anatomy exam 4 iupui
1/198
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
199 Terms
CNS
brain and spinal cord, no nerves
PNS
nerves and ganglia
afferent (sensory)
impulses are carried from sensory receptors through the PNS toward the CNS
sensory
ascending, afferent, dorsal
efferent (motor)
impulses are carried away from the CNS through the PNS, to the effectors
motor
descending, efferent, ventral
efferent (motor)
are tectospinal and retrospinal efferent (motor) or afferent (sensory)?
afferent (sensory)
is spinothalamic and spinalrulor efferent (motor) or afferent (sensory)
perineurium
surrounds each fascicle
Epineurium
surrounds the entire nerve
Endoneurium
surrounds each axon (fiber)
motor
the precentral gyrus is ventral, so what is its' pathway
sensory
the postcentral gyrus is dorsal, so what is its' pathway
autonomic nervous system
provides automatic control, regulating of smooth muscles, cardiac muscle and glandular activity
somatic nervous system
provides voluntary control over skeletal muscle contraction
faster
the more myelin wrapping around a neuron makes it faster or slower?
yes, through the nose
can you get things past the blood-brain barrier? if yes then how
taste
gustation=
neuroglia
nerve glue, supporting cells of the nervous sytem, phagocytes
because there are no centrioles
neurons are mononucleated and why can't they replicate?
nissl bodies
RER; free ribosomes, acitvely producing things, (neurotransmitter)
gray
______ matter is unmyelinated
white
______ matter in myelinated
terminal bouton
the area where one neuron synapses on another
ganglia
clusters of cell bodies in the PNS
nerves
bundles of axons in the PNS
dendrites
receptive regions that conduct signals from other neurons toward the neuron cell body
axon
most neurons have one _____ that generates and conducts nerve impulses away from the neuron cell body
synapse
A junction where information is transmitted from one neuron to the next.
astrocytes, microglia, ependymal cells, oligodendrocytes
neuroglia of the CNS include? 4 of them
Schwann cells and satellite cells
neuroglia of the PNS? 2 of them
subarachnoid space, ventricles of the brain and central canal
CSF lives in? 3 of them
chemotaxis
Cell movement that occurs in response to chemical stimulus and axons know where to go
astrocytes
largest, most numerous glial cells; maintain blood-brain barrier to isolate CNS from general circulation and prevent things from getting to the brain; forms matrix, provide structural support for CNS; regulate ion and nutrient concentrations;
Microglia
phagocytic cells of the CNS, remove disease (macrophages)
ependymal cells
glial cells of the CNS that line cavities of the brain and spinal cord, circulate cerebrospinal fluid
Oligodendrocytes
glial cells that maintain cellular organization in gray matter and produce myelin to sheath areas of white matter, one can myelinate many
Schwann cells
Type of glia in the PNS, Supporting cells of the PNS responsible for the formation of myelin, covers all peripheral axons whether myelinated or unmyelinated
Schwann cells
if you put a pin through, you'll hit _________ whether or not you're hitting myelinated axons
satellite cells
surround neuron cell bodies within the PNS ganglia, regulate the exchange of nutrients and waste products between the neuron cell body and extracellular fluid, keep the cell healthy
Nodes of Ranvier
gaps in the myelin sheath
sensory
______ neurons enter the spinal cord dorsally
motor
______ neurons exit the spinal cord ventrally
Exteroceptors
detect external stimuli (touch, temp, pressure, sight, smell, hearing)
proprioceptors
monitor the position and movement of skeletal muscles and joints
Interoceptors
monitor visceral organs and functions, deep pressure, pain and taste
myelin
fat wrapping, that gives white matter its whiteness
excitability
depolarization, ability of plasmalemma to conduct electrical impulses is?
Depolarization
a reduction in membrane potential (the interior of the neuron becomes less negative) (excitation)
Hyperpolarization
membrane potential becomes more negative (inhibiting)
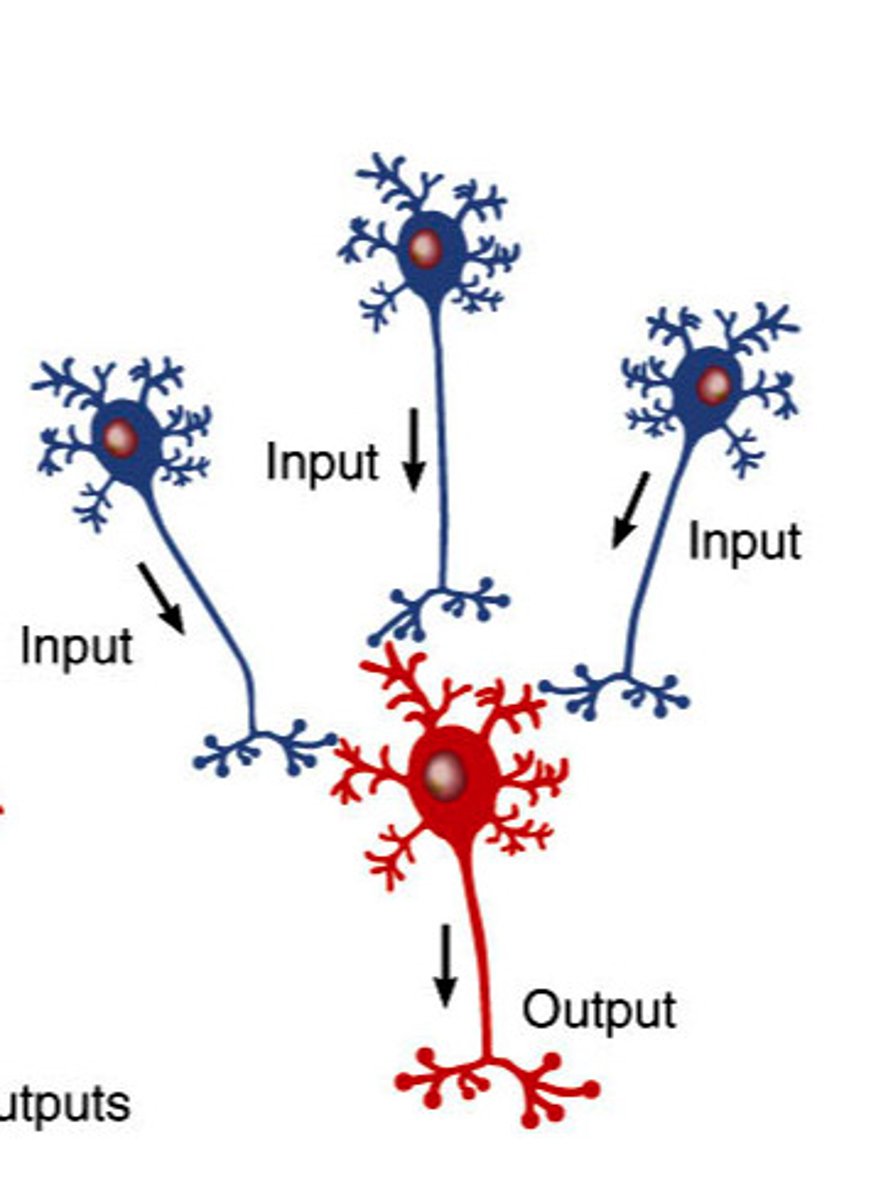
divergent
one to many
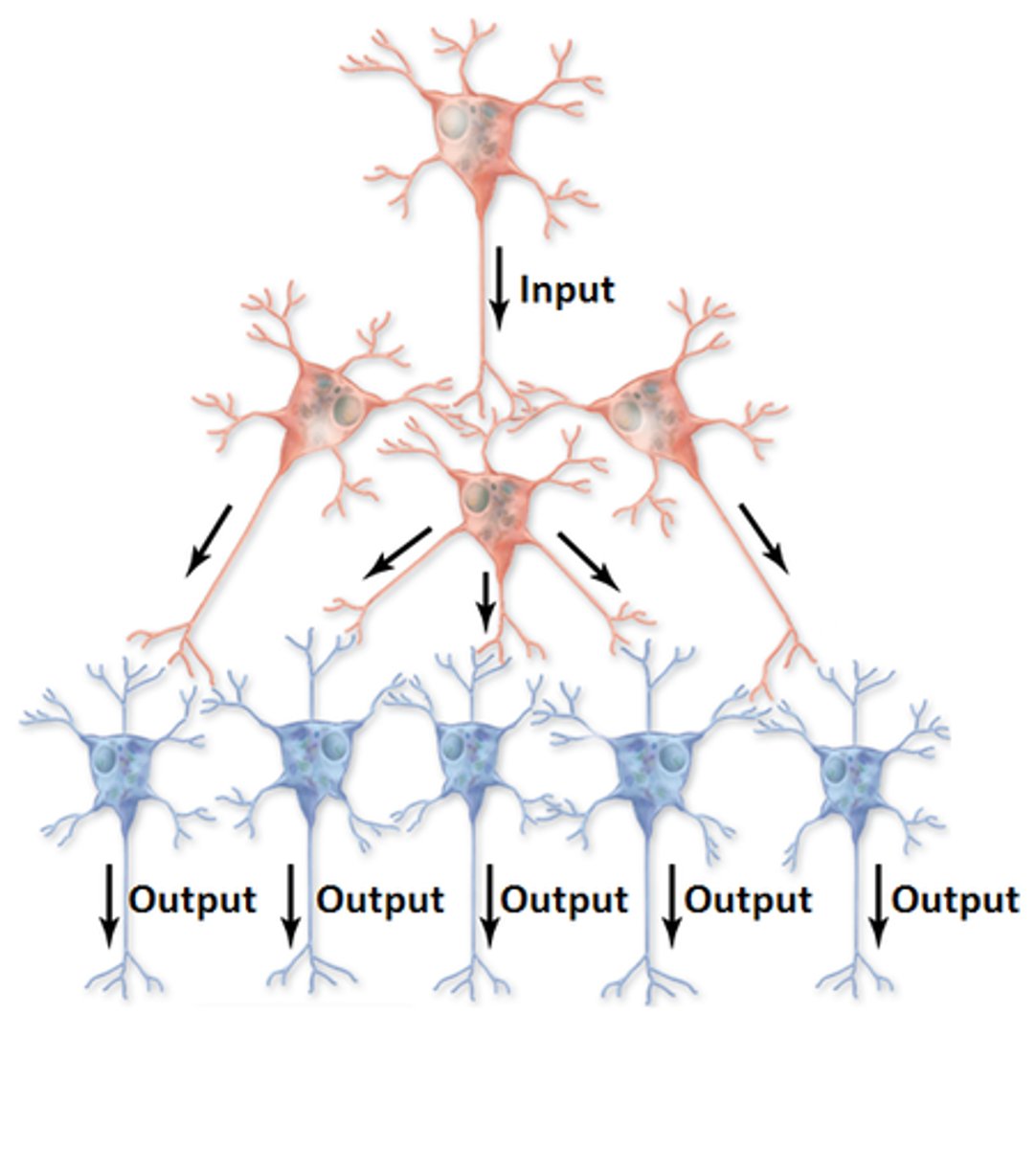
convergent
many to one
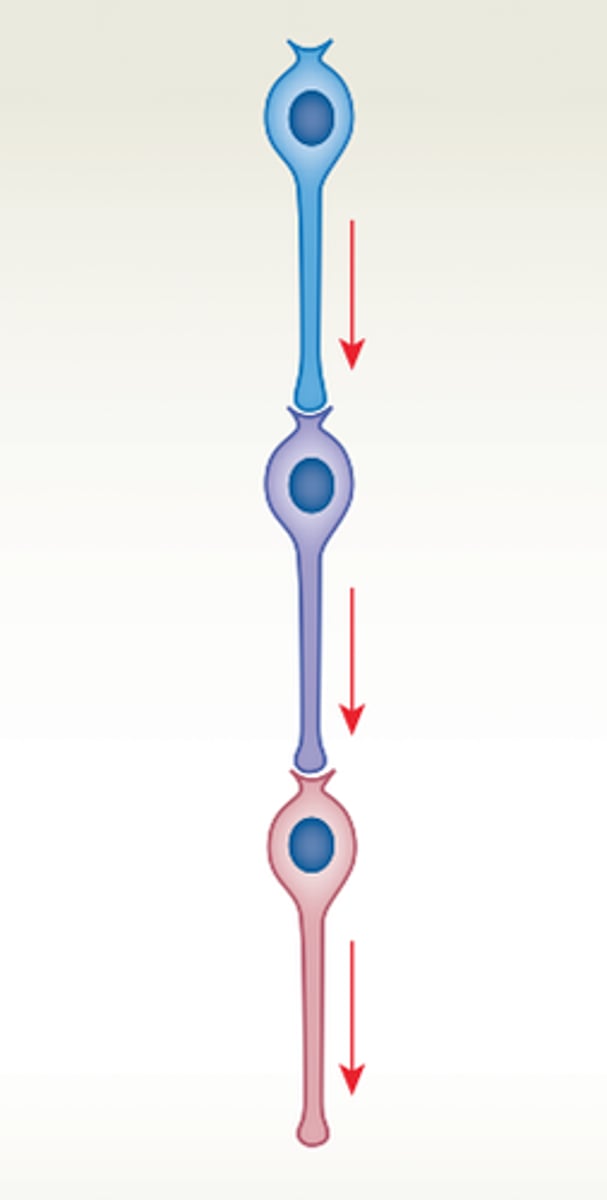
serial processing
single line
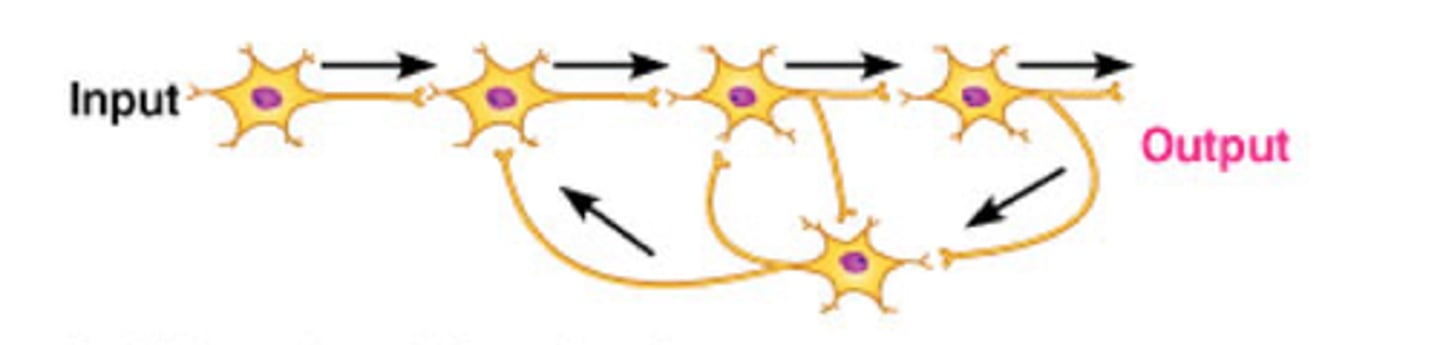
reverberation
homeostasis, maintained by negative feedback loops
CNS
responsible for processing and integrating sensory info, planning and coordinating responses to stimuli- short term
PNS
neural tissue outside the CNS whose function is to link the CNS with sense organs and other systems
ANS
CNS and PNS components that are concerned with control of visceral function
nucleus
CNS center with discrete boundaries
tract
Bundle of nerve processes inside the CNS.that share a common origin
column
group of tracts within specific region of spinal cord
neural cortex
a layer of gray matter at the surface of the brain
L1-L2
Spinal cord ends between
intervetebral foramen
spinal never enter or exit here
filum terminale
filament that holds the spinal cord in place
conus medullaris
end of spinal cord is called
dura
tough, fibrous layer that covers the spinal cord, contains epidural space
arachnoid
subdural space cavity.. subarachnoid space
pia mater
contains denticulate ligaments and filum terminale, inner layer, and cauda equina
deep
in spinal cord, gray matter is _____ to white
superficial
in brain, gray matter is _____ to white
visceral
lateral horns consist of ____ motor neurons
somatic
anterior gray horns provide _____ motor control
somatic and visceral
posterior gray horns consist of ____ and ____ nuclei
musculocutaneous nerve
most lateral brachial nerve
ulnar nerve
most medial brachial nerve
sciatic nerve
comes from sacral plexus, exits inferior to piriformis muscle, innervates all lower limb except anterior and medial thigh
ANS
regulates body temp and coordinates cardiovascular, respiratory, digestive, excretory, and reproductive functions, subconcious level, processes that maintain homeostasis
reflex
immediate involuntary response to a specific stimulus
Aquired reflexes
learned reflex is called
innate reflexes
basic neural reflexes formed before birth
sensory info
leg, hip, trunk, arm are part of what info
motor info
hand, arm, shoulder, trunk, flexors, extensors, are part of what info
motor
precentral gyrus=
sensory
postcentral gyrus=
Cerebrum
Area of the brain responsible for all voluntary activities of the body
choroid plexus
produces CSF, worm-like, floats within ventricles of brain
primary motor cortex
the section of the frontal lobe responsible for voluntary movement
primary sensory cortex
regions of the cerebral cortex parietal lobe that initially process information from the senses
visual cortex
The visual processing areas of cortex in the occipital and temporal lobes.
auditory cortex
the area of the temporal lobe responsible for processing sound information
association areas
areas of the cerebral cortex that are not involved in primary motor or sensory functions; rather, they are involved in higher mental functions such as learning, remembering, thinking, and speaking
claustrum
processes visual information at a subconscious level, "what is today"
corpus callosum
A thick band of axons that connects the two cerebral hemispheres and acts as a communication link between them.
basal ganglia
dopamine neurons
inability to make new memories
damage to the hippocampus would result in?
Amygdala
sex, fear, aggression
thalamus
Relay station for sensory information
pineal body
sleep/wake cycle, ceratonin metabolized in melatonin
Hypothalamus
most important visceral control center, regulates sleep cycles, hunger, thirst, body temp, section of pituitary gland, and ANS, can regulate some emotions and behaviors
Epithalamus
contains the pineal gland, controls circadian rhythm