Chapter 7- International Strategy: Creating Value in Global Markets
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
The global marketplace provides many opportunities for firms to increase their ___________ and their ____________
Revenue base and profitability
What is globalization?
The rise of market capitalization around the world
creates business opportunities for multinational corporations
what is the challenge of globalization?
Balancing emerging markets and developed markets
What does the diamond of national advantage explain?
why some nations and their industries outperform others.
What are the components of Michael Porter's Diamond of National Advantage?
1. Factor Endowments
2. Demand Conditions
3. Related and Supporting Industries
4. Firm Strategy, Structure, and Rivalry
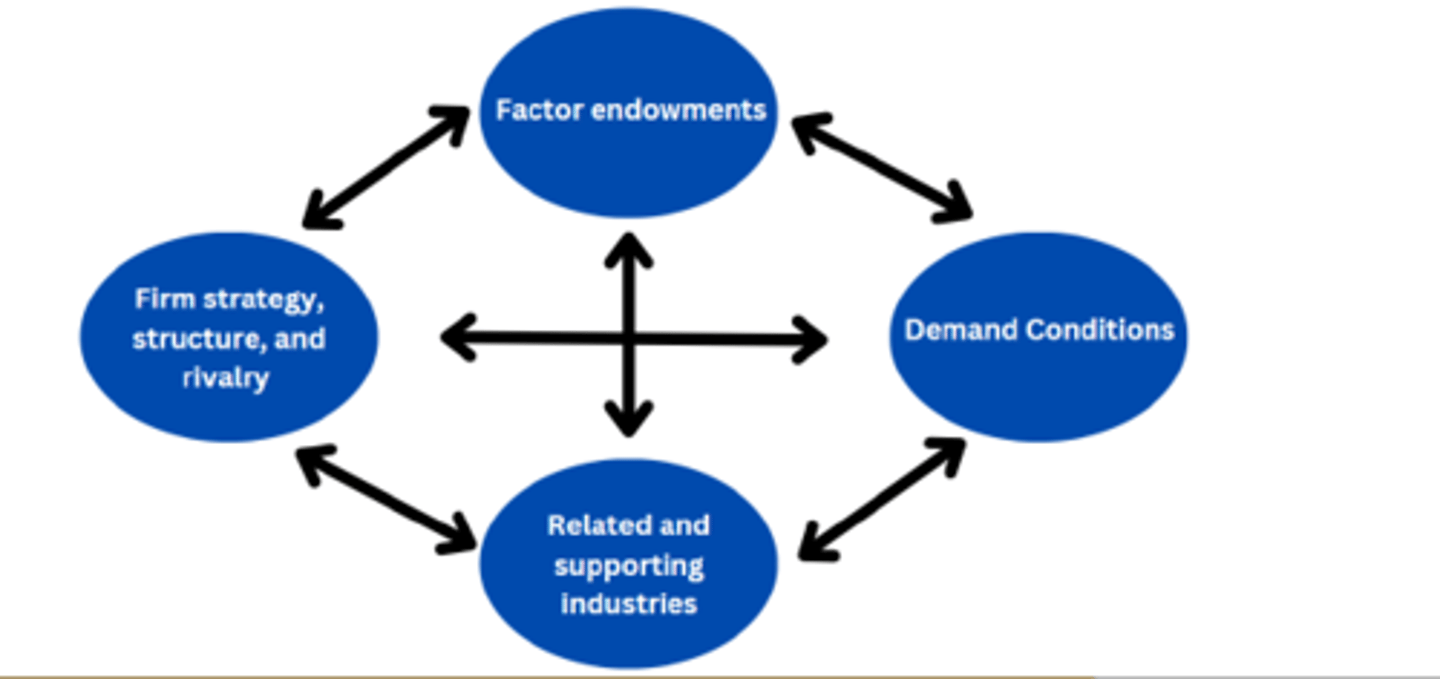
What are Factor Endowments?
The nation's position in factors of production (land, labour, capital) necessary to compete in a given industry
eg. Japan's 'just in time' inventory management due to little land availability
Factors of production must be ___________
-industry & firm specific
-Must be rare, valuable, difficult to imitate, and rapidly & efficiently deployed
what are demand conditions?
demand conditions refer to the demands that consumers plakce on an industry
eg. denmark demands enviornmentally friendly products/services
Demanding consumers drive firms in that country to:
-Meet high standards.
-Upgrade existing products and services.
-Create innovative products and services.
-Better anticipate future global demand.
-Proactively respond to product and service requirements.
what are related and supporting industries?
The presence or absence in the nation of supplier industries and other related industries that are internationally competitive
Related and supporting industries enable firms to manage inputs more effectively via:
- A competetive supplier base (reduces manufacturing costs)
- Close working relationships with suppliers (allows for joint R&D)
- Development of related industries (forces existing firms to practice cost control, innovation, and better distribution models)
how do firm strategy, structure, and rivalry affect competetiveness?
Rivalry is particularly intense in nations with conditions of:
1. Strong consumer demand
2. Strong supplier base
3. High new entrant potential from related industries
intense domestic competition is a strong indicator of ___________
global competetive success.
All of the factors below have made India's software services industry extremely competitive on a global scale except:
A. a large pool of skilled workers.
B. a large network of public and private educational institutions.
C. tax and antitrust legislation that protect the dominant players in the industry.
D. a large, growing market, and sophisticated customers.
C. tax and antitrust legislation that protect the dominant players in the industry.
- this would actually reduce competition.
A company decides to become a multinational firm in order to:
- Increase the size of potential markets (Attain economies of scale)
- take advantage of arbitrage opportunities (Applied to every stage of the value chain)
- Enhance a product's growth potential (reinvigorate the product life cycle)
- optimize the location of value chain activity (to enhance performance, reduce risk, reduce cost)
- take advantage of learning opportunities
- Explore reverse innovation
what are arbitrage opportunities?
buying something where it is cheap and elling it where it commands a higher price
what is reverse innovation?
when companies initially develop products for niche or underdeveloped markets, and then expand them into their original or home markets
eg. India's hub and spoke system
what are the risks multinational firms encounter?
1. currency risk
2. management risk
3. political risk
4. economic risk
what is currency risk?
the risk that the local currency exchange rate will fluctuate (affecting cost of production or net profit)
what is management risk?
risk that is due to culture, customs, language, income level, customer preferences, and/or distribution systems
could lead to the need for local adaptation of apparently standard products
what is political risk?
risk that is due to social unrest, military turmoil, terrorism, demonstrations, absence of the rule of law
what can political risk lead to?
- destruction of property
-disruption of operations
- non-payment for goods and services
- arbitrary government decisions
what is economic risk?
risk due to piracy and counterfeiting
Managing economic risk can be done through ___________
global dispersion of value chains
Various activities of the firm's value chain can be spread across several countries and continents via:
1. outsourcing
2. offshoring
what is outsourcing?
Firm decides to use other firms to perform value-creating activities that were previously performed in-house
what is offshoring
Firm decides to shift an activity that it was performing in a domestic location to a foreign location
what are the common savings from offshoring?
Lower wages, benefits, energy costs, regulatory costs, taxes.
what are the hidden costs from offshoring
Higher total wage and indirect costs, wage inflation.
Increased inventory due to longer lead time.
Reduced market responsiveness.
Increased coordination costs.
Cost of protecting intellectual property.
Disruption of global supply chains.
Levitt suggested strategies that favor global products and brands should do the following:
Standardize all products for all markets.
Reduce overall costs by spreading investments over a larger market.
levitt's suggestions assume:
Customers have homogenous needs and interests.
People prefer lower prices at high quality.
Global markets produce economies of scale.
why might these assumptions be incorrect?
one size fits all does not generally apply
- Product markets DO vary widely between nations
-There is a growing interest in multiple product features, product quality, and service.
-Technology permits flexible production; cost of production may not be critical to product cost; a firm's strategy should not be solely product driven
what is the opposing pressures chart?
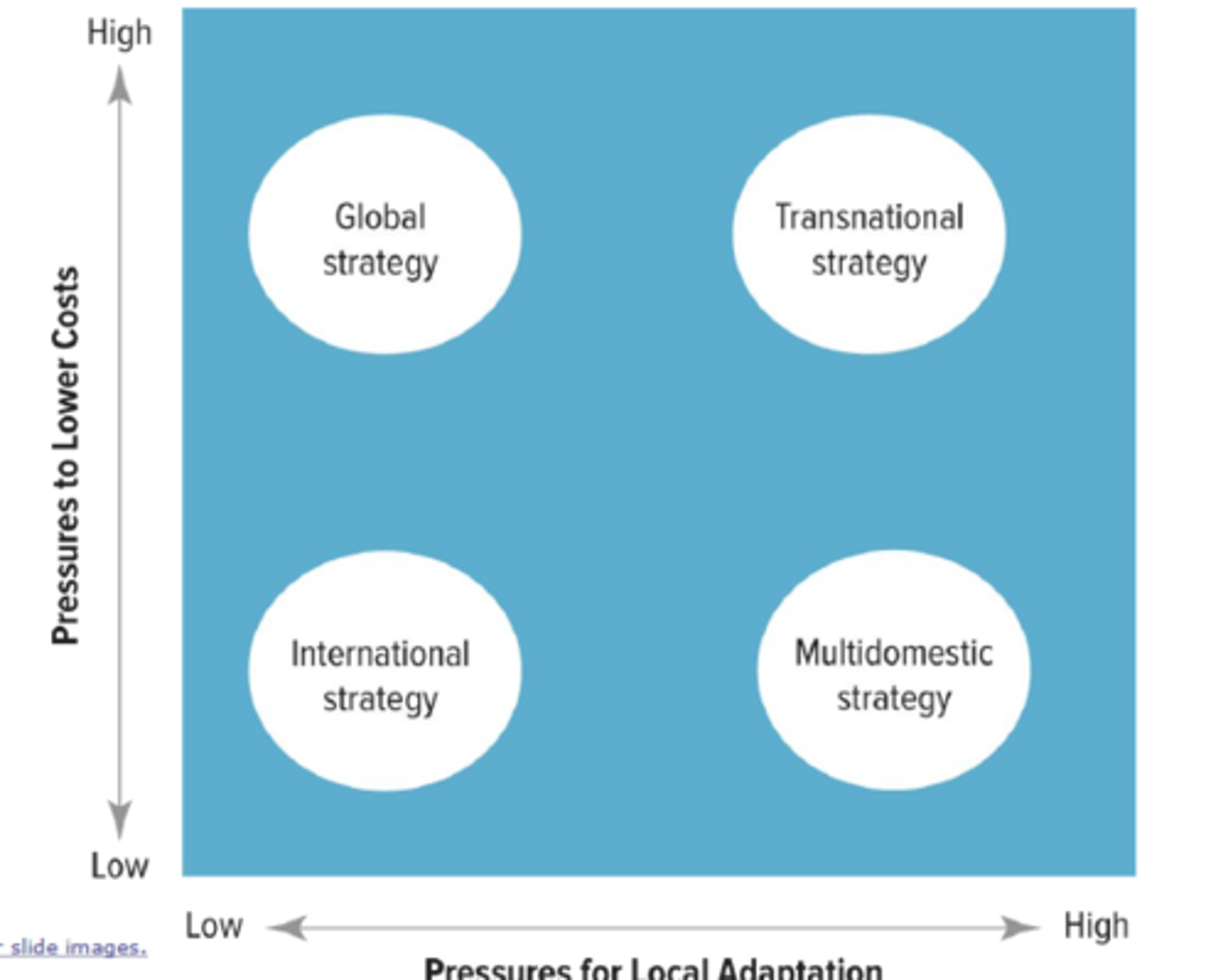
what is an international strategy
a strategy which requires diffusion and adaptation of the parent company's knowledge and expertise to foreign markets
primary goal is worldwide explotation of the parent firm's knowledge and capabilities
in an international strategy, pressure for local adaptation is ___________ and pressure for low costs is _____________
low and low
what are the strengths of international strategy
- Leverage and diffusion of a parent firms knowledge and core competencies
- lower costs becasue of less need to tailor products and services
what are the limitations of international strategy
- Limited ability to adapt to local markets
- inability to take advantage of new ideas and innovations occuring in local markets
what is a global strategy
one which implies a firm is interested in lowering costs
- competetive strategy is centralized and controlled by the corporate office
- products are standardized, operations centralized, producing economies of scale
- worldwide volume supports research and development
- there's a standard level of quality worldwide
in an global strategy, pressure for local adaptation is ___________ and pressure for low costs is _____________
low and high
what are the strengths of the global strategy
strong integration across various businesses;
standardization leads to higher economies of scale, which lowers costs;
helps create uniform standards of quality throughout the world
what are the limitations of the global strategy
limited ability to adapt to local markets,
concentration of activities may increase dependence on single facility,
single locations may lead to higher tariffs and transportation costs
what is a multidomestic strategy
a strategy that puts emphasis on differentiating products and services to adapt to local markets
- decisions are decentralized
- products and services are tailored to local use (consider language, culture, customer preference, etc)
- markets can expand rapidly
- prices are differenciated by market
in a multidomestic strategy, pressure for local adaptation is ___________ and pressure for low costs is _____________
high
Low
what are the strengths of the multidomestic strategy
- ability to adapt products and services to local market conditions
- ability to detect potential opportunities for attractive niches in a given market
what are the limitations of the multidomestic strategy?
-decreased ability to realize cost savings through scale economies
- greater difficulty in transferring knoweldge across countries. Possibility of leading to 'over adaptation' as conditions change
what is a transnational strategy
one which seeks global competetiveness via trade offs
- efficiency versus local adaptation versus organizational learning
- assets and capabilities are disbursed according to the most beneficial location for a specific activity; some value chain activities centralized, some decentralized.
Central philosophy: enhanced adaptation to all competitive situations as well as flexibility by capitalizing on communication and knowledge flows throughout the organization
in a transnational strategy, pressure for local adaptation is ___________ and pressure for low costs is _____________
high and high
what are the strenghts of the transnational strategy
- Ability to attain economies of scale
- Ability to adapt to local markets
- Ability to locate activities in optimal locations
- Ability to increase knowledge flows and learning
what are the limitations of the transnational strategy?
- unique challenges in determining optimal locations of activities to ensure cost and quality
- unique managerial chalenges in fostering knowledge transfer.
In order to realize the strongest competitive advantage, firms engaged in worldwide competition must:
A. require that all of their various business units follow the same strategy regardless of location.
B. ensure that all business units follow a strategy strictly tailored to their respective locations.
C. pursue a strategy that combines the uniformity of a global strategy and the specificity of a multidomestic strategy in order to achieve optimal results.
D. attempt to use the strategy that was most successful in their home country.
C. pursue a strategy that combines the uniformity of a global strategy and the specificity of a multidomestic strategy in order to achieve optimal results.
what is regionalization
Regionalization in international strategy means that a company focuses on growing its business in specific parts of the world (like Asia, Europe, or North America). It does this to take advantage of similarities in culture, economy, and customer needs within each region.
- distance still matters
-commonalities of language, culture, economics, etc all make a difference
-trading blocs and free trade zones ease trade restrictions
A domestic corporation considering expanding into international markets for the first time will typically:
A. start off by implementing a wholly owned foreign subsidiary so it can maintain standards identical to those at home.
B. consider licensing or franchising its operations.
C. consider implementing a low risk/low control strategy such as exporting.
D. form a joint venture with a reputable foreign producer.
C. consider implementing a low risk/low control strategy such as exporting.
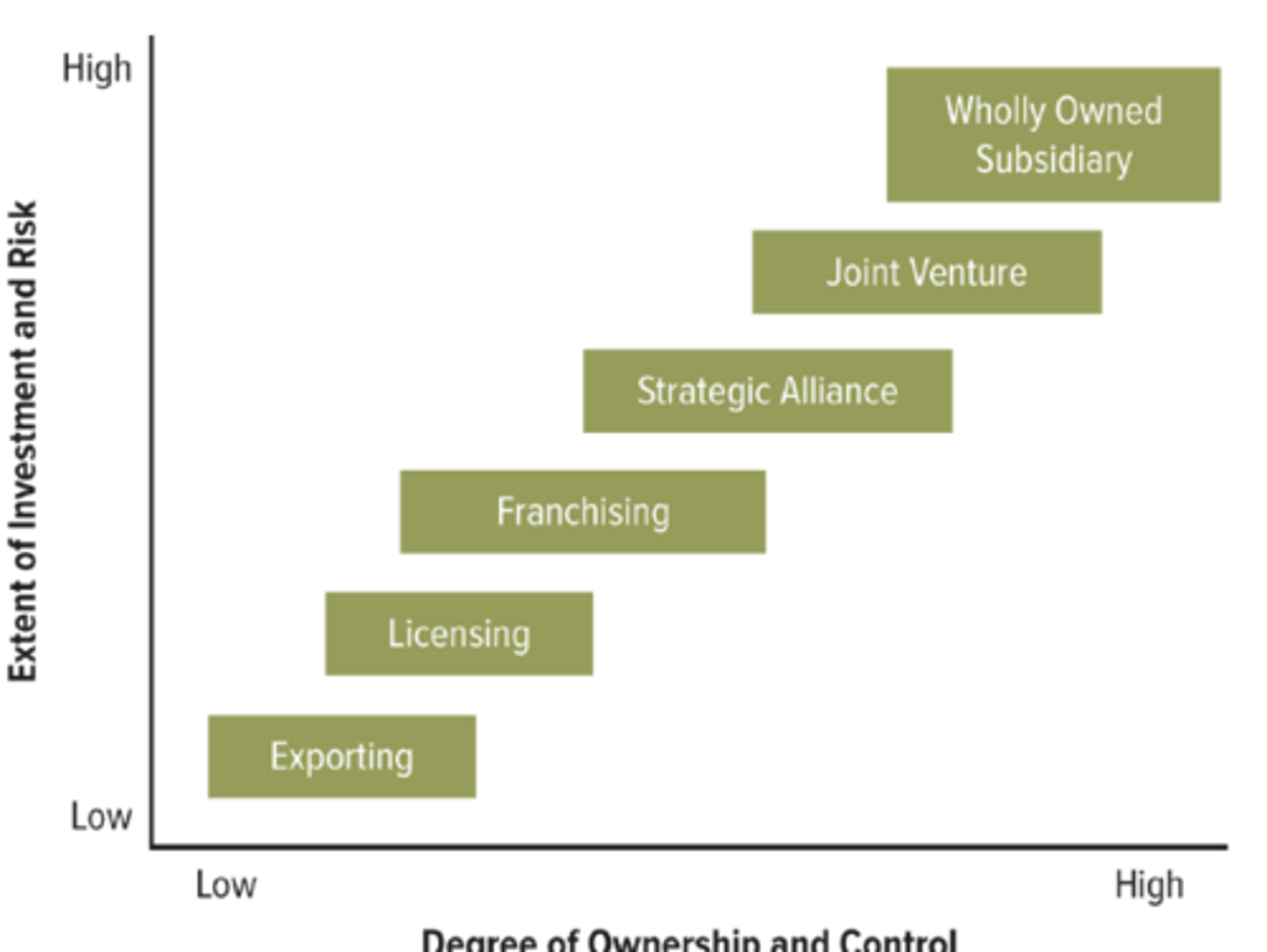
what are the options for international market expansion?
1. exporting
2. licensing or franchising
3. strategic alliance or joint venture
4. wholly owned subsidiary
what is exporting
the sale of goods and services to foreign markets
Low risk, locals know more; but products may not meet local needs.
what is licensing?
Form of contractual arrangement, enables company to receive a royalty or fee in exchange for the right to use its trademark or other valuable item of intellectual property
Limits risk; but licensor gives up control and profit. (brand name could also be tarnished)
what is franchising?
Right to use a company name of business process in a specific way.
Limits risk; but licensor gives up control and profit.
what is strategic alliance
partnership where there is no creation of a third-party legal entity but generally focuses on initiatives that are smaller in scope than joint ventures.
Shares risk; but trust and culture issues can lead to conflict.
what is joint venture
partnership where there is a creation of a third-party legal entity.
Shares risk; but trust and culture issues can lead to conflict.
what is a wholly owned subsidiary
Business in which a multinational company owns 100% of the stock by either:
1. Acquiring an existing company in the home country
2. Developing a totally new operation (greenfield venture)
Greatest control, highest returns; but expensive, greater potential for mis-steps.
entry modes chart