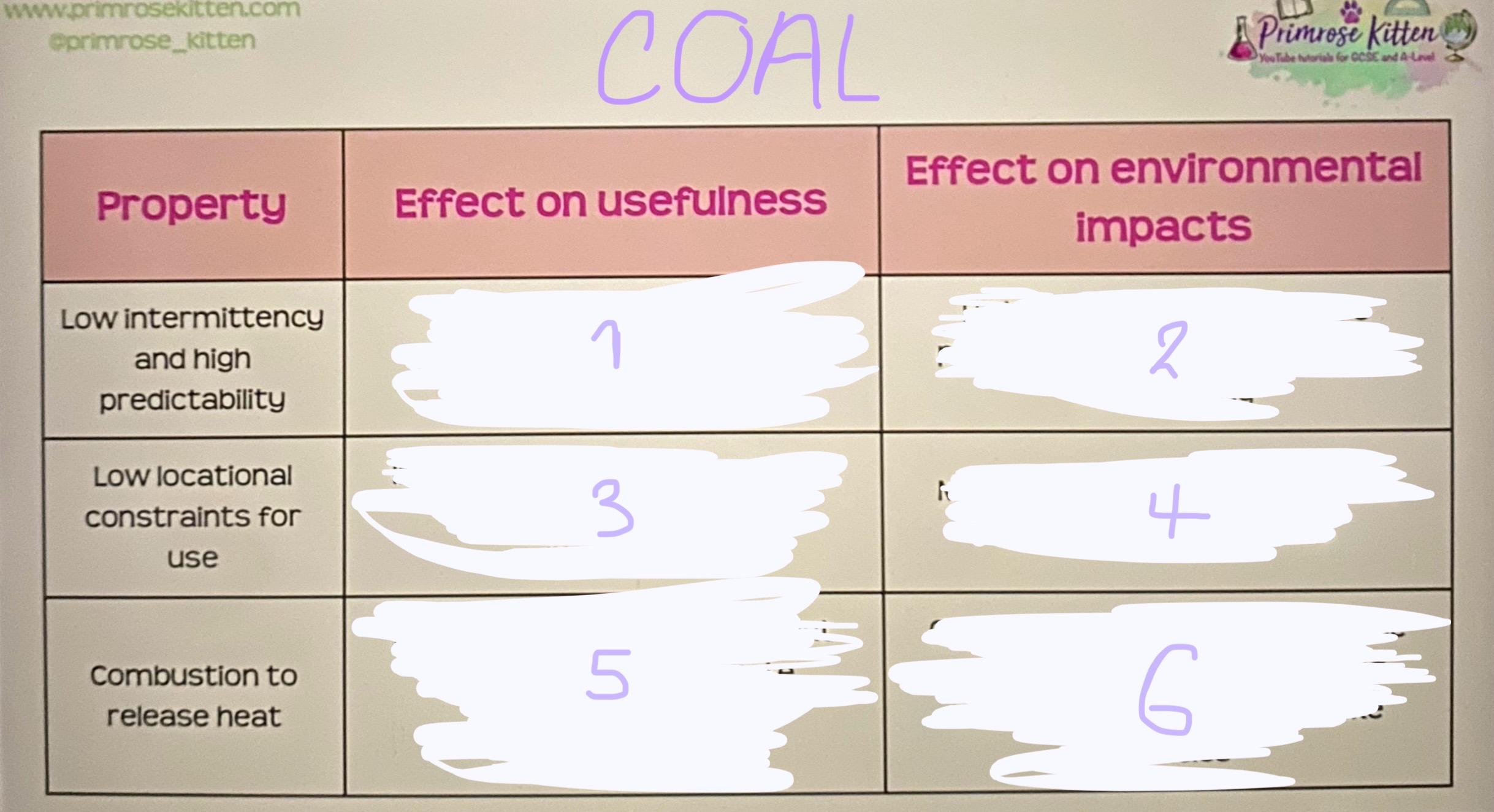
1- increases usefulness as shouldn’t ever be a shortage until we run out of
2- high usefulness means more profit available to restore areas after mining
3- increases usefulness as can be utilised for many purposes
4- means more is used so worsens environmental impacts
5-releases large volumes of heat energy used to generate electricity or smelt metals
6- combustion releases GHG which absorb IR causing warming also releases smoke particles
how to extract a coal deposit
The location must be found first which can be done via a range of exploratory techniques including seismic surveys, IR spectroscopy as resistivity
Trial drilling can then take place to collect a physical sample of the coal deposit data can then be collected such as purity, chemical form, depth and the extent of the deposit can be recorded to determine whether mining in that location would be economically viable
If considered viable then a mining method is chosen, if the deposit is thin and close to the surface = open cast mining, if deep underground then long wall method may be required
Open cast mining vs long wall
Open cast- causes more habitat destruction, lower risk as you aren’t sending people underground,
Both involve blasting to remove overburden and unwanted material

1- baffle mounds to absorb the noise
2- water sprays to immobilise dust particles
3- planting trees, cutting off the top to increase aesthetics and stability
4- add crushed limestone to neutralise
5- sedimentation pool so suspended solids settle
Environmental impacts of the COMBUSTION of coal
Large volumes of GHG are released which absorb infrared radiation trapping it in the troposphere causing warming
Rising temps lead to land ice melt and sea level rise
Combustion also produces large volumes of smoke particles which can contain toxic chemicals and cause irritation in breathed in, can also reduce light penetration and reflect UV radiation sometimes causing an area to cool slightly if remains for a prolonged period of time
Reduced light availability reduces the rate of photosynthesis in plants
The waste product of coal combustion is ash which must be disposed of in land fill sites which have further environmental impacts such as increased rate of anaerobic decomposition causing large volumes of methane release and habitat destruction
Coal processing before and during use
First it may be broken down into smaller pieces and once combusted, flue-gas desulphurisation may occur
What is flue-gas desulphurisation
Efuennt gases produced during combustion are passed through a bed KF crushed calcium carbonate which reacts with the sulphur dioxide to remove it from the gases before they are released reducing the formation of acid rain as there is less sulphur dioxide being released into the atmosphere and mixing with water
In order for a mine to be economically viable…
There has to be enough profit to outweigh the costs that would be involved
Factors affecting the viability of a mine
The cut of ore grade of the mineral being extracted determined by the peice it can be sold for at the time and tech available to extract
Overburden depth, hardness and stability
Availability of work force to extract the material safely
Land use conflicts eg protected areas
New technologies surrounding coal usage
Coal gasification- a process performed on coal too deep to ever be extracted, it’s combusted in situ to produce a syngas mixture that contains hydrogen, carbon monoxide and methane, this can then be used to create a synthetic version of natural gas, the main benefit is that we can utilise energy stored in coal without having to extract it so energy isn’t wasted
Coal liquefaction- coal is converted into a liquid fuel using a solvent which can be used in a wider range of used eg vehicle engines yet releases large amounts of carbon dioxide
Creating smokeless coal by heating raw coal to burn off the volatiles contained, reducing evironmental impacts to an extent yet will still release large volumes of GHG
Oil and gas natural formation
Originates in sedimentary rock and the source rock which releases the oil is made from dead marine plankton which are decomposed in anoxic conditions under high temps and pressure, it then matures becoming petroleum which migrated to the reservoir rock where oil is stored (a porous and permeable rock)
Properties of oil as an energy resource
Non renewable
Fairly easy to store as it’s a liquid
High energy density
Chemical energy form
High abundance currently but it’s running out
Depletable
Low intermittency and high predictability
How it’s used- liquid fuel for vehicles
Locational constraints- high for extracting oil as we deplete existing deposits but is used and available almost everywhere eg petrol stations
Conversion needed before use- needs fractional distillation to separate the petrol but no energy conversion needed, oil combusted to release heat energy so conversion occurs during use
How to locate oil deposits
Using seismic surveys or gravimetry
How to extract oil deposits
Drill down into reservoir rock, if naturally at high pressure then oil will flow to the surface through the pipe system (primary oil recovery)
If pressure isn’t naturally high enough carbon dioxide or water is injected into the rock to increase the volume of oil (secondary oil recovery)