Bio 10b Exam 3
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
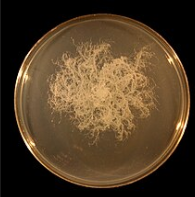
Actinomyces

Bacillus mycoides
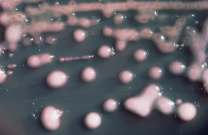
Klebsiella
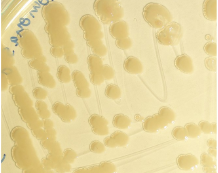
Pseudomonas
Staphylococcus aureus

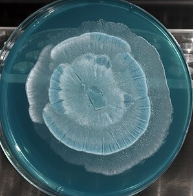
Streptomyces

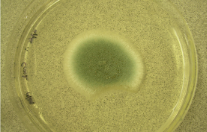
Aspergillus niger
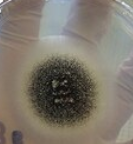
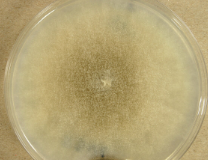
Fusarium
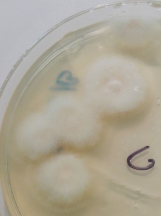
Mortierella
Mucor
Penicillin
Rhizopus
Rhodotorula
Excavata
parasites
SAR dode
protist that photosynthesize and form the foundation of food webs for most aquatic systems
Archaeoplastida
multicellular — land plants, red algae, ect
Unikonta
fungi, choanoflagellates, animals, amoebas
Prokaryotic cells
no organelles, DNA is just kinda floating around
Eukaryotic cells
DNA in nucleus, organelles
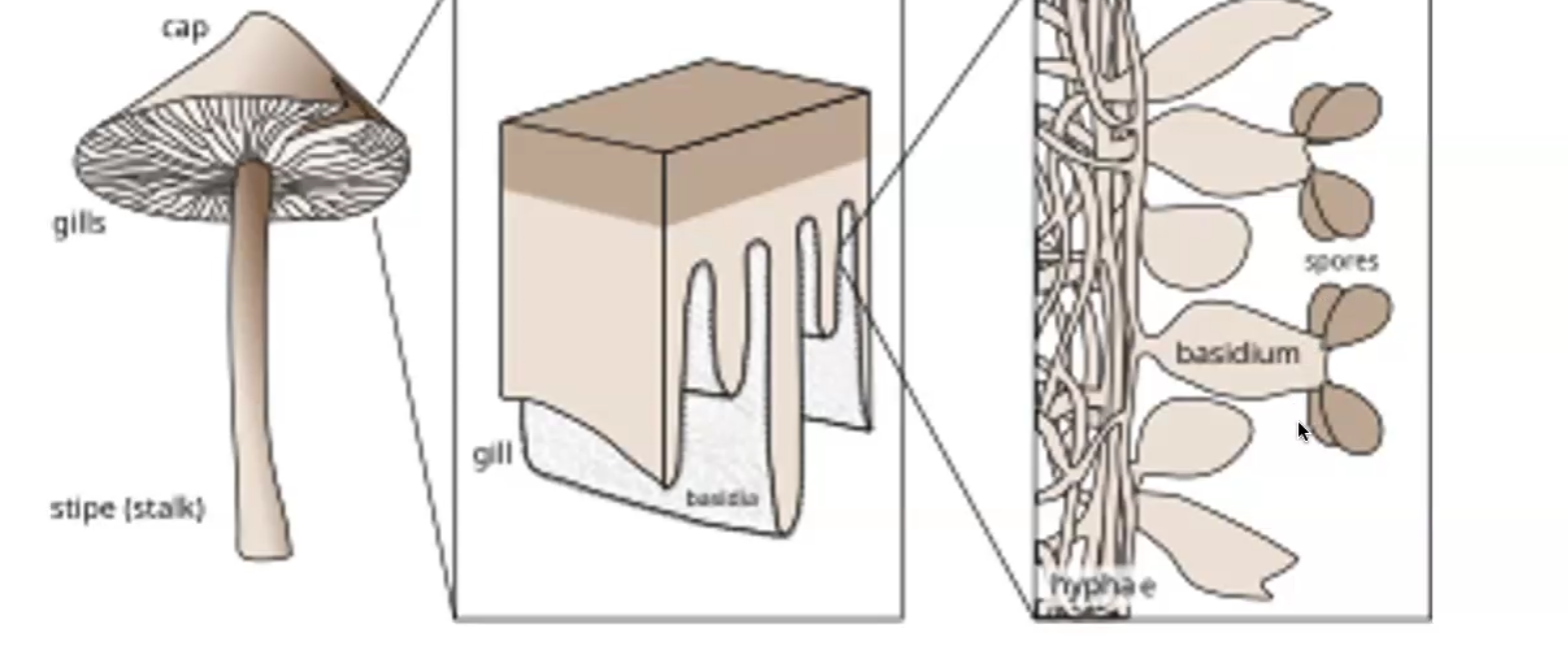
Mushroom
reproductive/fruiting body
Hyphae
extremely thin, web-like structures that grow, in a medium, like soil or water, they collect into the fruiting body in order to release spores
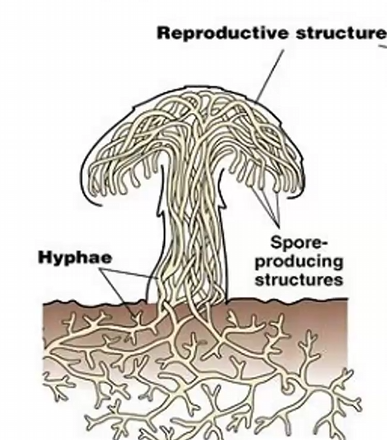
Mycelium
Hyphae that is eating and growing
Fungi
usually multicellular, heterotrophic, eukaryotic organisms that digest material out of their bodies—excrete enzymes into environment, digest, then slurp up
Chytridiomycota
Most basic ancestral group, out group, water molds
Mucuromycota
black/red molds, serve as decomposers, make up mycorrhizal fungi
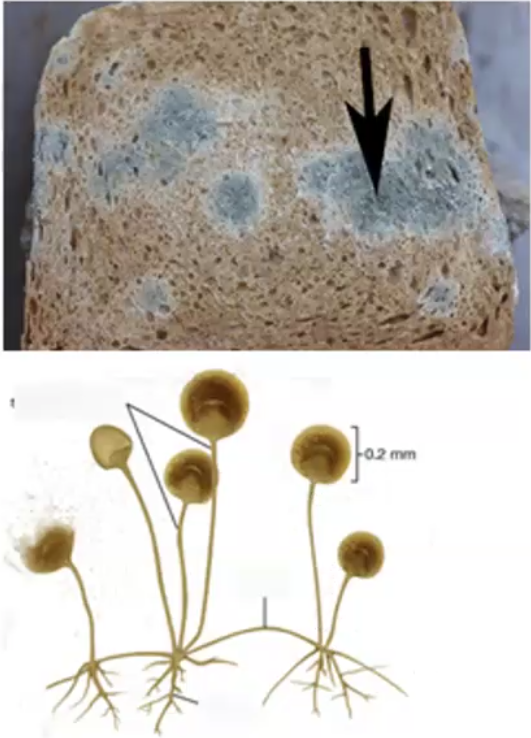
Ascomycota
cup fungi, yeast, vital primary decomposers, form symbiotic relationships with lichen and mycorrhizae
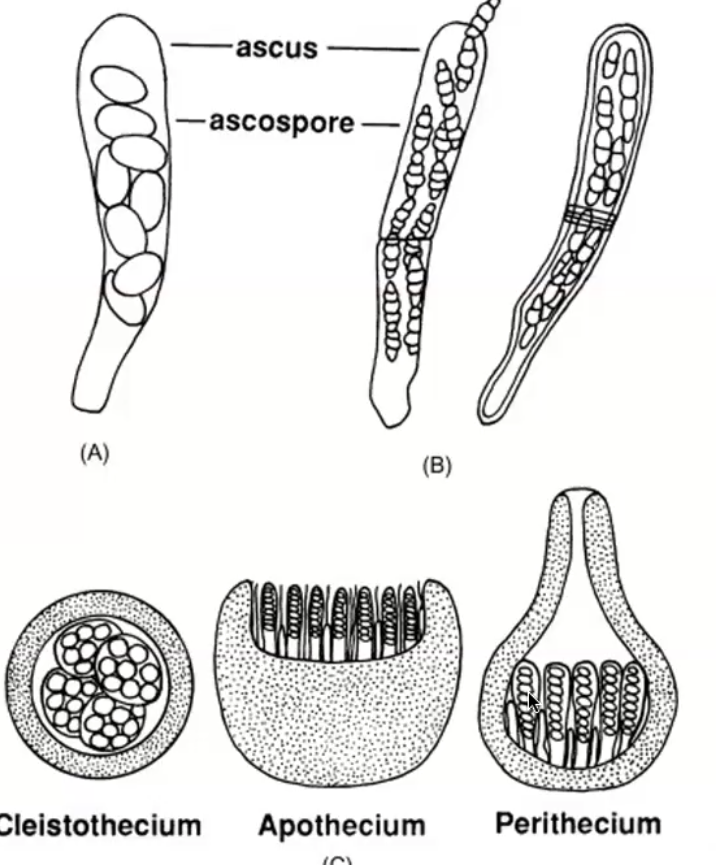
Basidiomycota
produce mushrooms, shelf fungi, smuts and rusts, serve as a food source
sporangia
containers that hold the spores
How much mycorrhizal fungi can be found in a pinch of soil?
up to 7 miles
How do mycorrhizal fungi make physical contact with the insides of tree roots? What is being exchanged during this contact?
Via tubes, and mineral nutrients. The tubes will stretch up toward the tree roots and communicates with chemical messages.
How do mycorrhizal fungi obtain minerals, in general, and nitrogen, specifically?
They hunt, mine, fish, and strangle. The fungus eat springtail bugs, when the tubes impale them, sucking the nitrogen up.
Explain what happens in a forest when a tree experiences stress from temperature fluctuations.
Trees release a chemical signal throughout their network, dumping their carbon into neighboring trees. This food typically goes to newer trees, who are better adapted to survive with temperature fluctuations.
Phenotypic Plasticity
the ability of an organism to express different phenotypes in different environments - evolved trait - most beneficial to plants
Light
highly heterogeneous environmental resource
Leaf shapes are…
controlled by hormones.
Reaction norms
a that plasticity results are often reported in papers
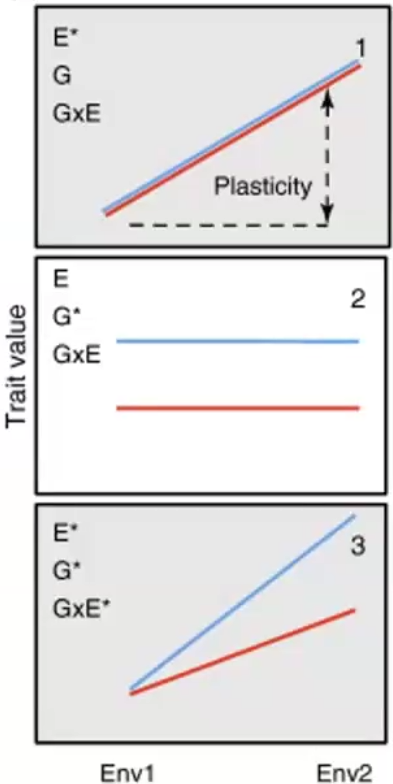
How might phenotypic plasticity be a mechanism for diversification?
Plastic traits allow colonization in new environments, New environments become selection pressures for other phenotypic change, Reproductive barriers evolve (e.g. flowering times (angiosperms))
Chaparral Biome
Mediterranean climate characterized by hot, dry simmers and mild, wet winters - drought resistant plants - periodic wildfires, which many plant species rely on for regeneration
South facing slopes…
are exposed to more sun per day
The average stomatal density is less on the…
south facing slope than the north facing slope
The average leaf area is area on the…
south facing slope than the north facing slope
Angiosperms
a plant that has flowers and produces seeds - include herbaceous plants, shrubs, grasses, and most trees (newest group)
Gymnosperms
a plant that has seeds unprotected by an ovary or fruit. Gymnosperms include the conifers, cycads, and ginkgo
Stomata
tiny pores mostly on the underside of plant leaves and stems that regulate gas exchange, allowing the plant to absorb carbon dioxide for photosynthesis and release oxygen
Plants come from…
Charophycean Green Algae (protist ancestor)
Bryophytes
liverworts, mosses, hornworts
Alternation of generations
plants alternate from a haploid phase to a diploid phase
Cuticle
a protecting film covering the outermost skin layer (epidermis) of leaves, young shoots and other aerial plant organs
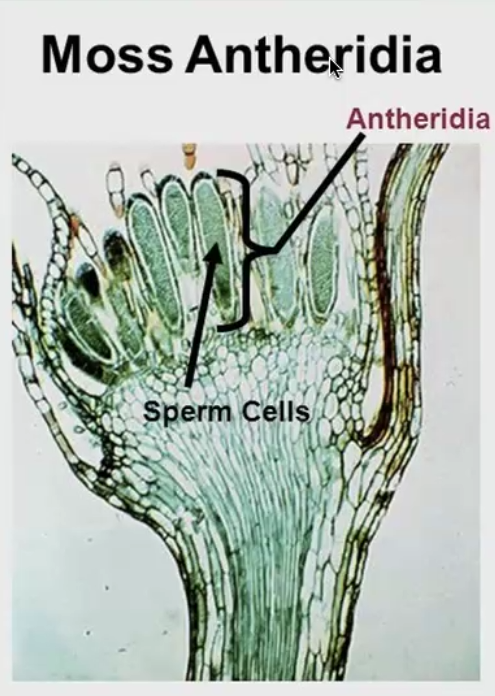
Antheridia (gametophyte)
male (flagellated) sperm cells in mosses
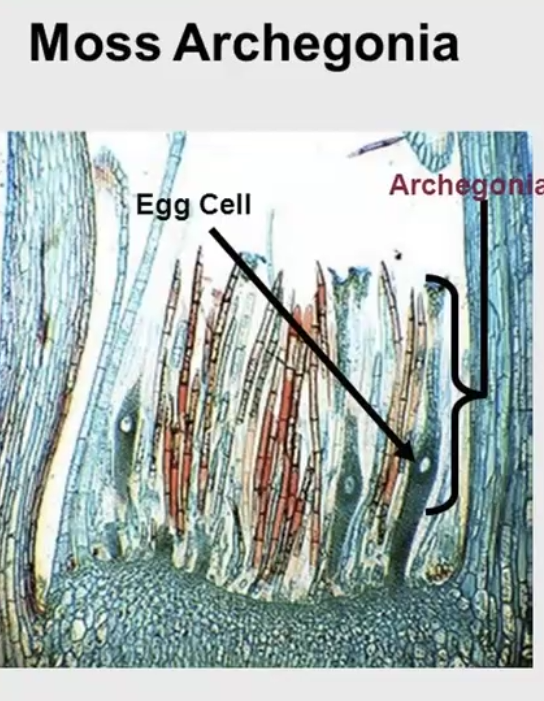
Archegonia (gametophyte)
females that produce eggs
Vascular Plants (lycophytes, ferns, gymnosperms, angiosperms)
roots, xylem and phloem, allows plants to get bigger, so they can tap into nutrients and water in the soil
Phylum: Tracheophyta, Class: Polypodopsida
Ferns
Carboniferous Time Period
Plants were dominant (ferns were tree sized), no gymnosperms/angiosperms yet
Pine (female)
pine cone (ovulated egg)
Pine (male)
very soft, brush-like structures, pollen is produced (replacing flagellated sperm)
Class Cycadopside and Pinopsida
cone-producing plants
Flowers can…
have both female and male part (lily flower)
Male structure for flowers
anther (produce pollen)
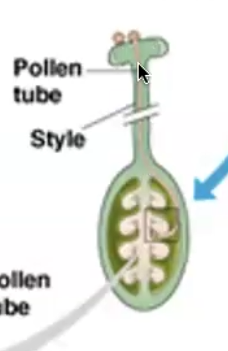
Female structure for flowers
ovules in an ovary, which is attached to a long tube called a style, stigma allows for pollen to stick
Fruit
ripened ovary from an angiosperm
Monocots - liliopsida
all of the grasses, bamboo, palm trees,

Dicots - magnoliopsida
“everything else”, peanuts

Community ecology
the study of how interspecific interactions affect the distribution and abundance of species in a community
Mutualism
occurs when one species lives in or on another species and both benefit from the interaction - ex. zooxanthellae on coral
Parasitism
occurs when one species needs to live on or in another species to complete its life cycle
Predation
occurs when one species eats another species
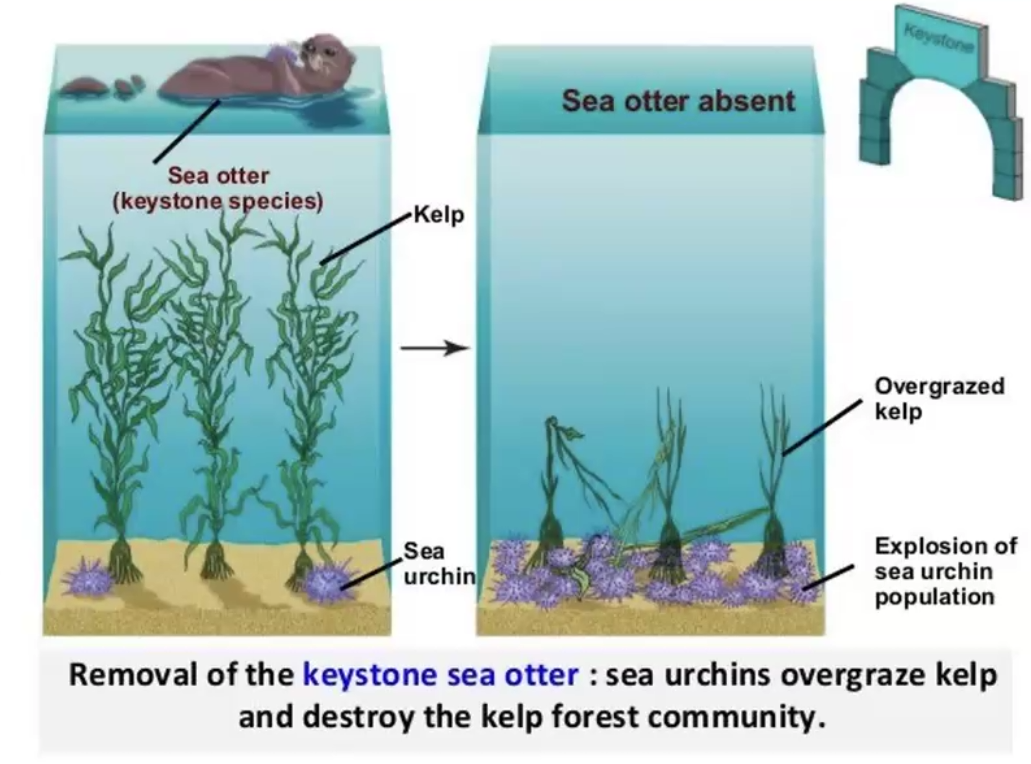
Keystone species
predators can maintain community diversity
Competition
occurs when two or more species use the same resources, can be indirect or direct
ecological niche
describes the functional position of organism in its environment
Competitive exclusion
competition cannot happen indefinitely, especially if there is great overlap in species niche
Niche differentiation
if a species is able to escape the competitor by altering its niche, then it could be a very successful strategy (chthamalus and balanus)
Coevolution
species that interact become selection pressures on one another
Coevolutionary arms race
Rough skin newts have a toxin (TTX) that garter snakes are immune to, therefore, the newts evolve to have enough toxin to kill 100 humans
Patterns of dispersion
uniform, random, clumped
Cohort life table
tracks a group of individuals born at the same time until the last individual dies
Static life table
sample of population and ages of individuals at one point in time
Net reproductive rate
the sum of the product of survivorship and fecundity multiplied together, any number above one=population increasing, below one=decreasing, =one=stable
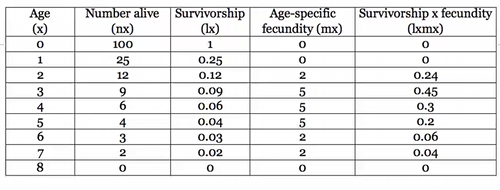
Intrinsic rate of increase r
ln R0 / T (generation time)
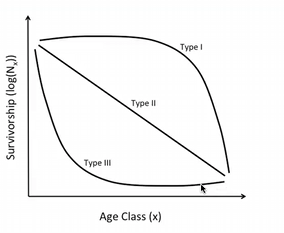
Survivorship curves
Type I - K-selected, long living and takes a long time to mature, Type II - middle of the road, squirrel, Type III - R-selected, short lives, spiders/bugs
Exponential model
describes growth rate under ideal, unregulated conditions - only happens w/ bacteria grown in lab and humans
Birth rates and death rate instantaneous, per capita value
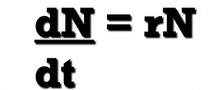
r
the per capita rate at which the population increases in size at each instant in time
Logistic growth model
describes density dependent growth - food, space, mates, predators, viruses, competition
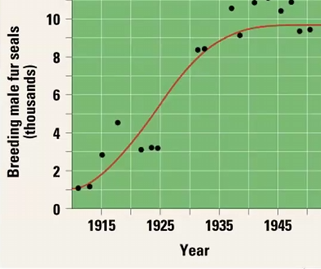
Density dependent growth

Life History
timing and relative energy put into growth, reprod, and survival
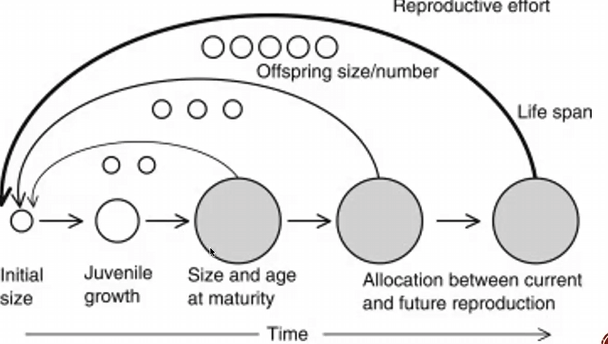
To yield the max lifetime reprod success…
begin reprod at young age, produce many offspring at each reprod attempt, reprod repeatedly, provision offspring and live for a very long time
Life History Traits
size at birth, growth pattern, age and size at maturity, number, size, and sex ratio of offspring, number of reprod attempts, parental investment, lifespan
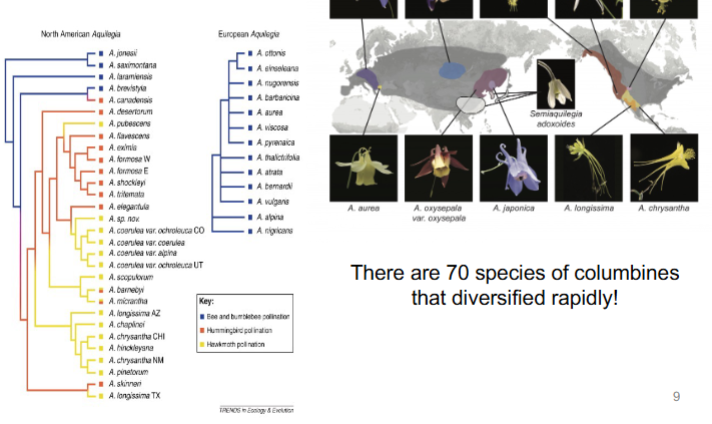
Diversification in Columbines
How does soil moisture promote bacterial and fungal diversity?
Water provides moisture — supports more species, promotes bacterial growth, water regulates temp -- biological processes can be carried out
How might industrial agricultural practices impact soil?
top soil erosion, monoculture/monocropping, not diverse enough conditions in the soil (microorganisms), tractors compress soil
Abiotic challenges in the rocky intertidal
drying from the sun, increased salinity from water evaporating, range of temperatures, dessication
Rocky intertidal interactions
mussel beds facilitate barnacles and buffer waves, sea stars predate on mussels, sea urchins predate on kelp/seaweed, competition for space for sessile creatures
Buzz pollination
bumble bees shake flowers by rapidly vibrating their wings — pollen falls from anthers all over bee
A. Formosa
Pollinator: Hummingbird

A. Pubescens
Pollinator: Hawk Moth

Behavioral isolation?
Hawkmoths will ignore downturned flowers, isolation ensues by not pollinating them w/ the upright pubescens (speciation)
Mechanical Isolation
when pollinators can no longer access the anthers of the flower —> speciation. Flowers w/ longer spurs cannot/do not reprod. w/ flowers w. shorter spurs