Clinical Skills
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What is the neonatal period?
First 28 days of life - the period where they are particularly susceptible to toxicity
Who fall under the category of paediatric patients?
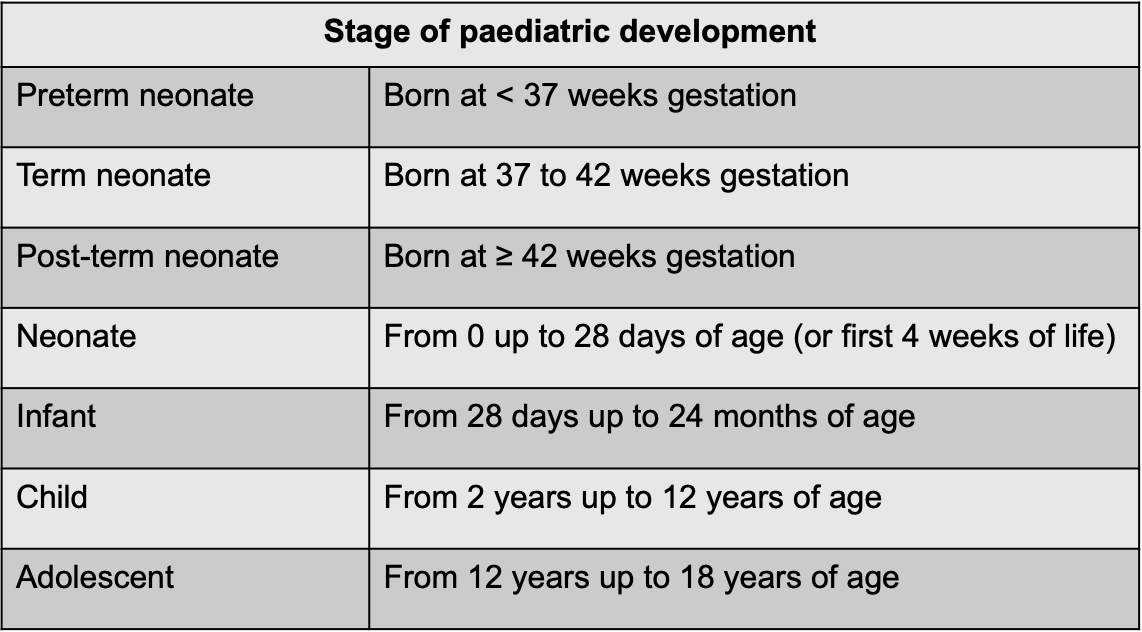
What is dosing in paediatrics determines by?
Mainly:
Dosing by total body weight (TBW)
Dosing by specific age ranges
However, can also be based on:
Dosing by body surface area (in m2)
Corrected gestational age for preterm neonates
Dosing by Ideal Body Weight (IBW)
What is corrected gestational age?
Corrected gestational age is the neonate's total age expressed in weeks from the start of the mother's last menstrual period —> some drugs may have dosed based on the corrected gestational age
e.g. 3-week old baby born at 27 weeks gestation is treated as having a corrected gestational age of 30 weeks
How do you calculate a child’s BSA?
1)Calculate weight in kilograms: 37 pounds ÷ 2.2 = 16.8 kg
2)Calculate height in centimeters: We know our patient is 97cm tall
3)Multiply height by weight and divide by 3600 (97 cm x 16.8 kg) ÷ 3600 = 0.45
4)Take the square root of 0.45 = 0.67 m2
Define Infant apnoea
"an unexplained episode of cessation of breathing for 20 seconds or longer”, generally associated with bradycardia, cyanosis, pallor, and/or marked hypotonia
How do we dose children who may be considered “obese”?
Using “Ideal Body Weight” due to the risk of toxicity if the BSA or the TBW is used
How can different drugs affect pregnancy?
During the first trimester drugs can produce congenital malformations (teratogenesis), and the period of greatest risk is from the third to the eleventh week of pregnancy
During the second and third trimesters drugs can affect the growth or functional development of the foetus, or they can have toxic effects on foetal tissues
Stages of Pregnancy
First 17 days - pre-embryonic phase
Exposure to a drug during this time will either result in survival of the intact embryo or death.
This is sometimes known as the “all or nothing principle”
18 to 55 days – embryonic phase
The embryo will be most vulnerable to teratogens during this time. Drugs can produce congenital malformations (teratogenesis).
56 days until birth – foetal period
Organs such as cerebral cortex and renal glomeruli continue to develop. Drugs can affect the growth or functional development of the foetus, or they can have toxic effects on foetal tissues e.g. a functional abnormality such as deafness may occur during this period.
PK Changes in pregnancy
Absorption:
meds may not stay down long enough to be absorbed if hyperemesis
Timing may change or given alongside an anti-emetic
Distribution
Plasma volume increases progressively through normal pregnancy
Total body water increases by 8 litres along with decreased plasma albumin concentration so free levels of drug may rise.
Regional blood flow changes e.g. more blood flow to the uterus and less to the muscle
Metabolism
Progesterone can also affect hepatic enzyme changes e.g. reduced N-demethylation activity
Elimination
Higher cardiac output (increased by 20% by 8 weeks of pregnancy) and GFR and renal plasma flow also increased – has an affect on renally excreted drugs
What is Childbearing Age?
15 – 55 years old so should consider giving “pregnancy” advice and warnings to these patients especially if on medications which are dangerous during pregnancy e.g. valporate 3-4/10 children are born with a defect/developmental problems
References for medications use in pregnancy
BNF
NICE
Specialist pharmacy Service
Medicines Complete
General monitoring in pregnancy patients
At least two ultrasounds (8-14 weeks and another at 18-21 weeks)
Blood tests
BP
Urine tests
Monitoring for gestational diabetes
Why is breastfeeding beneficial?
the immunological and nutritional value of breast milk to the infant is greater than that of formula feeds
What are the worries with breastfeeding?
The amount of drug or active metabolite of the drug delivered to the infant (dependent on the pharmacokinetic characteristics of the drug in the mother)
The efficiency of absorption, distribution, and elimination of the drug by the infant (infant pharmacokinetics)
The nature of the effect of the drug on the infant (pharmacodynamic properties of the drug in the infant).
Which PK factors are advantageous in breastfeeding?
Absorption:
Poor oral availability is good because less is transferred into the milk
Distribution
High Vd = lower plasma conc = lower conc in milk transferred
Plasma binding: less binding = more in milk
Metabolism
First pass
Elimination
Very little drug is transferred/eliminated into human milk
What special resources are used for drugs in breastfeeding?
Lactmed
UKDILAS
EMC
NIH
The Breastfeeding Network
Drugs in Breastmilk
Breastfeeding helpline
What is the monitoring in breastfeeding patients?
Is the baby thriving? Meeting expected milestones?
Plenty of wet and dirty nappies?
Is the milk supply ok?
Is the baby showing any signs of drowsiness or other changes in behaviour?
Resources for Pregnancy
British National Formulary (BNF) and BNF for Children (BNFc)
Summary of Product Characteristics (SPC)
UK National Teratology Information Service (UKTIS)
Specialist Pharmacy Service